reproductive system
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
Sex
Anatomical structure
“Male” organs/structures → sperm producing and sperm conducting
“Female” organs/structure → egg producing and gestational organs
Gender
How one identifies themself
What do sex and gender exist on?
A spectrum → a lot of variation between individuals
Primary sex organs (Gonads)
Testes and ovaries → produce gametes (sperm and ova) + secrete sex hormones
Testes
Lie within the scrotum (keeps testes out of pelvic cavity) → holds testes at 3 degrees Celsius less than rest of body > necessary for sperm production
Produces sperm
Surrounded by 2 tunics
Two tunics of testes?
Tunica vaginalis → outer derived from peritoneum
Tunica albuginea : forms fibrous capsule
What does each teste have?
~250 lobules each contains 1-4 seminiferous tubules
Seminiferous tubules
Have epithelium which contains spermatogenic cells (sperm forming cells) → embedded in support cells called (Sertoli cells)
Sperm pathway
From seminferous tubules → converge to form a straight tubule → rete testis → efferent ductules → epididymis (non fully motile sperm store here until eiaculation)
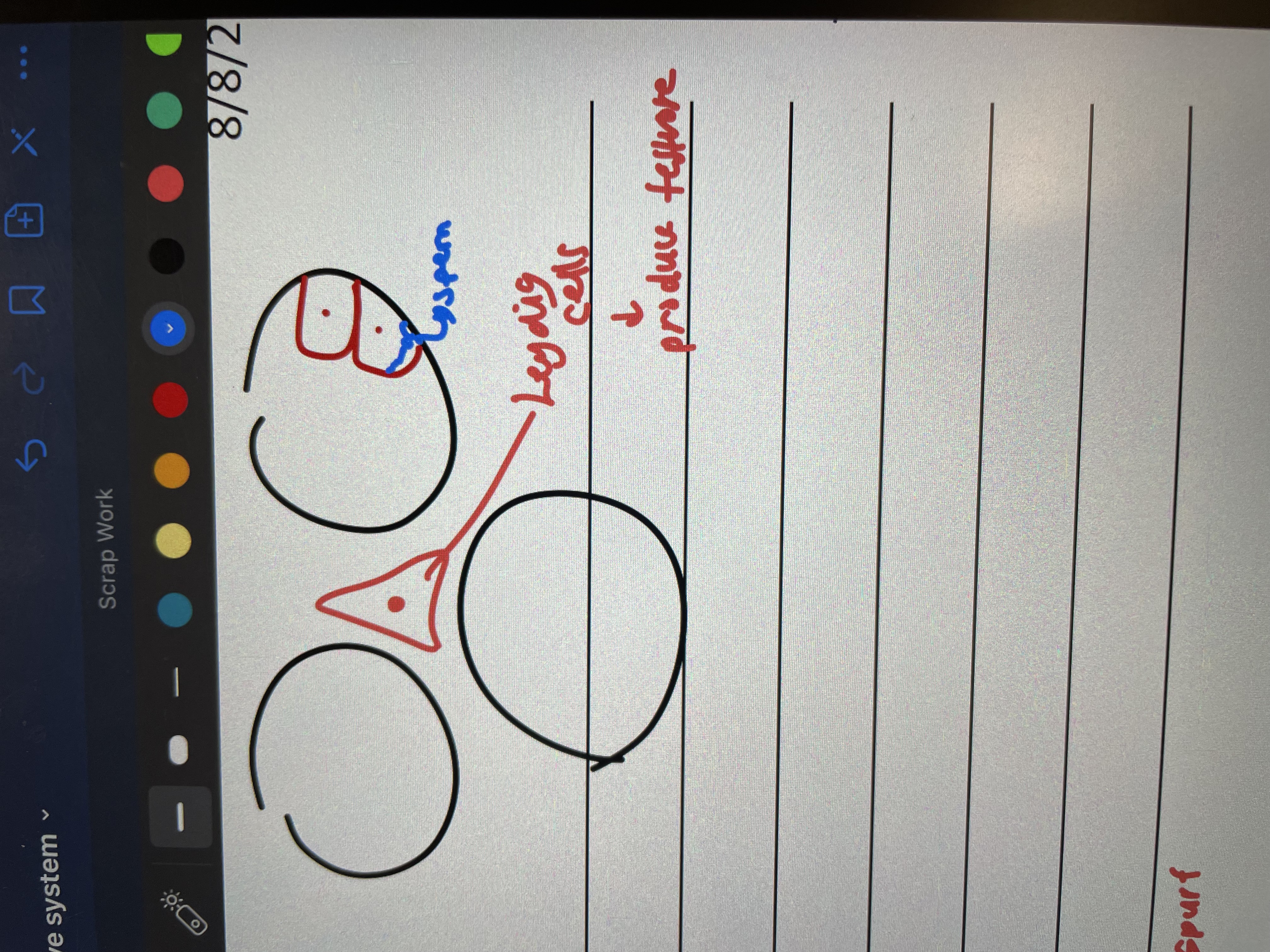
Interstitial endocrine cells (Leydig cells)
Located in tissue between seminiferous tubules
Produce testosterone
Blood supply to testes
Testicular arteries → arise from abdominal aorta
Testicular veins → from pampiniform venous plexus
Spermatic cord
Endoses nerve fibers, blood vessels, and lymphatics that supply testes (why testicular torsion is dangerous bc it cuts off blood supply)
Testicular cancer
Rare but most common cancer in men 15-35
Having mumps that leads to orchitis (inflammation of testis) can be risk factor + cryptorchudism is most common risk factor (non descent of testes)
90% cured by surgical removal and followed up by radiation or chemotherapy
Penis
copulatory organ (sexual inter course organ)
Consists of root and shaft that ends in glans penis + pepuce or foreskin
What is the penis made up of?
Spongy urethra and 3 cylindrical bodies of erectile tissue
Corpus spongiousum → surrounds urethra and expands to form the glans
Corpora cavernosa : paired dorsal erectile bodies
Erection
Érectile tissue fills with blood and becomes rigid and enlarged
Cause by sympathetic stimulation (vasodilation)
what do ducts do in penis/testes?
Carry sperm from testes to body exterior
Flow of ducts sperm takes?
Epididymis → ductus deferns → ejaculatory → urethra
Epididymis
Duct of it is ~ 6m in length
Microvilli absorb testicular fluid and pass nutrients to stored sperm
non motile sperm enter, pas slowly through (~20 days) become motile and can be stored for several months
Ejaculation
Sympathetic stimulation
Epididymis contracts, expelling sperm into ductus deferens
Ductus deferens
~45 cm long
Passes through inguinal canal to pelvic cavity → joins duct of seminal vesicle (ejaculatory duct)
Smooth muscle in walls propels sperm
Vasectomy occurs here
Vasectomy
Pinches tubes → cut and then corotize (burn it) → sperm can’t be passed then so semen is without sperm
Urethra
Conveys both urine and semen
3 regions
3 regions of urethra
Prostatic urethra : surrounded by prostate
Membranous urethra : in urofenial diaphragm
Spongy urethra : runs through penis → opens at external urethral orifice
Seminal glands
On posterior bladder surface
Produces viscous alkaline seminal fluid (fructose, coagulating enzyme and prostaglandins → need to provide sperm ATP to propel)
~60% of volume of semen
Duct of seminal gland joins ductus deferens to form ejaculatory duct
Prostate
Encircles urethra inferior to bladder
Smooth muscle will contract during ejaculation
Secretes milky slightly acid fluid → cleans out urethra from bacteria (contains prostate-specific antigen → very elevated levels for prostate cancer)
~30% of semen volume
Bulbo-urethral glands
Pea sized glands inferior to prostate
Produce thick clear mucus (lubricates glans penis + neutralizes traces of acidic urine in urethra)
Semen
Mixture of sperm and accessory gland secretions (like seminal fluid)
(2-5mL are ejaculated containing 20-150 million sperm/ml)
Contains fructose + alkaline fluid neutralizes acidity of urethra and vagina and enhances motility
Benign prostatic hyperplasia
Distorts urethra (reduced urine flow)
Treated with surgery but new options like drugs or radio frequency radiation
Prostate cancer
Second most common cause of cancer death in males
Treated with surgery + sometimes radiation
Erection
Artérioles are normally constricted → sexual excitement causes activation of parasympathetic neurons which release nitric oxide → causes vasodilation)
NO causes relaxation of local vascular smooth muscle → dilation
Corpora cavernosa expands + engorgement with blood and enlarges and stiffening penis
Ejaculation
Sympathetic NS → bladder sphincter muscle constricts preventing expulsion of urine + glands contract and cause expulsion of semen
Érectile dysfunction
Parasympathetic nerves of penis release too little NO (nitric oxide)
Possible causes : alcohol, drugs, hormones, blood vessels or NS problems, incompetent venous valves that fail to retain boood in penis
Spermatogenesis
Production of sperm (spermatoza) in testes → spermstogenic cells give rise to sperm
flow of sperm creation?
Spermatogonia aka stem cell (2n) → (mitosis) → 2 primary spermatocytes (2n) → (meiosis I) → 2 secondary spermatocytes (n) → (meiosis II) → 2 spermatids (n)
Spermiogenesis
Spermatids to sperm
Spermatid elongates, loses excess cytoplasm, and forms tail to become spermatozoon (sperm) in epididymis
Regions of sperm
Head (contains genetic material with acrosome containg hydrolytic enzymes to enable sperm to penetrate egg)
Mid piece ; contains mitochondria
Tail : flagellum by
Spermatids
Small, bonmotile haploids cells found close to lumen of tubule
Sustentocytes/ Sertoli cells
Large supporting cells (surround developing cells since part of wall of tubule)
Provides nutrients and signals to dividing cells
Move cells along lumen
Secrete testicular fluid for sperm transport
Phagoctyzie fsulty germ cells and excess cytoplasma
Sequence of hormonal regulatory events
Aka hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis
Hypothalamus (GnRH aka gonadatropic releasing hormone) → anterior pituitary gland (follicle-stimulating hormones aka FSH & Lutenizing hormone (LH) → gonads
What does follicle stimulating hormone stimulate in gonads?
Spermatogensis in male (gamete formation)
What does lutenizing hormone stimulate in gonad?
Secrete testosterone (from leydig cells)
What does testosterone stimulate?
Testis maturation , development/maintenance of secondary sex characteristics and libido
Regulation of FSH and LH?
Rising testosterone→ feedback to hypothalamus to inhibit GnRH → inhibits pituitary to inhibit gonadatropun release → inhibin released by Sertoli cells when sperm count is high, inhibits GnRH and FSH release