2.7 - Acetylcholine, Nicotine, and Muscarine
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
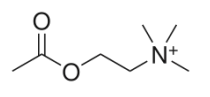
Acteylcholine (ACh)
- major NT at NMJ and ANS, acts as NT and neuromodulator in CNS
cholinergic agonists
- nicotine = toxic stimulant from Solanaceae
- Muscarine = convulsant A. muscaria
ACh synthesis
- acetylation of choline at -OH catalyzed by choline acetyltransferase (ChAT)
- consumes Acetyl coenzyme A
- availability of choline = limiting step
choline
- obtained from diet, used in cell membrane synthesis
- N+ prevents passage = take up via Na+ cotransport via choline transporter (CHT1)
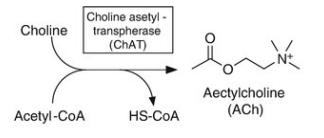
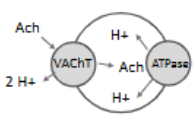
vesicular ACh transporter
uses co-transport to exchange pumped H+ for ACh
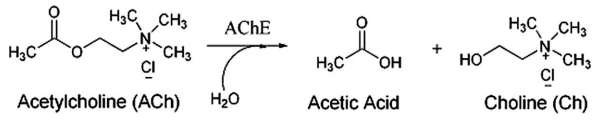
ACh metabolism
- AChE converts ACh into choline and acetate
- AChE is abundant in synaptic cleft; works fast
Ach Normal function
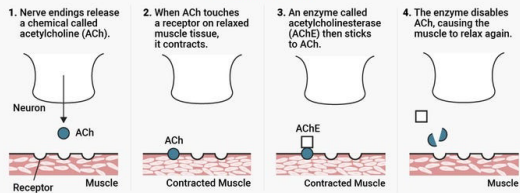
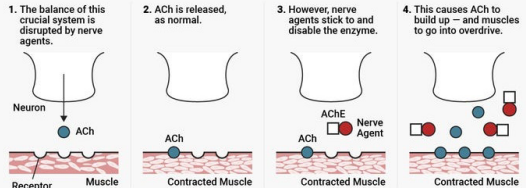
ACh nerve agent
nAChR
- ACh gated ion channel (↑ Na+influx, K+ efflux, and Ca2+ influx); excitatory
- depolarizes fast, non-selective cation channel
- composed of 5 subunits forming pentameric channel w/ pore
- composition dictates drug affinity, Ca2+ permeability, and kinetics
mAChR
ACh-metabotropic GPCR; five different types f(x) varies
M1 (mAChR receptor)
excitatory, Gq-linked; ↑ PLC, ↑IP3 and DAG
M2 (mAChR receptor)
inhibitory, Gi-linked; ↓ AC and cAMP
M3 (mAChR receptor)
excitatory, Gq-linked; ↑ PLC, ↑ IP3 and DAG
M4 (mAChR receptor)
inhibitory, Gi-linked; ↓ AC and cAMP
M5 (mAChR receptor)
excitatory, Gq-linked; ↑ PLC, ↑ IP3 and DAG
Type (alpha7)5 nAChR
- passes Na+, K+, and Ca2+
- mediates pro-cognitive effect
Type (alpha4)2(beta4)3 nAChR
- passes Na+ and K+
- mediates rewarding effects
Short interneurons in caudate/putamen
- regulate motor output (respond to environment to establish motor response)
- inhibited by dopamine neurons of substantia
Parkinson’s
loss of DA inhibition causes excess ACh → resting tremors
Pontomesencephalotegmental complex
- cholinergic cell bodies in brain stem (pedunculopontine nucleus + laterodorsal tegmental nucleus)
- activity mediated by M1AChR
- increases autonomic outflow; increases secretions
- regulates pain = M2 and M4; ↓ pain through nociceptor inhibition
AChE inhibtors
↑ ACh = ↑ analgesia
Basal forebrain
- cholinergic cell bodies originate from basal optic nucleus of Meynert and septal nucleus
- major brain ACh system = regulates and modulates MOST systems
neuromodulation
AChR auto receptors decrease NT release