Chem terms
1/51
Earn XP
Description and Tags
imported from quizlet
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
Chemistry
The study of the composition, structure, and properties of matter, the processes that matter undergoes; and the energy changes that accompany these processes
Organic Chemistry
the study of carbon containing compounds
Inorganic chemistry
the study of non-organic substances
Analytical chemistry
the identification of the composition of materials
Physical chemistry
the study of properties of matter, changes that occur in matter, and the relationships between matter and energy
Biochemistry
the study of the chemistry of living things
Theoretical chemistry
the use of mathematics and computers to design and predict the properties of new compounds
Basic research
pure research that aims to confirm an existing theory or to learn more about a concept or phenomenon
Applied research
scientific study that aims to solve practical problems
Technological development
typically involves the production and use of products that improve our quality of life
Pure substance
A substance made of only one kind of matter and having definite properties.
Mixture
A combination of two or more substances that are not chemically combined
Element
a substance made up of only one type of atom, all with the same number of protons
Compound
a substance formed by the chemical union of two or
elements or atoms in definite proportion by weight
Atom
fundamental building block of all matter
Molecule
two or more atoms held together by covalent bonds
Physical property
A property that can be observed without changing the identity of a substance
Chemical property
A property that describes a substance that has an identity change
Accuracy
A description of how close a measurement is to the true value of the quantity measured.
Precision
The degree to which repeated measurements show the same result.
Extensive property
A property that depends on the amount of matter in the sample
Intensive Property
A property that doesn't depend on the amount of matter in the sample
Hypothesis
a supposition or proposed explanation made on the basis of limited evidence as a starting point for further investigation.
Theory
A hypothesis that has been tested with a significant amount of data
Model
A pattern, plan, representation, or description designed to show the structure or workings of an object, system, or concept
Law
A statement based on repeated experiments or observations, that describes or predicts a range of natural phenomena
Mass
A measure of the amount of matter in an object
Weight
A measure of the force of gravity on an object
Group
A column on the periodic table
Family
Groups of elements with similar properties
Period
A horizontal row of elements in the periodic table
Metal
A class of elements characterized by physical properties that include shininess, malleability, ductility, and conductivity.
Nonmetal
an element that is a poor conductor of heat and electricity
Metalloid
an element that has physical and chemical properties of both metals and nonmetals
Kilogram
SI base unit for mass
Meter
SI base unit for length
Second
SI base unit for time
Mole
SI base unit for amount of a substance
Kelvin
SI base unit for temperature
Ampere
SI base unit for electric current
m^3
Derived SI unit of volume
kg/m^3
Derived SI unit of density
kg/mol
Derived SI unit of molar mass
Joule
Derived SI unit of energy
Decanting
A method of separating immiscible liquids by pouring the top layer into another container.
Filtration
the process that separates a solid from the liquid in a heterogeneous mixture
Evaporation
The liquid is evaporated, meaning it is convert from its liquid state to gaseous state. This often requires heat. Once the liquid is completely evaporated, the solid is all that is left behind.
Distillation
A process that separates the substances in a solution based on their boiling points
Chromatography
A technique that is used to separate the components of a mixture based on the tendency of each component to travel or be drawn across the surface of another material.
(Actual value-experimental value/actual value) x 100
How to calculate percent error
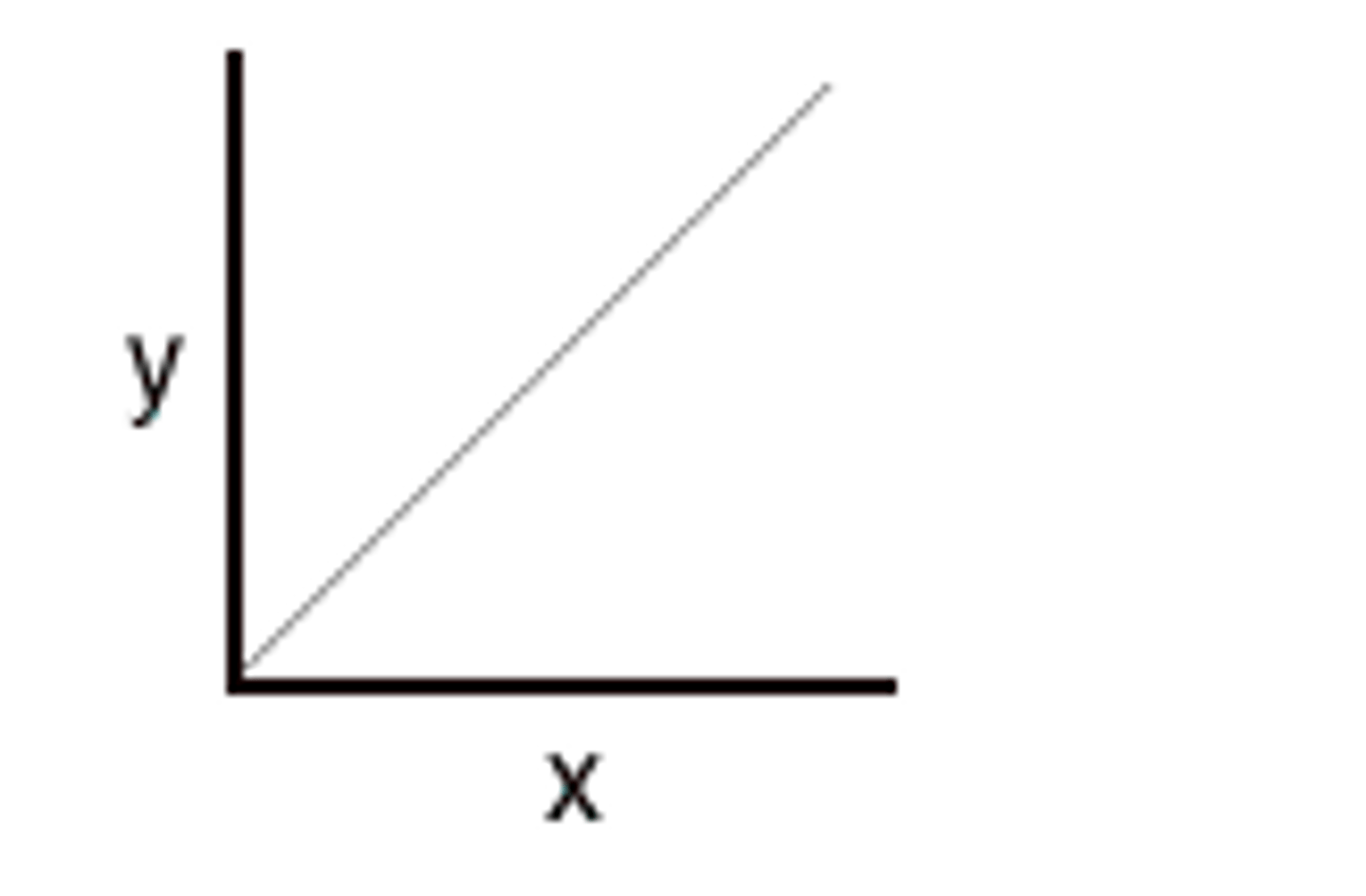
Direct relationship
a relationship in which one variable increases with an increase in another variable
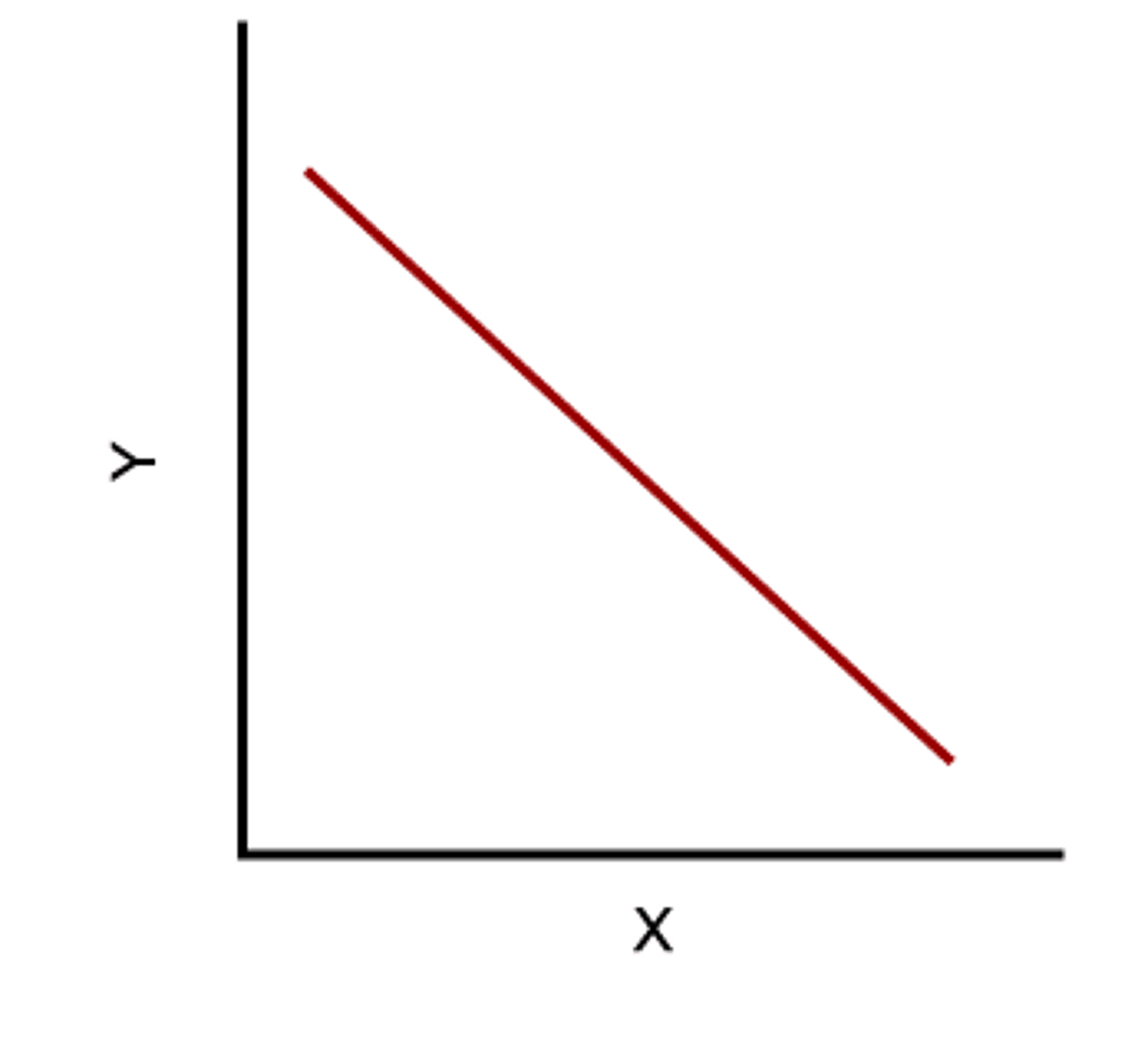
Indirect relationship
a relationship when one variable increases while the other variable decreases