econ test 1
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
New
Card Sorting
1/85
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
86 Terms
1
New cards
economic problem
although your wants are unlimited, the resources you want are scarce
2
New cards
scarcity
not enough resources to satisfy people's unlimited wants
3
New cards
capital goods
human creations (machines) used to produce goods and services
4
New cards
productive resources
inputs that produce the goods and services people want
5
New cards
economics
how people use their scarce recourse to satisfy their unlimited wants
6
New cards
human resources
\-all human effort/work
\-physical labor or mental ideas
\-physical labor or mental ideas
7
New cards
profit
revenue from sales minus cost of production
8
New cards
entrepreneur
someone who takes a risk to earn a profit (develop a product or create a new way to produce something more efficiently)
9
New cards
natural resources
raw materials supplied by nature
10
New cards
renewable resource
can be used indefinitely if used wisely and allowed sufficient time to recover
11
New cards
exhaustible resource
once used, they're used up (not renewable)
12
New cards
goods
something you can feel and touch (tangible)
13
New cards
services
not physical, uses scarce resources to satisfy human want (intangible)
14
New cards
“no free lunch”
nothing is ever "free" because every good and service requires scarce resources (everything costs someone something)
15
New cards
economic theory
a simplification of economic reality used to make predictions about the real world
16
New cards
rational self-interest
customers maximize expected benefit given the cost, or minimize cost for benefit
17
New cards
normative
someone's opinion (can't be shown to be true/false based on reference to facts)
18
New cards
positive statement
factual statements (ability to find out if true/false by referring to facts)
19
New cards
marginal cost
cost to consumer or producer for each additional unit
20
New cards
marginal benefit
revenue or enjoyment of each additional unit
21
New cards
microeconomics
focuses on your economic behavior and the economic behavior of individuals and firms
22
New cards
macroeconomics
performance of the economy as a whole
23
New cards
choice
decision makers will continue to acquire information as long as the marginal benefit from information exceeds marginal cost of gathering it
24
New cards
markets
where buyers and sellers carry out exchange where they buy and sell things
25
New cards
circular flow chart
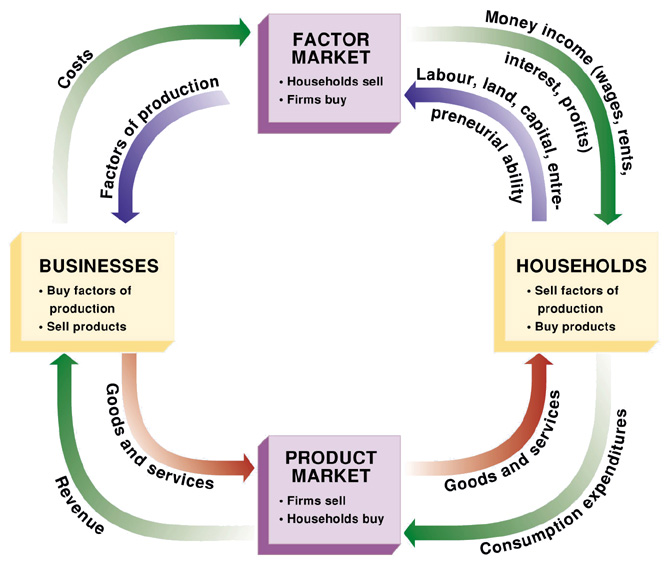
26
New cards
types of market participants
\-households
\-firms
\-governments
\-rest of world
\-firms
\-governments
\-rest of world
27
New cards
opportunity cost
value of the best alternative you must pass up
28
New cards
sunk cost
cost you already paid but can never recover no matter what you do
29
New cards
economic system
the set of mechanisms and institutions that resolves the what, how, and for whom questions for an economy
30
New cards
pure market economy
\-private firms own ALL means of production
\-no gov involvement
\-private groups own ALL resources
\-prices generated in free and competitive markets
\-no gov involvement
\-private groups own ALL resources
\-prices generated in free and competitive markets
31
New cards
invisible hand
no gov or institution is coordinating the market
32
New cards
monopolize
producers work to drive out competition and work with competitors to raise prices (higher prices\=more profit)
33
New cards
"no public goods"
public goods benefit everyone but individual firms don't want them because they can't sell them/earn a profit or keep people from use of it
34
New cards
externalities
costs that aren't considered when an item is produced
35
New cards
economic fluctuations
\-when markets both expand and contract (consumers and producers feel the pain of recession)
\-no safeguard because of no gov
\-no safeguard because of no gov
36
New cards
rules of the game
laws when there is no gov involved (i.e. don't steal, don't murder, etc.)
37
New cards
pure command economy
economy controlled by the gov (i.e. communist russia, north korea)
38
New cards
visible hand of central planners
\-gov setting prices
\-resources are allocated
\-told what to produce
\-resources are allocated
\-told what to produce
39
New cards
problems with command economies
\-no competition market
\-directing production through state run industries
\-prices set by central planners
\-goods and services may be rationed
\-directing production through state run industries
\-prices set by central planners
\-goods and services may be rationed
40
New cards
little freedom of choice
less freedom with decisions; might tell people where to work
41
New cards
central planning can be inefficient
\-central planners choose what to grow (can lead to inefficiency)
\-no incentive to make a profit (resources can be wasted)
\-no incentive to make a profit (resources can be wasted)
42
New cards
environmental damage
\-gov not concerned about environment
\-since no one owns it, we will use it all up
\-since no one owns it, we will use it all up
43
New cards
no role for entrepreneurs
since gov owns ALL resources, there is no goal for anyone seeking a profit
44
New cards
mixed economy
a little bit of central planning and competitive markets (ie the US)
45
New cards
market economy
competitive markets play majority role in setting prices (some gov control: health regulations, zoning, consumer regulations)
46
New cards
transitional economy
shifting from command economies to market economies (or vice versa) (ie China)
47
New cards
privatization
converting gov enterprises into private enterprises
48
New cards
traditional economy
economies shaped by custom or religion (i.e. caste system in india)
49
New cards
2 types of goods in PPF
1) consumer
2) capital
2) capital
50
New cards
production possibilities frontier (PPF)
shows possible combination of 2 types of goods that can be produced when resources are employed efficiently
51
New cards
simplifying assumptions
\-single snapshot in time
\-no new innovation
\-rules of game/legal system are fixed
\-no new innovation
\-rules of game/legal system are fixed
52
New cards
efficiency
\-maximum possible output from available resources (no more than 1 type of good can be produced without reducing amount of alternative product)
\-measure through comparative advantage, specialization)
\-measure through comparative advantage, specialization)
53
New cards
law of increasing opportunity cost
with each additional increment of a good produced requires economy to give up successfully larger increments of another good
54
New cards
constant cost curve
cost of producing an additional good is the same regardless of where you are along the curve
55
New cards
improvements in "rules of the game"
\-formal and informal institutions that support the economy (laws, law enforcement, etc.)
\-encourage people to be productive
\-encourage people to be productive
56
New cards
comparative advantage
ability to produce a good/service for a lower opportunity cost than a competitor
57
New cards
absolute advantage
ability to produce more of a good/service than a competitor
58
New cards
law of comparative advantage
the worker with lower opp. cost of producing a particular output should specialize in that output
59
New cards
specialization
allows the workers to become more efficient
60
New cards
bartering
a system of exchange where products are exchanged directly for other products
61
New cards
division of labor
organizing the production process so each worker specializes in a separate task so the group can produce more
62
New cards
households
everyone that lives together under one roof (single economic decision maker)
63
New cards
utility
level of satisfaction of happiness
64
New cards
firms
an economic unit formed by a profit seeking entrepreneur who combines resources to produce goods and services and accepts the risk of profit and loss
65
New cards
transaction costs
cost of time and information required for exchange
66
New cards
property rights
a legal claim that guarantees an owner the right to use a resource or charge others for its use
67
New cards
intellectual property rights
protect creators of new ideas and inventions
68
New cards
patent
laws to protect inventors and new devices or processes
69
New cards
copyright
assigns property rights to written (original) expression
70
New cards
trademarks
property rights to unique commercial symbols and marks
71
New cards
measurements and safety
\-ensure that weights and measures are standardized
\-agencies that protect consumers and firms: i.e. FDA and CPSA
\-agencies that protect consumers and firms: i.e. FDA and CPSA
72
New cards
market competition
\-when they are a monopoly, they are able to charge higher prices
\-businesses work to acquire smaller businesses to make more profit
\-businesses work to acquire smaller businesses to make more profit
73
New cards
anti-trust laws
\-laws that work to reduce anti-competitive behavior and promote competitive markets
\-ways to prevent monopolies
\-ways to prevent monopolies
74
New cards
regulating natural monopolies
where one firm can serve an entire market at a lower per unit cost then 2 or more firms can
75
New cards
fiscal policy
\-a fed gov's use of taxing and public spending to influence the macroeconomy
\-affects our interest rates (makes more expensive to take out loans)
\-ie. medicare, medicaid, and national defense
\-affects our interest rates (makes more expensive to take out loans)
\-ie. medicare, medicaid, and national defense
76
New cards
monetary policy
\-controlled in US by federal reserve
\-federal reserve attempts to control the money supply to influence the macroeconomy
\-federal reserve attempts to control the money supply to influence the macroeconomy
77
New cards
private goods
\-rival in consumption
\-exclusive: nonpayers can be excluded
\-once consumed by ONE person, it can't be used by someone else
\-exclusive: nonpayers can be excluded
\-once consumed by ONE person, it can't be used by someone else
78
New cards
public goods
\-non-rivalrous
\-non-exclusive: hard to exclude non payers
\-once produced they are available to all (i.e. police force, public roads)
\-non-exclusive: hard to exclude non payers
\-once produced they are available to all (i.e. police force, public roads)
79
New cards
natural monopoly goods
\-non-rivalrous
\-exclusive
\-multiple people can consume it at once (i.e. cell service, tv subscriptions)
\-exclusive
\-multiple people can consume it at once (i.e. cell service, tv subscriptions)
80
New cards
externalities
things that appear as a result of interaction in the company
81
New cards
negative externalities
\-byproducts of production or consumption that impose costs on third party (i.e. pollution)
82
New cards
positive externalities
\-byproducts that benefit producers and consumers (i.e. education)
\-when they are positive externalities, gov will try to increase levels of production that will be chosen privately
\-when they are positive externalities, gov will try to increase levels of production that will be chosen privately
83
New cards
open access good
\-rival in consumption
\-non-exclusive bc difficult to regulate (i.e. natural resources like water)
\-non-exclusive bc difficult to regulate (i.e. natural resources like water)
84
New cards
median income
\-middle income when a group of incomes is ranked lowest to highest
\-in a market economy, workers will have different incomes based on the job they have
\-in a market economy, workers will have different incomes based on the job they have
85
New cards
programs for the poor
programs designed to help people who lose income due to retirement, temporary unemployment, or inability to work due to injury or disability
86
New cards
we live in ___, but most of the world lives in ___
relative poverty, abject poverty