Neuromuscular Basis of Mastication
1/136
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
137 Terms
preplanning restorative care can be used for what 6 things
1) diagnostic wax up to preplan occlusion
2) fabricate preparation guide
3) design esthetic temporaries
4) lab communication
5) patient reassurance
6) fabcriate surgical implant guide
preplanning restorative care saves _____ and has ______ results for occlusion
time; better
what is mastication
the process whereby ingested food is cut or crushed into small pieces mixed with saliva and formed into a bolus in preparation for swallowing
what is heterodonty
having different/specialized tooth forms for the specific preparation of food
what are the 7 characteristics of mastication
1) a learned activity
2) enables the food bolus to be easily swallowed
3) enhance the digestibility of food
4) provides reflex stimulation for secretions
5) mixes food with saliva to initiate the digestion process
6) prevents irritation of the GI system and damage to the masticatory system
7) ensures healthy growth and development
recall the hierarchy of physiology of muscle contraction
muscle —> muscle fascicles/motor units —> muscle fibers —> myofibrils —> thick/thin filaments
muscles contract by what
by shortening in length
what is a sarcomere
the all or none unit of contraction
myosin heads of the thick filaments bind to what
the active sites on the actin thin filaments
what theory describes the main driver of contraction
sliding filament theory
contraction is triggered by what kinds of ions
calcium ions
muscle contraction is fueled by what
ATP
strength in muscles = number of __________ acting in parallel
sarcomeres
what is the strength of contraction per square centimeter
5.6 to 7.4 pounds
mandible pictures
temporal bone pictures
TMJ and ligaments pictures
lateral ligament: intrinsic thickening of the joint capsule that runs from neck of mandible to articular tubercle; strengths the joint laterally and helps prevent dislocation
sphenomandibular ligament: extrinsic ligament that runs from sphenoid bone to mandible's lingula; supports joint and acts as a prop during hinge movements
stylomandibular ligament: extrinsic ligament that runs from temporal bone's styloid process to mandible's angle; strengths joint
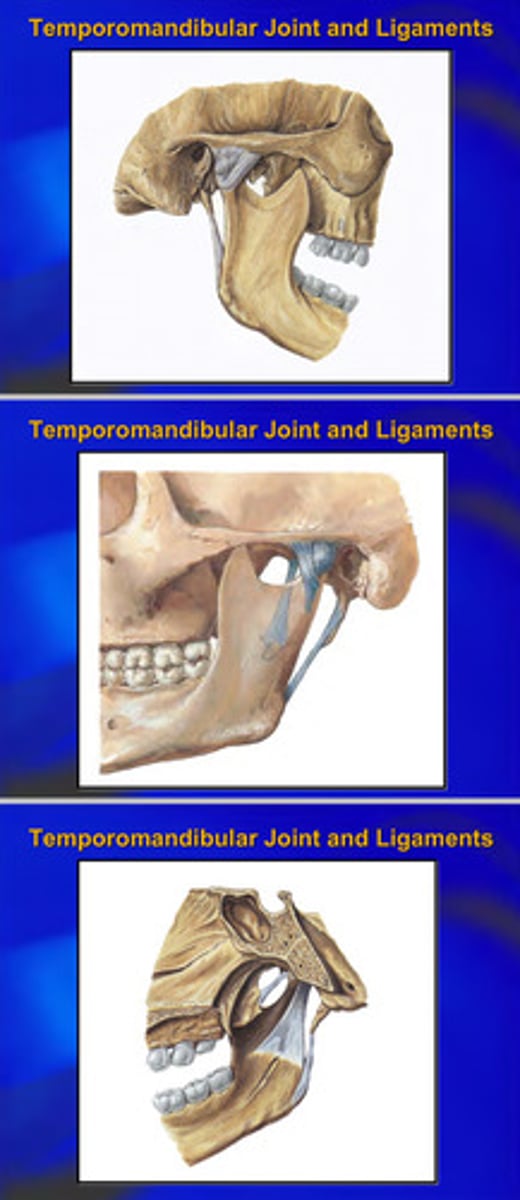
when giving a correct inferior alveolar nerve block, which ligament would you be closest to?
sphenomandibular ligament (IA nerve goes through the lingula on the mandible)
what is the basic unit of muscle contraction called
motor unit or fascicle
each muscle may have how many muscle fibers
10 to several hundred
muscles have ____ nerve cell connection
one
muscles have an ____ or _____ response
all or nothing
sustained muscle contractions are possible by timing of what
timing of nerve stimulus
muscle tone is important in maintaining what
posture and/or interocclusal rest space
muscle tone can be affected by what 4 things
stress, age, pain, and loss of teeth
muscle tone is also important in the maintenance of what
maintenance of airway
myotactic stretch reflex protects skeletal muscle from excessive ?; sensitive to muscle ?
stretching; length
describe the myotactic stretch reflex
rapid stretching of a muscle results in reflex contraction of the same muscle
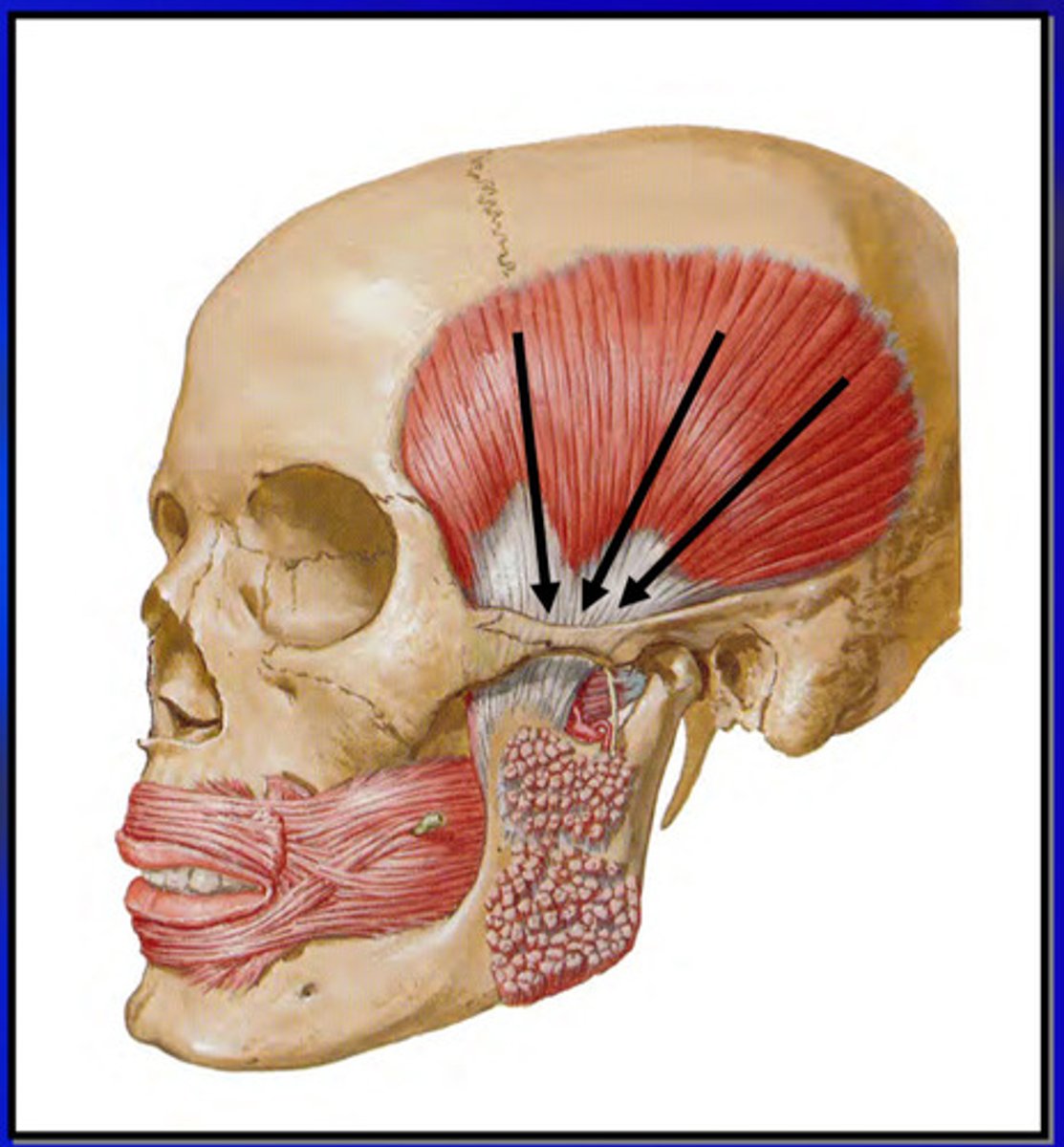
what is the temporalis muscle
principle elevator of the mandible; significant positioning muscle
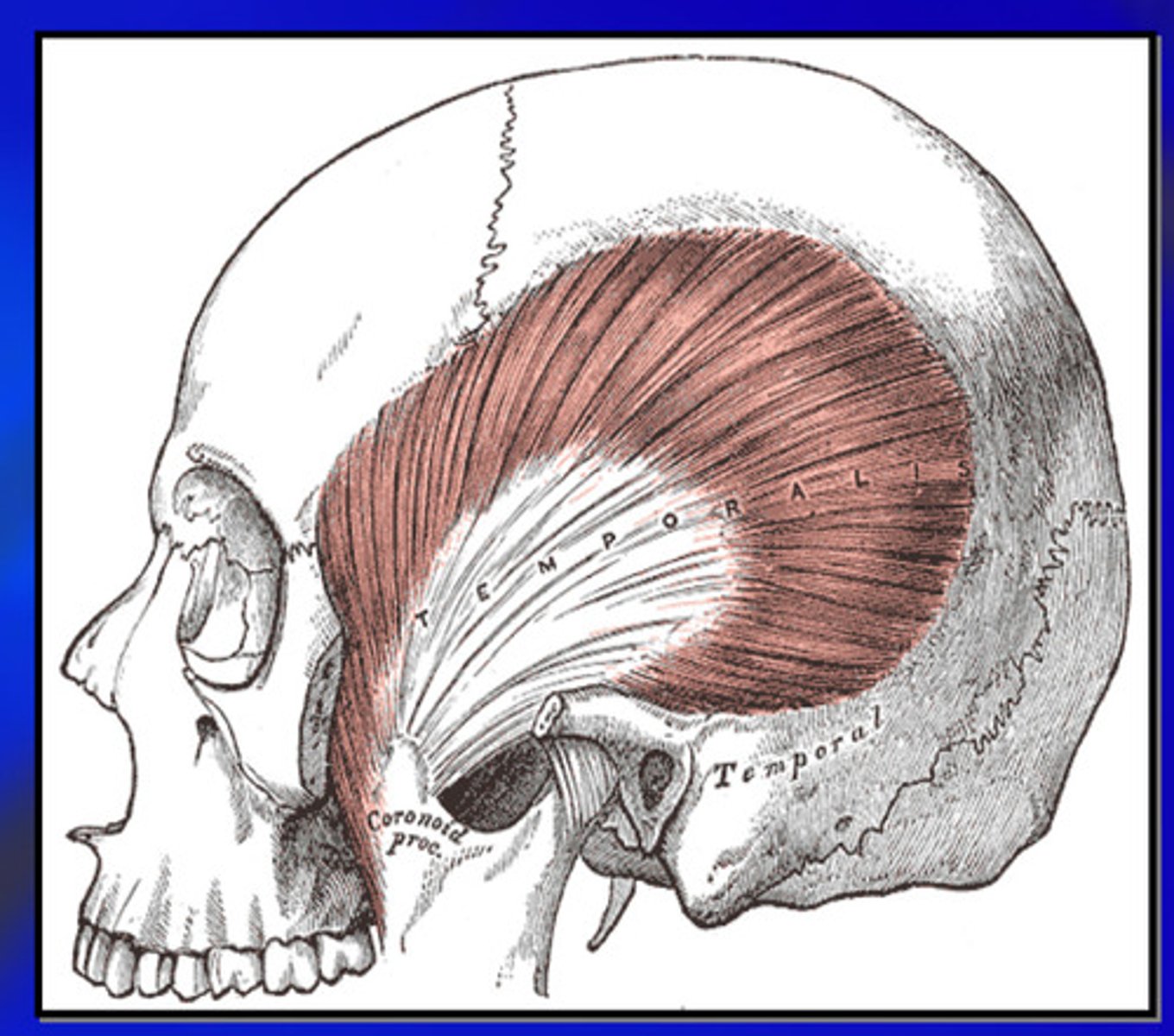
the temporalis muscle aids in what 3 things
retraction, positioning, and clenching
the temporalis muscle has a ______ origin and a ______ insertion
large origin (temporal fossa, parietal bone, frontal bone, occipital bone) , small insertion (coronoid process of mandible)
the temporalis muscle contracts by how many sections
contracts can be one or more of the 3 sections, OE all at once
contraction of the entire temporalis muscle produces what action
elevation
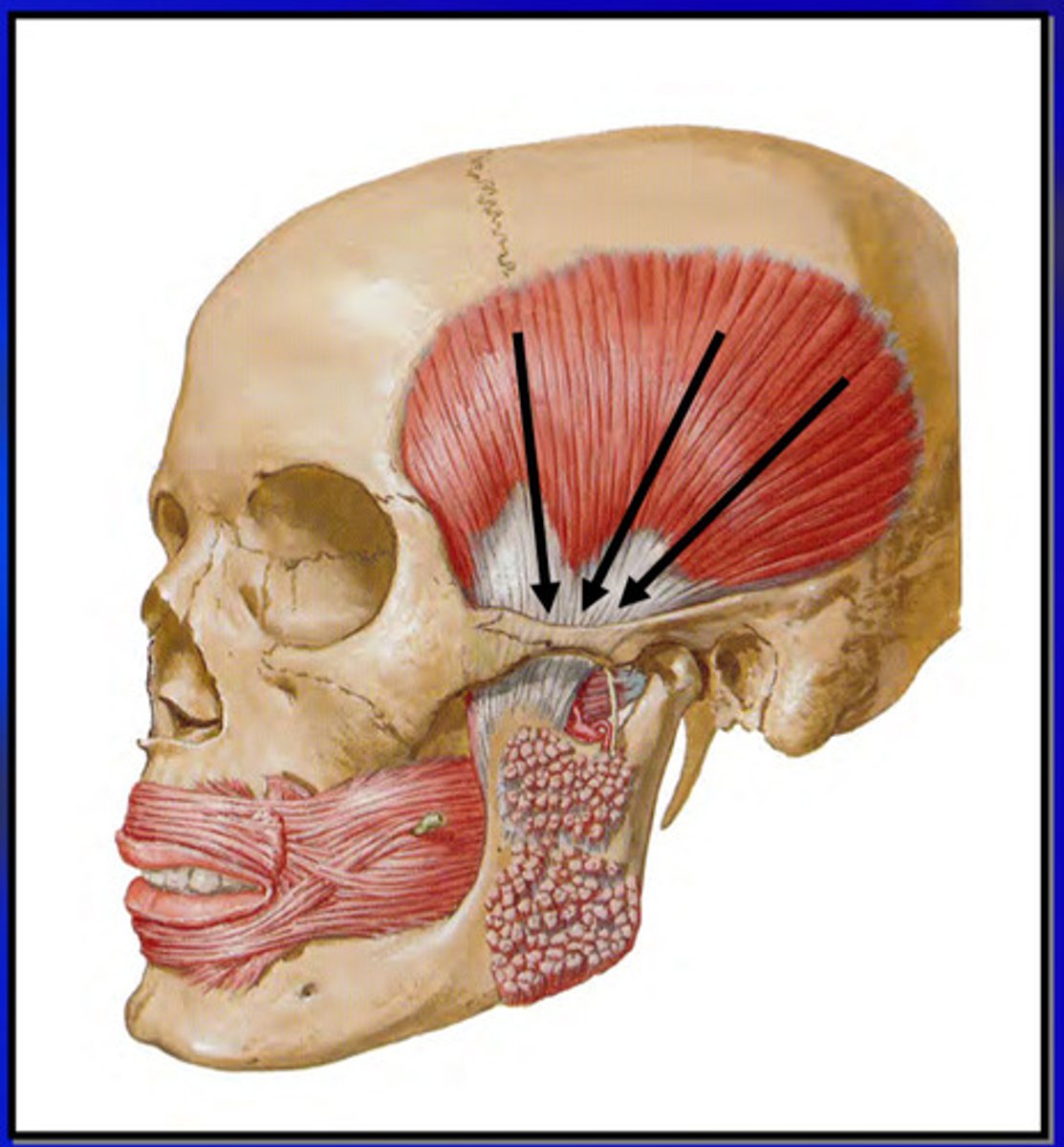
the anterior fibers of the temporalis run in which orientation and does what
vertical; elevates mandible
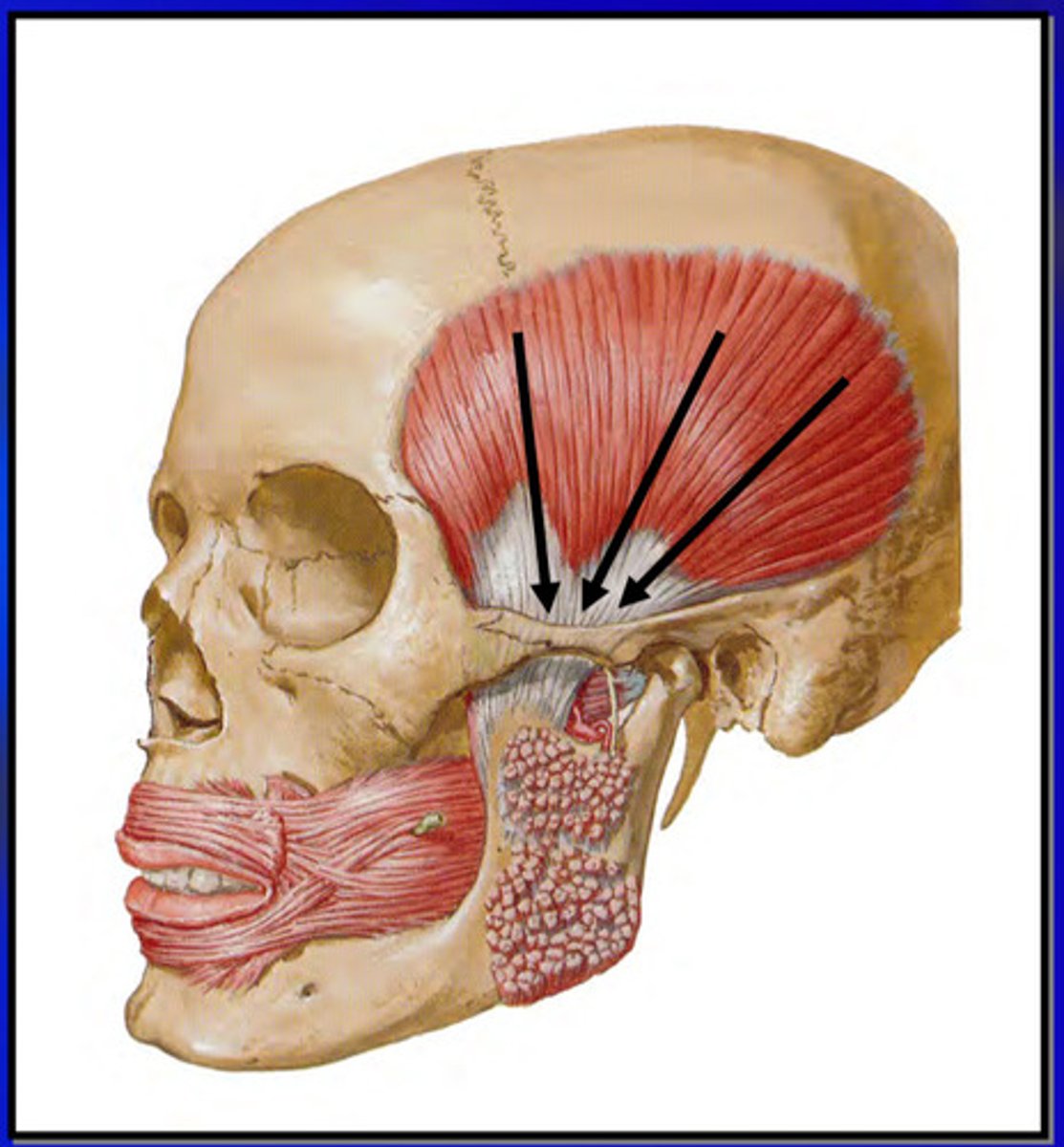
the middle fibers of the temporalis do what
elevate and slightly retrude the mandible
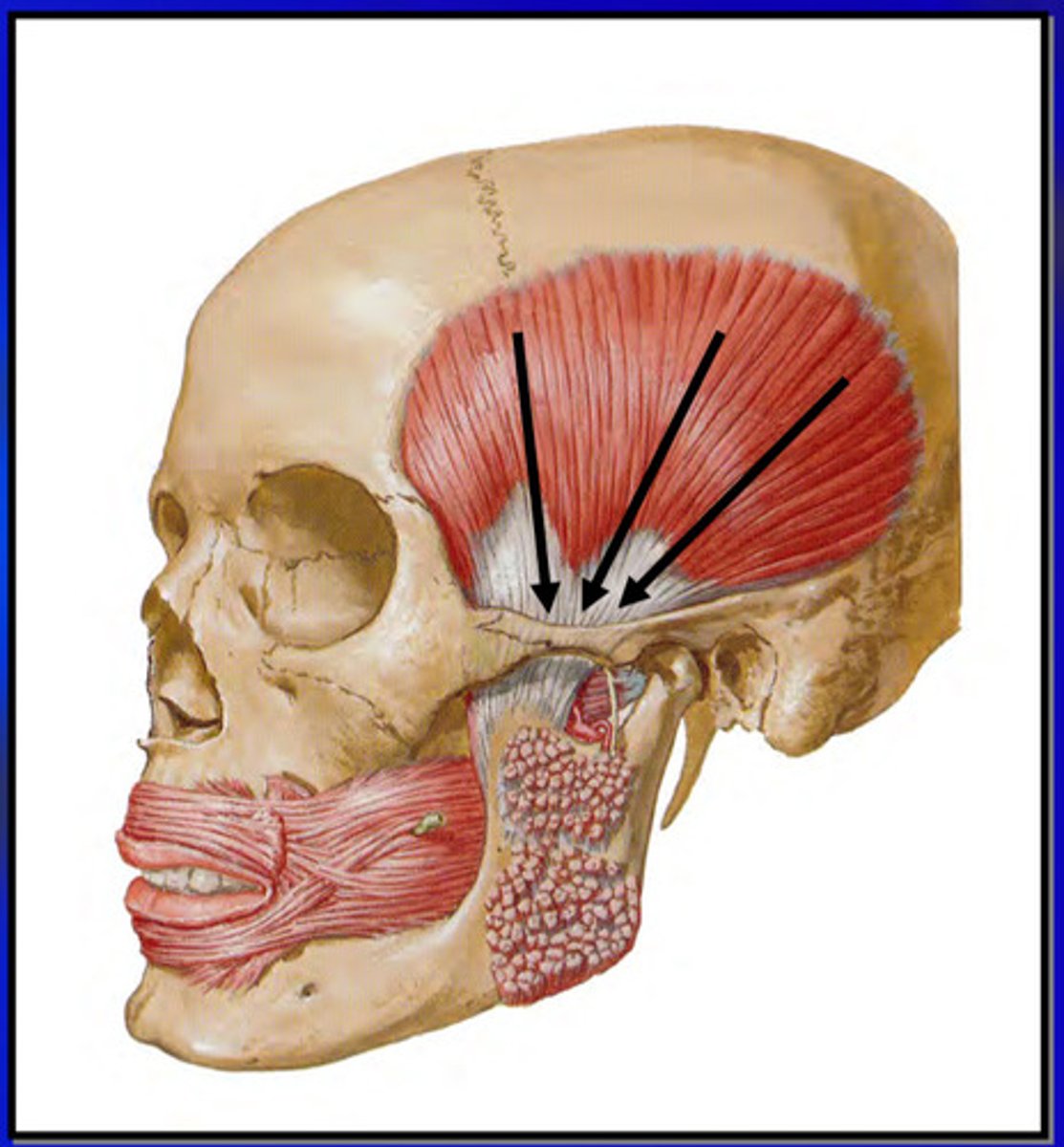
the posterior fibers of the temporalis do what
cause retrusion
the deep head of the masseter muscle aids in what
stabilizes the condyle when biting on incisors
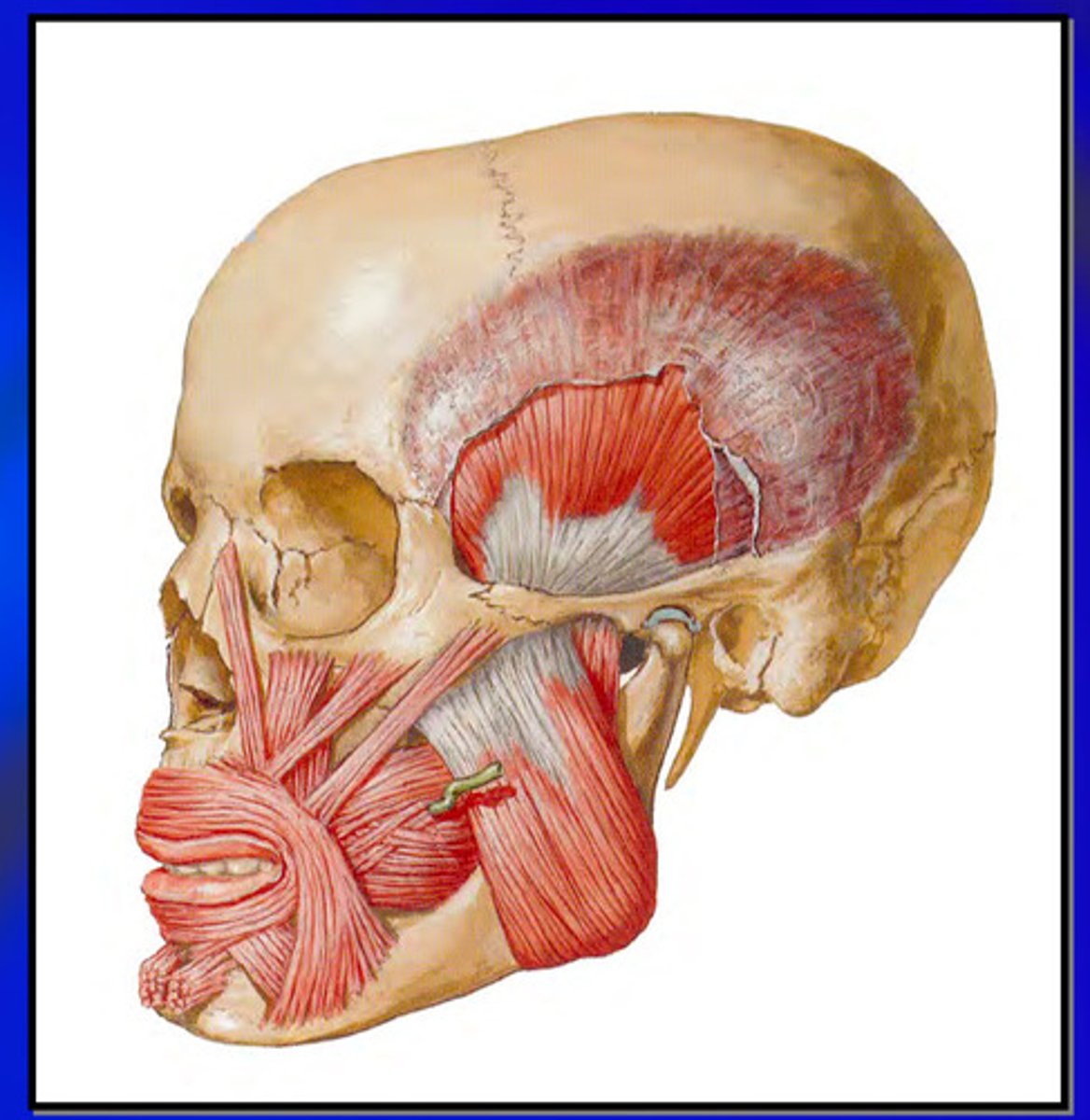
what is the action of the masseter muscle
elevates the jaw and clenches the teeth
what is the origin and insertion of the masseter muscle
origin: the outer surface of the zygoma
insertion: lower border of the ramus
the superficial head of the masseter muscle aids in what
protrusion
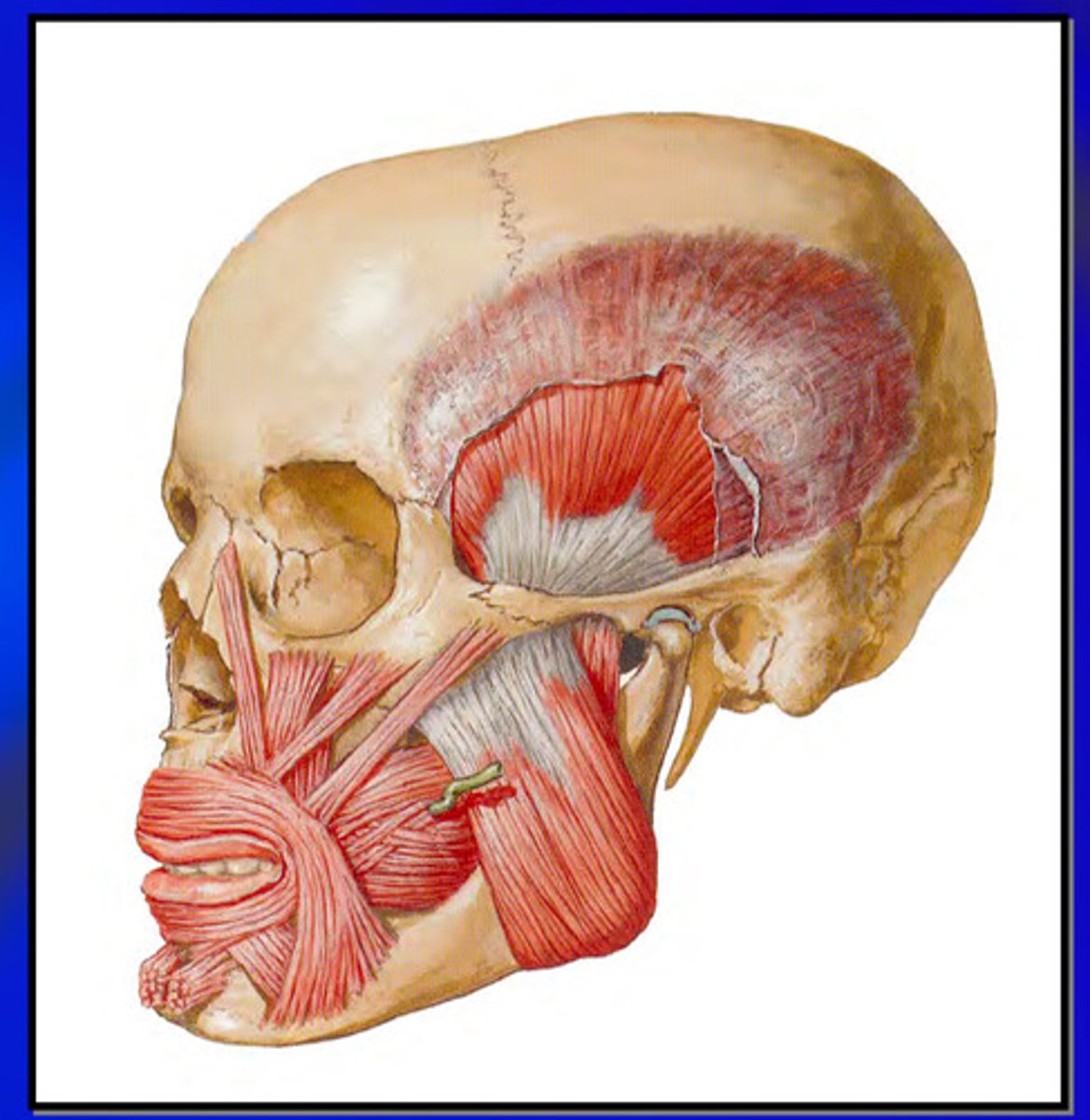
what is the masseter muscle
primary muscle for chewing force
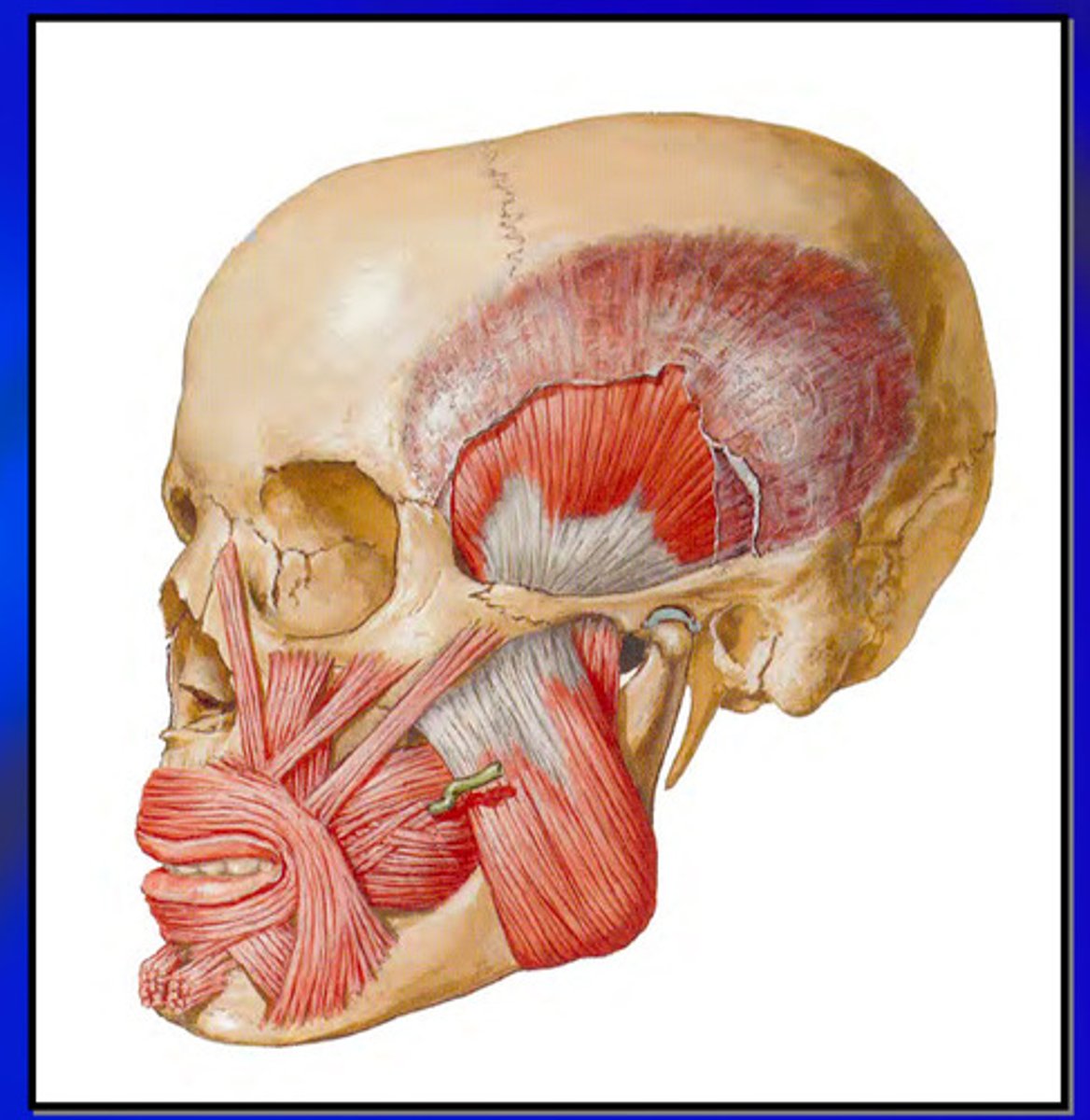
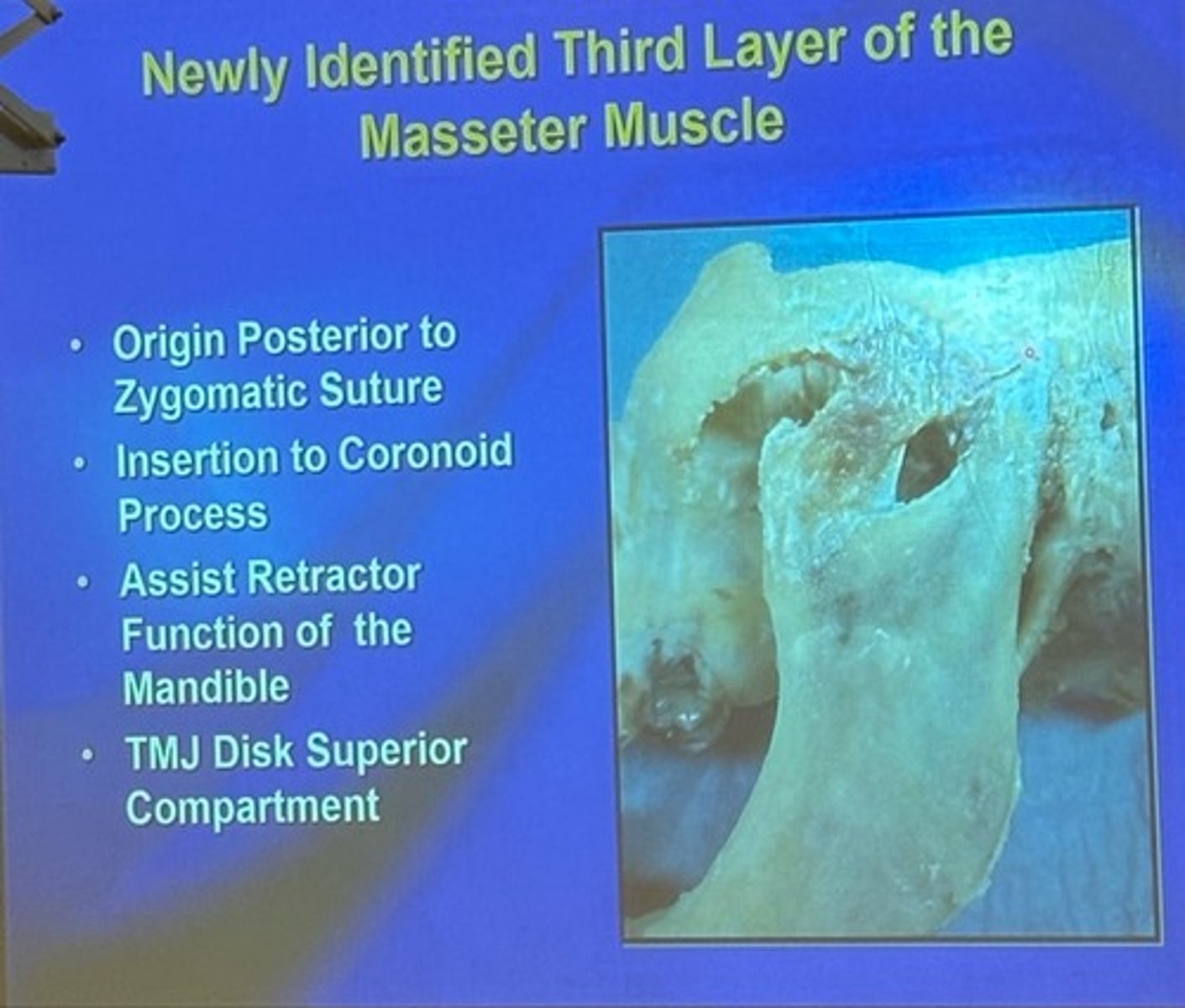
what is the origin and insertion of the newly identified third layer of the masseter muscle
origin: inferior border of zygomatic arch/posterior to zygomatic suture
insertion: masseteric tuberosity/coronoid process
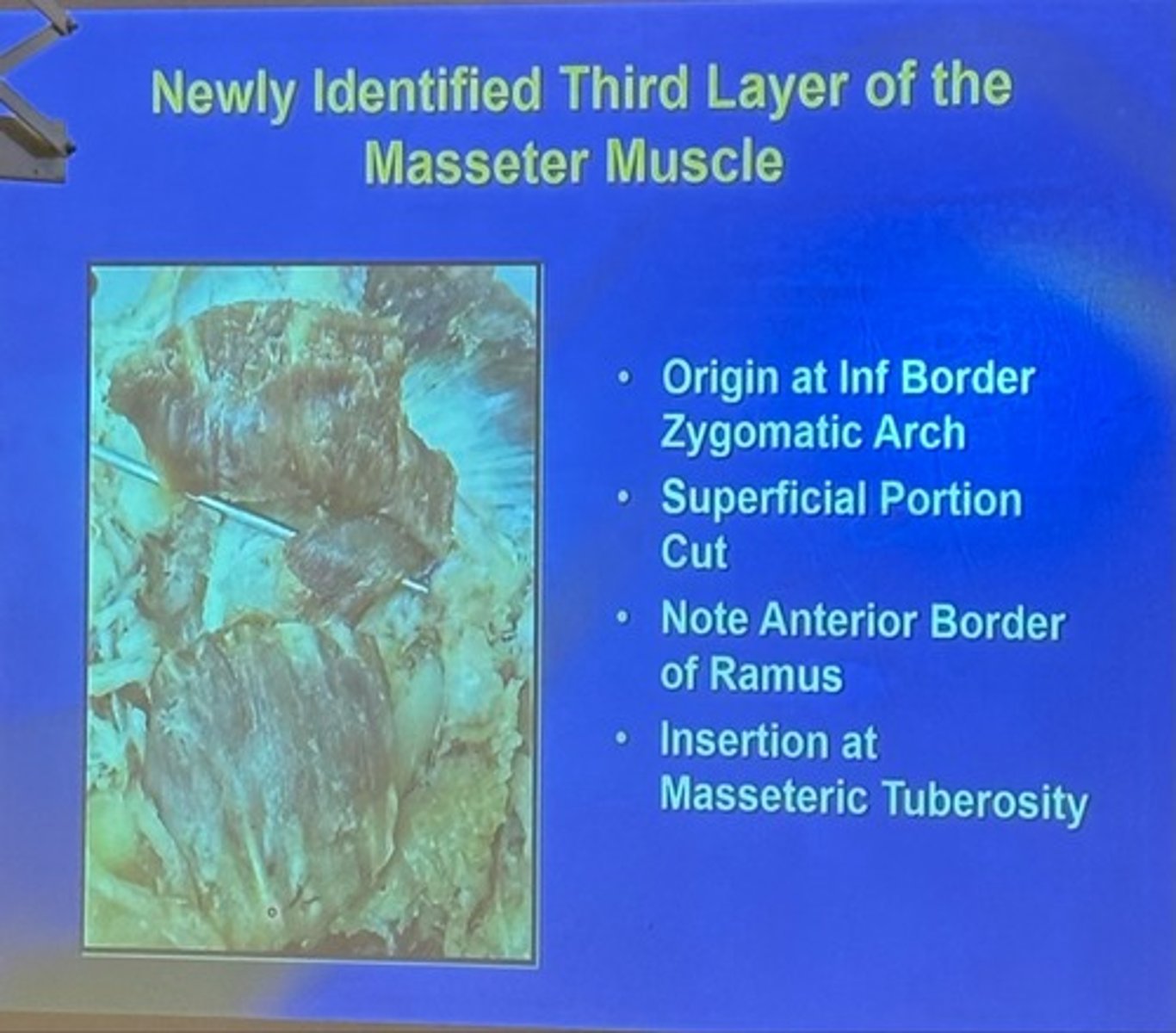
what is the action of the newly identified third layer of the masseter muscle
assists retractor function of the mandible
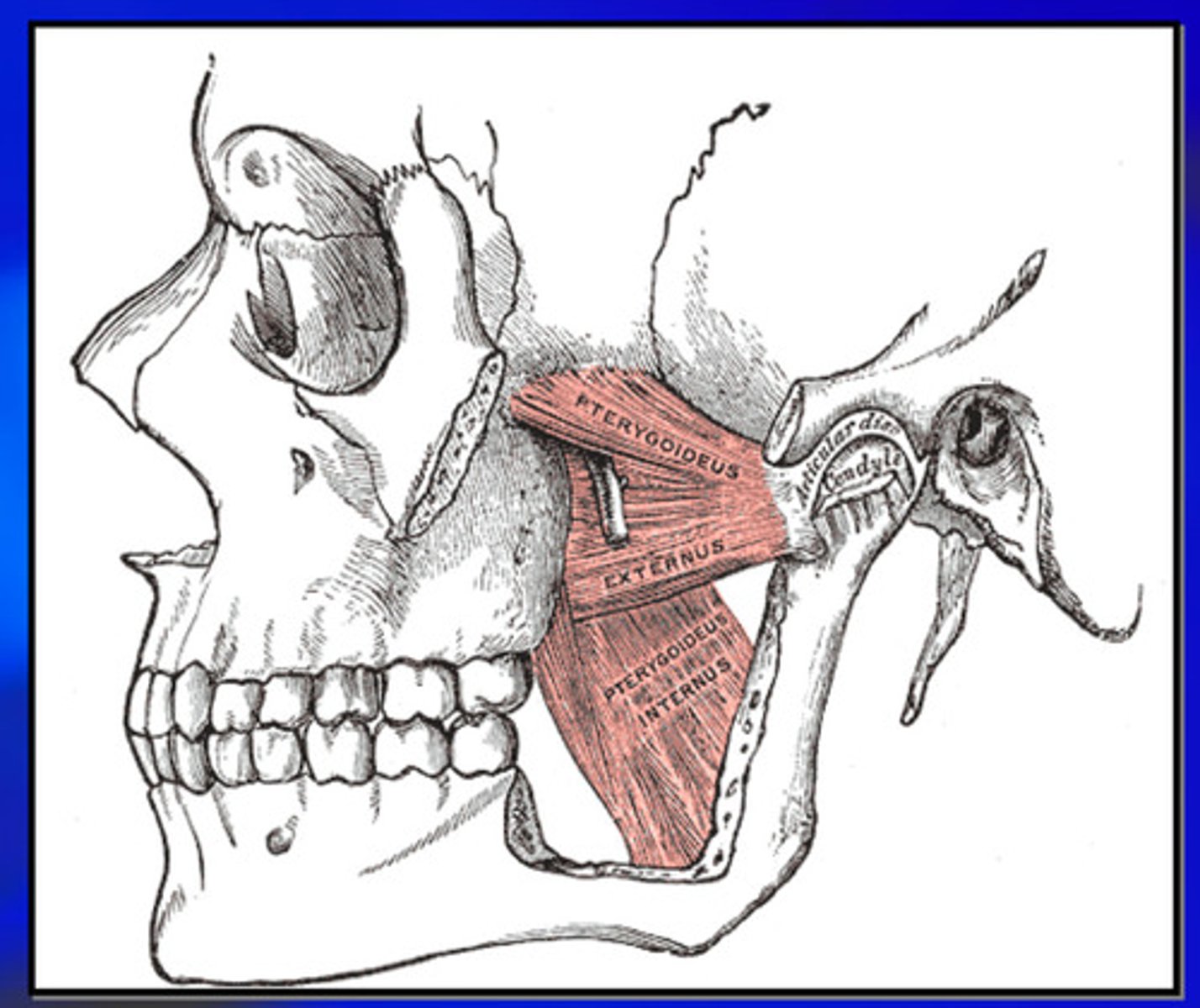
medial and lateral pterygoid pictures
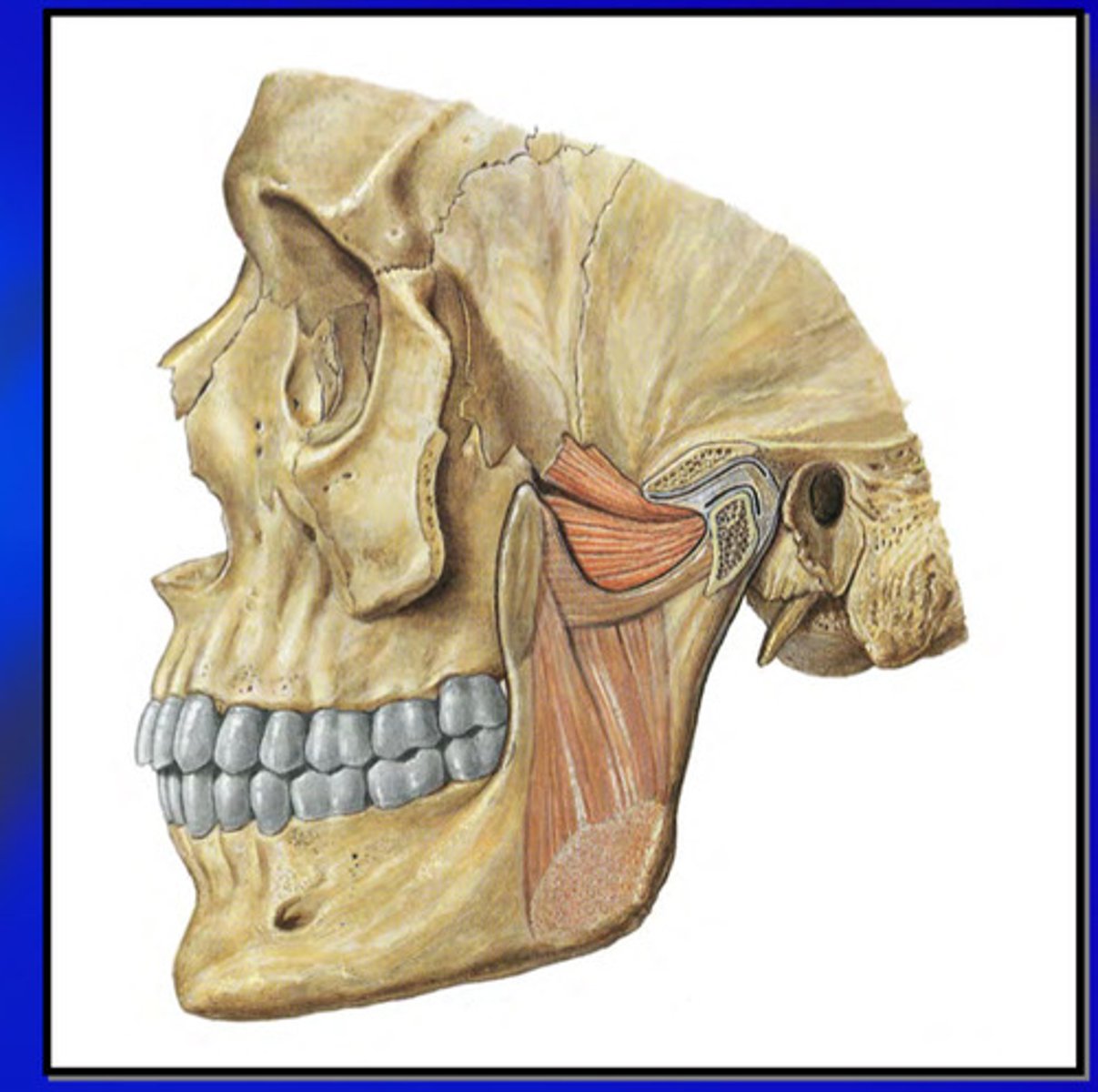
the lateral pterygoid muscle is the most important indicator of what
occlusal harmony
the lateral pterygoid muscle is highly active in what movements
opening/closing and excursive movements
the lateral pterygoid muscle is the only muscle to insert into where
the TMJ capsule
the inferior lateral pterygoid is active in what action
protrusion
when the inferior lateral pterygoid is in concert with depressor muscles, it will cause what kinds of movements
working and nonworking movements
the active side of inferior lateral pterygoid muscle contraction is the ___-__________ side
non-working
the superior head of the lateral pterygoid is _____ as large as the inferior head of the lateral pterygoid
1/3
the superior lateral pterygoid inserts onto where
onto the TMJ capsule and has some fibers that insert onto the disc
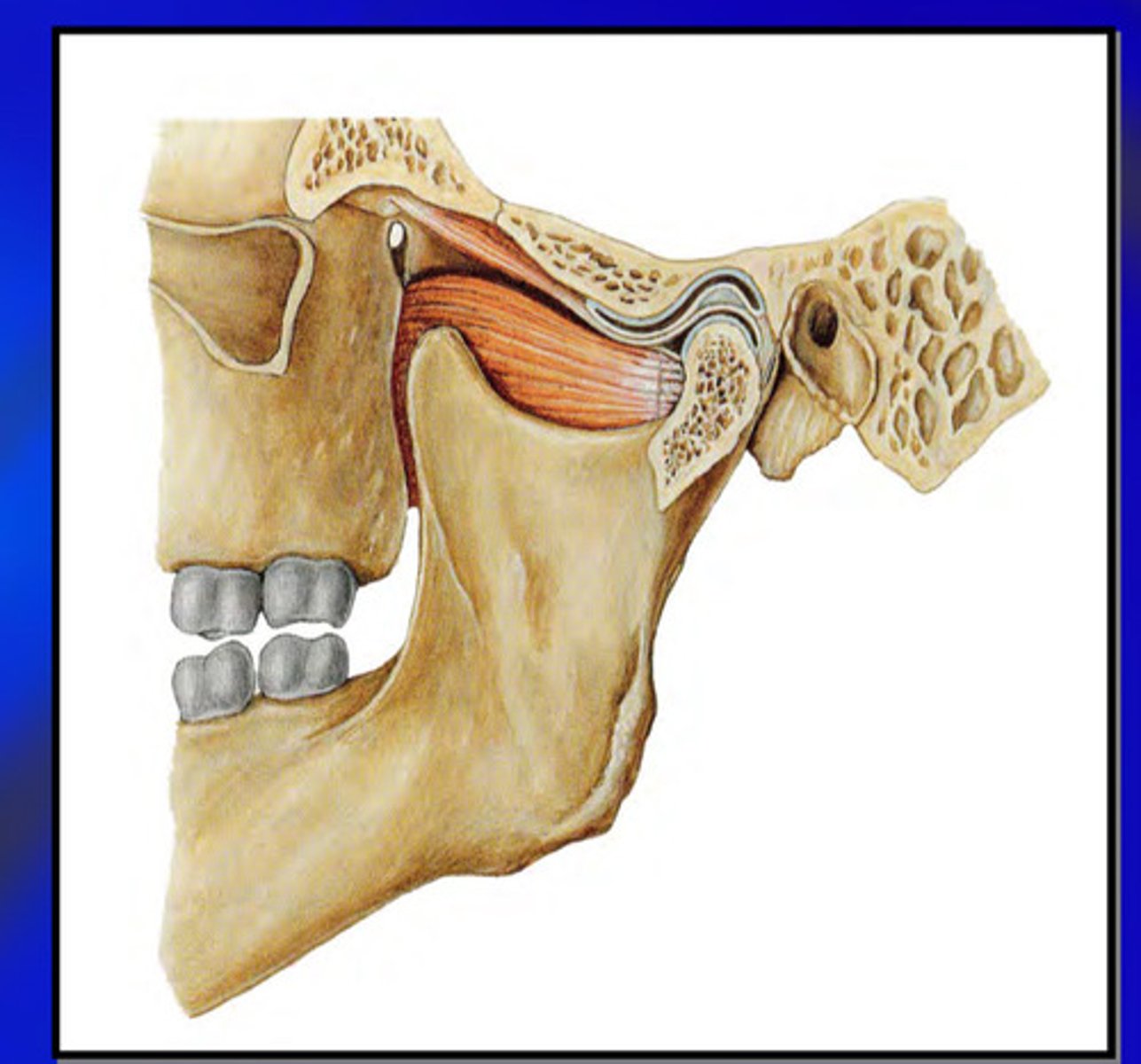
the superior lateral pterygoid is inactive during ______ and highly active during ________
opening; closure
the superior lateral pterygoid contracts while ?
while lengthening
the superior lateral pterygoid is most susceptible to what
to injury
what is the action of the medial pterygoid muscle
elevator of the mandible
the medial pterygoid muscle supports the activity of which muscle
lateral pterygoid muscle
the medial pterygoid muscle is highly active during what kinds of movement
rotary or protrusive movements
origin and insertion of medial pterygoid muscle
origin- pterygoid fossae of sphenoid bone
insertion- medial angle of mandible
origin and insertion of lateral pterygoid muscle
origin of superior head: inferior surface of greater wing of sphenoid (roof of infratemporal fossa)
origin of inferior head: lateral surface of lateral pterygoid plate
insertion: pterygoid fovea of mandible (on the neck of the condyle) - both run posteriorly from their origin to their insertion (superior also inserts onto TMJ capsule and some fibers into the disc)
the suprahyoid muscles act as the __________ of the hyoid bone and the __________ __________ of the mandible
elevators; depressor retractors
origin and insertion of digastric muscle (posterior head)
origin: mastoid portion of temporal bone
insertion: hyoid bone
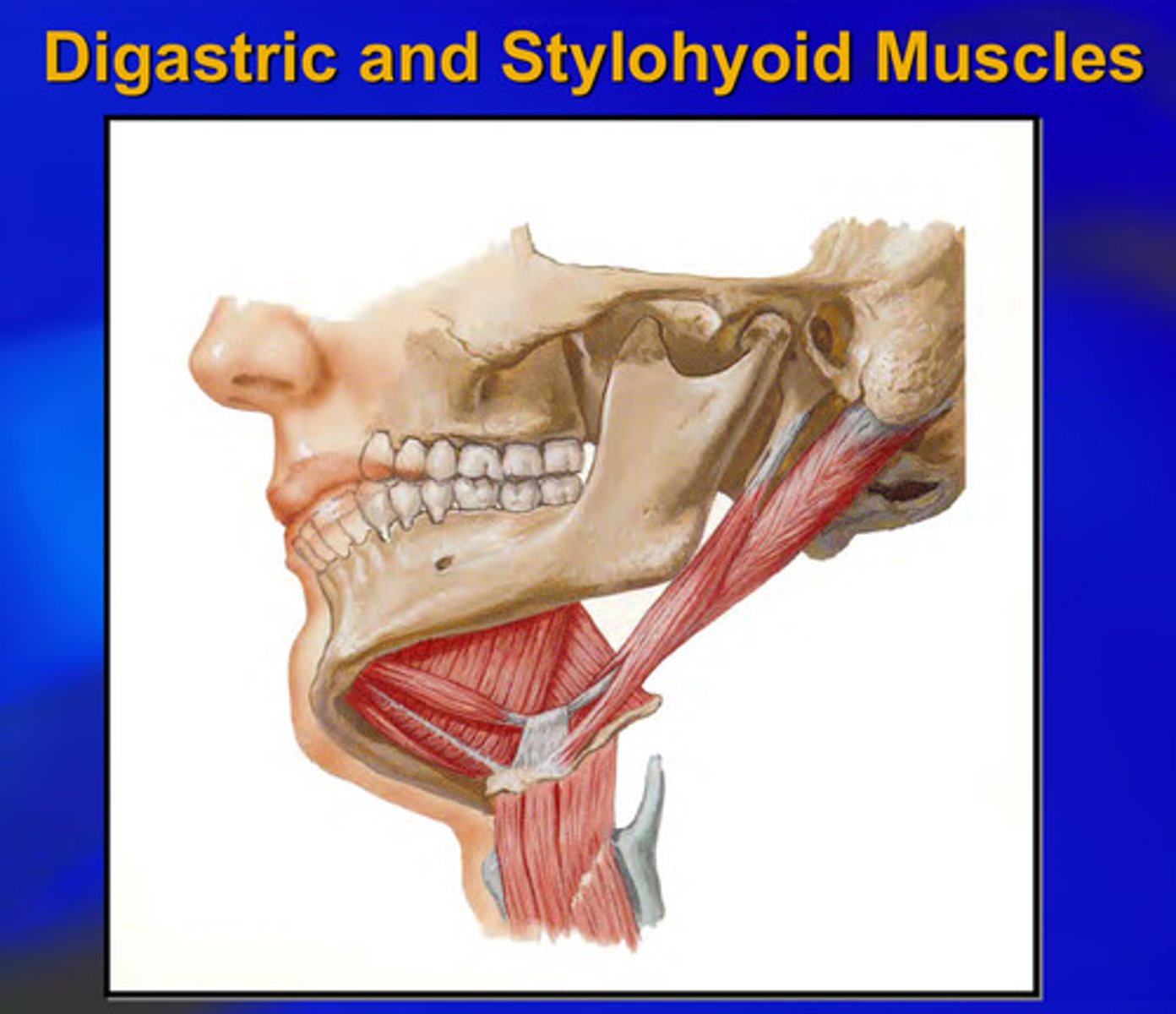
origin and insertion of stylohyoid muscle
origin: styloid process of temporal bone
insertion: body of hyoid
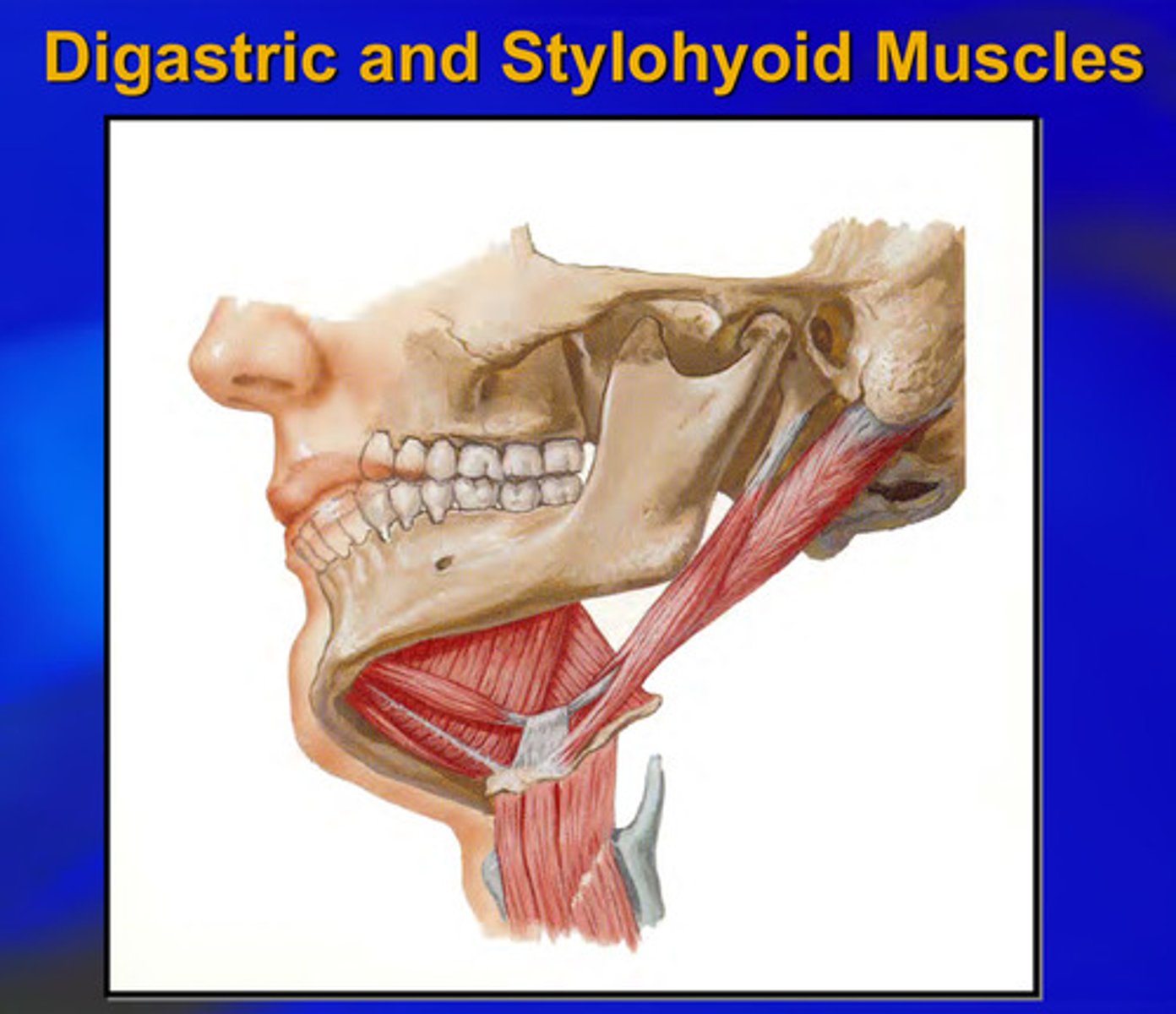
what are the 4 suprahyoid muscles
digastric, stylohyoid, mylohyoid, geniohyoid
how are the suprahyoid muscles and the tongue related
extrinsic muscles of the tongue act as depressor retractors and the suprahyoid muscles can elevate the tongue
what is the action of the geniohyoid
elevates the hyoid bone and the tongue
what is the origin and insertion of the geniohyoid
origin: mandible
insertion: hyoid
what is the action of the mylohyoid
elevates the hyoid bone, base of tongue, and raises the floor of the mouth
what is the origin and insertion of the mylohyoid
origin: mylohyoid line of the mandible
insertion: mylohyoid raphe and the body of the hyoid
what is the action of the digastric
raises the hyoid bone and the base of the tongue
what is the action of the stylohyoid
elevates the hyoid bone and the base of the tongue
what 4 muscles make up the infrahyoid muscles
sternohyoid, omohyoid, sternothyroid, thyrohyoid
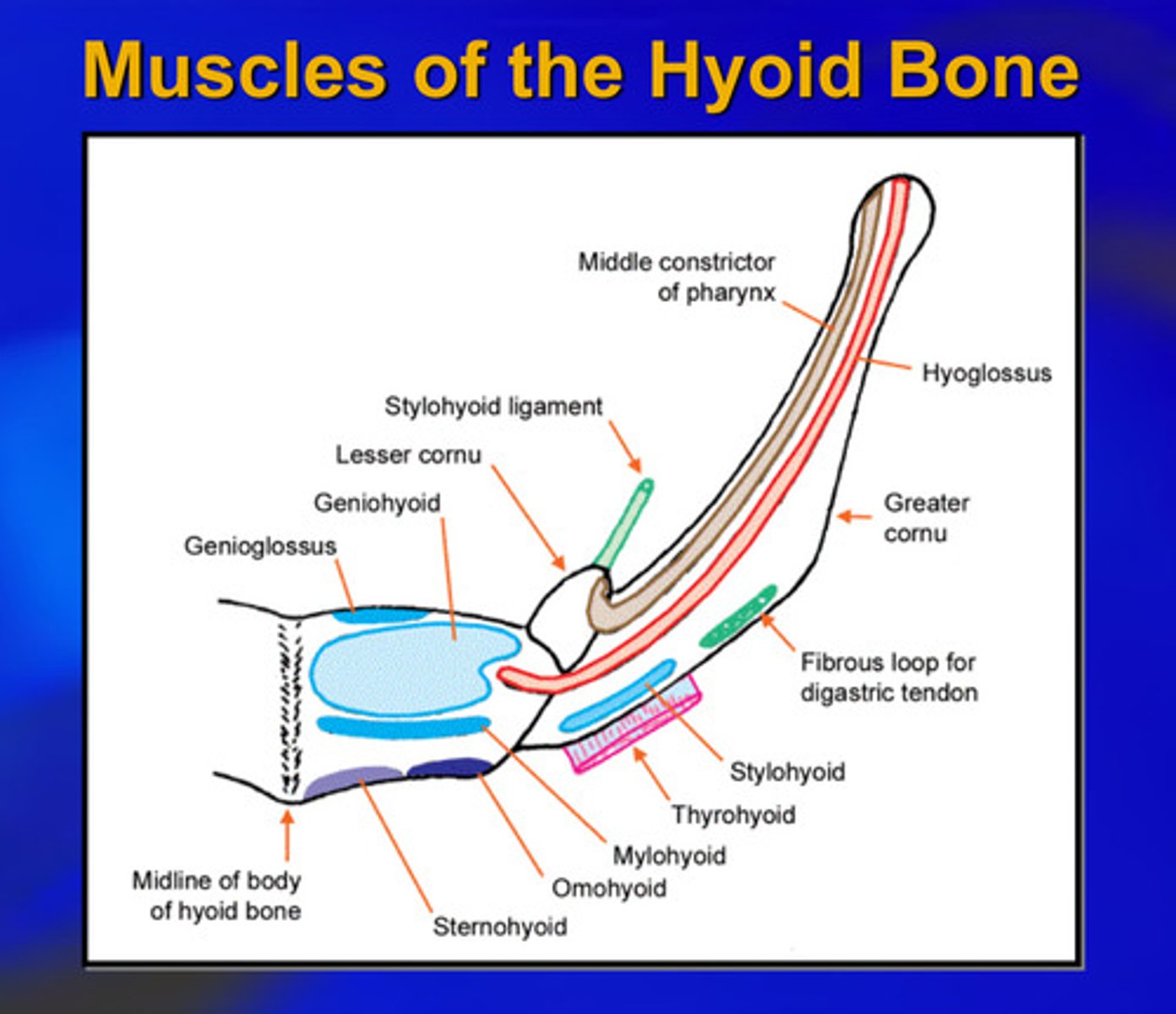
all of the infrahyoid muscles act to _______ the hyoid bone
fixate
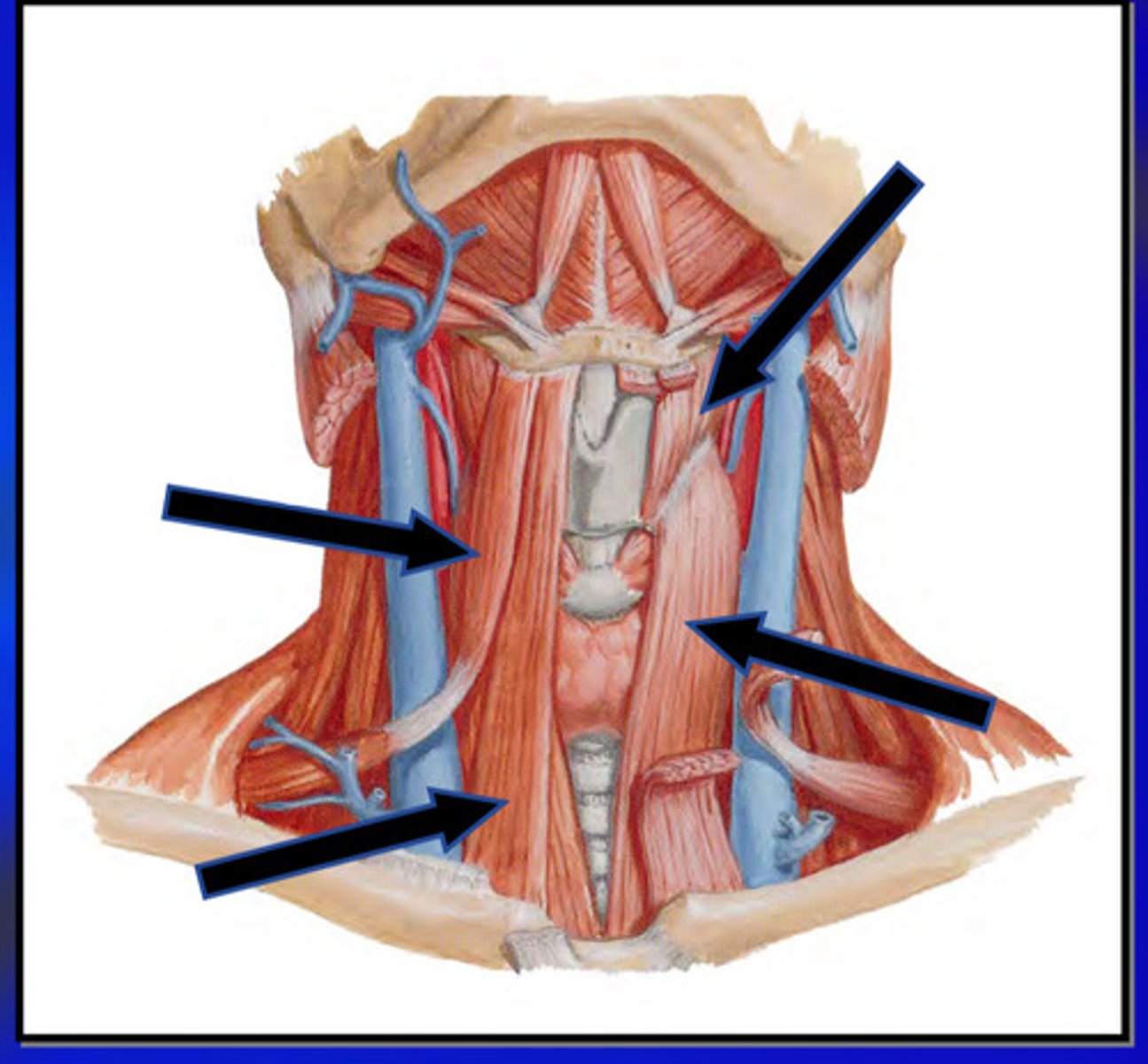
diagram of muscles of the hyoid bone
3/4 infrahyoid muscles are attached (3)
all suprahyoid muscles are attached (4)
genioglossus and hyoglossus (2)
total 9 muscles are attached to hyoid bone
mandibular muscles demonstrate standard __________ ___ _________ in healthy subjects during the vertical and horizontal movements of the mandible
patterns of activity
which muscle initiates the activity of mandibular opening, be specific
the inferior head of lateral pterygoid
which kinds of muscles help to follow the mandibular opening action to completion (general)
depressor/retractors
normal mandibular opening is a _________ function
depressor
forced (isometric) mandibular opening activates which muscle as soon as the lateral pterygoids are activated
digastric muscle
which 2 muscles act as assists during mandibular opening
temporalis and masseter muscles
which 3 muscles are active during elevation in unrestricted normal closing
medial pterygoid, anterior temporalis, and masseter muscles
which muscle group relaxes during unrestricted normal closing
suprahyoid muscles
in unrestricted normal closing, the _________ lateral pterygoid relaxes to the action of the _________ lateral pterygoid
inferior; superior
which 2 muscle fibers or the temporalis contract to aid positioning in unrestricted normal closing
posterior and middle
which 2 muscles can add power in centric?
masseter and temporalis
power muscles provide what kinds of capabilities to the mandible
crushing capabilities
what is the average power of the power muscles
320 pounds
what is the envelope of border movements
the volume of space within which all movements of a specified point on the mandible occur
what are chewing cycles
a pathway of symmetrical movements formed by the repeated opening and closing of the mandible during mastication
example of root angulations and maxillary occlusal plane
the envelope of border movements is limited by anatomical considerations such as?
ligaments and tooth contacts
most natural movements do not utilize this maximum volume but occur ____ ______ the envelope
well within
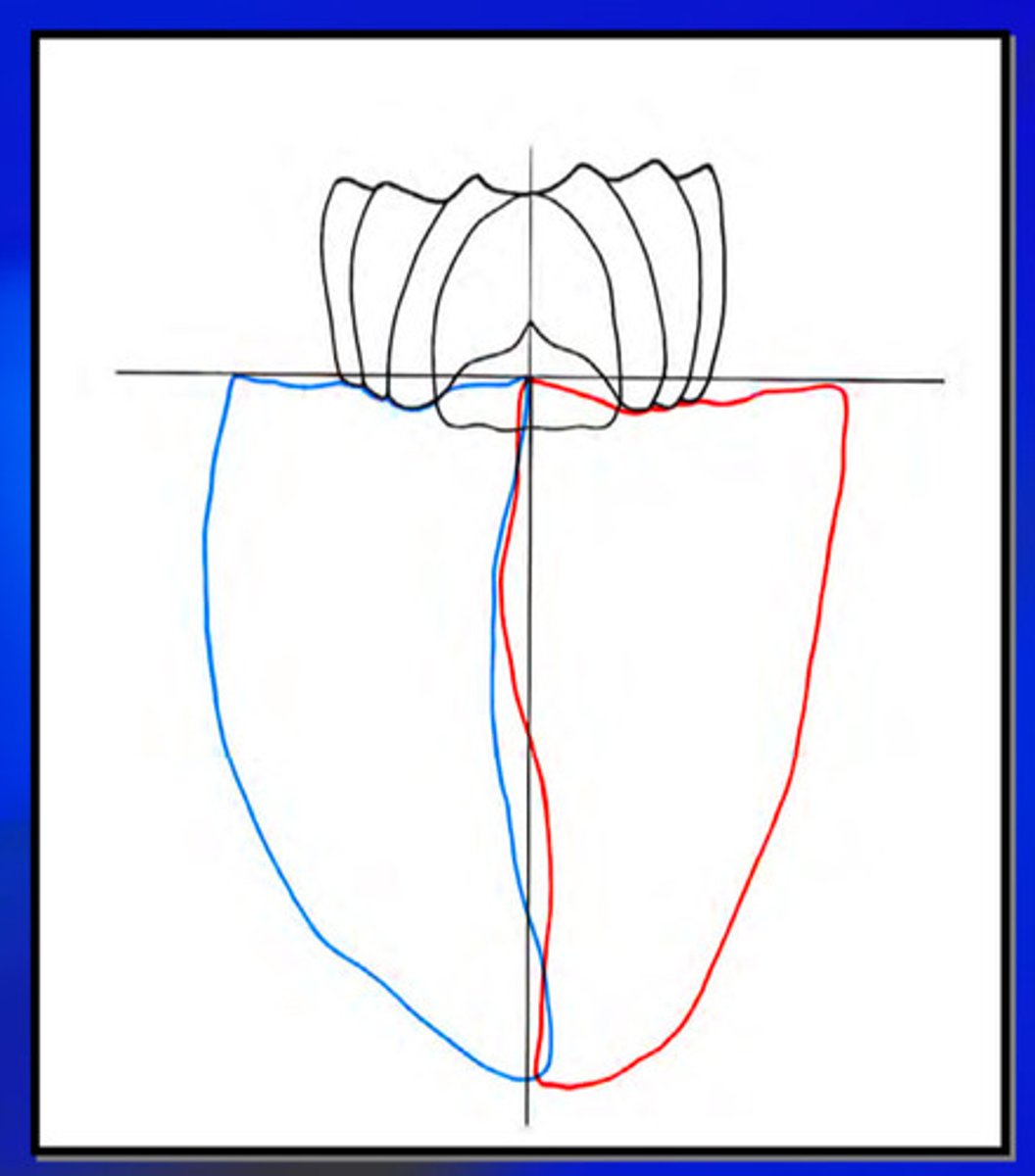
example of frontal plane envelope of border movements
shield shape
figures of sagittal and frontal plane envelope of border movements
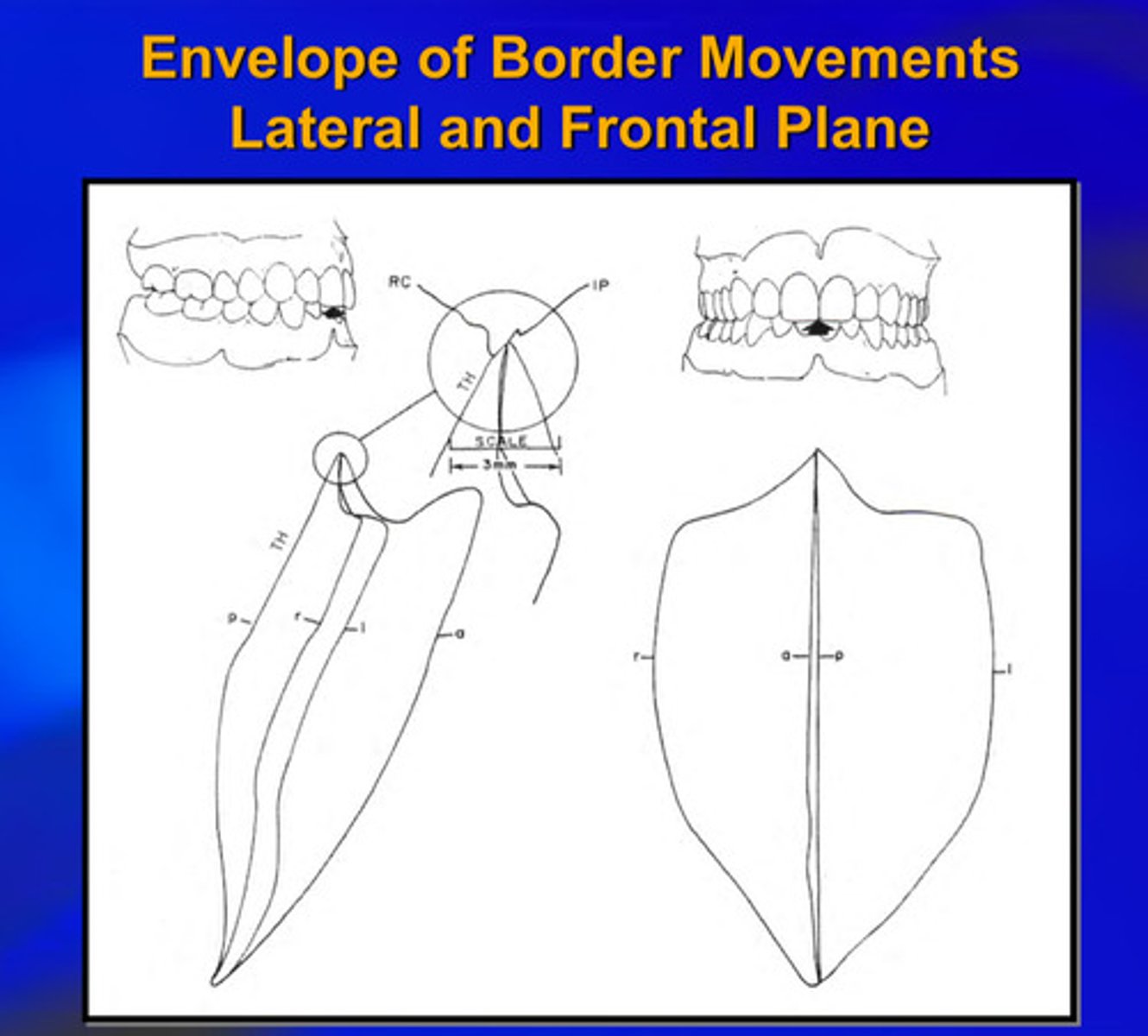
complex chewing movements can be better understood when they are related to the more familiar _______ _________
border movements
these relationships between chewing movements and border movements show where the chewing and border paths ______ and indicate where ________ _______ occur during chewing
coincide; occlusal contacts
unilateral chewing is characterized by wide _______ __________ movements and frequent ________ contacts between opposing teeth
lateral closing; sliding
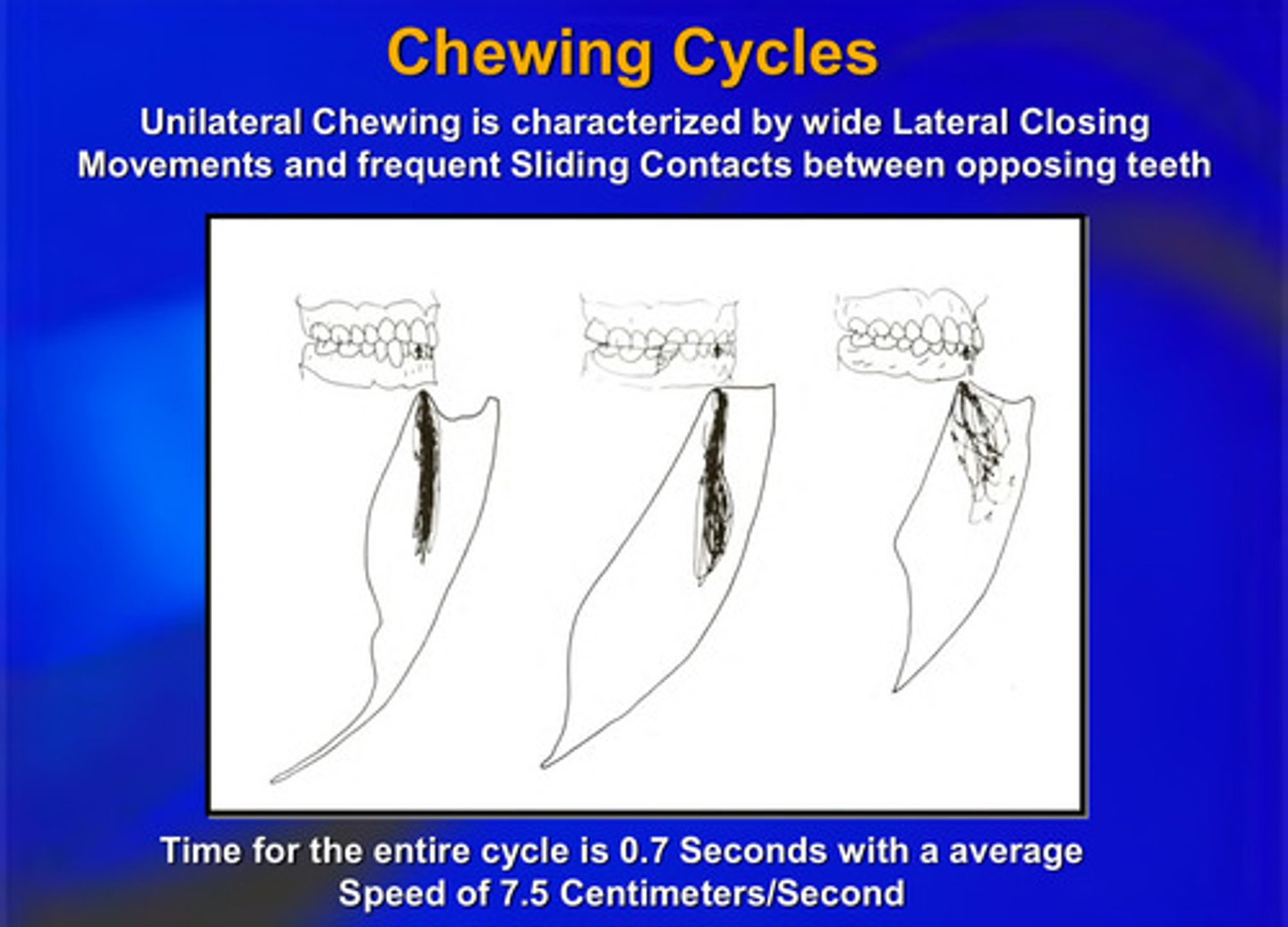
time for the entire chewing cycle is ____ seconds with an average speed of what
0.7 seconds with average speed of 7.5 cm/second
what are the 3 phases of the chewing cycle
1) closing stroke
2) masticatory or power stroke
3) opening stroke or free movement phase
what happens in the closing stroke in the chewing cycle
mandible is brought upward and outward to come into initial contact with the food