4.Transmission of the excitation (inhibition) from one excitable cell to another. Synapses- types of synapses. Chemical synapses. Neurotransmitters and modulators. Postsynaptic potential. Summation of the postsynaptic potentials
1/5
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
6 Terms
synapses / types of synapses
🔹 Synapse = presynaptic terminal + synaptic cleft + postsynaptic membrane
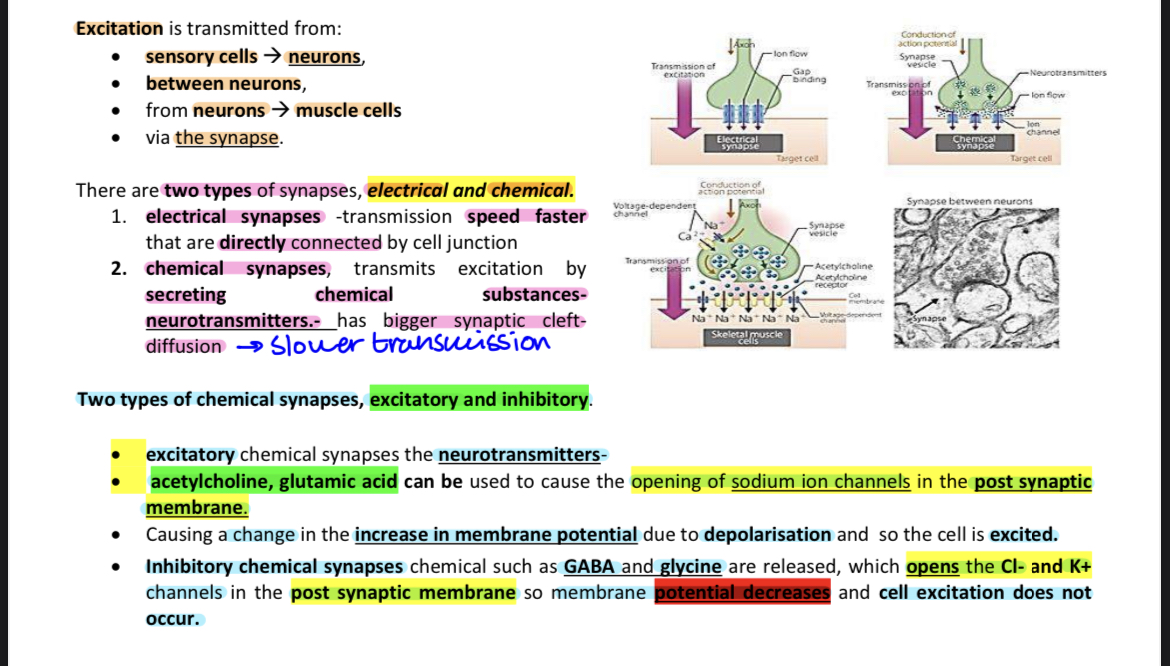
transmission of excitation
Depolarization of the presynaptic cell
Action potential reaches the axon terminal
Voltage-gated Ca²⁺ channels open, and Ca²⁺ enters the presynaptic terminal
Neurotransmitters are released via exocytosis
Neurotransmitters bind to ligand-gated ion channels (receptors) on the postsynaptic membrane
Depending on the receptor:
Excitatory: Na⁺ channels open → Na⁺ influx → further depolarization
Inhibitory: Cl⁻ channels open → Cl⁻ influx → hyperpolarization
If enough Na⁺ enters and threshold is reached → action potential generated in the postsynaptic cell
neurotransmitters and modulators
neuromodulators affect inhibitory or excitatory response of the RECEPTORS

post synaptic potential
post synaptic summation
Temporal summation = one neuron firing rapidly → each small signal adds up → possibly triggers an action potential in the next cell.
