1.3.1 compression, encryption and hashing
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
compression
the process used to reduce the storage space required by a file, meaning you can store more files with the same amount of storage space
important for sharing files over networks or the Internet
the larger a file, the longer it takes to transfer and so compressing files increases the number of files that can be transferred in a given time
lossy compression
reduces the size of a file while also removing some of its information
this could result in a more pixelated image or less clear audio recording
for example, audio files can be compressed lossily by removing the very high or very low frequencies which are least noticeable to the ear
there’s no way to go from the lossy version of the recording back to the full version as there’s no record of what the high and low frequencies were
lossless compression
reduces the size of a file without losing any information
the original file can be recovered from the compressed version
run length encoding
method of lossless compression
repeated values are removed and replaced with one occurrence of the data followed by the number of times it should be repeated
the string AAAAAABBBBBCCC could be represented as A6B5C3.
in order to work well, run length encoding relies on consecutive pieces of data being the same
if there’s little repetition, run length encoding doesn’t offer a great reduction in file size
dictionary encoding
method of lossless compression
frequently occurring pieces of data are replaced with an index and compressed data is stored alongside a dictionary which matches the frequently occurring data to an index
the original data can then be restored using the dictionary
data compressed using dictionary compression must be transferred alongside its dictionary

encryption def
a method used to keep data secure when it’s being transmitted
can be used to scramble data before it’s transmitted and then decipher it once it arrives at its destination
symmetric encryption
both the sender and receiver share the same private key, which they distribute to each other in a process called a key exchange
this key is used for both encrypting and decrypting data, so it’s important that the private key is kept secret
if the key is intercepted during the key exchange then any communications sent can be intercepted and decrypted using the key
asymmetric encryption
two keys are used: one public and a second, private, key
the public key can be published anywhere, while the private key must be kept secret
together, these keys are known as a key pair and are mathematically related to one another
messages encrypted with the recipient’s public key can only be decrypted with the recipient’s private key, which should only be in the possession of the recipient
hashing
transforms a string of characters into a fixed length value or key that represents the original string
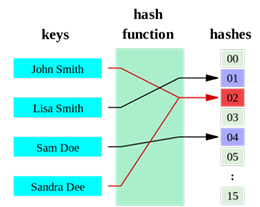
uses of hashing
unlike encryption, the output of a hash function can’t be reversed to form the key
this quality makes hashing useful for storing passwords
a hash table is a data structure which holds key-value pair
a hash function can be used to lookup data in an array/hash table in constant time
when data needs to be inserted, it is used as the key for the hash function and stored in the bucket corresponding to the hash
collisions when using hashing
if two pieces of data (keys) produce the same hash, a collision is said to have occurred
hash table
utilises a key to index and retrieve data efficiently, providing fast access to stored values
goal is to immediately find an item a sorted or unsorted list without the need to compare other items in the data set
hashing function is used to calculate the position of an item in a hash table
overcoming a collision
open addressing - repeatedly check the next available space in the hash table until an empty position is found
linear probing - hashing function delivers the start position from which a linear search can then be applied until the item is found
prevents other items being stored in their correct location
clustering
rehashing
can increase the size of the hash table to avoid collisions
2D hash table - two items can occupy the same position
use linked list / overflow table
properties of a good hashing function
calculated quickly
low chance of collisions
use the least amount of memory possible
operations on a hash table
add
delete
retrieve