Biomechanics Exam V: Tendons & Ligaments Part II
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
What is the mechanical behavior of tendons and ligaments?
they have a viscoelastic quality, meaning they are strong but have some degree of flexibility
What is the mechanical behavior of tendons?
they are strong enough to create and absorb forces, but are also flexible to allow for joint movement and stability
What is the mechanical behavior of ligaments?
they are strong enough to stabilize joints, but flexible enough such that the joints can move in the way they were intended
What are tendons composed of?
collagen fibrils
proteoglycan matrix
fibroblasts that are arranged in parallel rows
What are ligaments composed of?
collagen fibers that are slightly less organized than those in tendons
a higher percentage of proteoglycan matrix
fibroblasts
What are the functions of tendons (5)?
to transmit forces from muscle to bone
to carry compressive forces when wrapped around a bone like a pulley
to facilitate skeletal muscle movement
proprioception
to store energy
Proprioception
The body's ability to sense its position and movement in space
What are the functions of ligaments (3)?
to maintain correct bone and joint alignment
to junction as a passive joint stabilizer when working with joint capsules
proprioception
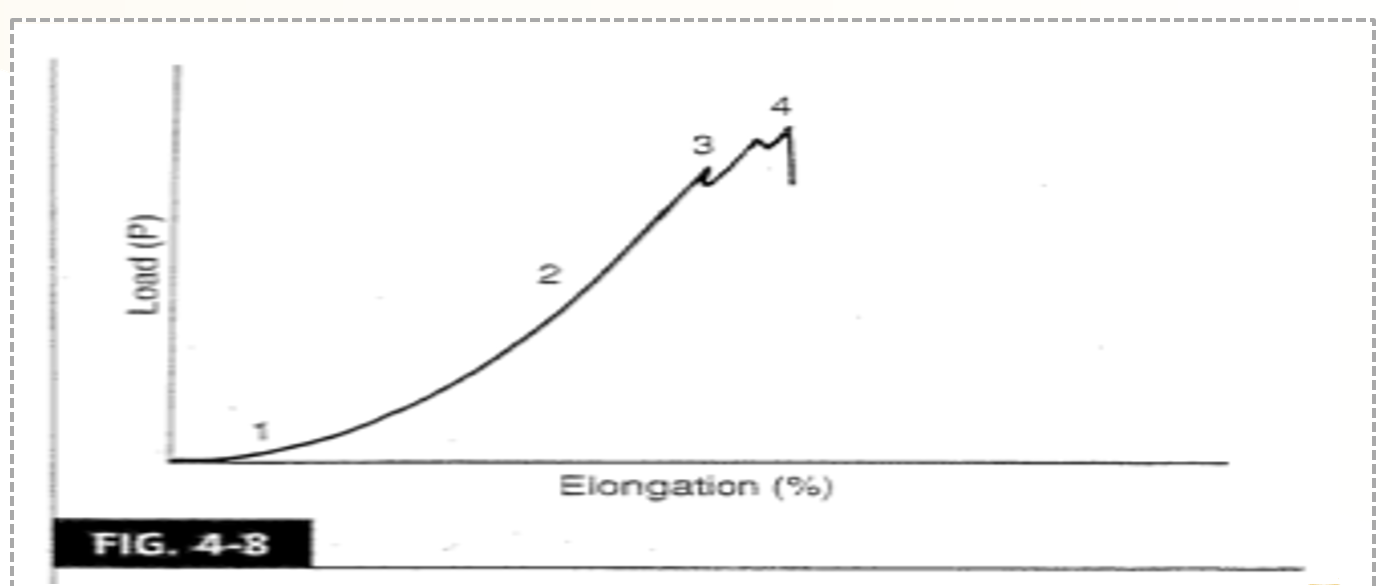
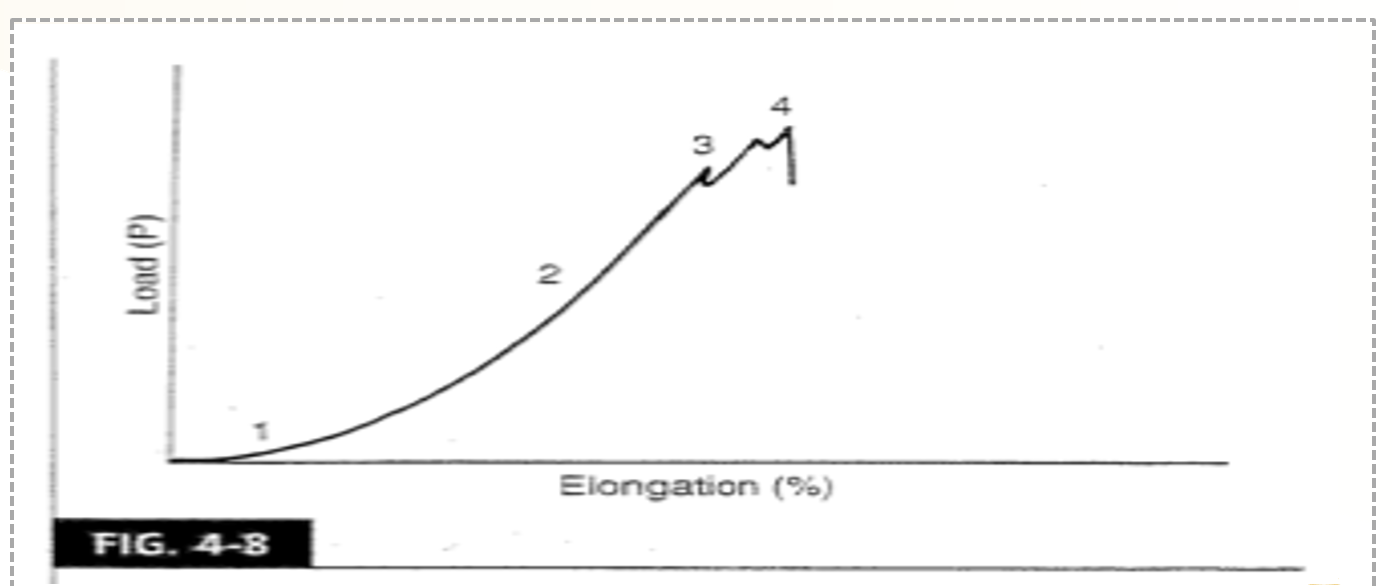
What are the mechanical properties of tendons and ligaments based off this curve?
top region: some elongation occurs when very little load is applied
linear region: there is a significant change in elongation due to increased loading
microfailure: small fiber damage occurs, but overall structural continuity remains and the tissue can still respond to load
macrofailure: the curve stops because the tendon/ligament loses structural continuity and can no longer respond to applied loads
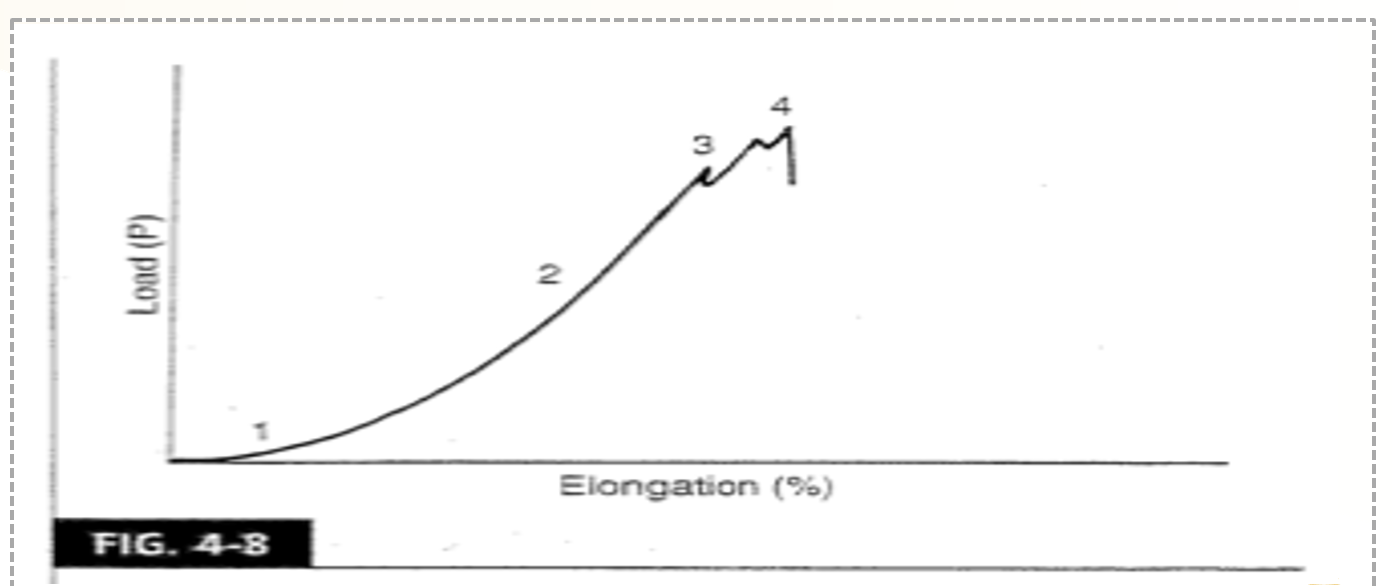
Beyond the linear region _____ is unpredicatble.
fiber failure
What is the hysteresis loop relative to ligaments?
the same load repeated over time creates small deformations in the ligament, resulting in energy loss and reduced stiffness upon subsequent loading
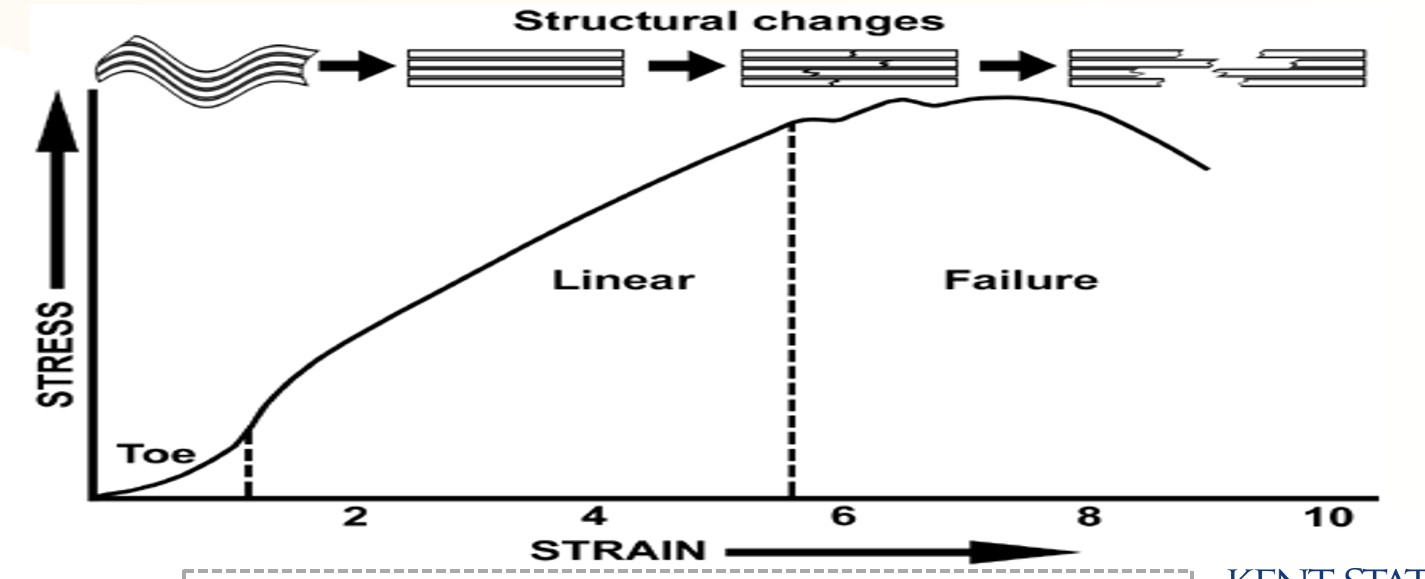
What is the Load Elongation - Stress Strain Curve showing?
the relationship between load and elongation, including an image of the structure of tendons and ligament in response to a load
Stress
the application of a load
Stresses cause ____.
strain
Strain
the deformation in a tendon / ligament that is caused by stress
Viscoelastic qualities are rate dependent. What does this mean?
how tendons and ligaments respond to a load depends on the rate at which the load is applied
Faster loading = _____.
a steeper linear region on the load / elongation graph
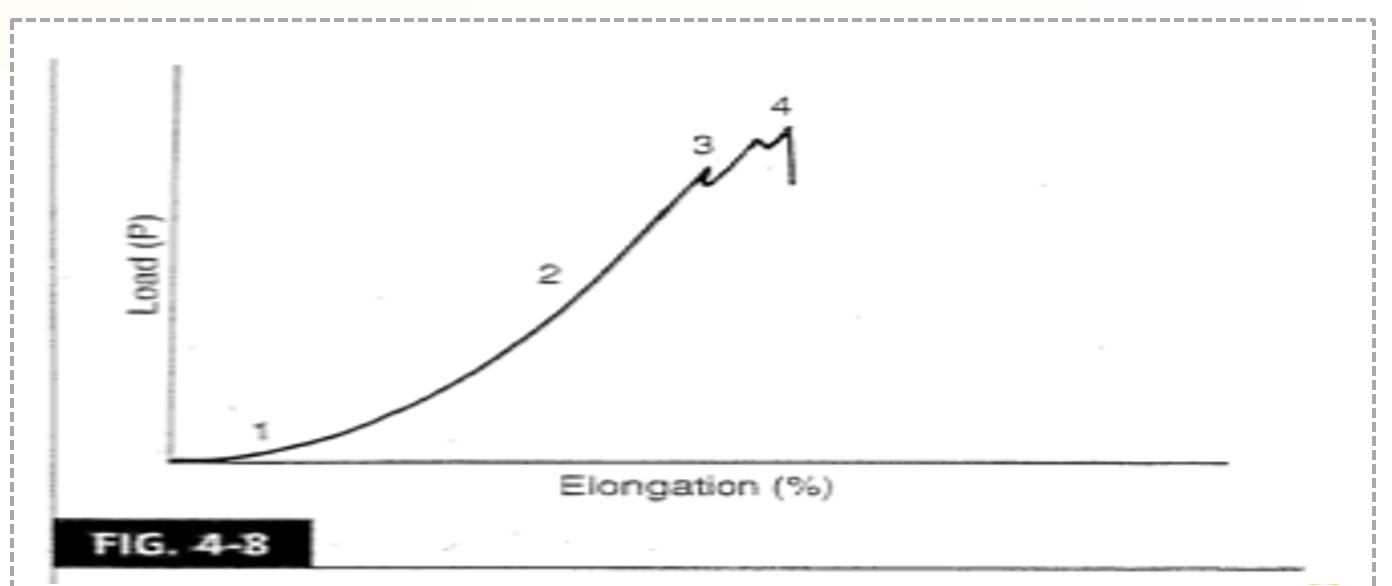
What does “faster loading = a steeper linear region” mean?
it means that faster loads cause greater elongation in tendons / ligaments quicker. The graph shifts to the left, and you get to micro and macrofailure sooner
What are the effects of repeated loading on the load elongation curve?
structures that are loaded chronically create microfailure that accumulates over time. In other words, you are stretching the tendon / ligament over time.
What is the end result of repeated loading on the load elongation curve?
the curve shifts to the right slightly over time
Viscoelastic properties:
stress and strain are not constant, but depend upon the time of displacement
the major types of behavior of viscoelasticity are: creep and stress relaxation
What is creep?
increasing deformation under constant loading
this is different than elastic material which does not exhibit increased deformation over time
What is stress relaxation
stress will be reduced or will relax under constant deformation
What is the stress-relaxation test?
a test that measures viscoelasticity by applying a low level load and keeping strain constant over time to observe stress reaction

What is the creep test?
a test that measures viscoelasticity by applying a low level load and keeping stress constant over time to observe strain reaction

Hysteresis / Energy Dissipation Curve
a graph that shows if a viscoelastic material is loaded and unloaded, the unloading curve will not follow the loading curve
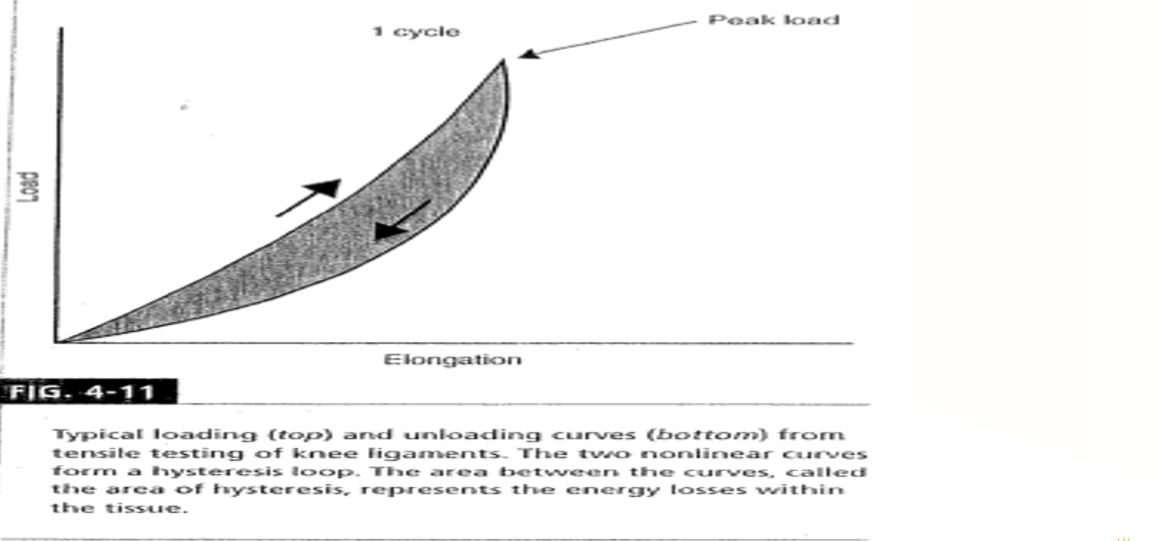
What does the difference between the two curves on the hysteresis graph represent?
the amount of energy that is lost during loading
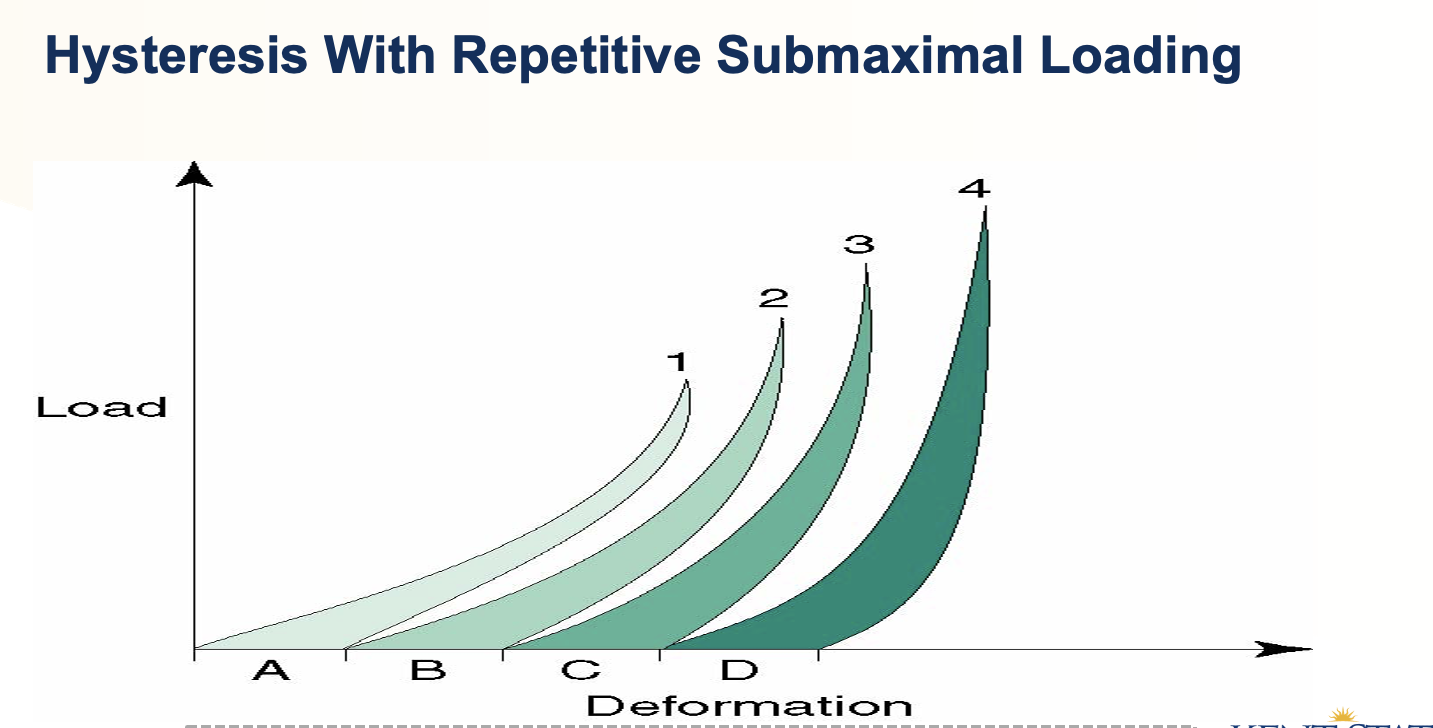
What do the two curves on the hysteresis graph show?
that the amount of hysteresis under cyclic loading is reduced and eventually the stress strain curve becomes reproducible