Male Reproductive System: word parts
1/62
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Exam #3: anatomy, word parts
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
Origination and transportation of sperm
formed in seminiferous tubules (testes) —> epididymis —> vas deference —> seminal vesicle and duct —> urethra —> prostate gland —> penis —> outside body
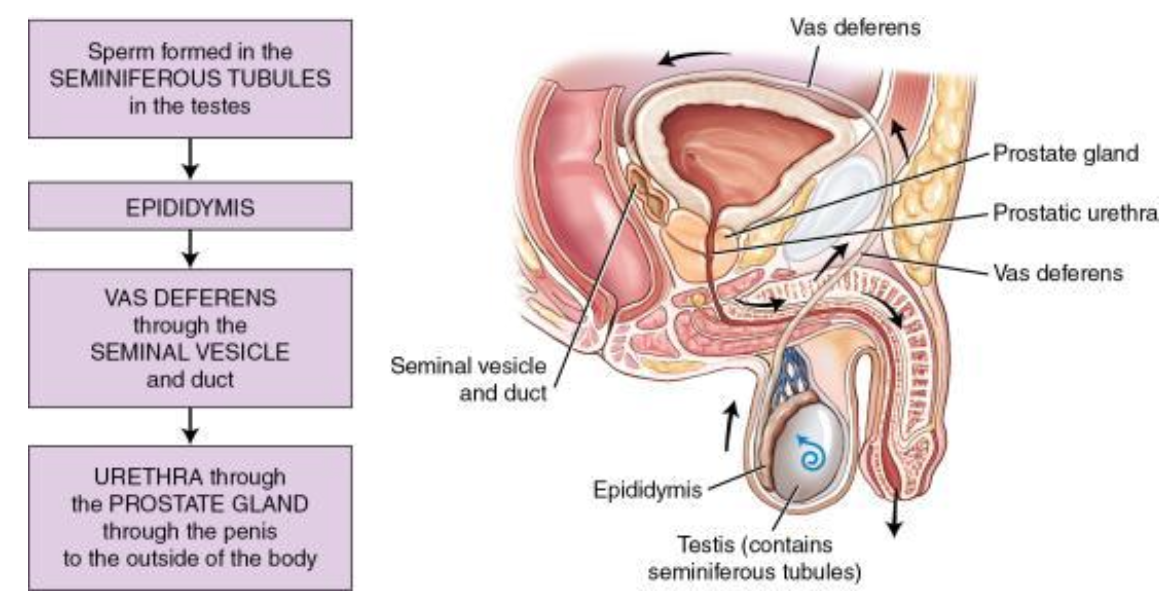
testis (pl. testes)
primary sex organ, paired, oval-shaped, and enclosed in a sac called the scrotum; produces spermatozoa (sperm cells) and testosterone
aka testicle
seminiferous tubules
approximately 900 coiled tubes w/n the testes in which spermatogenesis occurs
sperm
the microscopic male germ cell, which, when united w. the ovum, produces a zygote (fertilized off) that w. subsequent development becomes an embryo
aka spermatozoon, pl. spermatazoa
testosterone
the main male sex hormone
Fx: stimulate the development of the male reproductive organs and 2ndary sex characteristics (ex: facial hair)
epididymis
coiled tube attached to each testis that provides for storage, transit, and maturation of sperm; continuous with each vas deferens
vas deferens
duct (tube) carrying the sperm from the epididymis to the urethra
the spermatic cord enclosed each ___ w. nerves, lymphatics, arteries, and veins. Since the urethra also connects with the urinary bladder to carry urine out the body, a circular muscle constricts during intercourse to prevent urination
aka ductus deferens
seminal vesicles
2 accessory glands located posterior to the base of the bladder that open into the vas deferens. The glands secrete a thick fluid that forms part of the semen
prostate gland
walnut-shaped gland that encircles the proximal section of the urethra. It secretes a fluid that aids in the movement of the sperm and ejaculation
(located anterior/before) the bladder
semen
composed of sperm, seminal fluids, and other secretions
scrotum
sac containing the testes and their corresponding epididymides, from which each vas deferens begins. It is suspended on both sides of and posterior to the penis.
penis
male organ of urination and coitus (sex)
glans penis
enlarged tip on the end of the penis
prepuce
fold of skin covering the glans penis in uncircumcised males (foreskin of the penis)
genitalia (aka genitals)
reproductive organs (M/F); includes internal and external reproductive organs
gonads
primary reproductive organs; testes = M; ovaries = F
andr/o
male
balan/o
glans penis
epididymis/o
epididymis
orch/o
testis, testicle (o)
orchi/o
testis, testicle (i)
orchid/o
testis, testicle (d)
prostat/o
prostate gland
sperm/o
sperm, spermatozoon (pl. spermatozoa)
spermat/o
sperm, spermatozoon (pl. spermatozoa) (t)
vas/o
vessel, duct (vas deferens in terms of describing the M repro system)
vesicul/o
seminal vesicle(s)
cyst/o
bladder, sac
crypt/o
hidden
lith/o
stones, calculus
olig/o
scanty, few
a-
absence of, w/o
an-
absence of, w/o (N)
hyper-
above, excessive
-algia
pain
-ectomy
excision, surgical removal
-ia
diseased or abn state, condition of
-ic
pertaining to
-ism
state of
-itis
inflammation
-lith
stone(s), calculus
-tomy
cut into, incision
-pexy
surgical fixation
-pathy
disease
-plasia
condition of formation, development, growth
-plasty
surgical repair
-rrhea
flow, discharge
-stomy
creation of an artificial opening
andropathy
disease of the male (specific to the male)
anorchism
state of absence of testis (uni or bilateral)
balanitis
inflammation of the glans penis
balanorrhea
discharge from the glans penis
benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH)
excessive development pertaining to the prostate gland
(nonmalignant enlargement; causes narrowing of urethra = interferes w. passage of urine) Sx: frequency of urination, nocturne, utinary retention, incomplete emptying of bladder
aka benign prostatic hypertrophy
prostatic hyperplasia
tissue changes resulting from an abnormal incr. in the # of cells as may occur w. age
cryptorchidism
state of hidden testis; aka undescended testicle(s)
(during fetal development testes are located in abdominal area near kidneys. Before birth they move down into scrotal sac; failure to descend from abd cavity results in this)
epididymitis
inflammation of the epididymis
orchiepididymitis
inflammation of the testis and the epididymis
orchitis (aka orchiditis)
inflammation of the testis
prostatitis
inflammation of the prostate gland
prostatocystitis
inflammation of the prostate gland and the (urinary) bladder
prostatolith
stone(s) in the prostate gland
prostatorrhea
discharge from the prostate gland
prostatovesiculitis
inflammation of the prostate gland and the seminal vesicles