CH10: MOTIVATION AND EMOTION
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
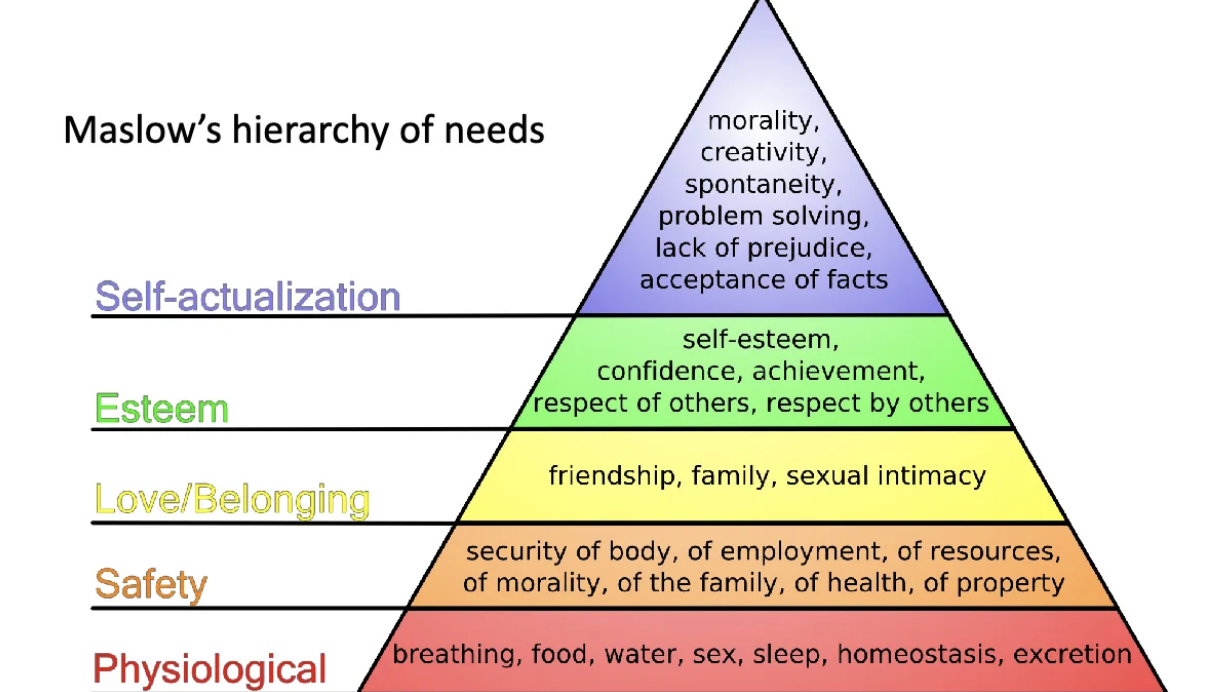
maslows hierarchy of needs stage
2 theoretical approaches to motivation
evolutionary perspective
humanistic perspective
4 observations that drive the theory of evolution
organisms vary in endless ways: size, speed, strength, visual/hearing abilities, digestive processes, wisdom
some of these characteristics are heritable—can be passed down from one generation to the next
availability of resources can never catch up with the rate of reproduction— competition for resources occur within and across species
a heritable trait will become prevalent if this trait enhances the survival of an organism and its offspring
natural selection
natural selection posits that heritable characteristics (e.g., the long neck of a giraffe) that provide a survival or reproductive advantage are more likely than alternative characteristics (e.g., short neck) to be passed on to subsequent generations
giraffe example fo rnat selecftion
“long neck” is selected whereas “short neck” is eliminated over time
fitness
fitness refers to the reproductive success (number of descendants) of an individual organism relative to the average reproductive success in the population
adaptation
adaptation is an inherited characteristic that increased in a population (through natural selection) because it helped solve a problem of survival or reproduction during the time it emerged
directional selection
for one extreme trait
against other extreme
stabilizing selection
for moderate trait
against both extremes
disruptive selection
for both extremes
against moderate traits
batemans principle
Reproductive variance (number of sex partners) differs between genders for a number of reasons.
Females: Lower variance (one mating fertilizes eggs).
Males: Higher variance (reproductive success tied to number of mates)
t/f few males have very high reproductive output, many males have little or no reproductive output
true
which gender is choosier when picking mate partner
females
what are females that carefully select their mates at lower risk ffor
losing their reproductive investment
cross sectionally, men prefer what age group women
Cross culturally, men prefer women younger than themselves because younger women tend to produce more healthy children, and women the opposite because of ability to sustain the family
harem
one dominant male mates with multiple females, while other males have little or no access to reproduction. This leads to high reproductive variance in males (a few males father many offspring, while many males father none) and low variance in females (most reproduce at a similar rate).
harem meaning in animal kingdom
an animal group consisting of a dominant male, a number of females, and their offspring
what does harem imply of reproductive success
males maximize reproductive success by seeking a large number of sexual partners
females maximize reproductive success by seeking a partner with high status and resource
what do females vs males expect from partner
males expect chastity from partners
females expect security from a partner
traits can evolve as an
adaptation or byproduct of behaviour
goal of life in evolution
to reproduce
answers to these from a humanistic approach:
What is your (ultimate) goal of life?
What motivate you to set this goal?
How do you accomplish this goal?
To self-actualize (to live to full potential, to achieve personal dreams & aspirations)
Need for achievement
Set a SMART goal • Self-discipline • Have grit • Have resilience
SMART goal
specific
measurable
achievable
realistic
time bound
hot cognition
• Thoughts, behaviors, and decisions are affected by emotions or immediate physiological needs.
• Act on impulse
• E.g., “I will eat fast food now because I am hungry.”
cold cognition
Think critically and make decisions based on logic and evidence.
Delay gratification
Give yourself a reason why you shouldn’t do something.
E.g., “Fast food is unhealthy. I will go home to make a low-carb dinner.”
grit
courage
people with grit have
passion for their goals
willingness to work
perseverance
what is grit a good predictor of
Grit is a better predictor than intelligence for achieving long-term academic goals and grades in college
people with less grit tend to
people with less grit tend to:
Get discouraged more easily
Get sidetracked from their goals by new interests
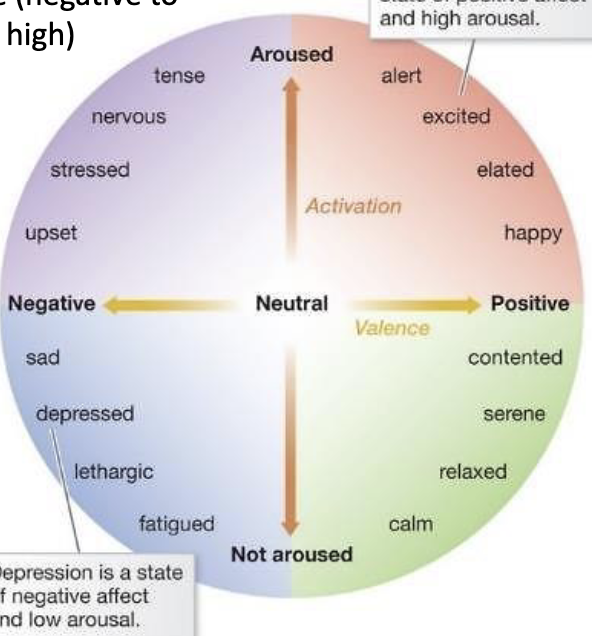
how can emotions be categorized
by valence (negative to positive) and level of arousal (low to high)
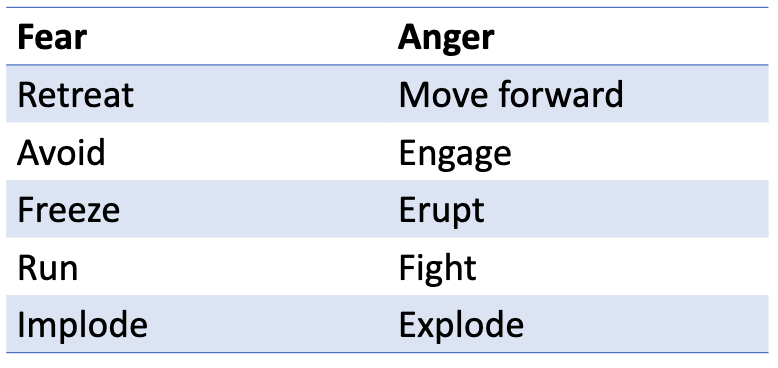
relationship between fear and anger
biochemically identical, but differ in behavioural responses
difference between fear and anger
3 components of anger
physiological arousal
cognitive appraisal
behavioural reactinons
evolutionary approach to emotion by darwin
• Emotional expressions are universal.
• Emotional responses have adaptive functions.
• Emotions are inherited, specialized mental states designed to deal with a certain class of recurring situations (e.g., attacked by predators, falling in love, etc) in the world
t/f book by darwin- expression of emotins in man and animal
true
7 primary emotions
fear
disgust
happy
surprise
anger
sad
contempt
r/f primary emotions are a combination of other emotions
false
part of body key to processing emotions
limbic system
thalamus
amygdala
how does amygdala hijacking occur
stimuli reaches thalamus to amygdala
reaches neocortex to process
james lange theory
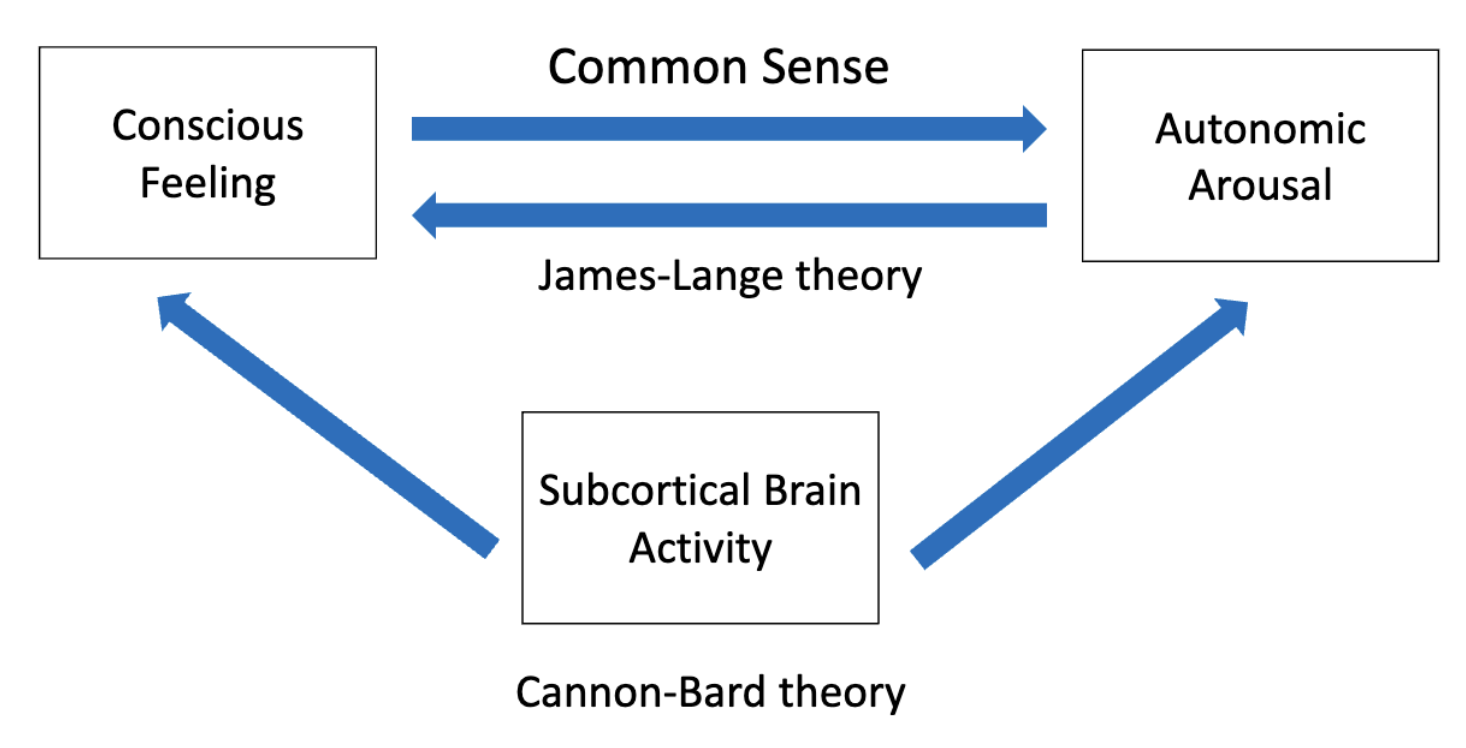
physiological arousal or action is the cause of emotional feeling
• Examples:
• - In a dangerous situation, our body trembles, then we feel afraid (the body is the first to respond to the situation).
• - When we are offended, we raise our voice, then we feel angry (we act before we feel).
common sense belief of emotions
Emotional feeling is the cause of physiological arousal (or action).
•Examples: •- We are afraid, then we tremble.
•- We are angry, then we raise our voice
problems with james lange theory
physiological arousal like heartbeat is an act performed by ans
ans responses are 2 slow to be source of split second elicted emotions
Cannon-Bard Theory of Central Neural Processes
Subcortical brain activity in the thalamus is the cause for both physiological arousal and emotional feeling
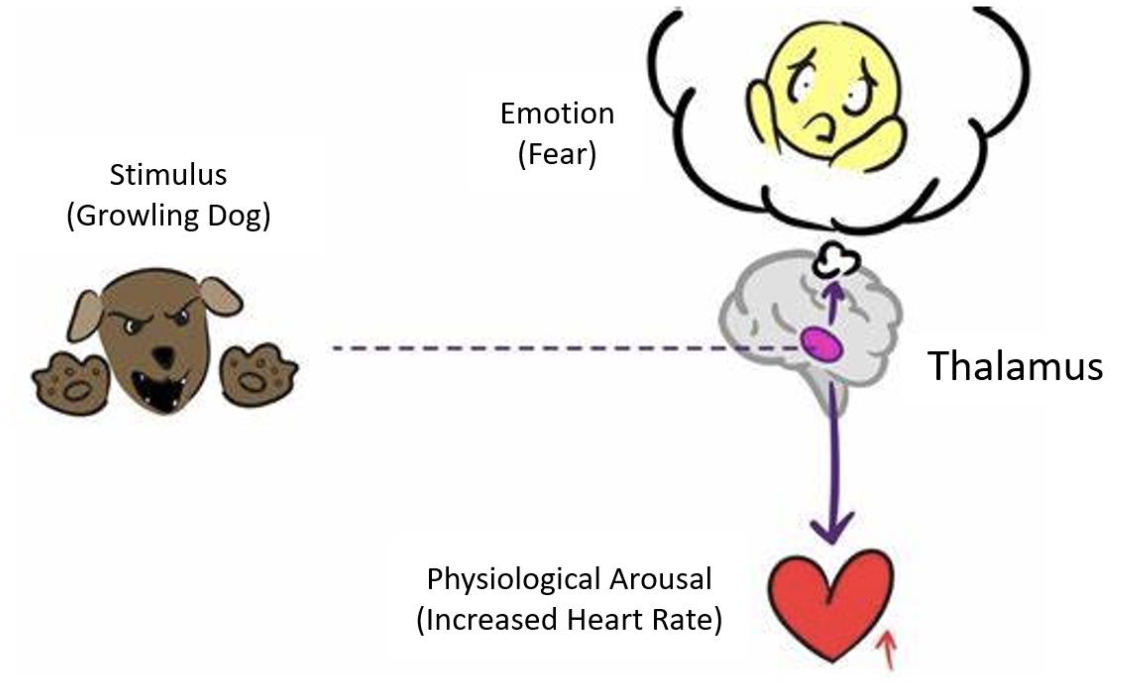
what do emotion theories not address
These theories describe the sequence of biological and psychological responses to a stimulus (what happens first, what happens next); they do not explain why a particular emotion is formed (e.g., how do you know that you are angry, excited, or anxious when your heart is pounding?
schachters 2 factor theiry is part of
cognitive appraisal theory
schachters 2 factor theory
he experience of emotion is the joint effect of autonomic arousal and cognitive appraisal, with both parts necessary for an emotion to occur
context matters
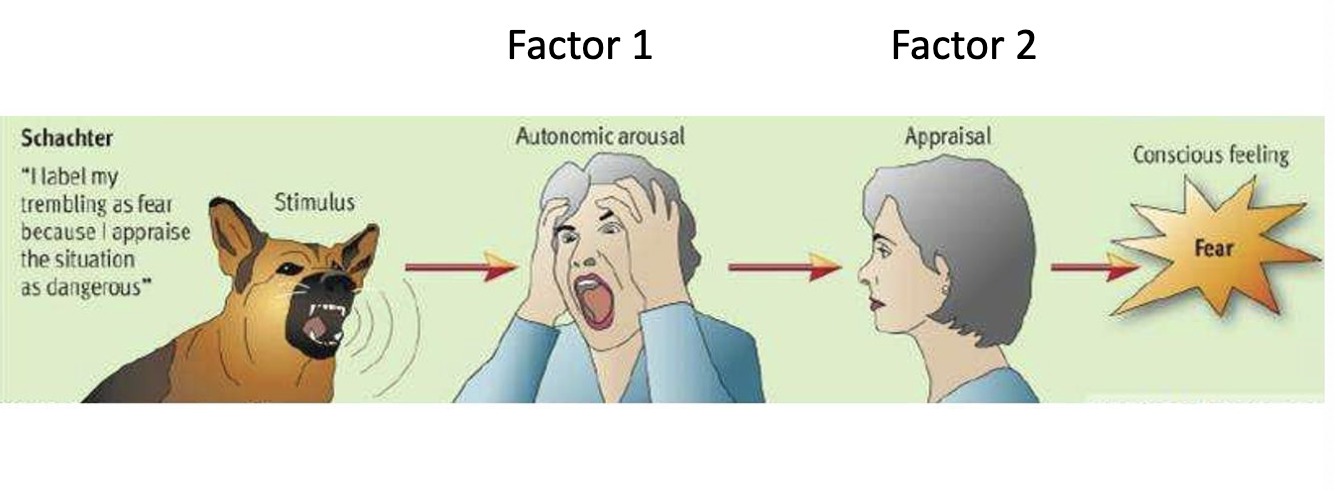
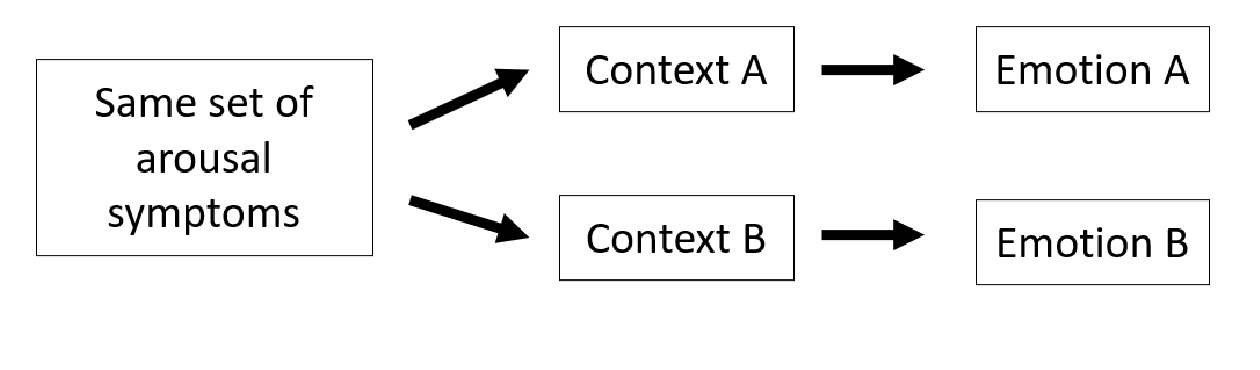

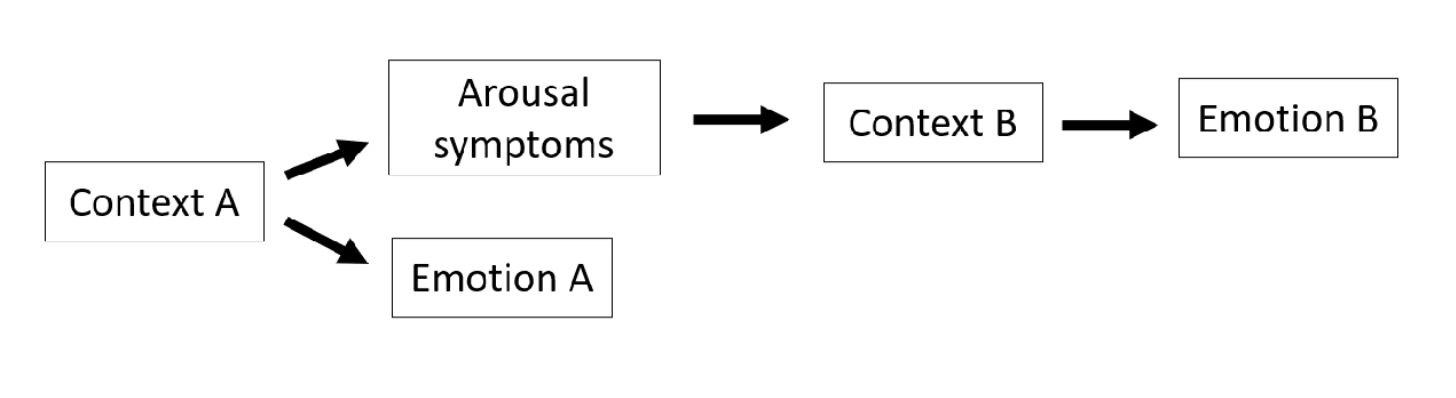
schachter singer experiment
Schachter and Singer injected participants with epinephrine (which causes arousal) and placed them in different social environments (with either a happy or angry person). Participants labeled their emotion based on the context, proving that cognition plays a key role in how we experience emotions