Chapter 4-Microbiology for sterile processing technicians
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
Vegetative stage: 🌱
State of active growth of microorganisms.
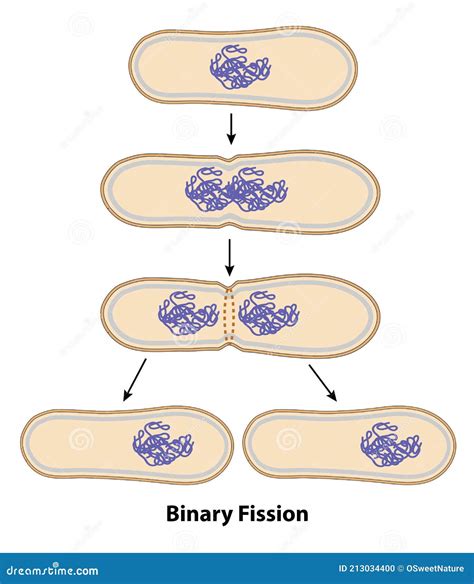
Binary Fission: 🦠🦠
The typical method of bacterial reproduction in which a cell divides into two equal parts.
Prion:
-An infectious protein particle
-contains no nucleic acid
-does not trigger an immune response
-is not destroyed by extreme heat or cold.
Contamination:
The state of being soiled by contact with infectious organisms or other materials.
Microbiology:
The study of microorganisms.
Pathogen:
Capable of producing disease
Aerobic:
Requiring the presence of air or free oxygen.
Micron:
1/25,000 of an inch or 1/1000 of a millimeter.
Anaerobic:
Bacteria that can live in the absence of atmospheric oxygen.
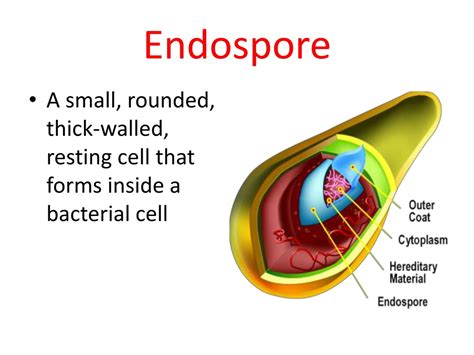
Endospores (spores):
Microorganisms capable of forming a thick wall around themselves, enabling them to survive in adverse conditions.
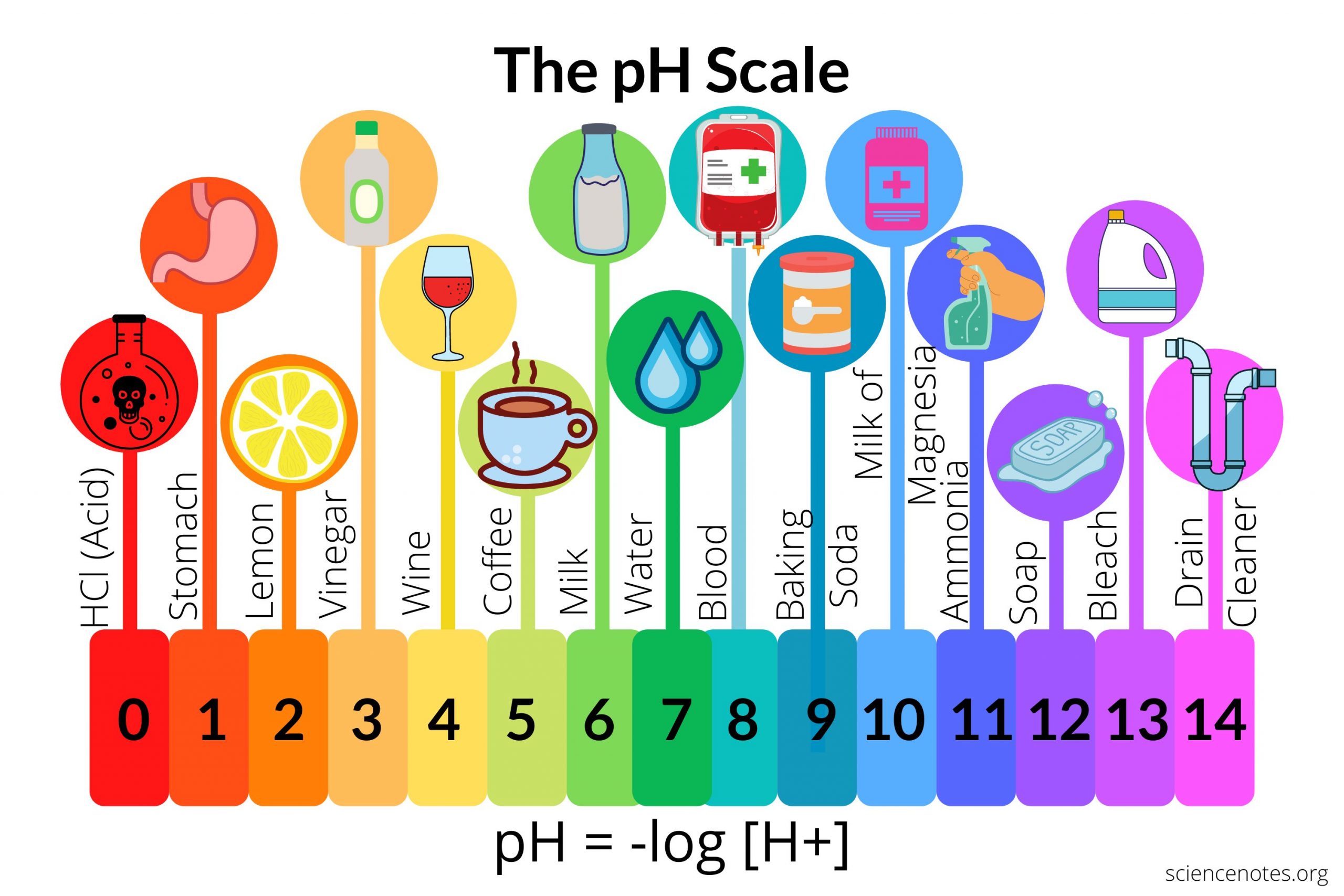
pH:
Measure of alkalinity or acidity on a scale of 0 to 14; pH of 7 is neutral, below 7 is acid, above 7 is alkaline.
[Notes] How are staph infections spread?
Direct contact with infected person or by touching contaminated surfaces.
[Notes] One example of a fungus infection
Ringworm
[Notes] The incubation period for ebola after exposure?
2 to 21 days
[Notes] What can e.coli cause?
Intestinal disease
diarrhea
urinary tract infections
respiratory illness
pneumonia
[Notes] How to identify bacteria?
Shape
color change
oxygen needs
[Notes] what does HAIs stand for?
Healthcare associated infections
[Notes] how many people acquire HAI per year?
1.7 million
[workbook] what percentage of bacteria that are beneficial and essential?
95%
[Notes] Neisseria Gonorrhoeae is most likely to grow where?
Mucous membranes of the reproductive system
[Notes] the different shapes of bacteria?
Spherical
Rod
Spiral
[Notes] How is hepatitis B transmitted?
Bloodborne
[Notes] What is the principle of Asepsis?
The absence of microorganisms that cause disease.
[Notes] What does the Filo Virus cause?
Ebola Virus
CRCST
CERTIFIED
REGISTERED
CENTRAL
SERVICE
TECHNICIAN
AORN
ASSOCIATED
Perioperative
REGISTERED
NURSE
TJC
THE
JOINT
COMMISSION
[Notes] WHAT IS THE PURPOSE FOR HANDWASHING?
TO STOP THE SPREAD OF GERMS
HOW OFTEN SHOULD YOU WASH YOUR HANDS?
ENTERING DEPARTMENT
LEAVING DEPARTMENT
BATHROOM
EATING
DONNING
DOFFING
DOCTORS PREFERENCE CARD
INSTRUMENTS
SUPPLIES
SURGEON
PATIENT DRAPING
PATIENT WEIGHT
SEX
ALLERGIES
MEDICATIONS
DATE OF BIRTH
NAME
ROOM NUMBER
ETHNICITY
NAME OF HOSPITAL
EQUIPMENT
[Notes] What virus is NOT transmitted by the airborne or droplet route
Ebola
This bacterium is found in soil
Acinetobacter
[workbook] Viruses are
smaller than bacteria
[workbook] A spore is
very difficult to kill
[workbook] Staphylococcus is classified as a
Gram-positive bacteria
[workbook] The measure of alkalinity and acidity refers to
pH
[workbook] Which hepatitis virus is said to be the most prevalent chronic bloodborne infection today?
Hepatitis C
[workbook] Athlete’s foot
is an example of a fungus
[workbook] The functional center of a cell is the
Nucleus
[workbook] Which is NOT a common bacteria shape?
Cylindrical
[workbook] Microorganisms reproduce by a process called:
Binary fission
[workbook] Which of the following is a gram-positive bacteria?
Geobacillus
[workbook] Pseudomonas is transmitted through:
Hand to hand contact or contact with contaminated surfaces
Gram stain:
Differential stain used to classify bacteria as gram positive or gram negative, depending on whether they retain or lose the primary stain (Crystal violet) when subjected to a decolorizing agent