Organic Chemistry Ganley Test 2
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/155
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 3:33 AM on 9/24/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
156 Terms
1
New cards
Hydrocarbon
composed of hydrogen and carbon atoms
2
New cards
Saturated hydrocarbon have
no C-C pi bonds
3
New cards
Unsaturated hydrocarbon have
C-C pi bonds
4
New cards
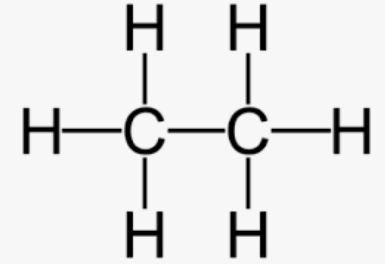
Ethane is ___ and has a chemical formula of __
saturated, C2H6
5
New cards
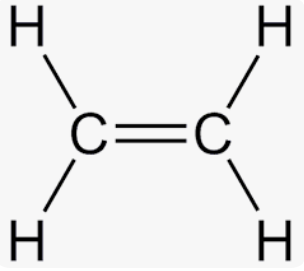
Ethylene is __ and has a chemical formula of __
unsaturated, C2H4
6
New cards
Acetylene is __ and has a chemical formula of __
unsaturated, C2H2
7
New cards
Benzene is __ and has a chemical formula of __
unsaturated, C6H6
8
New cards
Formula for saturated hydrocarbons
C(n)H(2n+2)
9
New cards
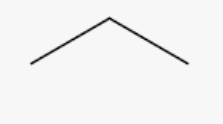
Propane
C3H8
10
New cards
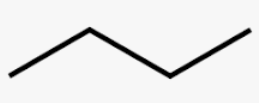
Butane
C4H10
11
New cards
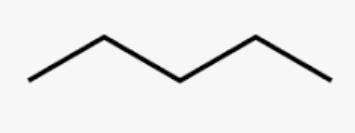
Pentane
C5H12
12
New cards
Nomenclature
“Name Calling”
* to communicate, each unique molecule must have a unique name
* the suffix *ane* is used for saturated hydrocarbons (a.k.a. alkanes)
* to communicate, each unique molecule must have a unique name
* the suffix *ane* is used for saturated hydrocarbons (a.k.a. alkanes)
13
New cards
Why should we not use a chemicals common name?
they have little/no relation to the structure
you would need to memorize a different name for every molecule
you would need to memorize a different name for every molecule
14
New cards
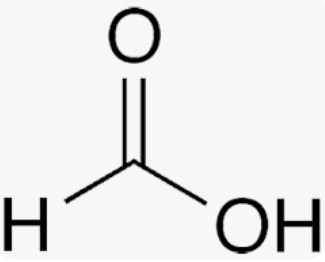
Formic Acid
isolated from ants and named after the Latin word for ant, Formica
15
New cards
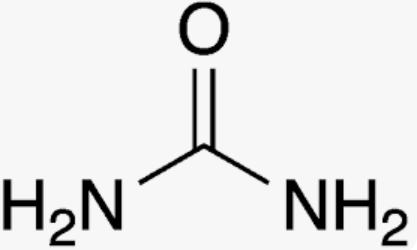
Urea
isolated from urine
16
New cards
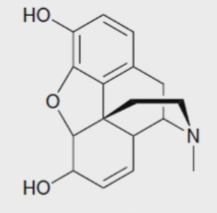
Morphine
a painkiller names after the Greek God of dreams, Morpheus
17
New cards
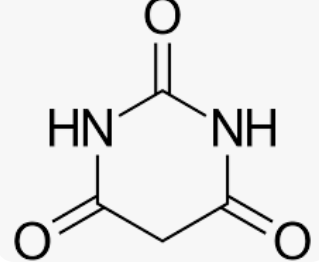
Barbituric Acid
Adolf van Baeyer named this compound in honor of his friend Barbra
18
New cards
Parent chain
the longest consecutive chain of carbons
19
New cards
1 carbon in parent chain
meth
20
New cards
2 carbon in parent chain
eth
21
New cards
3 carbon in parent chain
prop
22
New cards
4 carbon in parent chain
but
23
New cards
5 carbon in parent chain
pent
24
New cards
6 carbon in parent chain
hex
25
New cards
7 carbon in parent chain
hept
26
New cards
8 carbon in parent chain
oct
27
New cards
9 carbon in parent chain
non
28
New cards
10 carbon in parent chain
dec
29
New cards
if there is more than 1 possible parent chain
choose the one with the most side chains attached
you want to avoid having to name complex branch
you want to avoid having to name complex branch
30
New cards
if carbons are not in a chain they are in a
cyclo ring
31
New cards
for cyclic acids
count the number of carbon in the ring and name it according to that number, add cyclo prefix
32
New cards
Cyclopropane
cyclic acid with 3 carbons

33
New cards
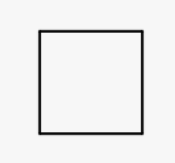
Cyclobutane
cyclic acid with 4 carons
34
New cards
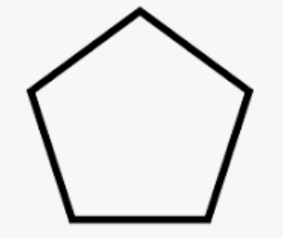
Cyclopentane
cyclic acid with 5 carons
35
New cards
formula for cyclic acids
C(n)H(2n)
36
New cards
You cannot include carbon that are both in ___
a ring and outside a ring
use the ring to name as the parent chain
use the ring to name as the parent chain
37
New cards
Identifying Substituents
name the same way as parent, but end in “ly”
ex: ethyl= 2 carbon chain, propyl= 3 carbon chain
ex: ethyl= 2 carbon chain, propyl= 3 carbon chain
38
New cards
cycloalkanes naming
* if ring is bigger/as big: name chain as prefix
* if chain is bigger: name the ring as prefix
* if chain is bigger: name the ring as prefix
39
New cards
40
New cards
41
New cards
42
New cards
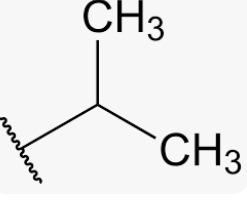
common name for 1-methylethyl
Isopropyl
43
New cards
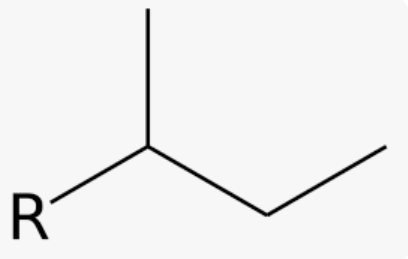
common name for 1-methylpropyl
sec-butyl
44
New cards
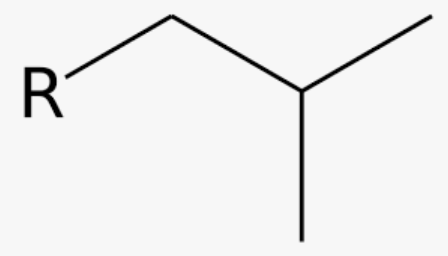
common name for 2-methylpropyl
isobutyl
45
New cards
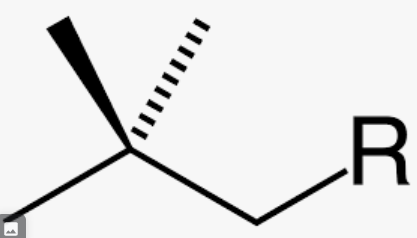
common name for 2,2- dimethylpropyl
neopentyl
46
New cards
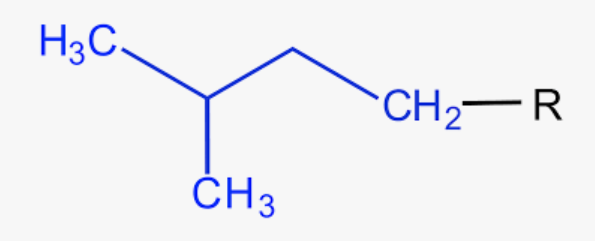
common name for 3-methylbutyl
isopentyl or isoamyl
47
New cards
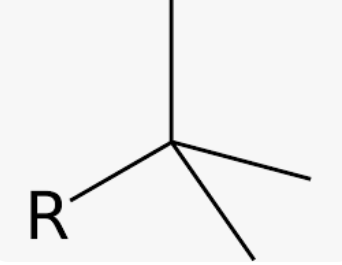
common name for 1,1-dimethylethyl
tert-butyl
48
New cards
Rules for assembling the entire name
1) list substituents in alphabetical order
2) use Greek prefix for multiple identical substituents
3) prefixes are not used for alphabetical purposes, except for the prefixes “iso” and “cyclo”
2) use Greek prefix for multiple identical substituents
3) prefixes are not used for alphabetical purposes, except for the prefixes “iso” and “cyclo”
49
New cards
use commas between ___ when naming
numbers
50
New cards
use hyphens between ___ when naming
letter and number
51
New cards
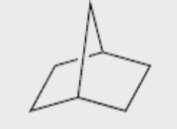
Name the molecule
Bicyclo\[2.2.1\]heptane
52
New cards
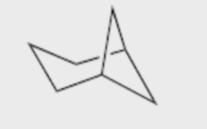
Name the molecule
Bicyclo\[3.1.1\]heptane
53
New cards
Why are there 3 numbers in the name for bicyclic compounds?
there are 3 ways to get from one bridge head caron to the other
54
New cards
what does it mean in you have \[3.1.1\] in a bicyclic acid name
for the first route to get from one bridge head carbon to the next, you have to pass 3 other carbons. For the second and third route, you have to pass 1 carbon.
55
New cards
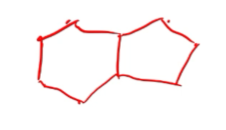
name this compound
bicyclo\[4.3.0\]nonane
56
New cards
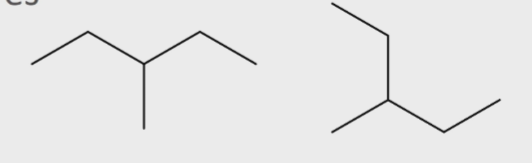
Are these molecules constitutional isomers?
yes
57
New cards
constitutional isomers
molecules with different structures but the same formula (differ in connectivity)
58
New cards
Rules for naming bicyclic compounds
1) count the total carbon in the fuse ring (parent name)
2) Number carbons (start at bridgehead carbon and number the longest carbon chain first (bridge is last)
3) use the “bicyclo” prefix
4) figure out bridgehead carbons
5) figure out bracketed numbers
2) Number carbons (start at bridgehead carbon and number the longest carbon chain first (bridge is last)
3) use the “bicyclo” prefix
4) figure out bridgehead carbons
5) figure out bracketed numbers
59
New cards
2 ways to recognize constitutional isomers
1) flip one of the molecules in 3D space and rotate around its single bonds until it is superimposable on the other molecule
2) name them (same name=identical)
2) name them (same name=identical)
60
New cards
how to find more stable isomer
most branches= less energy= more stable
61
New cards
Is an isomer with more branches or less branches better for fuel
less= more energy= more reactivity
62
New cards
what are cracking and reforming? why do they do it with alkanes
cracking: making large molecules smaller (breaking them apart)
reforming: making small molecules bigger (adding them to each other)
they need hydrocarbons with 5-12 carbons for gas and only 19% of crude oil is suitable for gas. Using cracking and reforming methods, they can make that 19% turn into 47%.
reforming: making small molecules bigger (adding them to each other)
they need hydrocarbons with 5-12 carbons for gas and only 19% of crude oil is suitable for gas. Using cracking and reforming methods, they can make that 19% turn into 47%.
63
New cards
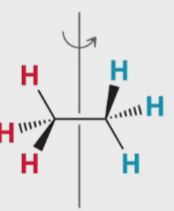
What kind of 2D drawing is this
wedge and dash
64
New cards
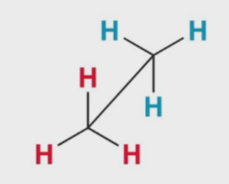
What kind of 2D drawing is this
sawhorse (wont see often)
65
New cards
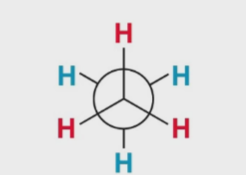
What kind of 2D drawing is this
newman projection (best way)
looking directly down C-C sing bong axis
keep wedges and dashes on same side
looking directly down C-C sing bong axis
keep wedges and dashes on same side
66
New cards
what are conformations
a different rotational state of a molecule
single bonds in molecules can rotate
single bonds in molecules can rotate
67
New cards
Dihedral/Torsional angle
angle between atoms on adjacent C
68
New cards
How is VESPR useful when considering the stability of rotational conformations
* e- on the same carbon what to get as far away as possible from other e-
* similar for e- on adjacent carbons and they are still repelling each other, they will space themselves out equally
* the more spaced out the bonds are, the more stable they are
* similar for e- on adjacent carbons and they are still repelling each other, they will space themselves out equally
* the more spaced out the bonds are, the more stable they are
69
New cards
staggered conformation vs eclipsed conformation
staggered: lowest energy, more stable
eclipsed: highest energy, least stable, 0 degrees dihedral angle (maximizes repulsive interaction)
eclipsed: highest energy, least stable, 0 degrees dihedral angle (maximizes repulsive interaction)
70
New cards

Which one is staggered? Which one is eclipsed?
Left: staggered
Right: eclipsed
Right: eclipsed
71
New cards
In order to go from staggered to eclipsed, you have to ___ energy
absorb
72
New cards
torsional strain
resistance to rotation- How much energy was needed?
specifically adjacent atoms
specifically adjacent atoms
73
New cards
torsional strain for ethane
12 kJ/mol; 4kJ/mol per pair of hydrogens
74
New cards
Will there be more eclipse conformers in room temp or high heat?
High heat because there is more energy for the molecules to absorb
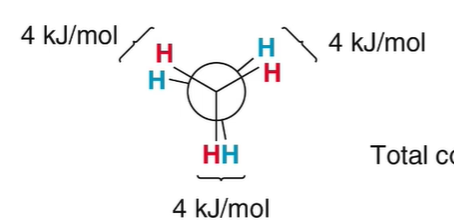
75
New cards
does it take more energy for a pair of H to eclipse or a H and a methyl group?
takes more energy for the H and methyl group because he methyl group is bulkier
76
New cards
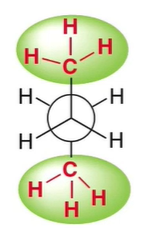
What conformation is this?
Anti
less steric hinderance
methyl groups are farthest apart
dihedral angle of 180
less steric hinderance
methyl groups are farthest apart
dihedral angle of 180
77
New cards
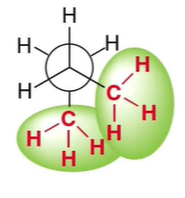
What conformation is this?
Gauche
methyl groups aren’t eclipsing but bump into each other a little bit
more steric hinderance
not as stable, higher energy
methyl groups aren’t eclipsing but bump into each other a little bit
more steric hinderance
not as stable, higher energy
78
New cards
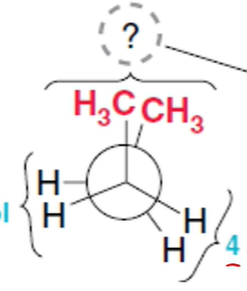
What conformation is this?
“totally eclipsed”
methyl groups eclipse one another
highest energy, least stable
11kJ/mol for methyl’s
methyl groups eclipse one another
highest energy, least stable
11kJ/mol for methyl’s
79
New cards
What is an “eclipsed” butane conformation
when the methyl’s eclipse with hydrogens
higher energy that staggered
less energy that totally eclipsed
higher energy that staggered
less energy that totally eclipsed
80
New cards
Cyclic alkane hybridization and bond angle?
sp3, 109.5
81
New cards
optimal bond angle
109\.5
82
New cards
2 reasons why cyclopentane in unstable
1. angle strain (60 degrees, poor sigma bond overlap; bends bonds)
2. torsional strain: all H are eclipsed
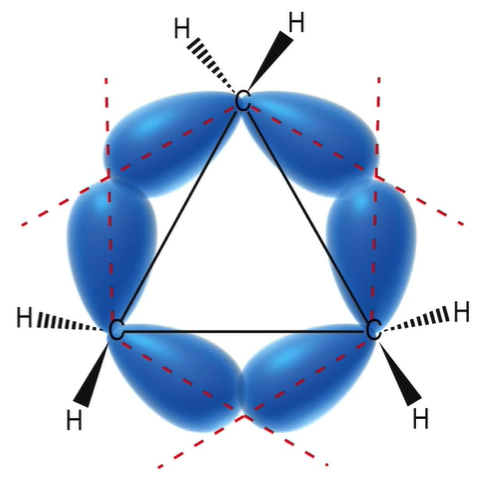
83
New cards
What cycloalkane is the one that has to be flat
cyclopropane
84
New cards
Cyclobutene properties
unstable, 88 degree bond angle, H are partially eclipsed, puckers to relieve stress
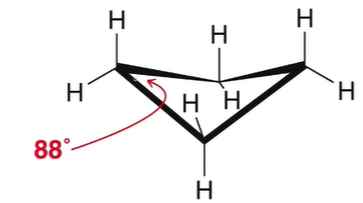
85
New cards
Cyclopentane properties
nonpolar “envelope”, minimal ring strain (close to 109.5 degree angle), minimal torsional strain (H slightly eclipsed)
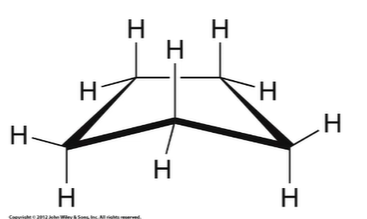
86
New cards
“chair” conformation for cyclohexane properties
lowest energy, zero ring strain, no angle strain (all angles= 109.5), no torsional strain (all H= staggered)
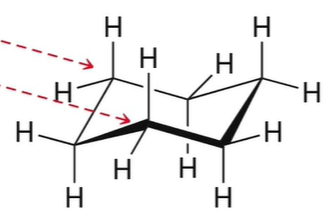
87
New cards
“boat” conformation for cyclohexane properties
no angle strain, torsional strain (4 pairs of eclipsing H), steric (crowding) strain (“flagpole” interactions)
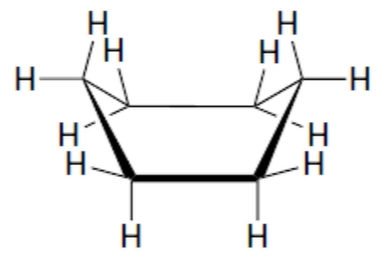
88
New cards
steric strain
type of torsional strain
H can be on any carbon
crowded, bump into each other
H can be on any carbon
crowded, bump into each other
89
New cards
What is the highest/most unstable energy conformation of cyclohexane?
half chair
angles are being stretched= significant amount of angle strain
torsional strain- partial eclipse
\
would be planar is it existed= too high of energy for molecule to handle
angles are being stretched= significant amount of angle strain
torsional strain- partial eclipse
\
would be planar is it existed= too high of energy for molecule to handle
90
New cards
“twist boat” conformation for cyclohexane properties
109\.5, relives eclipsing or some H
91
New cards
axial element
point straight up or down on ring
92
New cards
equatorial element
alternating slightly up or down around ring
if C has a H in the axial position point up, then it will also have a H in the equatorial position point down and vise versa
C will always have one of each
if C has a H in the axial position point up, then it will also have a H in the equatorial position point down and vise versa
C will always have one of each
93
New cards
Monosubstuituted cyclohexane
vast majority exist in chair conformation at any given time
when energy '(45 kJ/mol) is available, it flips from one chair to another
anything that was axial is now equatorial and vise versa (direction doesn’t change; ex: axial straight up will become equatorial slightly up)
prefers methyl group in equatorial state
when energy '(45 kJ/mol) is available, it flips from one chair to another
anything that was axial is now equatorial and vise versa (direction doesn’t change; ex: axial straight up will become equatorial slightly up)
prefers methyl group in equatorial state
94
New cards
Chair flip
C-C single bonds rotating only
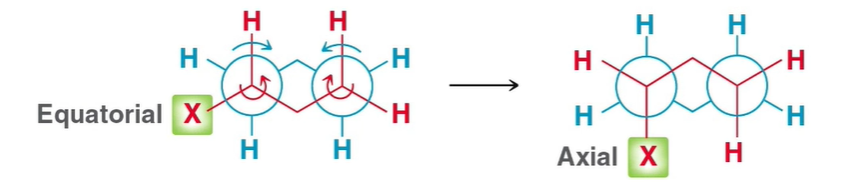
95
New cards
why does monosubstuituted cyclohexane prefer the methyl group in equatorial state
in axial conformation the methyl group bumps into the H in axial formation
equatorial state get the methyl group further away
1,3-dixial interactions are like gauche interactions
Equatorial interactions are like anti interactions
equatorial state get the methyl group further away
1,3-dixial interactions are like gauche interactions
Equatorial interactions are like anti interactions
96
New cards
the larger the substituent, the __ the molecules will __ the equatorial conformation
more, favor
97
New cards
in disubstituted cyclohexane the dash is __ and the wedge is _
down, up
98
New cards
if you have 2 conformations (one with a methyl in the axial position and one in the equatorial position and vise versa) which one do you choose?
the one with the methyl in the axial position because it is smaller than the ethyl
99
New cards
cis:
the 2 groups are on the same side of the ring
100
New cards
tras
the 2 groups are on the opposite side of the ring