DSAT Math Concepts and Techniques
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
59 Terms
Linear Equations in One Variable
Form: ax + b = c
Step 1 (Linear Equations)
Subtract b: ax = c − b
Step 2 (Linear Equations)
Divide by a: x = (c−b)/a
Tactic (Linear Equations)
Always isolate x. Check your answer by plugging it back in.
Slope (Linear Functions)
m = (y2 - y1) / (x2 - x1)
Slope-intercept Equation
y = mx + b
Point-slope Equation
y - y1 = m(x - x1)
Find y-intercept (Graphing)
Plot y-intercept = b
Use slope to find next point
e.g., m = 2 → up 2, right 1
Standard Form (Linear Equations in Two Variables)
Ax + By = C
Find x-intercept
Set y = 0, solve for x.
Find y-intercept
Set x = 0, solve for y.
Slope from Standard Form
m = -B/A
Methods to Solve Systems of Linear Equations
1. Substitution, 2. Elimination, 3. Graphing (use Desmos for accuracy)
One Solution (Systems of Linear Equations)
Lines intersect.
No Solution (Systems of Linear Equations)
Parallel lines (same slope, different intercepts).
Infinite Solutions (Systems of Linear Equations)
Same line (identical equations).
Solving Linear Inequalities
Same as equations, but flip the sign if multiplying/dividing by a negative.
Graphing Linear Inequalities
Solid line for ≤ or ≥; Dashed line for < or >.
Shifting a Function Horizontally
f(x) → f(x-h): horizontal shift to the right [(-)→right, (+)→left]
Shifting a Function Vertically
f(x) → f(x) + k: vertical shift up [(-)→down,(+)→up]
Quadratic Functions
y = ax^2 + bx + c
Sum of the Roots (Quadratic Functions)
-b/a
Product of the Roots (Quadratic Functions)
c/a
Vertex of a Parabola
x = -b/(2a)
Systems with nonlinear equations
Substitute or graph to find intersection points.
Equivalent Expressions
Simplify: Combine like terms, factor, or expand.
Rational expressions
Factor numerator and denominator, then cancel common terms.
Ratio
a to b or b to a.
Proportion
Cross-multiply: ad = bc.
Unit conversion
Use conversion factors (e.g., 1 km = 0.62 mi).
Part Formula
Part = Whole × Percent / 100.
Whole Formula
Whole = part × 100 / percentage.
Percentage Formula
Percentage = Part / Whole × 100.
Percent change
Percent change = (New - Old) / Old × 100%.
Mean
Mean = Σx / n.
Median
Middle value when ordered.
Mode
Most frequent value.
Range
Max - min.
Standard deviation
Measure of spread (larger = more spread out).
Line of best fit
Approximates the trend (use linear regression on Desmos).
Correlation (r)
r = 1: Perfect positive linear relationship; r = -1: Perfect negative linear relationship; r = 0: No linear relationship.
Basic probability
P(A) = Favorable outcomes / Total outcomes.
Conditional probability
P(A|B) = P(A and B) / P(B).
Margin of error
MOE ≈ 1 / √n (for 95% confidence).
Observational studies
No intervention (correlation ≠ causation).
Experimental studies
Treatment applied (can infer causation).
Rectangle Area and Perimeter
A = lw, P = 2l + 2w.
Triangle Area
A = 1/2 bh.
Circle Area and Circumference
A = πr², C = 2πr.
Rectangular prism Volume
V = lwh.
Pyramid Volume
V = 1/3 b h.
Cylinder Volume
V = πr²h.
Cone Volume
V = 1/3 πr²h.
Sphere Volume
V = 4/3 πr³.
Pythagorean theorem
a² + b² = c² (right triangles).
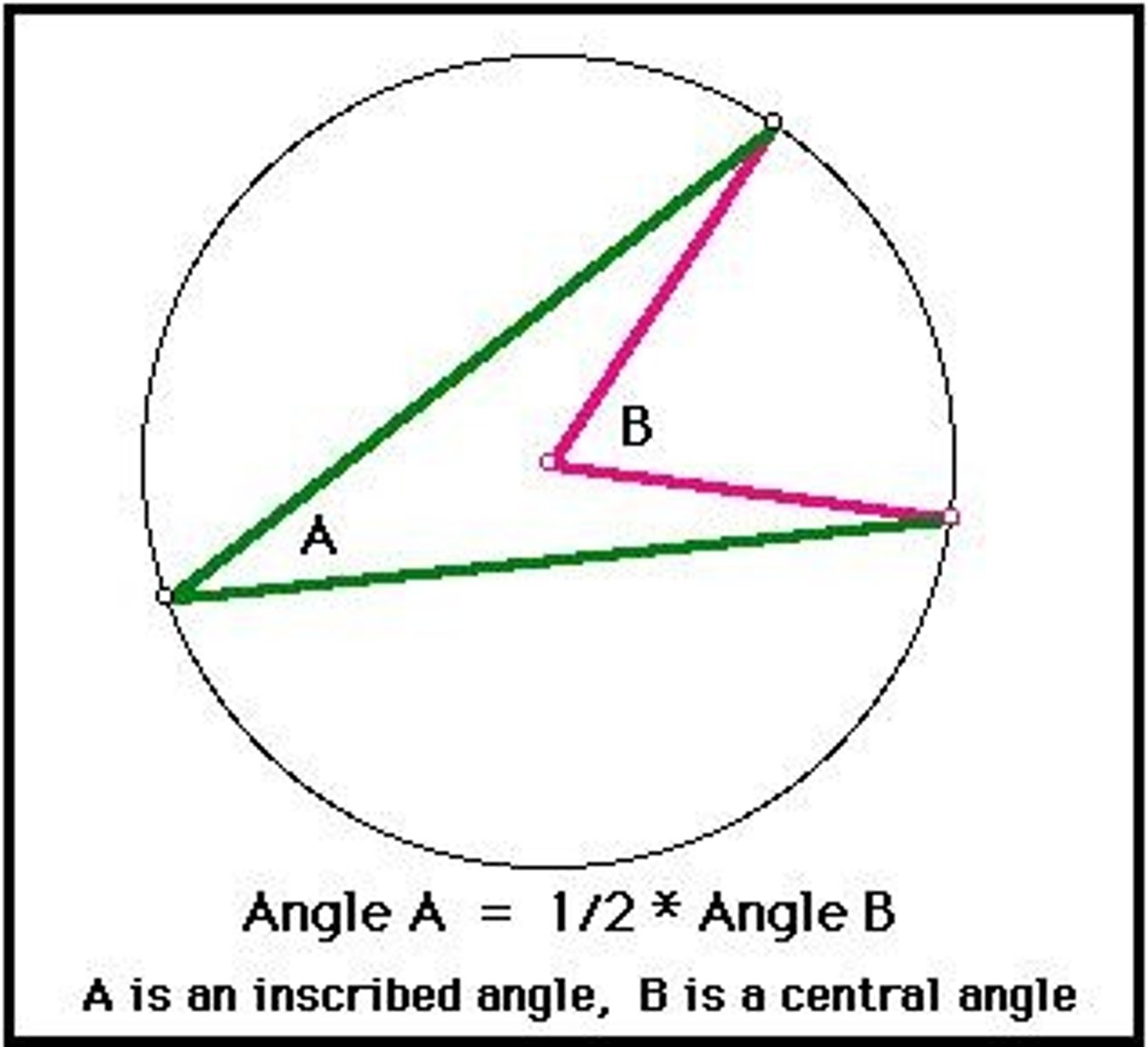
Inscribed Angles
Angles formed by two chords in a circle.
Arc length
L = (θ / 360) × 2πr.
Sector area
A = (θ / 360) × πr².