Nat 5 Physics | Space and Cosmology
1/29
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms

What is a Planet?
A spherical natural body orbiting a star, big enough to clear it’s orbital path.

What is a Dwarf Planet?
A natural body orbiting a star, but not having cleared it’s orbital path.

What is a Moon?
Any natural satellite orbiting a planet.
What is the Sun?
The star in our solar system.

What is an Asteroid?
A rocky object, smaller than a dwarf planet.
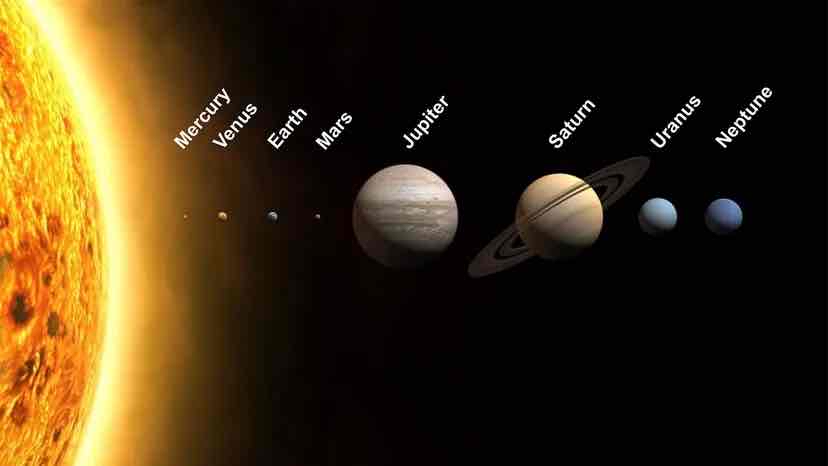
What is a Solar System?
This consists of the Sun, the planets and their moons, asteroid and comets.

What is a Star?
A large ball of gas where nuclear reactions produce heat and light.

What is an Exoplanet?
A planet orbiting any star other than the Sun.

What is a Galaxy?
Millions of stars held together by gravity.

What is a Universe?
All the stars, dust, gas, all matter, all space and time. (Everything)

What is a Sattelite?
A satellite is an object that orbits another object. Usually an object orbiting a planet.

What is a Communication Satellite?
Provides long distance telephone calls
Television
Data Transfer

What is a GPS Satellite?
Used for Navigation
Vehicle tracking
Speed data for sporting events

What is a Weather Satellite?
Can predict the weather and give storm warnings.

What is Agricultural Tracking?
Monitors the growth of crops over a large area.
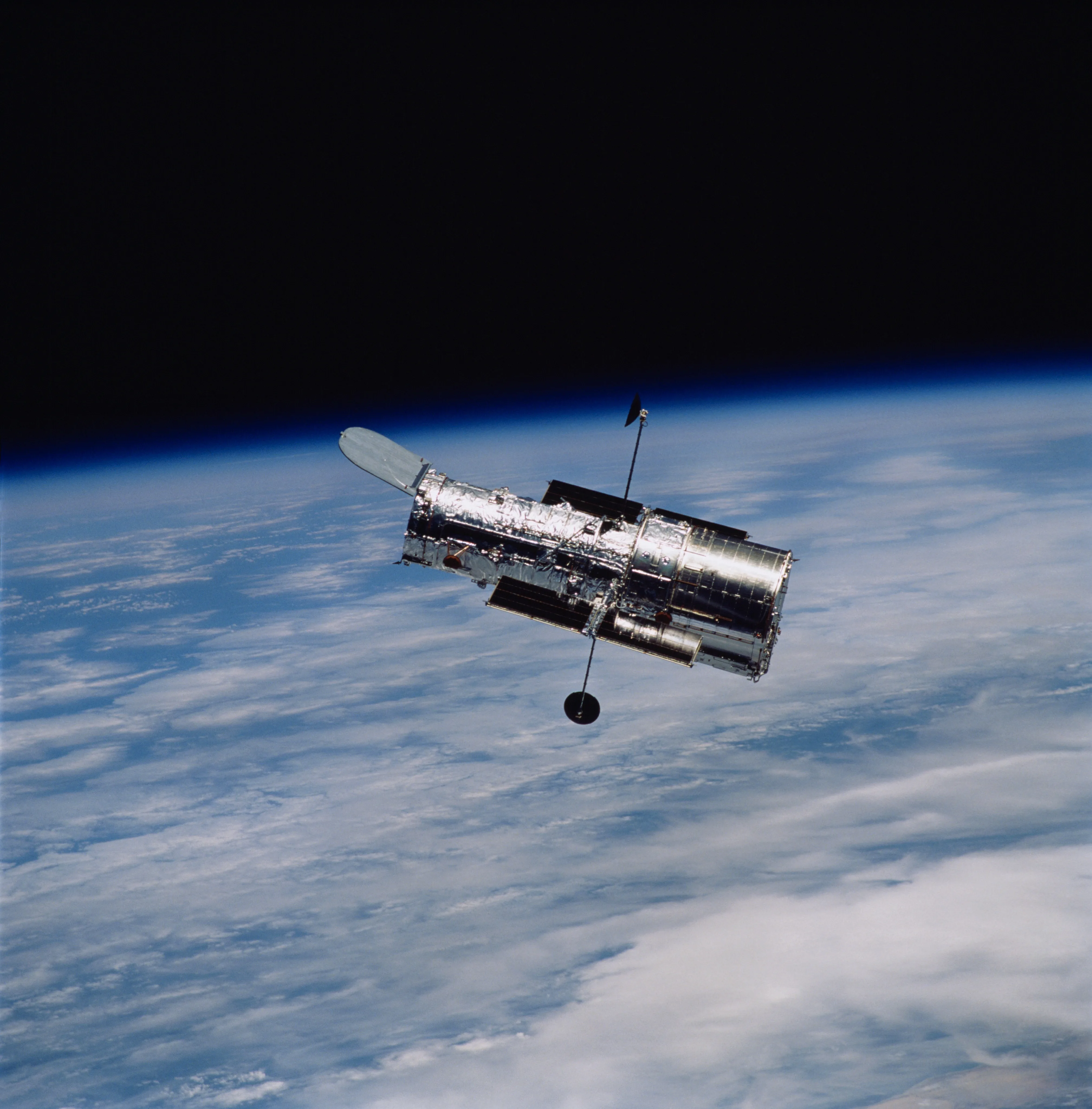

What is a Space Teliscope?
Telescopes in space to explore the sola system and deep space.

Risks of Space Exploration.
Unbreathable oxygen beyond the earths atmosphere
Low Temperatures
Risks of explosion during launch
Radiation exposure increased during space flight
Re-entering the earths atmosphere from space causes dangerous heating of the spacecraft.

Challenges of Space Travel.
Travelling large distances
Manoeuvring a space craft in a zero-friction enviroment.

What is a Light Year?
A light year is the distance travelled by light in a vacuum in one year. (3.0×10{8}ms{-1}.)

All about the Universe.
The universe was balled up in a hot dense state nearly 14 Billion years ago expansion started.
As it expanded it also cooled, and this theory is named the “the big bang”.
After around 370,000 years the expanding universe had cooled sufficiently for atoms of hydrogen and helium to form. These atoms gathered together under the influence of gravity to form stars and groups of stars called galaxies.
The universe is continuing to expand making the distances between galaxies larger over time.
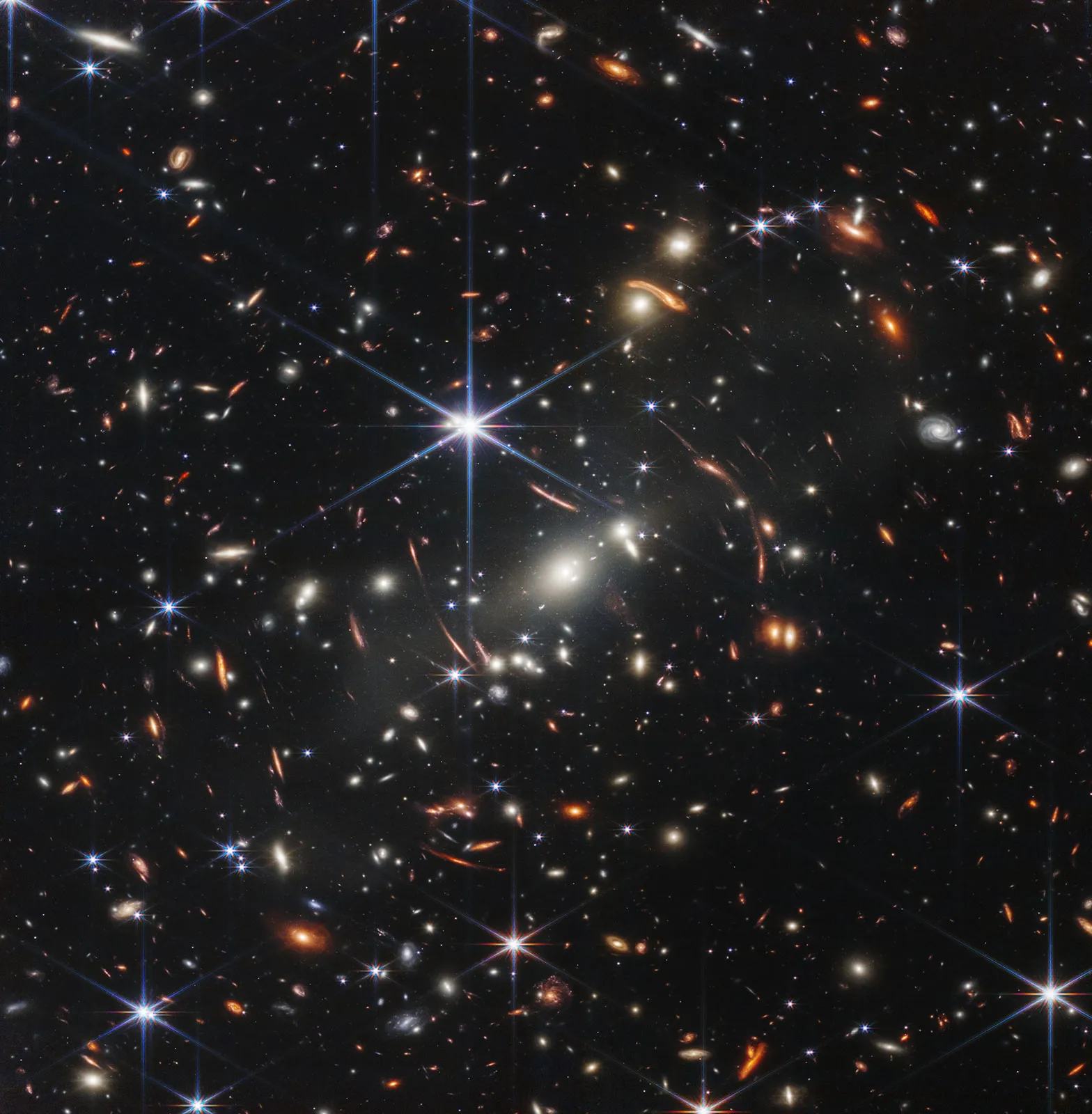

What Size is the Observable Universe?
The size of the observable universe is 93 billion light years. There are the parts of the universe which are beyond what it is possible to observe.
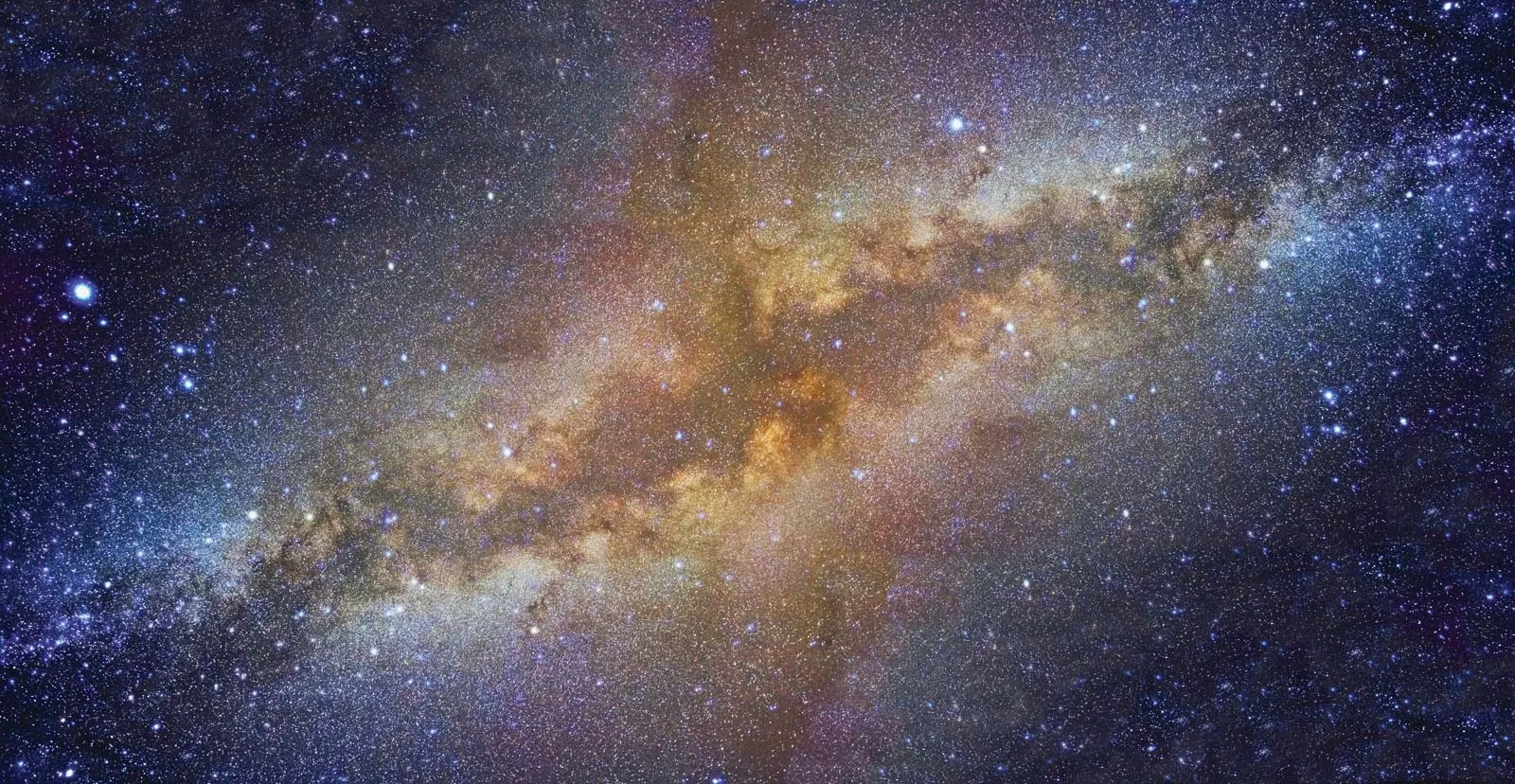

What is the Milky Way and when was it Formed?
The Milky Way is our solar system and was formed 4.6 billion years ago. It contains 100 to 400 billion stars.
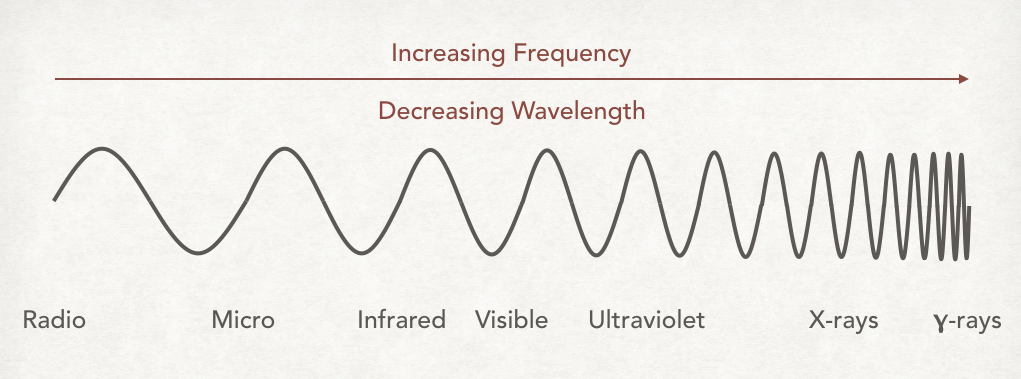
What order does the Wavelengths on the Electromagnetic Spectrum Increase?
Radio, Microwave, Infrared, Visible, Ultraviolet, X-rays, Gamma Rays.
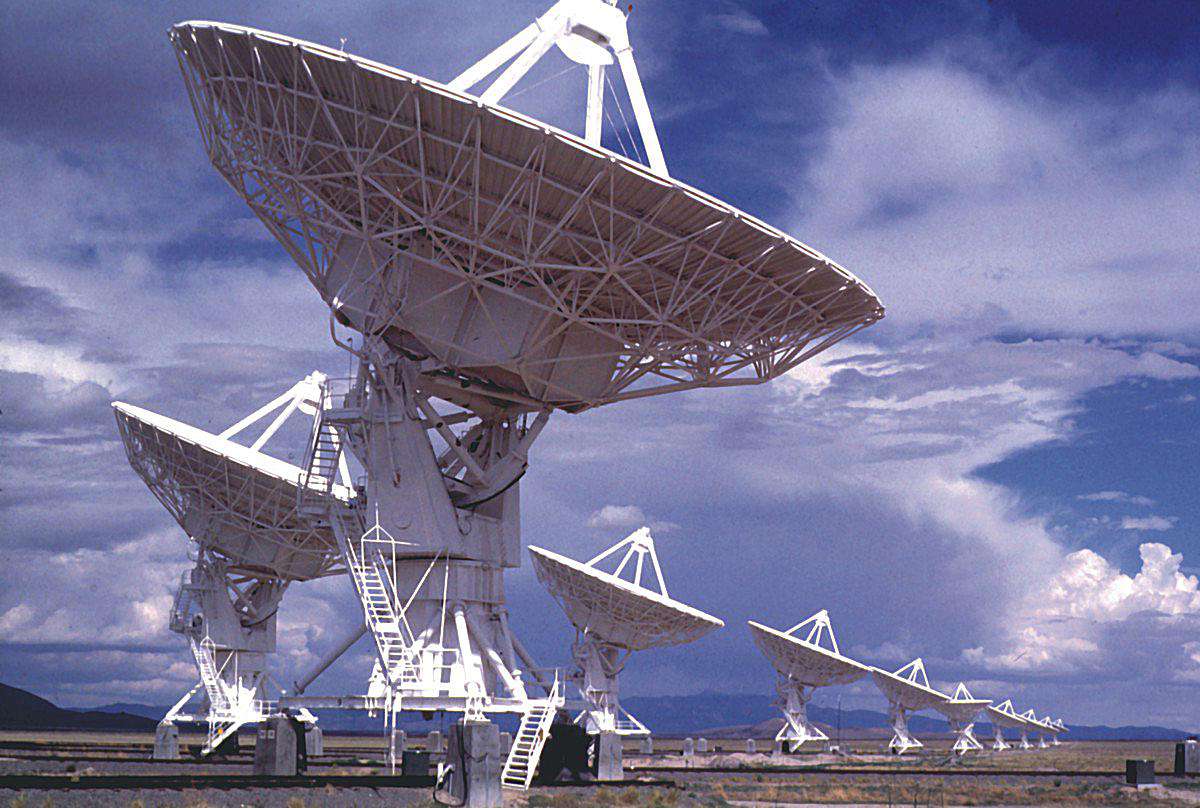

Radio Telescopes.
These are large satellite dish telescopes frequently used in groups called arrays in order to form images of radio sources in galaxies.

Microwave Telescopes.
These are usually used to look at the cosmic microwave background radiation which is radiation left from the formation of the universe.
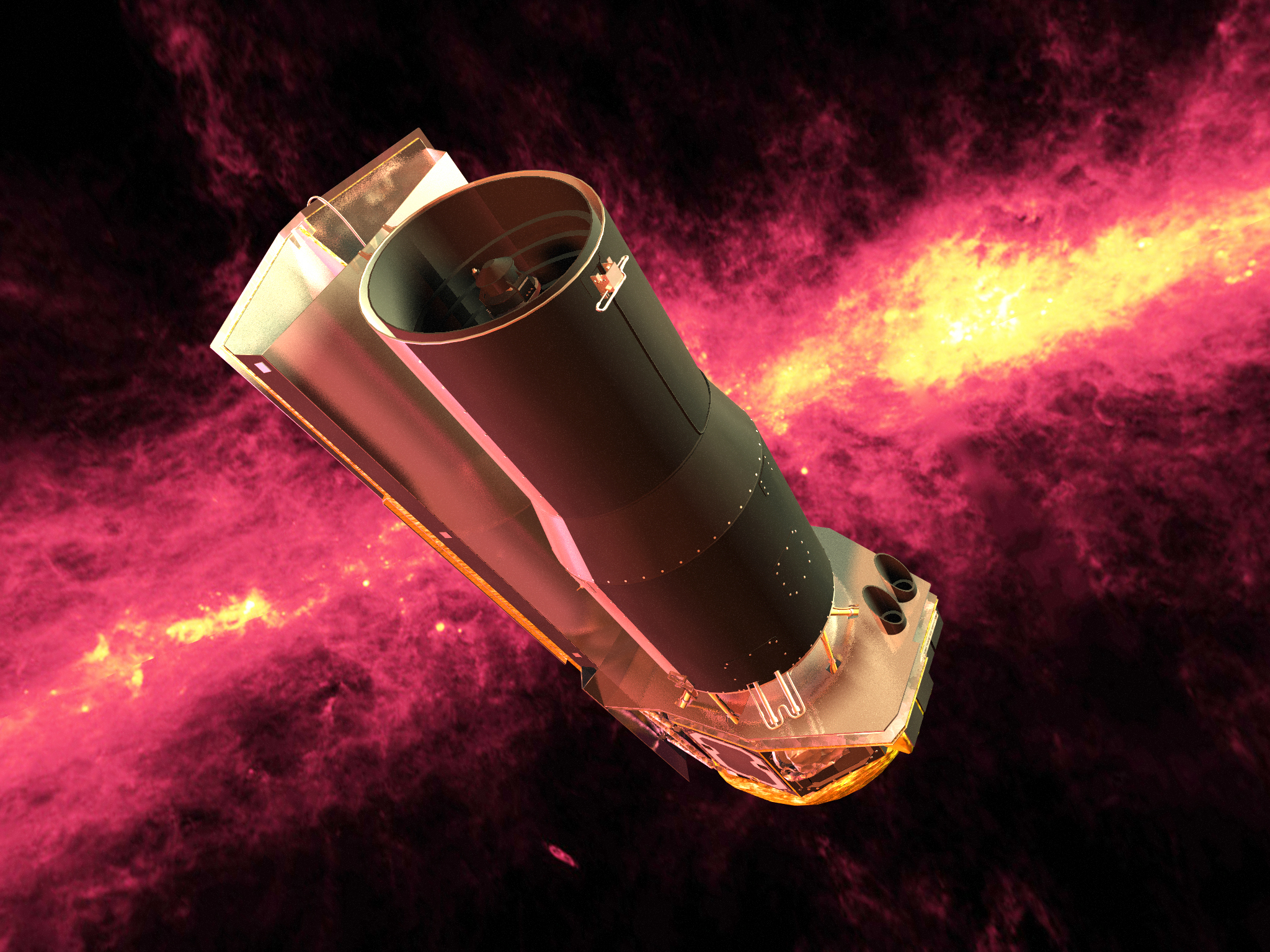

Infrared Telescopes.
These telescopes are frequently used to observe the sun. These telescopes can also be used to see through the dust cloud around the center of our galaxy. They are either places in orbit around earth or around the sun.
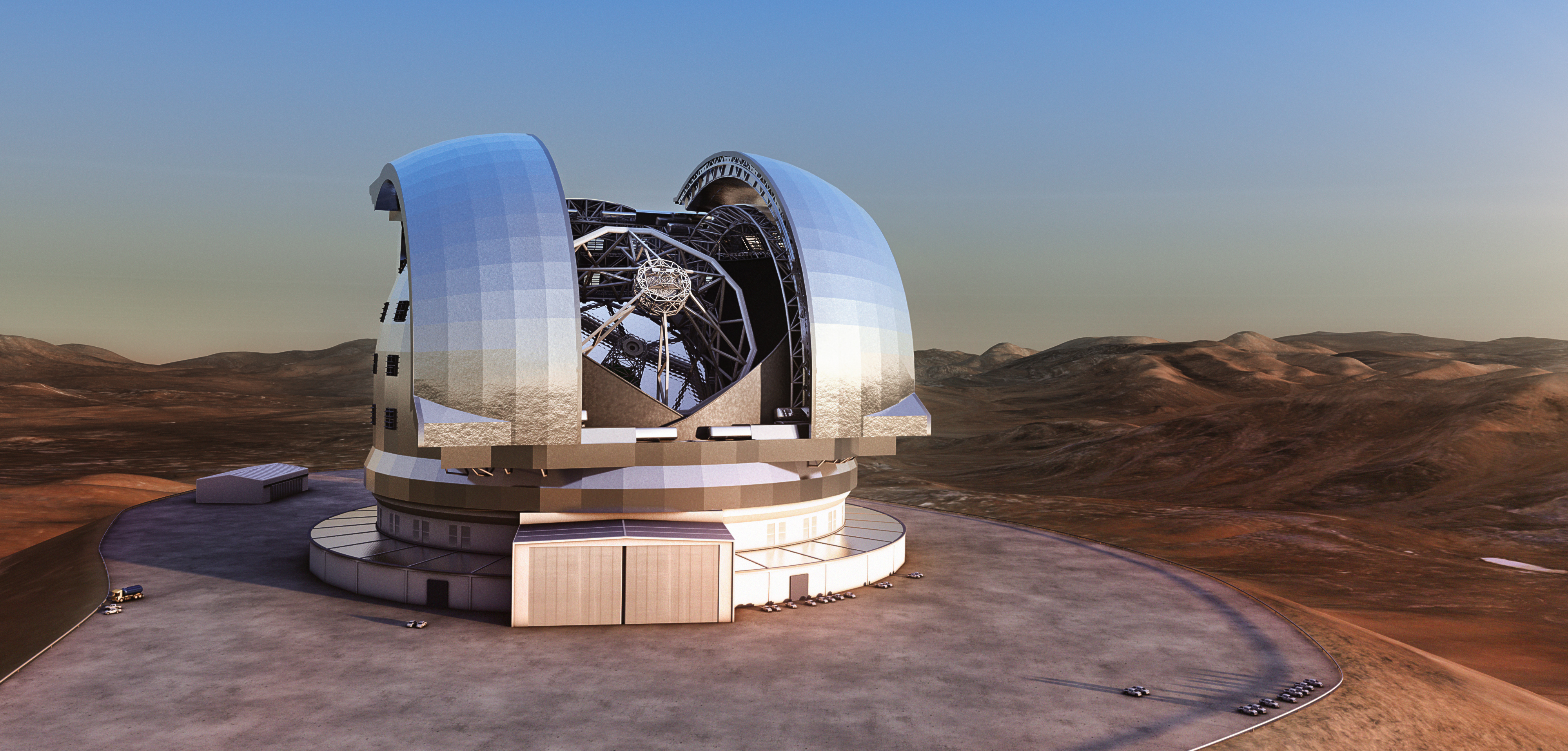

Visible Telescopes
These are used to observe planets, stars, galaxies and other astronomical objects. They can be on Earth or in orbit. They best known example is the Hubble Telescope.
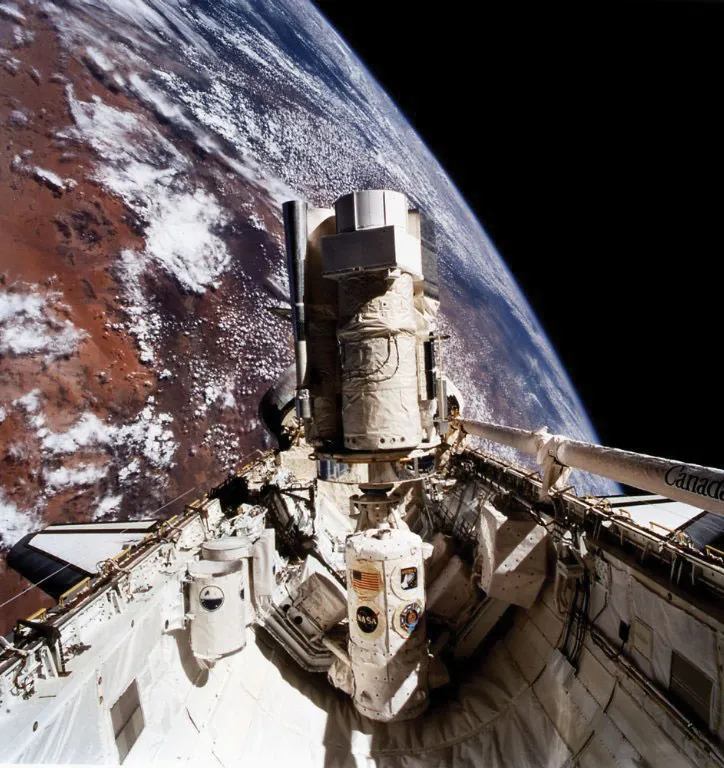

Ultraviolet Telescopes.
There have been very few ultraviolet telescopes as they must be above Earth’s atmosphere. These have been used to observe comets.
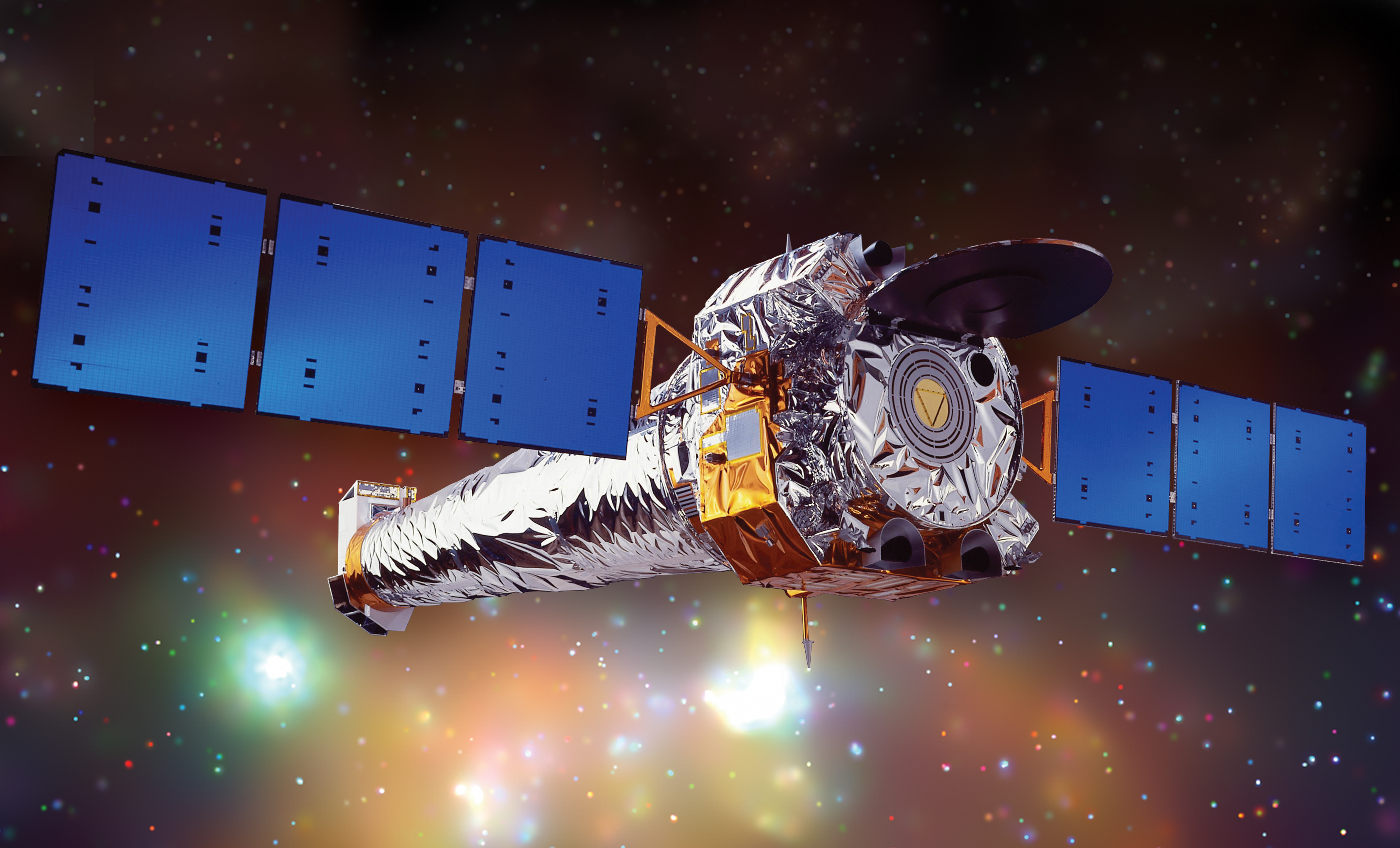

X-ray and Gamma.
These telescopes are placed in orbit and are used to look for high energy x-rays and gamma rays coming from distant quasars )very active distant galaxies).
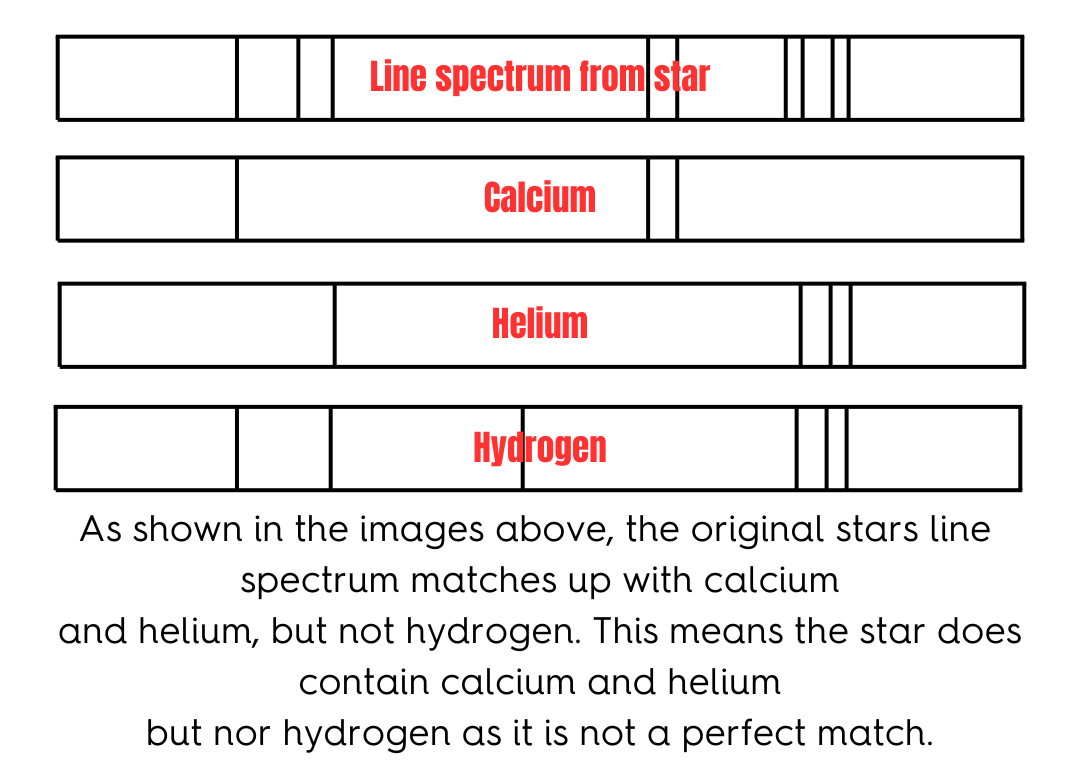
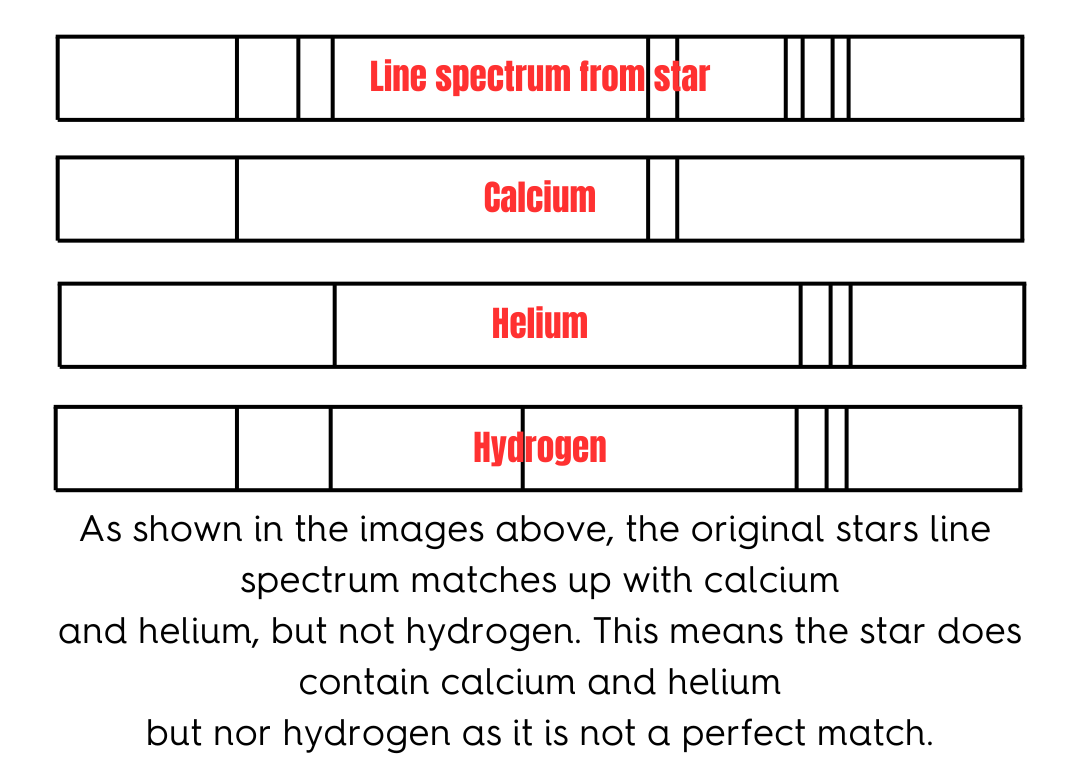
Line Spectra.
Matching each of the lines in each of the elements to the lines in the spectrum. Every line in the element must match the Line spectrum from the star, or the star does not compose of this element.