Nuclear Physics - Topic 7
5.0(1)Studied by 2 people
Card Sorting
1/53
Last updated 5:19 PM on 2/22/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
1
New cards
Nucleus
small, dense region consisting of protons and neutrons at the centre of the atom
2
New cards
Nuclide
a particle type of nucleus that is characterized by the number of protons, neutrons, and the energy state
3
New cards
Nucleon
a proton or neutron
4
New cards
Atomic Number (Z)
number of protons in nucleus
5
New cards
Mass Number (A)
number of protons + neutrons
6
New cards
Neutron Number (N)
number of neutrons in nucleus
7
New cards
Isotopes
nuclei with same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons
8
New cards
Unified atomic mass unit (u)
1/12th the mass of a carbon-12 nucleus
9
New cards
Atomic mass
mass number \* unified atomic mass unit
10
New cards
Gravitational force
a long range, attractive but very weak force between masses
11
New cards
Colomb/Electromagnetic
long range, repulsive or attractive, magnetic or electrostatic forces with a relatively strong force
12
New cards
Strong nuclear force
very short range, attractive and strongest force between any two nucleons that keeps the protons together inside the nucleus
13
New cards
Weak nuclear force
very short range force that is involved in radioactive decay, often involves lighter particles and heavier particles
14
New cards
How does emission spectra work?
1) Low pressure gas is energized by applying a potential difference across it, causing it to heat up.
2)The hot gas emits light energy only at certain well-defined frequencies, as seen through a diffraction grating or prism.
2)The hot gas emits light energy only at certain well-defined frequencies, as seen through a diffraction grating or prism.
15
New cards
How does the absorption spectra work?
1. Light is shone through a cool, low pressure gas
2. A diffraction grating or prism is used to determine the frequencies at which the gas passes through is absorbed
16
New cards
Spectral Lines
Lines characteristic of the particular element producing them.
17
New cards
What is Alpha Decay?
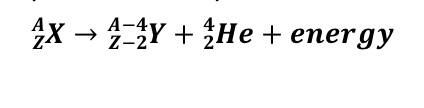
18
New cards
What is a positron?
The anti-matter version of an electron, which shares its mass but has a positive charge instead of a negative charge. It forms in beta-positive decay.
19
New cards
What forms during Beta-minus?
An electron
20
New cards
What forms during beta-positive?
Positron
21
New cards
Beta-minus decay
V represents an anti-neutrino particle
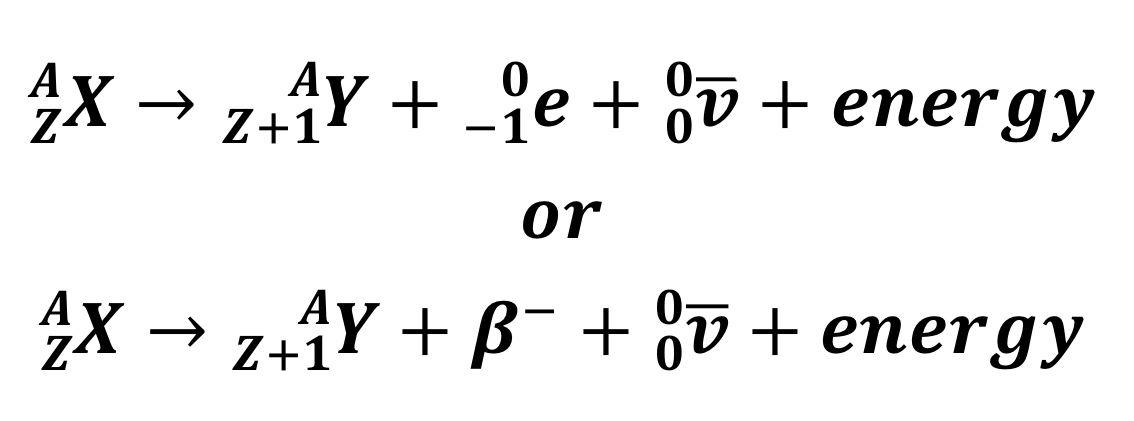
22
New cards
Beta-positive decay
e represents an anti-electron particle, and v is a neutrino
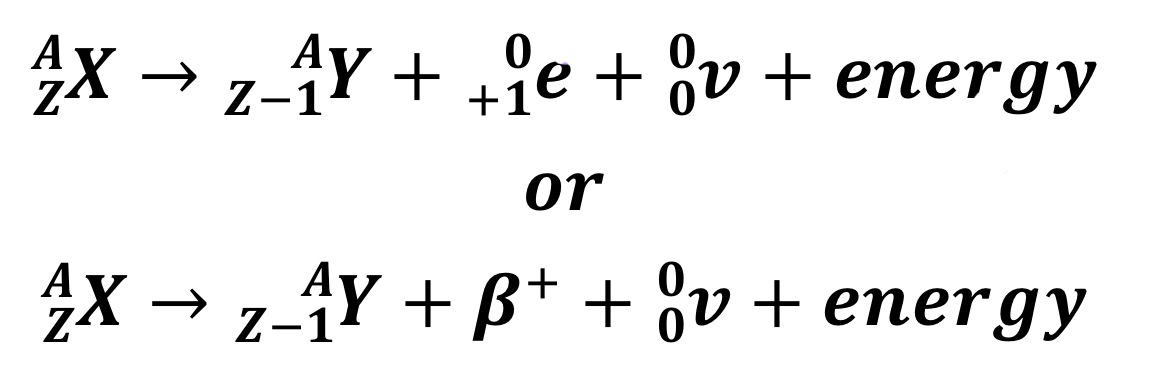
23
New cards
Gamma decay
y is a high energy photon
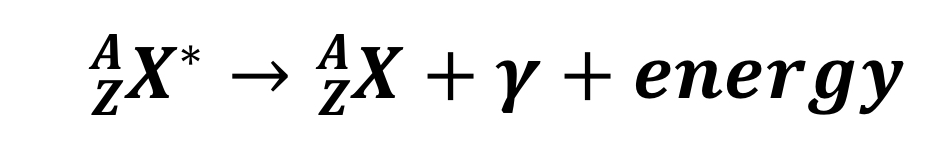
24
New cards
Energy spectra of radiation for each decay process
Alpha spectra - discrete
Beta spectra - continuous
Gamma spectra - discrete
Beta spectra - continuous
Gamma spectra - discrete
25
New cards
Ionizing Radiation
As radiation passes through materials, it “knocks off” electrons from neutral atoms, thereby creating an ion pair: free electrons and a positive ion.
26
New cards
ionizing property
Allows radiation to be detected but is also dangerous since it can lead to mutations in biologically important molecules in cells, such as DNA
27
New cards
Summarized properties of alpha (Particle, penetration ability, material needed to absorb it, path length in air, and speed)
Particle - Helium nucleus
Penetration ability - low
Material needed to absorb it - Sheet of paper; a few cm of air
Path length in air - a few cm
Speed - about 10^7 m/s
Penetration ability - low
Material needed to absorb it - Sheet of paper; a few cm of air
Path length in air - a few cm
Speed - about 10^7 m/s
28
New cards
Summarized properties of beta (Particle, penetration ability, material needed to absorb it, path length in air, and speed)
Particle - Electron or positron
Penetration ability - low
Material needed to absorb it - 1 mm of aluminium
Path length in air - less than 1 m
Speed - About 10^8 m/s, very variable
Penetration ability - low
Material needed to absorb it - 1 mm of aluminium
Path length in air - less than 1 m
Speed - About 10^8 m/s, very variable
29
New cards
Summarized properties of gamma (Particle, penetration ability, material needed to absorb it, path length in air, and speed)
Particle - high-energy photon
Penetration ability - high
Material needed to absorb it - 10 cm of lead
Path length of air - infinite
Speed - 3 x 10^8 m/s
Penetration ability - high
Material needed to absorb it - 10 cm of lead
Path length of air - infinite
Speed - 3 x 10^8 m/s
30
New cards
Geiger counter
Detects and counts the number of ionizations taking place
31
New cards
Half-life
The time taken for half of the nuclides in a sample to decay
32
New cards
Activity (A)
The number of radioactive disintegrations per unit time (decay rate)
33
New cards
The Radioactive Decay Law
The rate at which radioactive nuclei in a sample decay (the activity) is proportional to the number of radioactive nuclei present in the sample at any one time.
34
New cards
Mass defect (mass deficit)
Difference between the mass of the nucleus and the sum of the masses of its individual nucleons
35
New cards
Nuclear binding energy
Energy requires when nucleus is separated into its individual components
36
New cards
Formula for nuclear binding energy
E = mc^2
37
New cards
Artificial (Induces) Transmutation
A nucleus is bombarded with a nucleon, an alpha particle or another small nucleus, resulting in a nuclide with a different proton number (a different element)
38
New cards
Nuclear Fusion
Two light nuclei combine to form a more massive nucleus with the release of energy
39
New cards
Nuclear Fission
A heavy nucleus splits into two smaller nuclei of roughly equal mass with the release of energy.
40
New cards
Natural Radioactivity
When an unstable (radioactive) nucleus disintegrates spontaneously, the nucleus emits a particle of small mass and/or a photon.
41
New cards
Release of energy in nuclear reactions
Energy is usually released in the form of kinetic energy for the products.
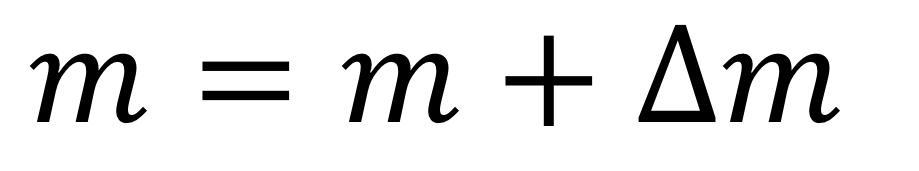
42
New cards
Binding energy per nucleon
Greater for product nuclei than for original nuclei since energy is released.
43
New cards
What is the main source of the sun’s energy? What is the problem with using that on earth? How is is fused?
It is the fusion of hydrogen to helium. The problem with using fusion on earth is that the nuclei in fusion are positively charges and to fuse them, the need to be close enough to the point where the strong nuclear force becomes stronger than the coulomb repulsion force. This is done by colliding them at a very high speed in temperatures above 10°C.
44
New cards
Anti-particle
A particle with the same rest mass but opposite charge
45
New cards
Elementary particle
A particle with no internal structure that cannot be broken down further.
46
New cards
Exchange particles
A virtual particle that transfers between force between interacting particles.
47
New cards
Pair production
Process by which an electron and positron are produced.
48
New cards
Quantized energy
Energy values that are continuous
49
New cards
Rest mass
Mass of the object measured in the object’s rest frame
50
New cards
Random decay
Cannot predict when the nucleus will decay next
51
New cards
Quark confinement
Quarks cannot be directly observed as free particles because the energy given to nucleons creates other particles rather than freeing quarks
52
New cards
Standard model
The theory that describes the electromagnetic and weak interactions of quarks and leptons
53
New cards
Spontaneous decay
The decay cannot be modified in any way
54
New cards
Virtual Particle
A particle that mediated one of the fundamental forces