metals
1/15
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
What happens in metallic bonding
metals loose their outer shell electrons to form positive ions
Where do the delocalised electrons go in metallic bonding
They surround the metal ions and create a ‘sea of electrons’
What happens to the metal ions in metallic bonding
they form neat and regular patterns
Why do the electrons not leave the metal ions
there is electrostatic attraction between the positive ions and delocalised electrons
Why are metals good conductors
because the delocalised electrons can carry an electrical current around the structure
Why do metals have high melting and boiling points
The strong electrostatic forces of attraction between positive metal ions and delocalised electrons require a lot of energy to overcome
Why are metals malleable
because the positive ions are arranged in neat layers which can slide over eachother
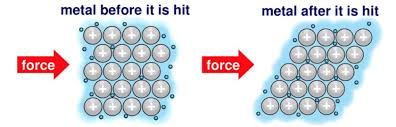
Metals are ________ (starts with d)
Metals are DENSE
metals aren’t very strong because ……
they are malleable so they move a lot
What is an alloy
a mix of 2 or more metals
What happens if an alloy is formed
the regular arrangement is disrupted and not regular
Why aren’t alloys malleable
because the mix of smaller and larger atoms mean there isn’t a regular pattern and the layers can’t slide over each other (this is why alloys are harder than pure metals)
Why are alloys created
because sometimes pure metals don’t have the property needed (e.g. hard, strong, ect)
What are steels
alloys made mainly of iron
What are some properties of magnalium (5%)
made from aluminium and magnesium
stronger
lighter
more resistant to corrosion
used in cars and airplanes
what are some properties of magnailum (50%)
very reactive
burns brightly
used in fireworks