Bio 225 Exam 1 - Cellular Physiology - Lloyd
1/75
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
76 Terms
What is the basic chemical composition of cells
Water - 70%, organic molecules and inorganic ions
Organic molecules in cells
carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids
Inorganic molecules in cells (less than 1% of mass)
Na+, Mg2+. K+, Ca2+, Cl-, phosphate, bicarbonate, etc
plasma membrane functions (4)
Helps maintain composition of intra and extracellular fluids
Forms framework for protein components of cell
Detects chemical messengers at cell surface
Links adjacent cells together
Membrane junctions
tight junctions, desmosomes, and gap junctions
tight junctions
Functions as impermeable barrier
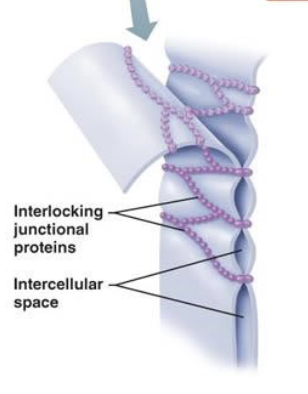
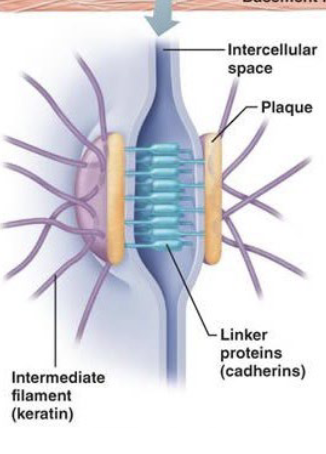
desmosomes and adherens junctions
(Spots and bands) Functions to anchor adjacent cells
gap junctions
Aids in communication between adjacent cells
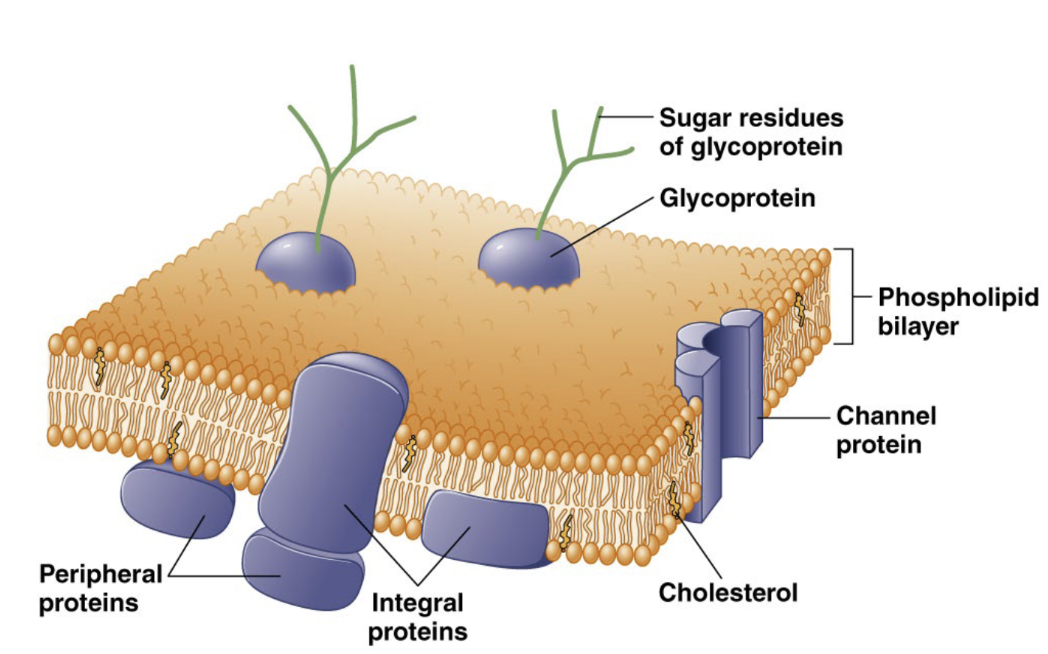
Major structures of the plasma membrane
cholesterol, integral proteins, channel proteins, peripheral proteins, glycoprotein and sugar residues of glycoprotein
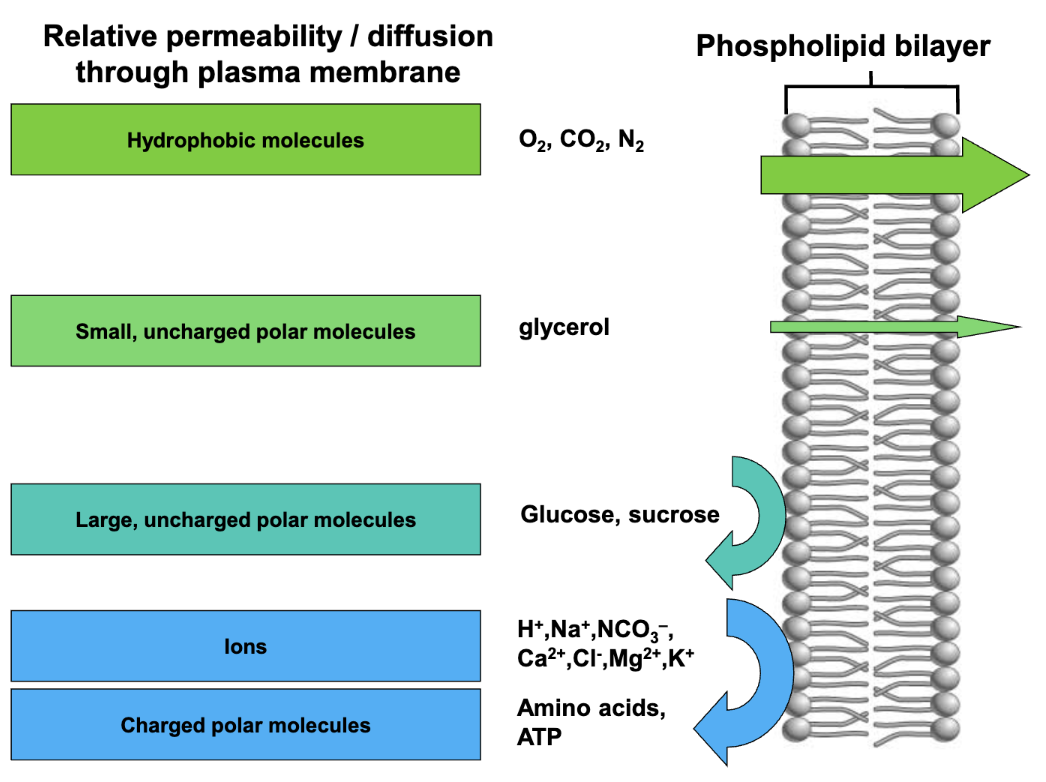
Relative permeability / diffusion thru plasma membrane of certain molecules.
refer to image
Steroid molecules are
lipids, nonpolar, and hydrophobic
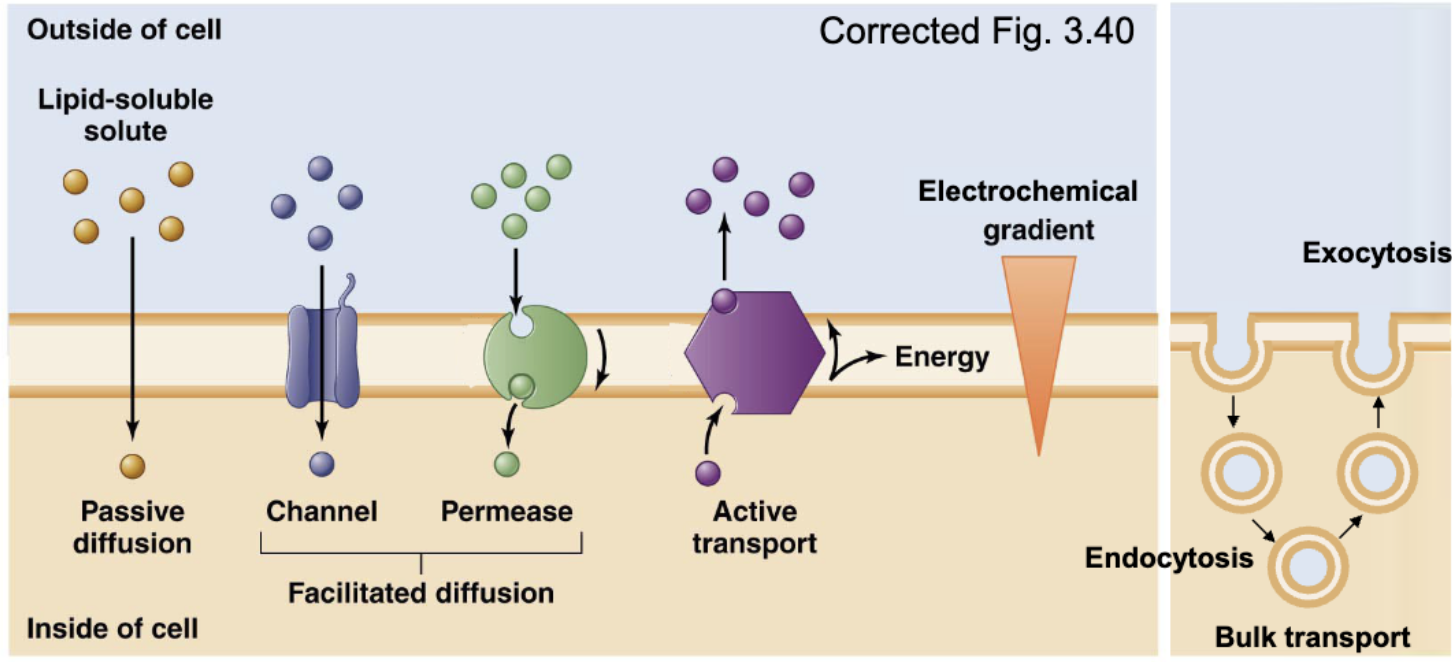
Different ways that molecules move across the cell membrane
simple (passive) diffusion, facilitated diffusion, active transport, bulk transport (endo-/exo-cytosis)
integral protein
Tightly bound to the plasma membrane. Either embedded or span the entire bilayer and involved in structural support, signaling, and transport
peripheral protein
Attached to the surface of the plasma membrane. Interact with the membrane surface or with integral proteins
glycoprotein
Plasma protein with sugar chains attached. Can be integral or peripheral and involved in cell-cell recognition and binding (adhesion)
Molecules with high relative permeability through the plasma membrane include ___ and ___
hydrophobic molecules and small uncharged polar molecules
Molecules with low relative permeability (cannot diffuse freely through plasma membrane) include ___, ___, and ___
large uncharged polar molecules, ions, and charged polar molecules
what is a gradient
The difference between two points
diffusion is
A random dispersing process due to random thermal motion and entropy (second law of thermodynamics: entropy of a system must always increase or stay constant)
flux
A measure of the diffusion rate; a measure of the net gain of molecules by one side and the net loss from the other side
net flux is
the difference b/w the two one-way fluxes
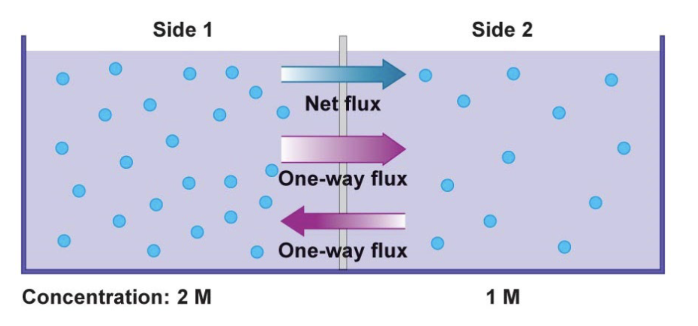
T or F: Diffusion stops once equilibrium is reached
F
Equilibrium means
that the rate of the forward rxn equals the rate of the reverse rxn
simple (passive) diffusion
No metabolic energy (ATP) used, movement from high to low concentration, and net flux (rate of diffusion) = 0 at equilibrium
the movement of molecules due to the intrinsic kinetic energy of molecules (and entropy)
T or F: For passive diffusion, each substance diffuses against its own gradient, independent of the concentration gradients of other substances
T
The direction and magnitude of net flux depends on
permeability, concentration gradient, temperature, surface area, size of molecule, and distance:
T of F: Water can pass through the plasma membrane by simple diffusion
F ; water is excluded by the hydrophobic tails of the phospholipid bilayer
There is new evidence that shows that water can indeed pass thru the membrane via simple diffusion
Different types of gradients
chemical, electrical, or electrochemical
Gradients are forms of
energy storage (potential energy)
An electrochemical gradient is
a gradient of electrochemical potential; a concentration gradient and an electrical field gradient combined
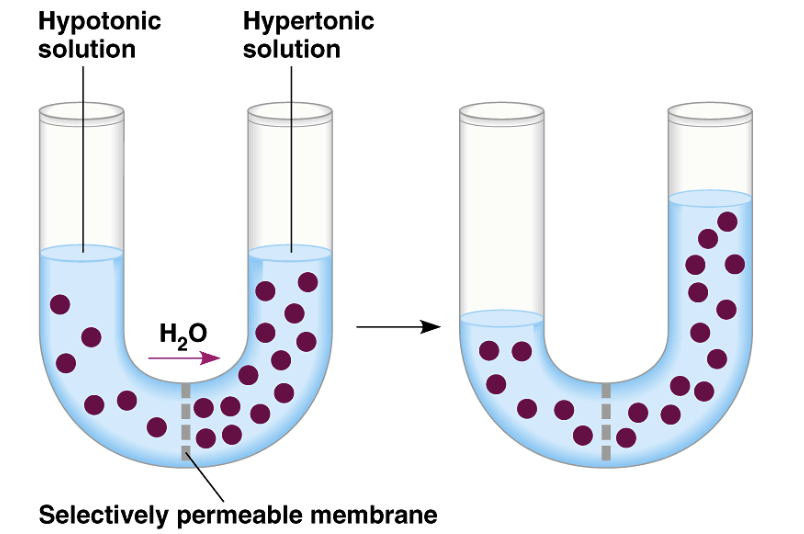
osmosis is
Passive transport of water; Net diffusion of water from a region of high water concentration to a region of low water concentration
Direction of water movement is determined only by difference in total solute concentration, not type of solute
Aquaporins
integral channel proteins that facilitate osmosis
T or F: Direction of water movement is determined only by difference in total solute concentration, not type of solute
T
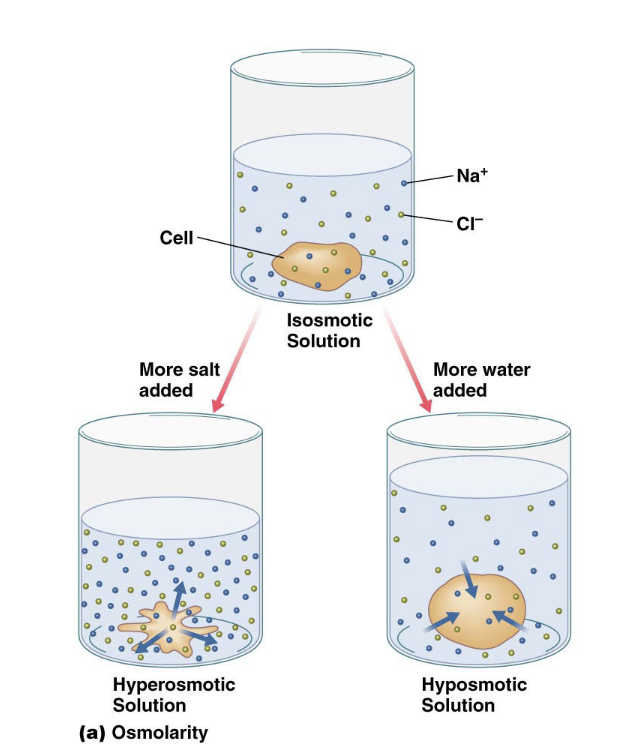
osmolarity is
Total concentration of solutes in a solution; depends on the total number of molecules not individual types
isosmotic
Same osmolarity (surrounding compared to cell)
hyperosmotic
Higher osmolarity (surrounding compared to cell)
hyposmotic
Lower osmolarity (surrounding compared to cell)
osmotic pressure
Pressure generated by water moving based on osmolarity
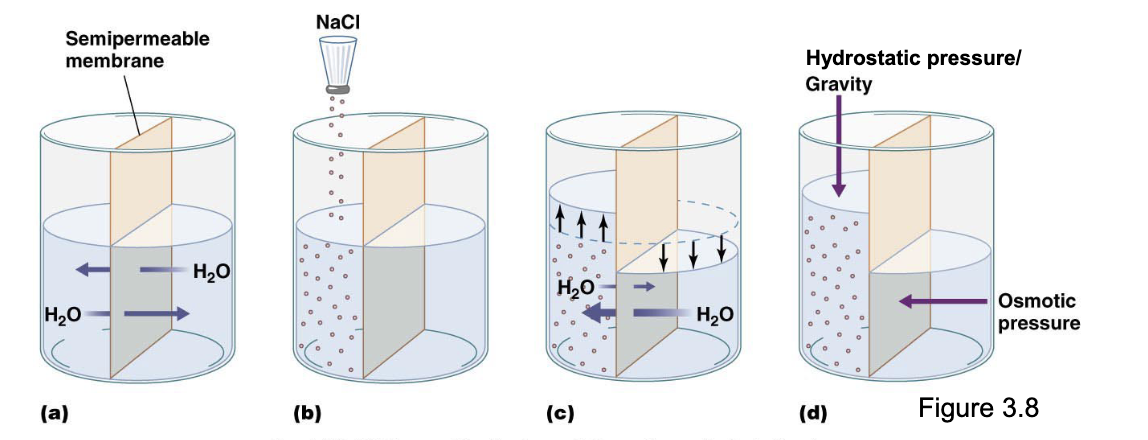
hydrostatic pressure
Pressure exerted by the standing column of water (gravity)
System used to transport molecules too large or too polar to diffuse across the plasma membrane
mediated transport system
facilitated diffusion
Transmembrane proteins facilitate diffusion of some polar or charged molecules across the plasma membrane. Molecules move down their electrochemical gradient. No metabolic energy (ATP) required for transport
channel proteins
Provide a corridor for polar or charged molecules to pass through the plasma membrane (facilitated diffusion)
specificity of channels depends on the charge and pore size
Ion channels may be
selective or non-selective
Selective ion channels include ___, ___, and ___ channels
Na+, K+, and Cl-
Non-selective ion channels are ______ ______ channels that allow ___, ___, and ___ ions to pass through
monovalent cation, Na+, K+, and Li+
constitutive channels
Channels that are always open
An example of a constitutive channel are ___
aquaporins
gated channels
Channels that open transiently in response to stimulus
The three types of gated channels are ___-gated channels, ___-gated channels, and ___-gated channels
ligand, voltage, and mechanically
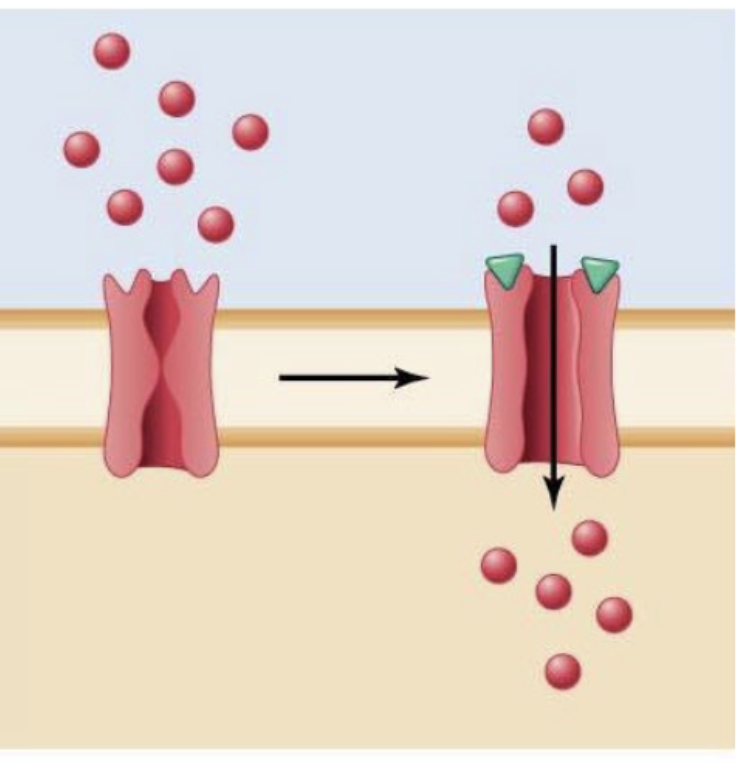
ligand-gated channel
A signal molecule binds to the receptor/channel regulating the opening and closing of the gates (type of channel)
eg) acetylcholine regulates entry of Na+ into muscle cell
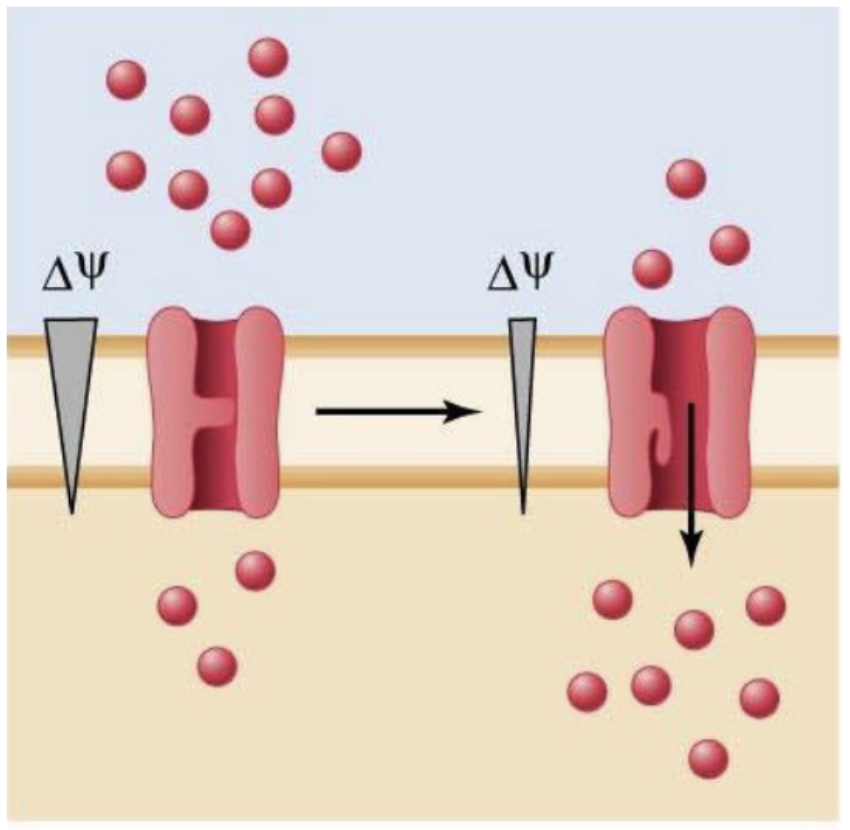
voltage-gated channel
Regulated by the electrical state of the cell (type of channel)
ex: voltage-gated Na+ channels activated by membrane potential
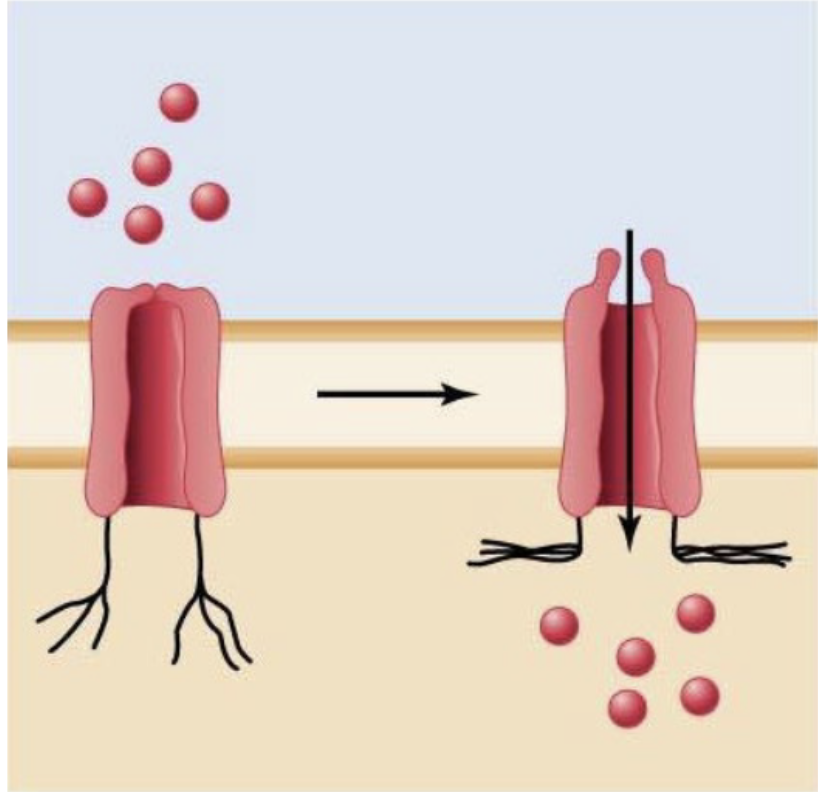
mechanically-gated channel
Regulated by a physical change
ex: pressure
permease/carrier protein
Substrate binds to protein, undergoes a conformational change, and releases the substrate to the other side (a form of facilitated diffusion); down [] gradient
ATP not needed
eg) GLUT protein
molecules that are too large and/or polar to diffuse are transported across plasma membrane by mediated transport mechanisms:
facilitated diffusion, active transport, bulk transport
active transport
Transport where transported molecules must bind to the transporters. Metabolic energy (ATP) is required directly or indirectly.
types of active transport
secondary active transport and primary active transport

primary active transport
ATP is required directly and involved movement of solutes against their gradient. specific membrane-bound transport proteins involved
Binding to recognition site of proteins that act as ATPase and convert ATP → ADP → Pi which causes a conformational change in the transport protein → movement of the solute across the membrane
ex: Maintains electrochemical gradients
Primary active transport Example 1
Ca2+ ATPase/Pump: hydrolysis of ATP directly required for the function of the carriers. molecule or ion binds to the “recognition site” on one side of carrier protein —> binding stimulates phosphorylation (breakdown of ATP) of the carrier —> carrier protein undergoes conformational change —> hinge-like motion releases transported molecules to the opposite side of the membrane
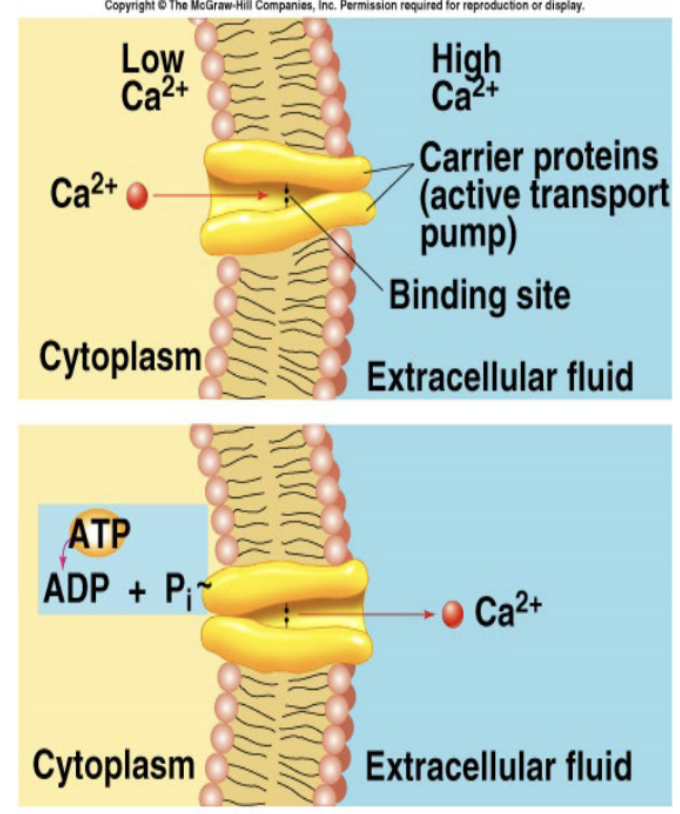
Primary active transport Example 2
Na+/K+ ATPase/Pump
Carrier protein is also an ATPase enzyme that converts ATP to ADP and Pi. Actively exports 3Na+ and imports 2K+ inward against [] gradient.
![<p>Na+/K+ ATPase/Pump</p><p>Carrier protein is also an ATPase enzyme that converts ATP to ADP and Pi. Actively exports 3Na+ and imports 2K+ inward against [] gradient.</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/094ec33c-48e8-42cf-8596-d9f9f424af4e.png)
functions of steep gradient (from Na+/K+ ATPase):
involvement in electrochemical impulses
promotes osmotic flow'
regulates resting calorie expenditure and basal metabolic rate
provides energy for “coupled transport” of other molecules
secondary active transport
No direct input of energy required but depends on the electrochemical difference established by primary active transport
“coupled” transport
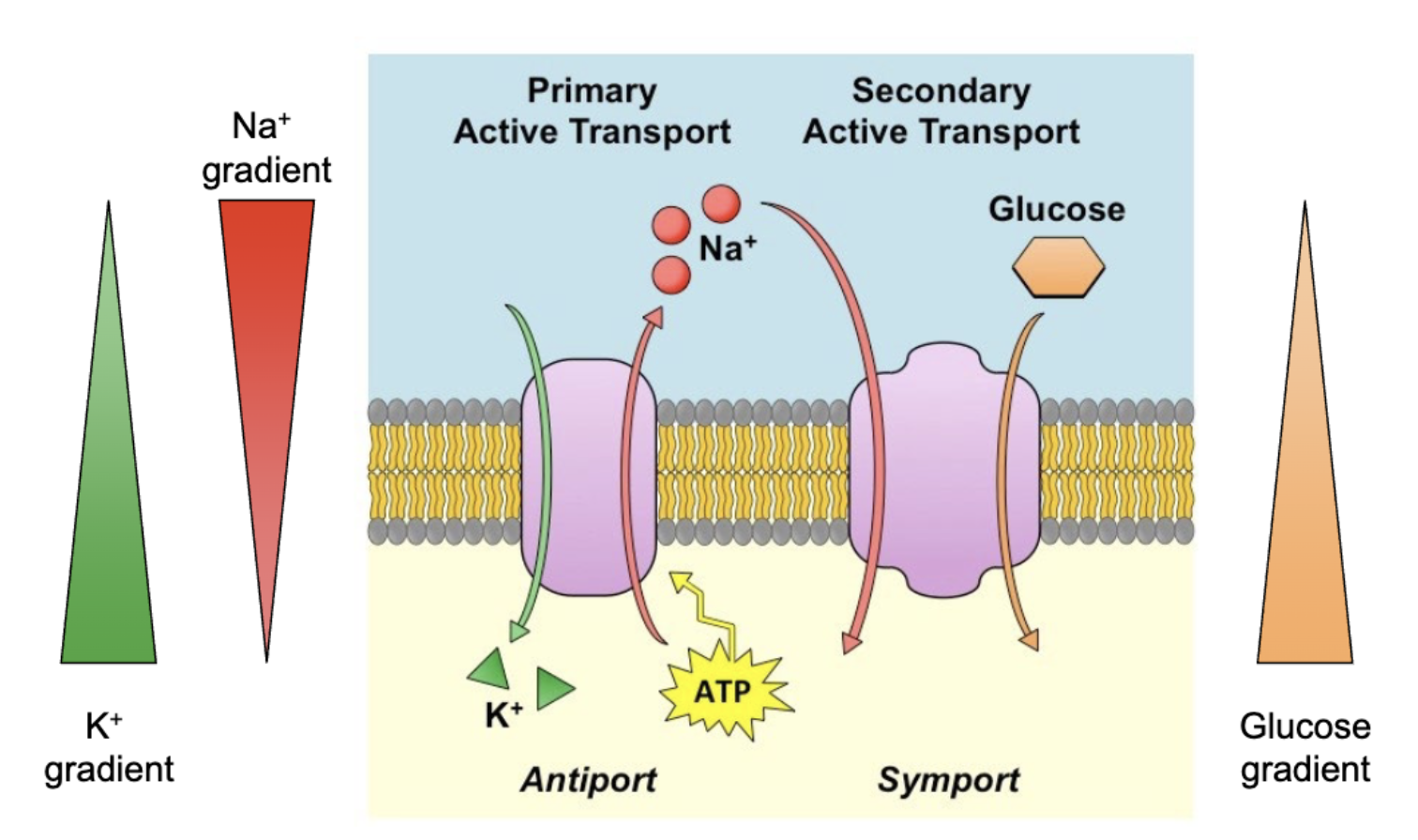
Types of transporters
ion channels
antiporters
symporters
electroneutral cotransporters
electroneutral exchangers
uniporter
The specific transport of a single substance in or out of cells
symporters
transport moves 2 different molecules in the same direction. Both may or may not be charged
ex: SGLT transporters move sodium down electrochemical gradient into cell to concentrate glucose
antiporters
transport similarly charged molecules in opposite directions
ex: Na+/K+ ATPase
ion channels
move single ions down electrochemical or [] gradient
ex: CFTR
electroneutral cotransporters
move anions and cations in same direction
ex: NKCC transporters
electroneutral exchangers
reversible transporters driven by electrochemical gradients
ex: Cl-/HCO3- exchanger in RBCs
bulk transport
Simultaneous movement of many large molecules that cannot be transported by carriers
endocytosis and exocytosis
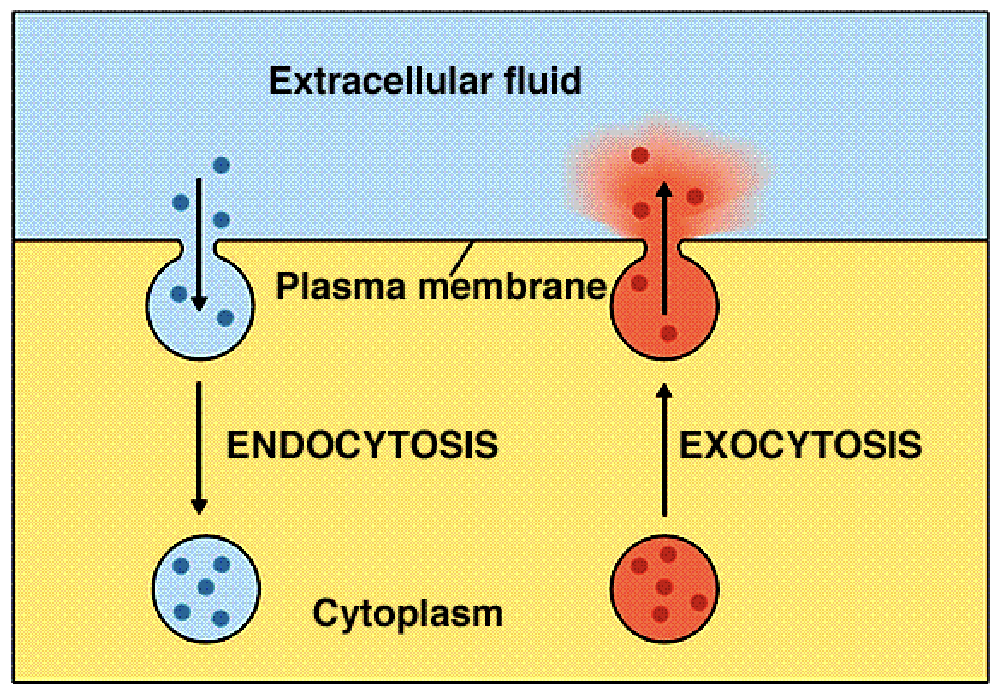
exocytosis
A process by which the contents (cellular products) of a cell vesicle are released to the exterior through fusion of the vesicle membrane with the plasma membrane
endocytosis
A process by which cells absorb external material by engulfing it with the cell membrane due to the interaction of the molecule and protein receptor
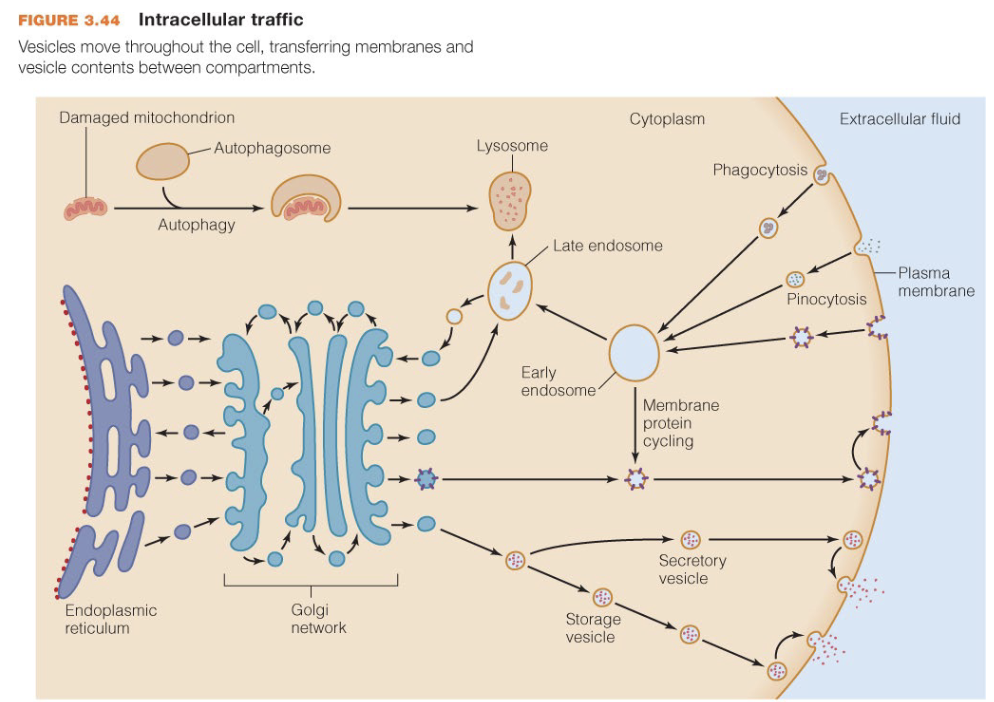
pinocytosis
The uptake of extracellular fluids and small molecules by a cell
phagocytosis
The process by which a cell engulfs and internalizes a large particle by extending its membrane around it
Unifying Theme: The ___ and ___ of a characteristic are connected.
form and function
Unifying Theme: In the face of environmental variation, ___ and ___ are used to compensate for environmental variation.
regulation and homeostasis
What is another word for a carrier protein?
permease