Lesson 1 Ohm's Law
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
Electric Current
Amount of charge passing through any point in a conductor per unit time.
the movement of tiny charged particles (electrons) through a wire, making devices like bulbs and fans work.
Conventional current
It assumes that positive charges flow from the positive terminal of a battery to the negative terminal.
This is the traditional way scientists originally defined current, before they knew electrons were the actual charge carriers.
Electron Current (I)
electrons (which are negatively charged) move in the opposite direction—from the negative terminal of the battery to the positive terminal.
This is what actually happens in a circuit.
Direct current
current that travels in one direction
Alternating current
a charge that changes direction at a regular interval
Resistance (Ω)
Opposition of a material to the flow of electric current.
Resistors
Regulate the amount of current passing through a conductor. Values may be fixed or variable.
Fixed Resistors
has a resistance value that cannot be changed or adjusted.
Variable Resistor
it allows the resistance value to be adjusted manually.
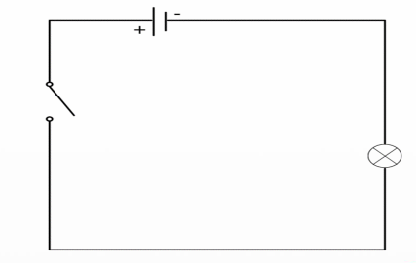
Circuit Diagram
Represent the electrical circuit using industry- standard symbols.
It shows the path of the electrical energy flow, and how the components are connected.
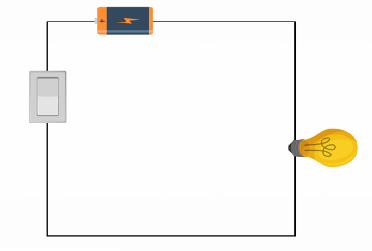
pictorial style and schematic style
two types of circuit diagrams
pictorial style
type of circuit diagram that uses simpler illustrations of the components
so that it would be more understandable to a less technical audience.
schematic style
type of circuit diagram that uses industry-standard symbols