Bioenergetics and muscle metabolism I
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP)
ATP hydrolysis to ADP and phosphate ΔG = -31kJ mol-1
ATP is not a long-term energy store
The body must constantly synthesise new ATP
Three ATP synthesis pathways
1. ATP-phosphocreatine system (anaerobic metabolism)
2. Glycolytic system (anaerobic metabolism)
3. Oxidative system (aerobic metabolism)
1. ATP - phosphocreatine system
Phosphocreatine (PCr): ATP recycling
PCr energy cannot be used for cellular work
PCr energy can be used to reassemble ATP
Replenishes ATP stores during rest
Recycles ATP during exercise until used up
Glycolysis
1. Preparation phase:
Traps glucose in cell
Forms a compound that is readily converted into 3C molecules
2 molecules of ATP consumed
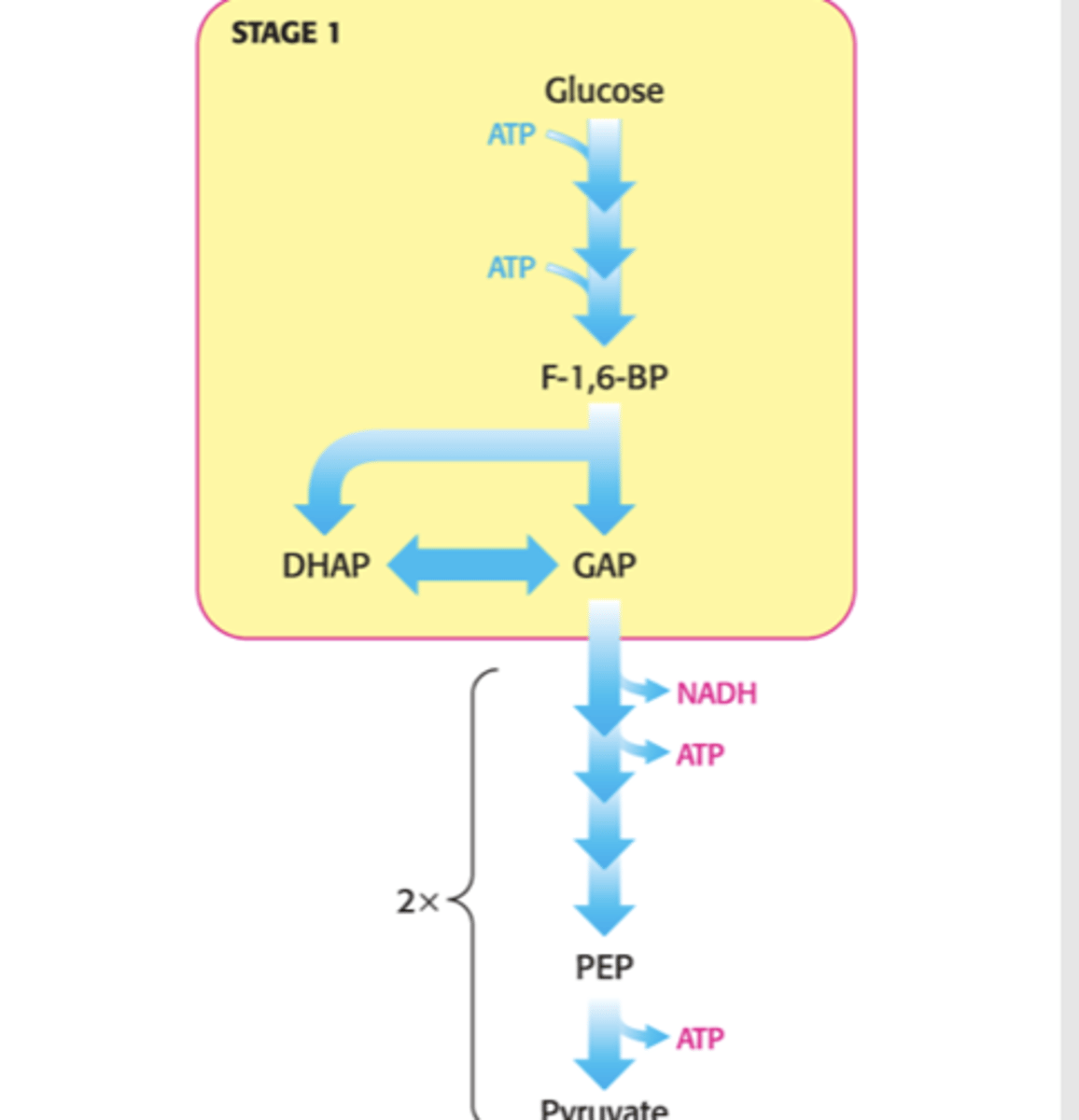
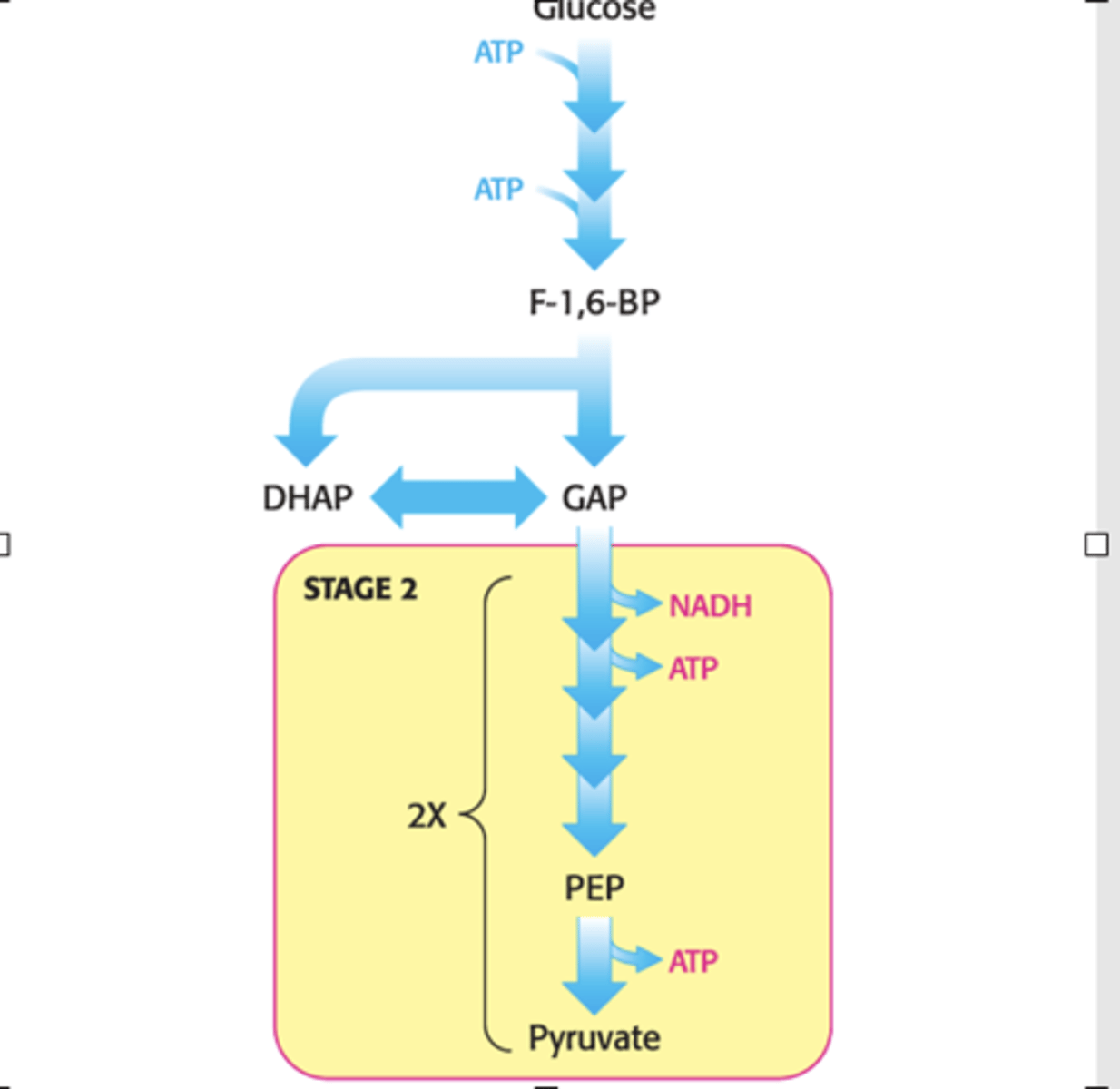
Glycolysis
2. Payoff phase:
Harvesting of some of the free energy of the intermediates
4 ATP produced
2 NADH produced
Anaerobic glycolysis - lactate dehydrogenase
Used when:
the supply of oxygen is inadequate
Allows formation of ATP by glycolysis by regenerating NAD via lactate dehydrogenase
Lactate The Cori Cycle
- lactate from muscle is converted to glucose in the liver (via the conversion to pyruvate)
- glucose returns to the muscle and is used in glycolysis
Aerobic metabolism
- Glycolysis
- Citric acid cycle
- Oxidative phosphorylation
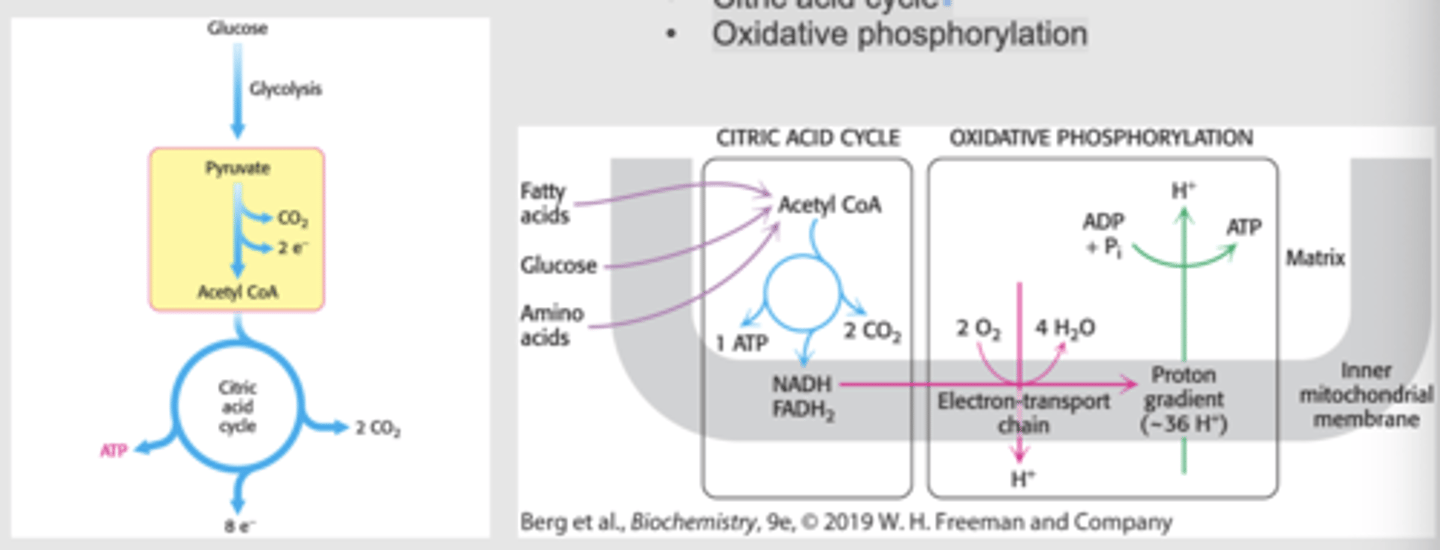
Source of energy in the body
Carbohydrates
Fats
Proteins
Glycogen metabolism
Glycogen synthesis - glycogenesis - key enzyme = glycogen synthase
Glycogen breakdown- glycogenolysis- key enzyme = glycogen phosphorylase
Fat ( Triacylglycerol) metabolism
Hormonal signals control mobilisation/.storage of TAGs in adipose
Insulin- promotes TAG storage
Glucagon/adrenaline- promotes lipolysis
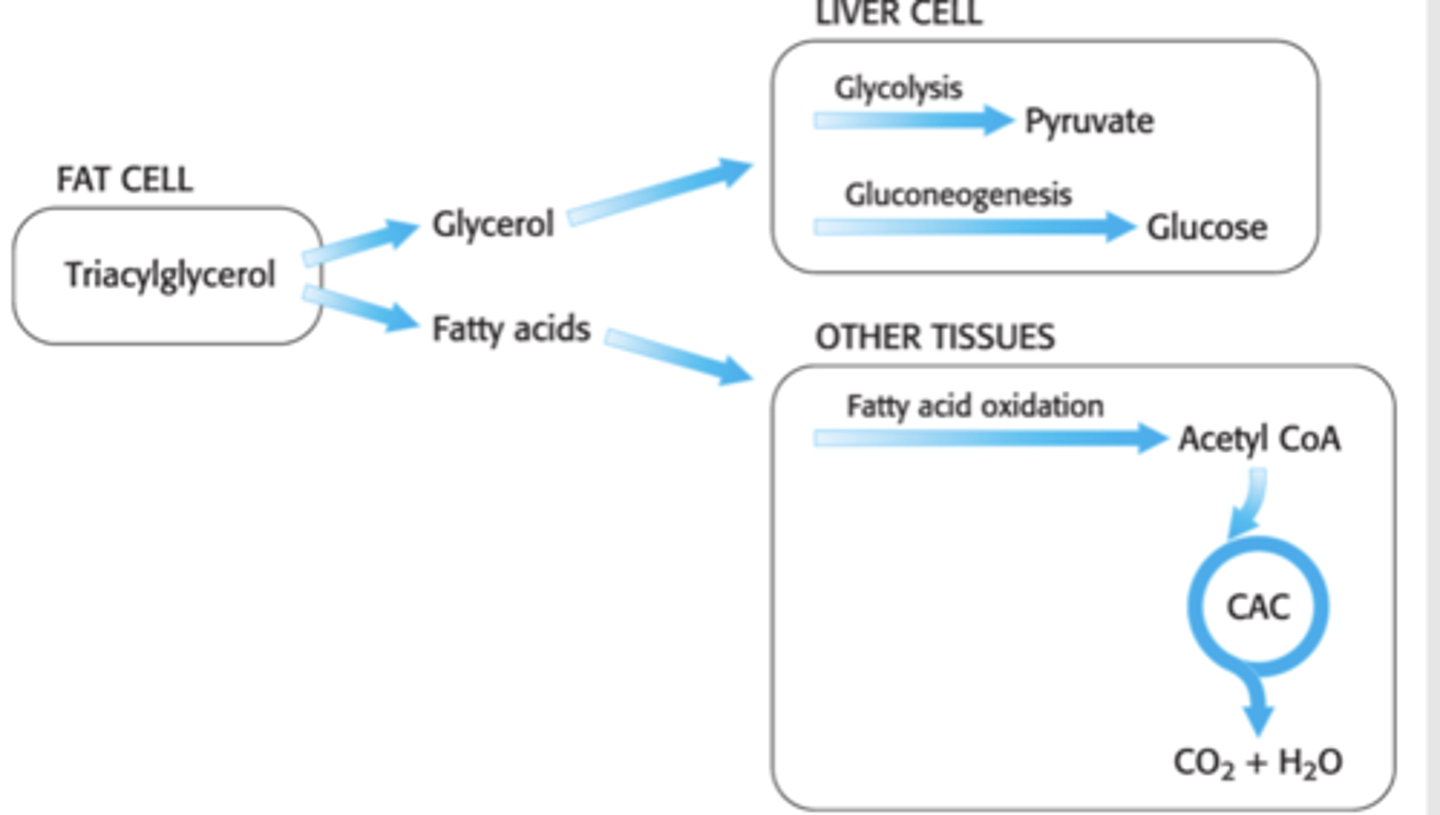
Common pathways used to provide energy
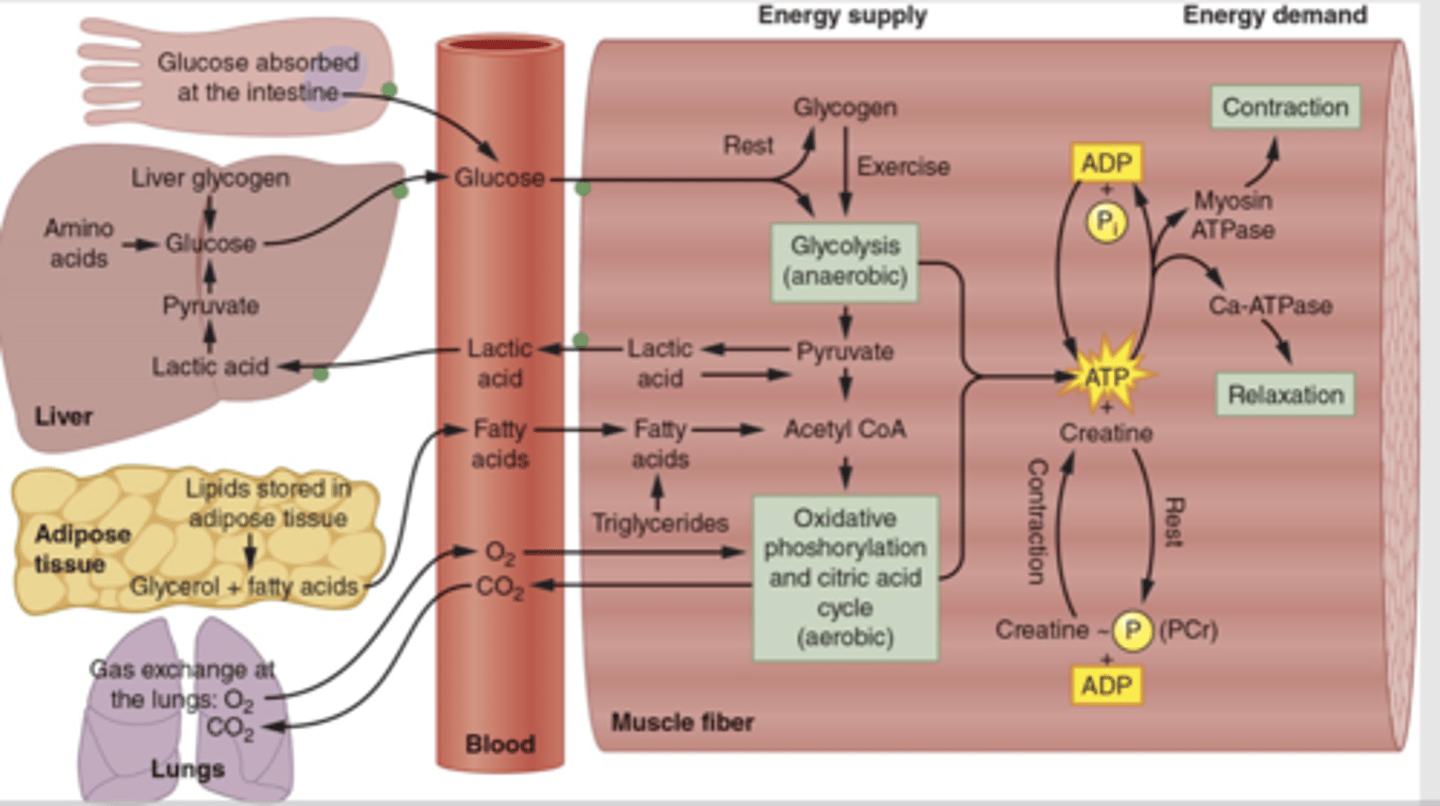
Interaction of different energy systems
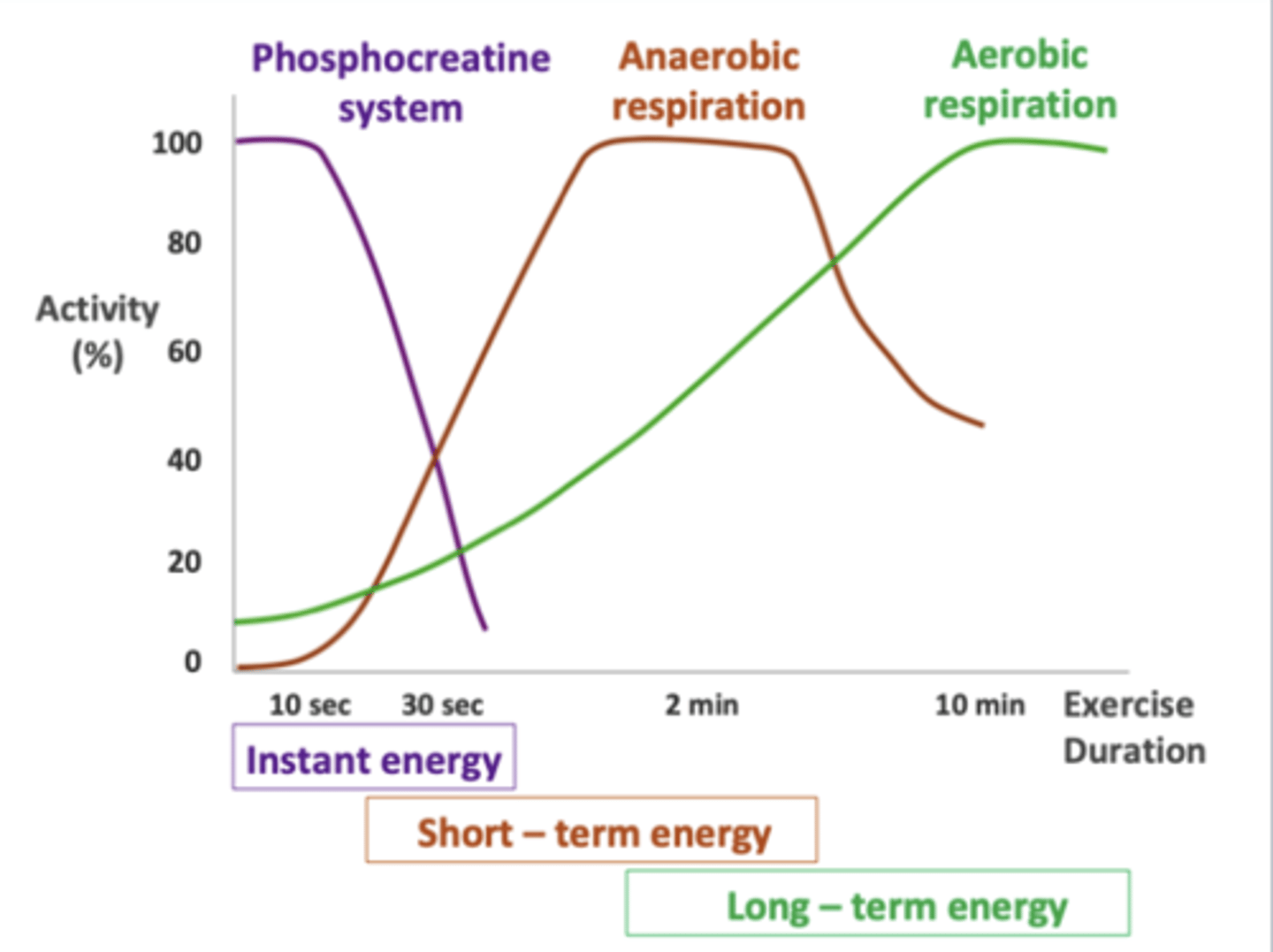
Different pathways active at different times
Short sprint
PCr and Anaerobic Glycolysis
PCr carbohydrate
Long distance run – PCr, Aerobic metabolism (Ox Phos)
carbohydrate & lipid
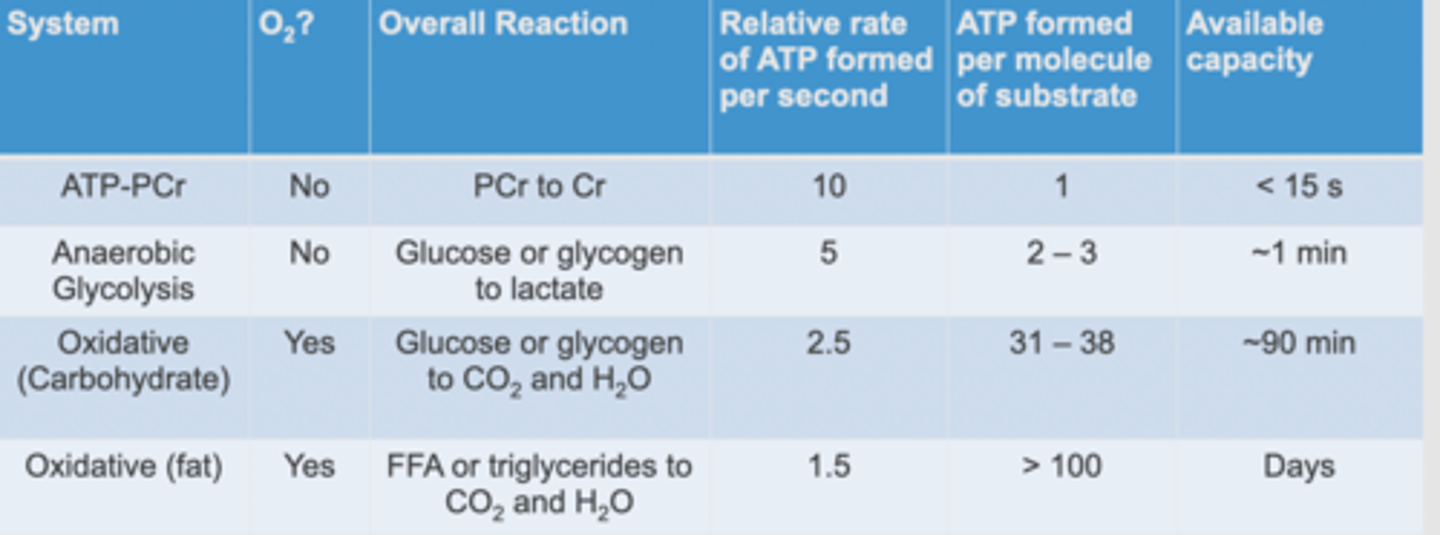
Capacities of different energy systems
Changes in fuel use during prolonged, moderate exercise
Oxidative capacity in muscle
Different muscles exhibit different oxidative capacity
Determined by activity of oxidative enzymes
Muscle fibre types
Type I fibres during exercise:
High aerobic endurance
Can maintain exercise for prolonged periods
Require oxygen for ATP production
Efficiently produce ATP from fat, carbohydrate
Type II fibres during exercise:
Poor aerobic endurance, fatigue quickly
Produce ATP anaerobically