Final
1/189
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
190 Terms
What is the body’s normal response when carbohydrates are ingested?
Blood glucose levels increase and insulin release is stimulated
how long does it take for blood glucose levels to return to homeostatic levels with a normal insulin response?
3.5 hours
Eating —> ____ increases —> ____ —> ____increases —> ____ increases —> ____ decreases
blood glucose
pancreatic islets
insulin
cellular uptake of glucose
blood glucose
Fasting —> _____ decreases —> pancreatic islets —> ___ decreases and ____increases —> _____ decreases and_____ increases —> ____increases
blood glucose
insulin
glucagon
cellular uptake of glucose
glucose secretion into blood by liver
blood glucose
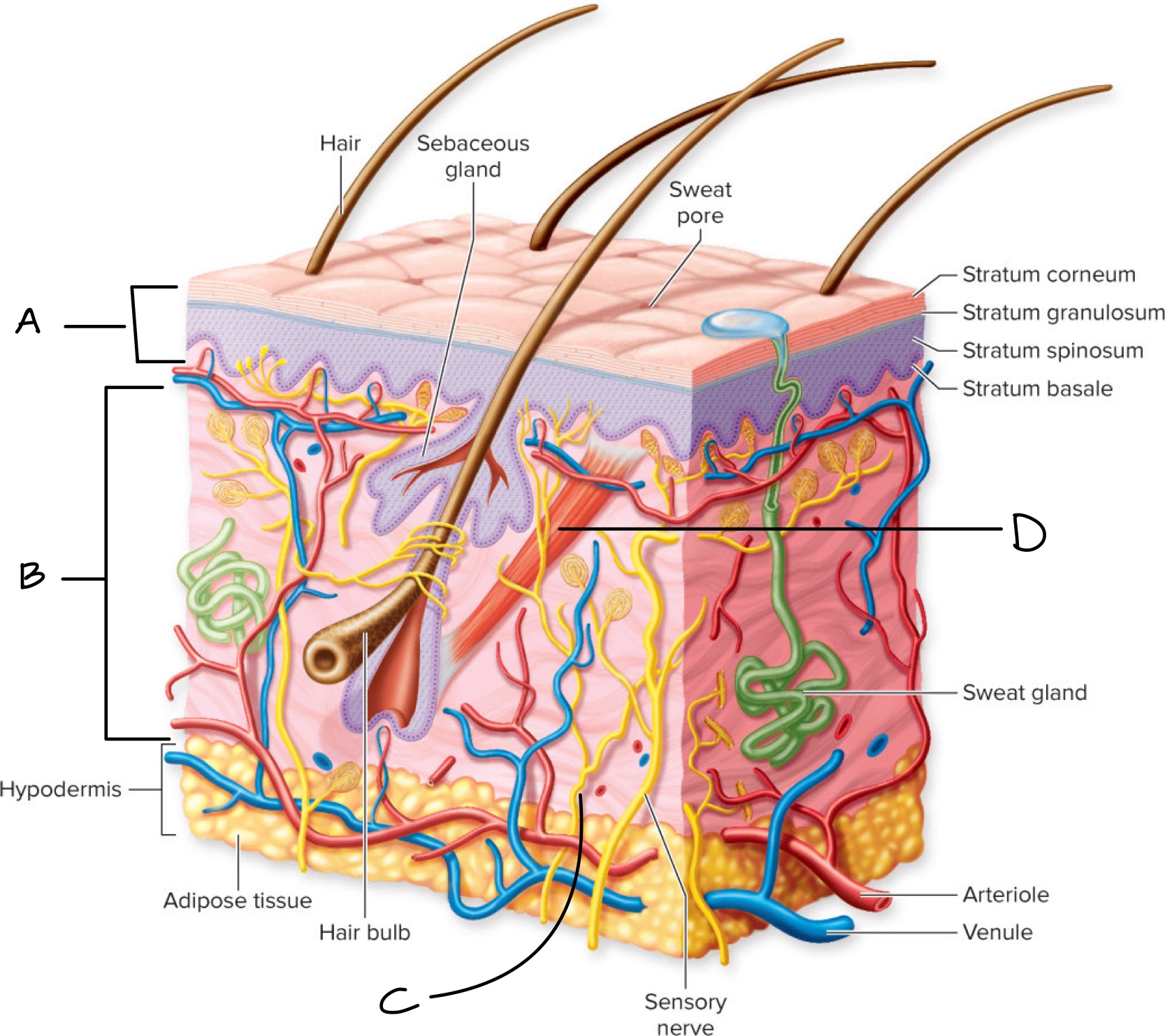
Label the four primary tissue types
A: Epidermis (epithelial tissue)
B: Dermis (connective tissue)
C: Motor nerve (nervous tissue)
D : Arrector pili muscle (muscle tissue)
What type of primary tissue is each of the following?
Neuroglia
tendons
cardiac
simple squamous
Nervous tissue
Connective tissue
Muscular tissue
Epithelial tissue
What is teh function of smooth muscle?
peristalsis of the esophagus
What is the function of transitional epithelium?
distention of the urinary bladder
What is the function of cartilage?
protection of joint surfaces in movable joints
What is the function of neurons?
communication
What is the function of keratinized stratified squamous epithelium?
protection and waterproofing
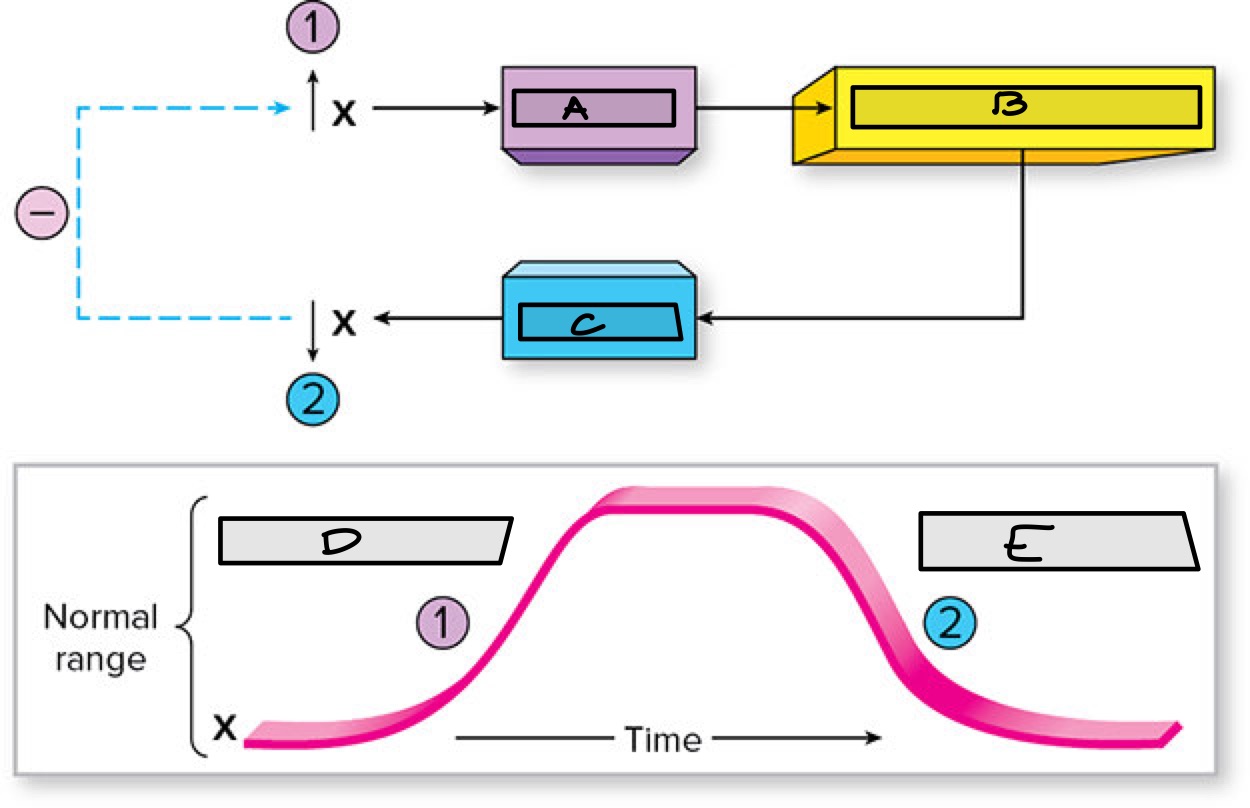
Label the components of the negative feedback loop
A: Sensor
B: Integrating Center
C: Effector
D: Sensor activated
E: effector activated
The basic ____ unit of all living organisms is the cell
structural and functional
A child was born with Alport's syndrome, a genetic condition affecting the genes for the production of a type of collagen. Where are these mutated genes located in a cell?
Nucleus
The major types of tissues are:
muscle, nervous, epithelial, and connective.
Alport's syndrome affects collagen found in basement membranes. The effects of Alport's would therefore likely be associated with which tissue type?
Epithelial tissue
What compartment?
fluid contacting multiple blood cell membranes
Extracellular
Compartment for connective tissue matrix
extracellular
Compartment for cerebrospinal fluid
extracellular
compartment for fluid contacting mitochondrial membranes
intracellular
compartment for fluid surrounding the cytoskeleton
intracellular
compartment for cytosol
intracellular
compartment for ATP produced by the cell
intracellular
What tissue forms the lining of bodily surfaces?
epithelial
What tissue provides resistance to mechanical and frictional trauma?
epithelial
what tissue moves nutrients through the digestive tract?
muscle
what tissue creates pressure gradients for blood transportation?
muscle
what tissue is the transitional tissue between surfaces and muscles?
connective
what tissue provides rigidity to protect deeper, sensitive tissue?
connective
what tissue provides rubbery surfaces on the ends of bones?
connective
what tissue provides rapid communication via electrochemical signals?
nervous
The arrival of the action potential at the presynaptic terminal causes ________.
calcium to enter the presynaptic terminal through voltage-gated calcium channels
The increase in calcium ion concentration causes ________
release of acetylcholine from the synaptic vesicles into the synaptic cleft
Acetylcholine diffuses across the synaptic cleft and ________.
binds to ACh receptors that open ligand-gated sodium channels
What is the purpose of acetylcholinesterase on the postsynaptic membrane ________.
it is an enzyme that breaks acetylcholine down into acetic acid and choline
The neurotransmitter at the neuromuscular junction is ___________.
acetylcholine
T/F: The area between the presynaptic nerve cell and the postsynaptic muscle cell is termed the synaptic cleft.
True
T/F: . Receptors that bind the neurotransmitter on the postsynaptic cell membrane are voltage-gated.
False
An action potential arriving at the presynaptic terminal causes
calcium ions to diffuse into the cell
At the neuromuscular junction, acetylcholine __________.
diffuses across the synaptic cleft and binds to acetylcholine receptors on the postsynaptic muscle fiber
What is the effect of the neurotransmitter at the neuromuscular junction?
It causes ligand gated sodium channels in the muscle fiber to increase their permeability to sodium, which depolarizes the postsynaptic membrane
T/F: Once threshold is reached on the postsynaptic membrane, an action potential is generated and propagated over the postsynaptic cell membrane.
True
Label the locations on the neuron
A: nucleus
B: axon hillock
C: Dendrite
D: node of ranvier
E: schwann cell nucleus
F: axon
G: myelin
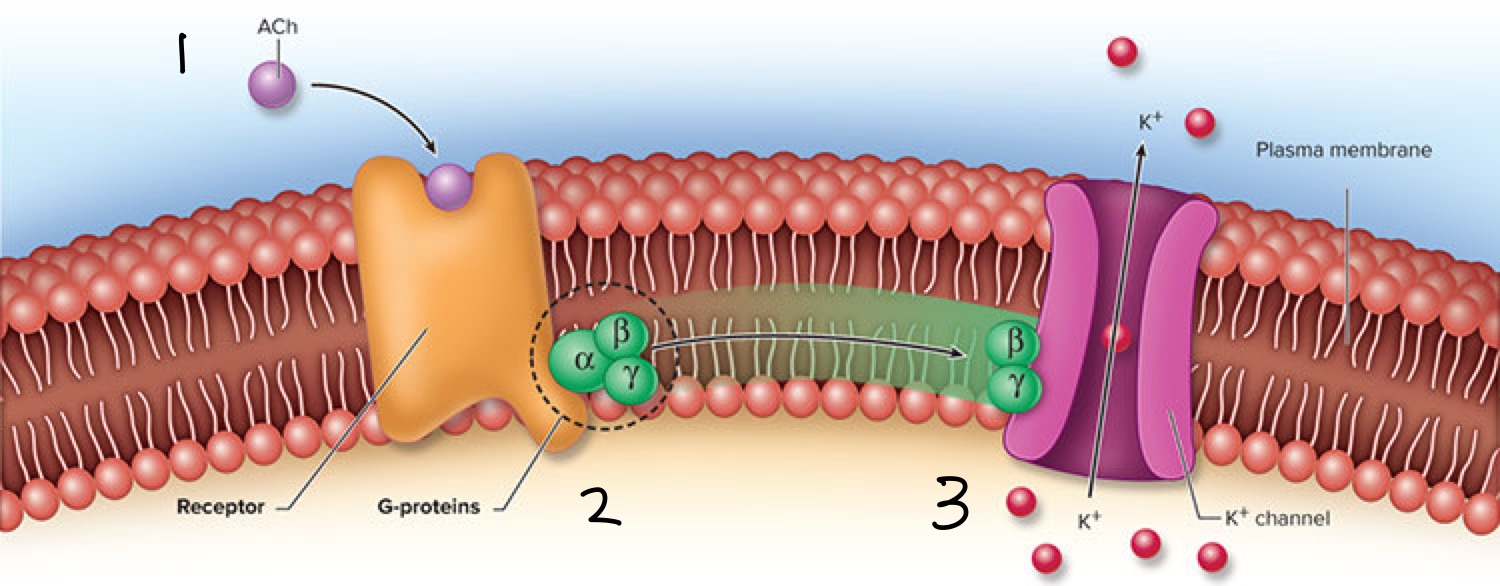
Label the events in the correct order
ACh binds to receptor
G-protein subunit dissociates
G-protein binds to K+ causing it to open
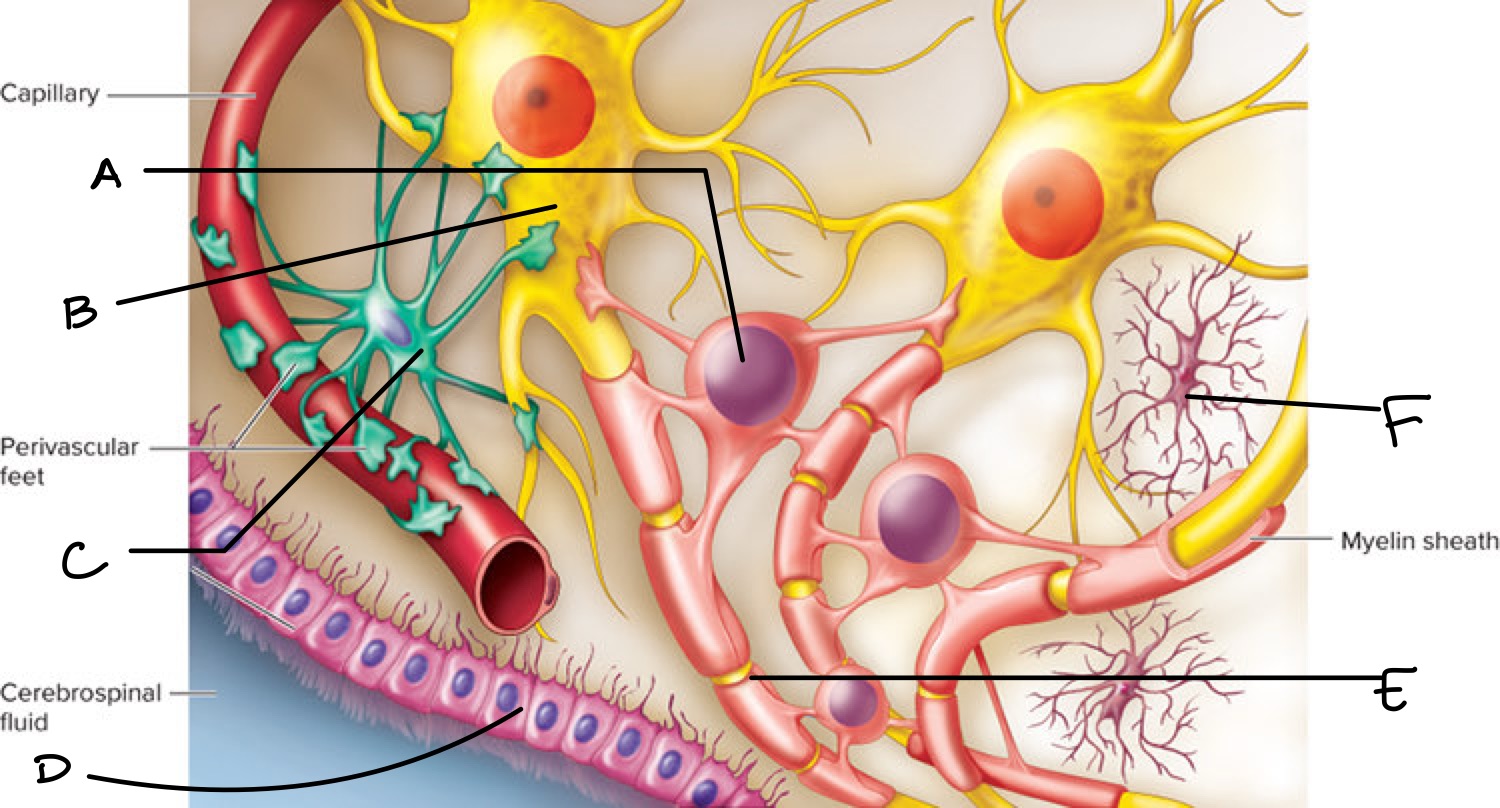
Label the different types of neuroglia
A: oligodendrocyte
B: neuron
C: astrocyte
D: ependymal cell
E: axon
F: microglia
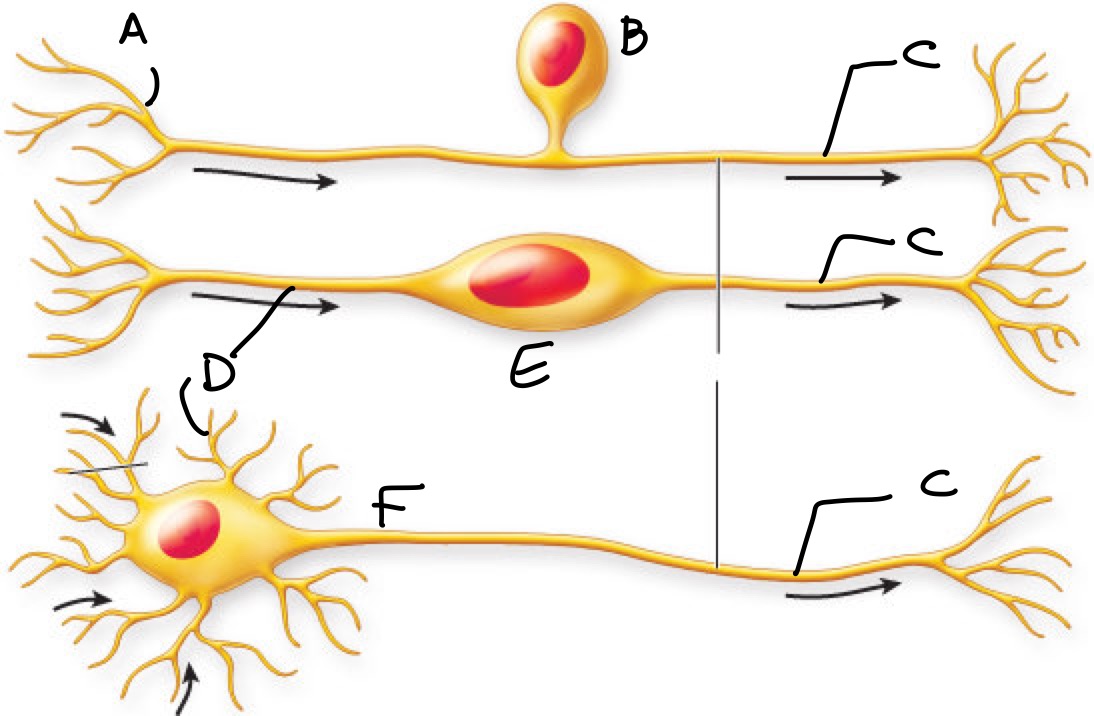
Label the three different types of neurons and their features
A: dendritic branches
B: pseudounipolar neuron
C: axon
D: dendrite
E: bipolar neuron
F: multipolar neuron
The muscarinic ACh receptors are formed from only a single subunit and do not contain _____ like the _____ ACh receptors. Rather, binding of ACh to the muscarinic receptor activates a complex of proteins in the cell membrane known as _____, because their activity is influenced by GDP and GTP, guanosine nucleotides.
There are three G-protein subunits: alpha, beta and gamma. Binding of ACh causes the ____ subunit to dissociate from the other two, which form the_________ complex. Either the alpha subunit or the____ complex then diffuses through the membrane until it binds to an ion channel and causes it to open or close.
ion channels
nicotinic
G-proteins
alpha
beta, gamma
beta, gamma
The binding of ACh to the muscarinic receptor indirectly affects the permeability of _ channels. This can produce —- in some organs if channels are opened, and __ in others if channels are closed.
K+
hyperpolarization
depolarization
For example, in the heart it is the beta-gamma complex that binds to the K+ channels of heart muscle and causes them to open. This leads to K+ diffusion ___ of the cell and the cell becomes ____ resulting in a decrease in heart rate.
out
hyperpolarized
In contrast, in smooth muscle of the stomach the alpha subunit binds to K+ channels causing them to close. This reduces the outward diffusion of K+ and the cell becomes _______resulting in smooth muscle contraction.
depolarized
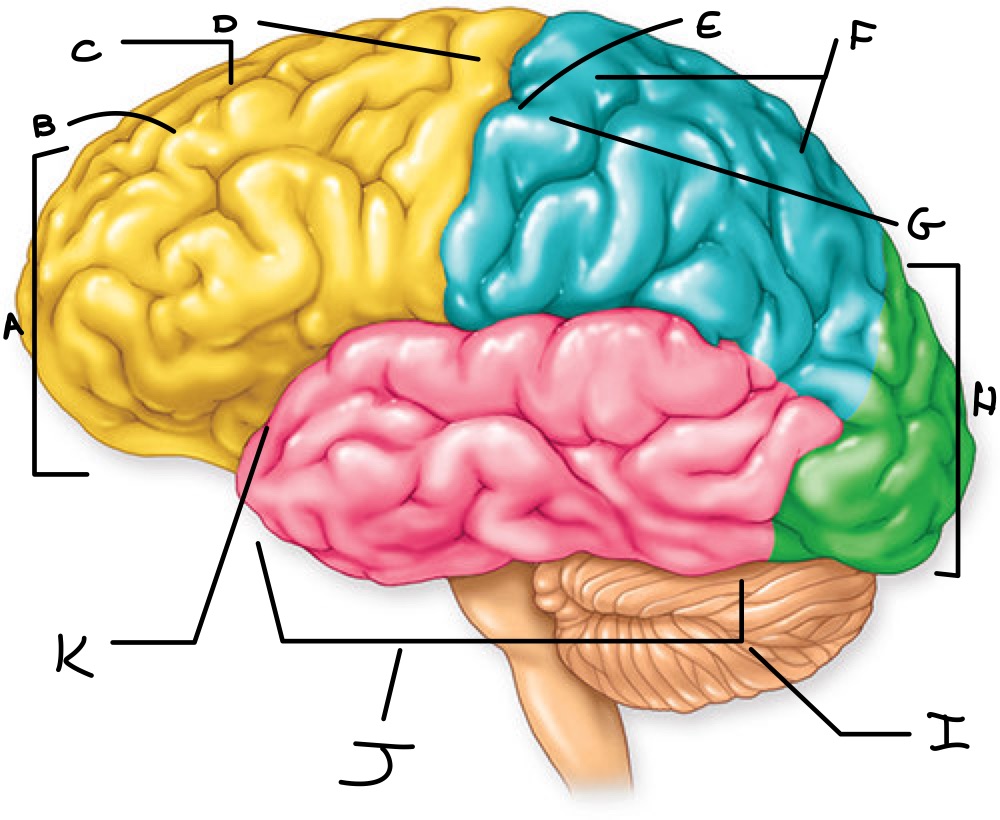
Label the approrpiate locations
A: Frontal Lobe
B: Superior Frontal Sulcus
C: Superior Frontal Gyrus
D: Precentral gyrus
E: Central sulcus
F: Parietal lobe
G: postcentral gyrus
H: occipital lobe
I: Cerebellar hemisphere
J: Temporal lobe
K: Lateral sulcus
Which lobe is responsible for voluntary skeletal muscle contrl
frontal
Which lobe is responsible for auditory interpretation and storage
temporal
Which lobe is responsible for memory, smell, taste, sensory integration from viscera
insula
Which lobe is responsible for somateshtetic interpretation, understanding speech
parietal lobe
Which lobe is responsible for visual perception, eye coordination
occipital lobe
Keeping an email address in mind until you type it in an email is an example of
working memory
Remembering a vacation trip to the Grand Canyon is an example of
episodic memory
Knowing the bones of the body is an example of
semantic memory
Knowing how to double crochet an afghan is an example of
procedural memory
What regulates hunger and thirst
hypothalamus
what regulates the autonomic nervous system
hypothalamus
what is the relay center for sensory input
thalamus
what regulates circadian rhythms
hypothalamus
what regulates body temperature
hypothalamus
what function is arousal from sleep
thalamus
What structure coordinates complex motor skills
cerebellum
what plays a role in drug addiction
midbrain
what contains caridac, respiratory, and vasomotor control centers
medulla oblongata
what is the area where nerve tracts cross to the contralateral side
medulla oblongata
what contains the apneustic center which aids in respiration center
pons
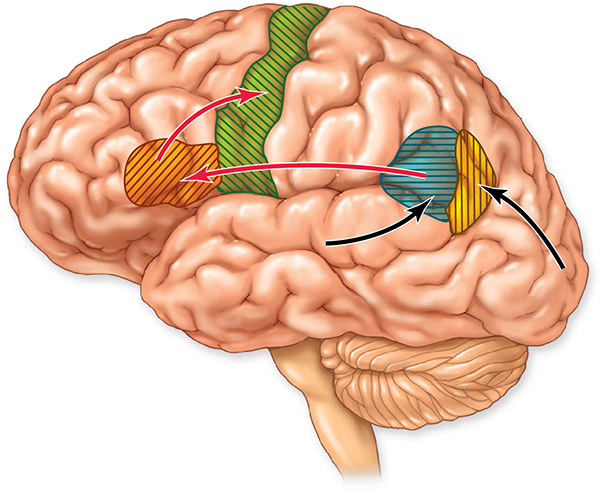
What are the correct terms?
A: Motor cortex
B: Broca’s Area
C: Hearing
D: VIsion
E: Wernicke’s Area
What causes the release of acetylcholine from the synaptic vesicles?
Influx of calcium ions
What causes ligand-gated sodium channels to open on the postsynaptic membrane?
Acetylcholine binding to its receptor on the channel
What would occur if the ACh receptors are damaged or destroyed?
All of the choices are correct
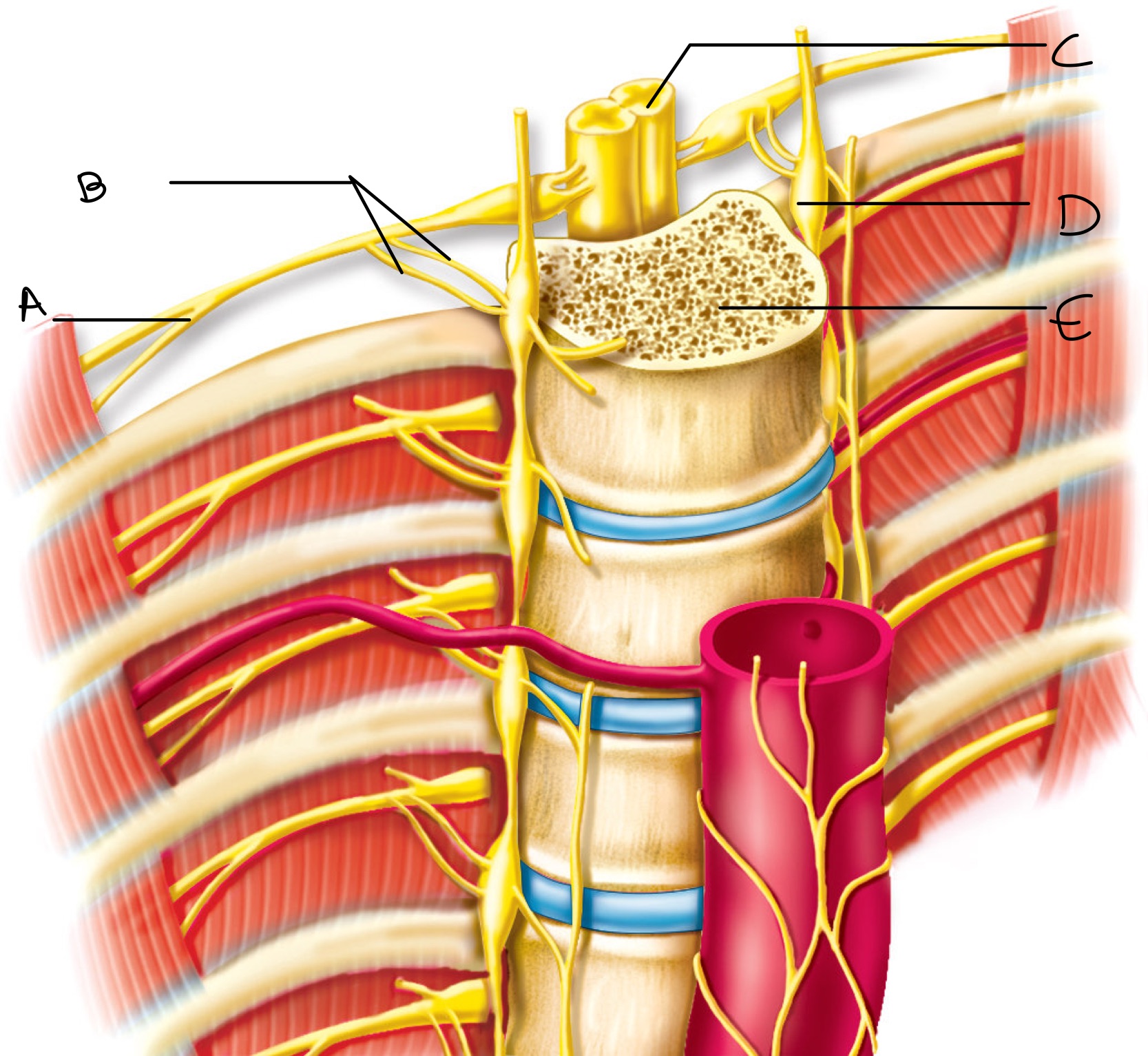
Label the appropriate location
A: spinal nerve
B: rami communicantes
C: spinal cord
D: sympathetic ganglion
E: vertebral body
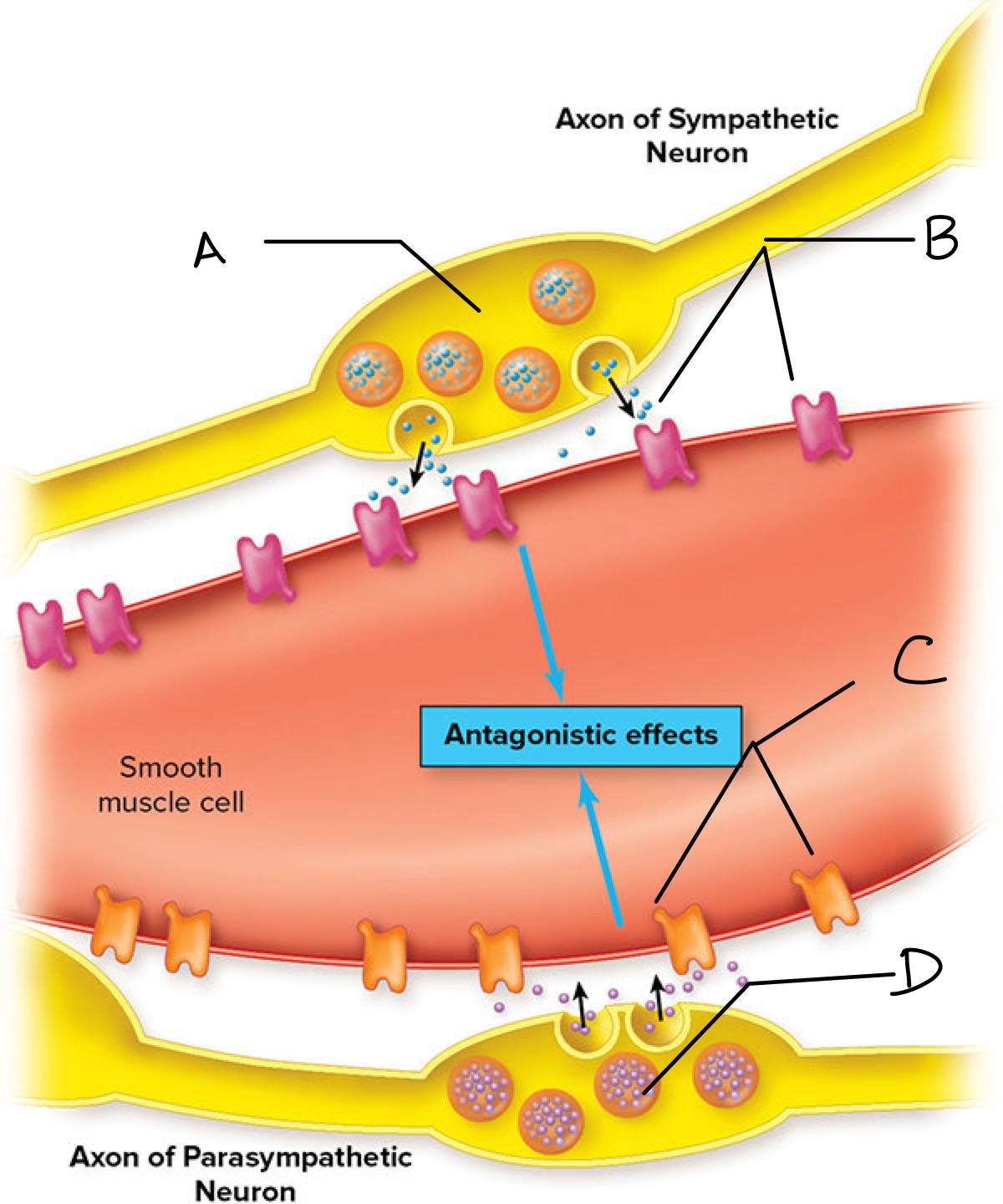
Label
A: Synaptic vesicle with NE
B: Adrenergic receptors
C: Cholinergic receptors
D: synaptic vesicle with ACh
Which effect (PS or S) is contraction of urinary bladder?
parasympathetic
Which effect (PS or S) is constriction of pupil
parasympathetic
Which effect (PS or S) is increased motility in gastrointestinal tract?
parasympathetic
Which effect (PS or S) is increased HR
sympathetic
Which effect (PS or S) is dilation of bronchioles
sympathetic
Which effect (PS or S) is ejaculation of the penis?
sympathetic
Which effect (PS or S) is stimulation of fat hydrolysis?
sympathetic
Which effect (PS or S) is increase in strength of heart muscle contraction?
sympathetic
The effects of ACh on an organ depend on the nature of the ____
receptor.
cholinergic
There are ___types of cholinergic receptors
two
Somatic motor neurons stimulate ____ receptors.
nicotinic
Visceral organs contain muscarinic receptors which produce a _____ effect.
parasympathetic
Nicotinic receptors are always ____.
excitatory
All ____ motor neurons are cholinergic.
somatic
What was necessary in order to have acetylcholine release into the synaptic cleft?
An action potential in the presynpatic membrane
What would occur if the ACh receptors are increased in number across the postsynaptic membrane?
Enhanced sensitivity of the postsynaptic membrane
What hypothetical drug would decrease the likelihood of reaching threshold if all other factors were to be held constant?
Drug A: An ACh inhibitor
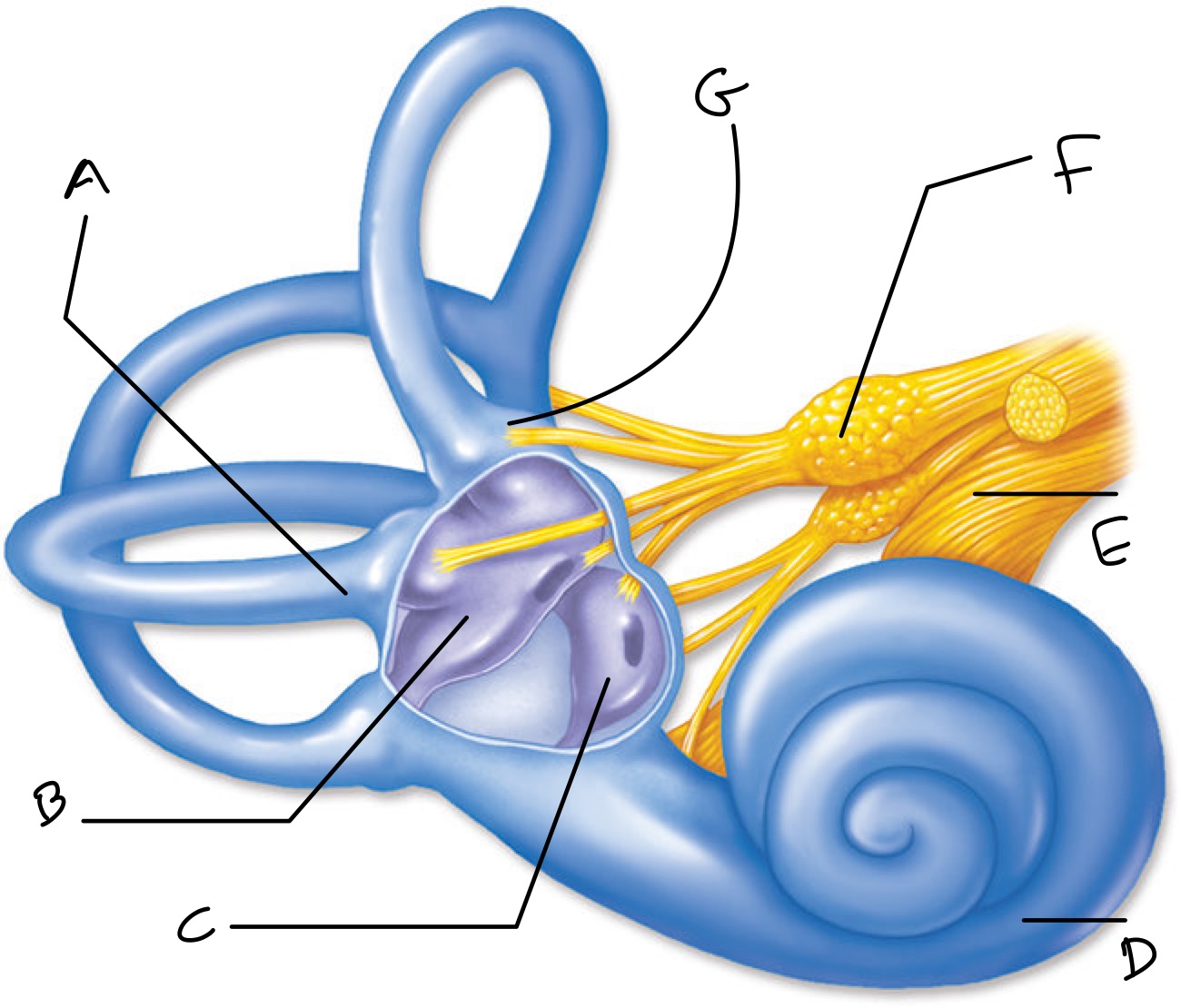
Label
A: Lateral Canal
B: utricle
C: saccule
D: cochlea
E: auditory nerve
F: Vestibular nerve
G: ampulla
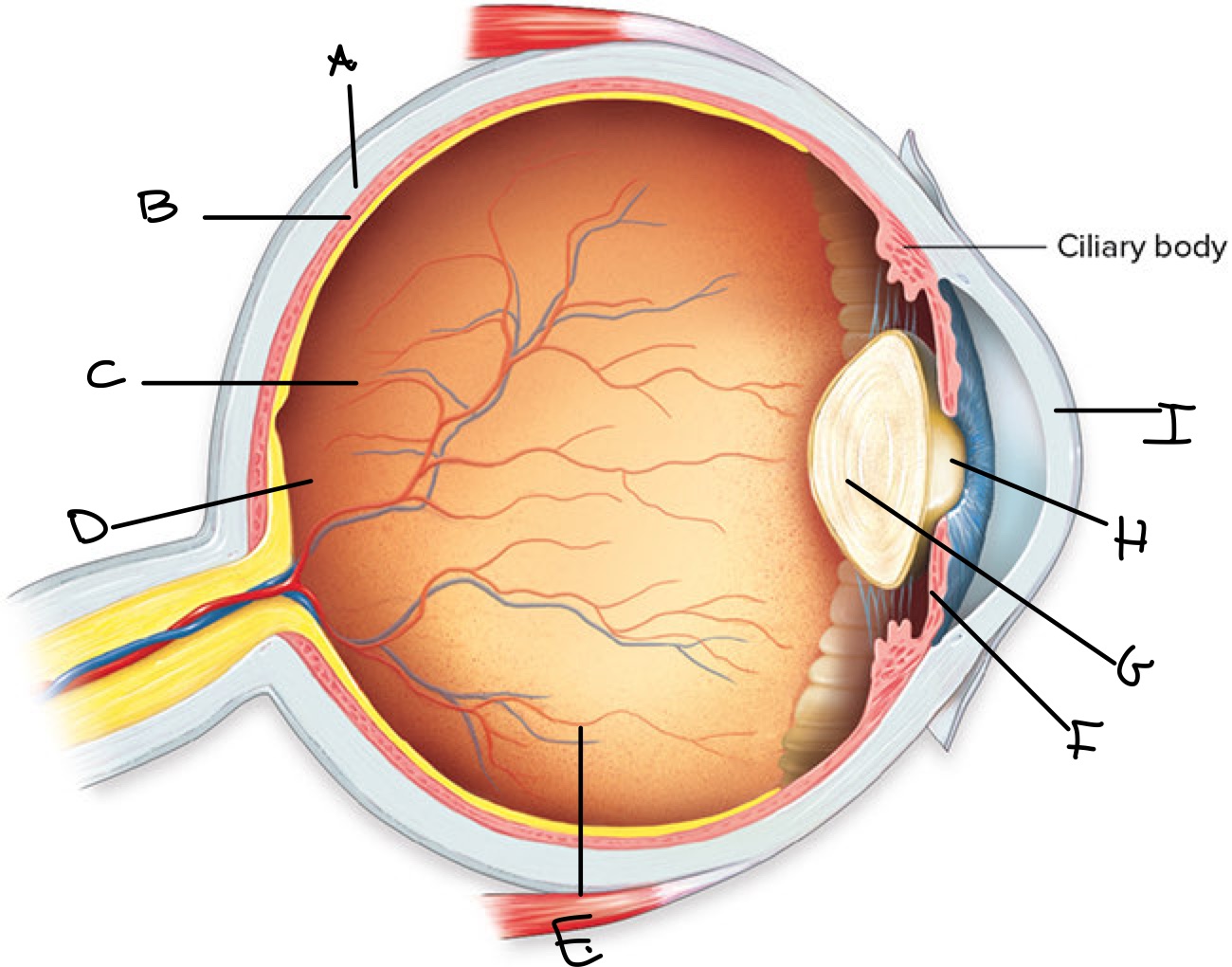
Label
A: Sclera
B: Choroid
C: Retina
D: Fovea Centralis
E: Vitreous Chamber
F: Iris
G: Lens
H: Pupil
I: Cornea
T/F: The greater the receptor density, the greater the sensory acuity
True
T/F: High-pitched sounds produce a peak displacement of the basilar membrane near the apex of the cochlea.
False
T/F: The farther an object is from the eye, the rounder the lens will be.
False
T/F: Light causes Na+ channels in rods to close, causing hyperpolarization, and the release of inhibitory neurotransmitter to bipolar cells
False