Mammology Exam 3
1/104
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
105 Terms
__________ characteristics:
secretes milk onto brood patch
altricial young
lays eggs (kept in pouch (echidna) or in burrow (platypus)
Monotreme
__________ characteristics:
altricial young
young are kept in “marsupium” (pouch)
Marsupial
__________ characteristics:
produce young on gradient from altricial to precocial
long gestation period relative to lactation period
Placental
Which is more energetically expensive: lactation or gestation?
Lactation
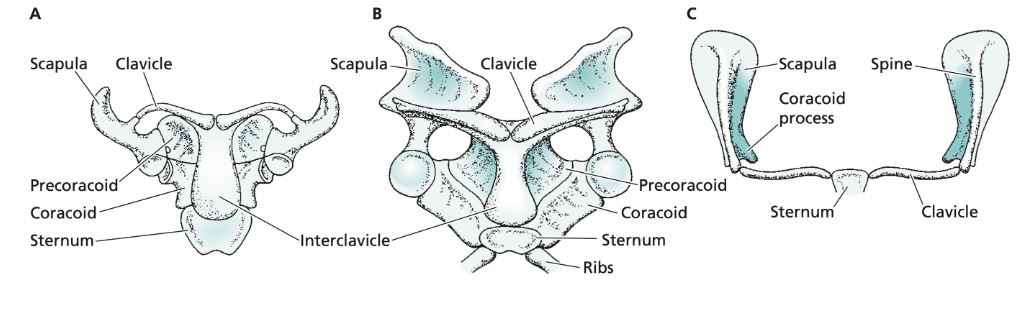
A
Early Synapsid
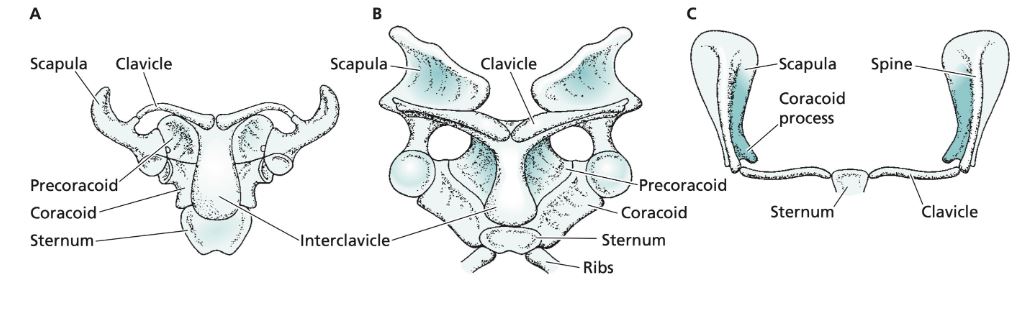
B
Monotreme
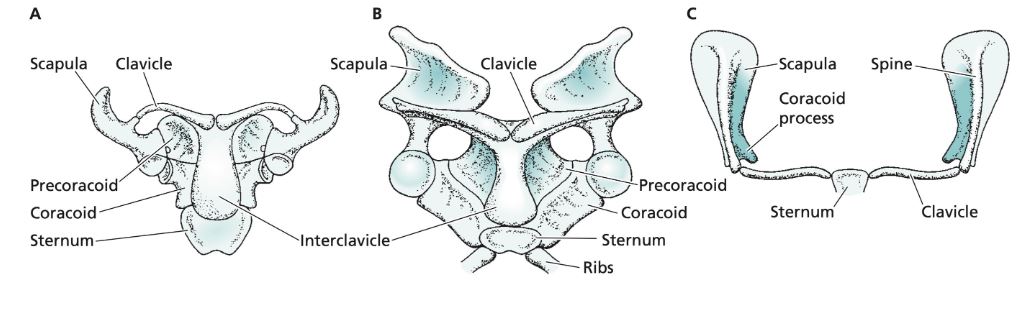
C
Marsupials and Placentals
__________ characteristics:
males have venomous spur
semi aquatic, semi fossorial
insectivores
electroreception in bill
Ornithorhynchidae
Platypus belong to family __________
Ornithorhynchidae
__________ characteristics:
insectivorous (myrmecophagus)
quills
electroreception in bill
Tachyglossidae
Echidnas belong to family _________
Tachyglossidae
Platypus and Echidna are __________
Monotremes
Marsupials make up __% of mammals
6
The only marsupial in N. America: ____________
Virginia Opossum
__________ characteristics:
found in N. America
opposable pollex (thumb)
incrassated tail
marsupial
Didelphidae

These are all ________
Marsupials
____________ ___________ is when two unrelated species evolve similar characteristics to occupy a similar niche
Convergent Evolution
The “superorder” ___________ means “Beasts of Africa”
Afrotheria
Afrotheria contains clades ____________ and ____________
Afroinsectiphilia Paenungulata
Clade ________________ of Afrotheria contains Orders Tubulindentata, Macroscelidea, and Afrosoricida
Afroinsectiphilia
Family _______________ characteristics:
proboscis
Easter, Central, Southern Africa
large hind limbs
large ears
mostly insectivorous
morphologically convergent with rodents
ecologically convergent with shrews
socially monogamous
maintain intricate trail network
Sengis and Elephant Shrews
Macroscelididae
Tenerecidae, Potamogalidae, and Chrysochloridae are all members of Order ______________
Afrosoricida
Family _______________ characteristics:
Restricted to Madagascar
31 species, 8 genera
Highly diverse
adaptive radiation
Tenrecidae
Family _______________ characteristics:
Restricted to Congo Basin
semi aquatic
endangered
eats aquatic insects
poorly studied
otter shrews
Potamogalidae
Family _______________ characteristics:
blind
fossorial
insectivorous
soft soil specialists
daily/seasonal torpor
convergent with moles
Chrysochloridae
Aardvarks are the monotypic member of Order ________________
Tubulindentata
Family _______________ characteristics:
Aardvarks
distributed south of Sahara
insectivorous (myrmecophagus)
long sticky tongue
peg-like teeth
strong diggers
claws are nail/hoof-like
Orycteropodidae
Clade _____________ of Afrotheria contains Orders Sirenia, Hyracoidea, and Proboscidea
Paenungulata
Characteristics of Clade ____________________:
herbivorous
hindgut fermenters
lateral molar progression (mesial drift)
Only Proboscidea and Sirenia
two mammae
short nails (no claws)
Paenungulata
Order ___________ of clade Paenungulata characteristics:
Contains families Dugongidae (Dugong) and Trichechidae (Manatees)
marine/aquatic
only herbivorous marine mammals
restricted to shallow water
hind gut fermenters
horizontal lungs
lateral molar progression
Sirenia
Order ___________ of clade Paenungulata characteristics:
5 species
Hyraxes
Three hind toes
glandular pads for climbing
tree and rock species
colonial
upper incisors form tusks
two large cecum
Hyracoidea
Order ___________ of clade Paenungulata characteristics:
large proboscis
large ears
sparsely furred
fatty cushion on bottom of foot
lateral molar progression
elephants
Proboscidea
These characteristics are shared by all ____________
Refined hands and digits with nails instead of claws
Binocular stereoscopic vision
postorbital bar or plate
long lived, slow reproduction, extended development time relative to body size
spectrum of social systems
bunodont molars, large canines, incisors (mostly omnivorous)
reduced rostrum and sense of smell
large absolute and relative brain size
Primates
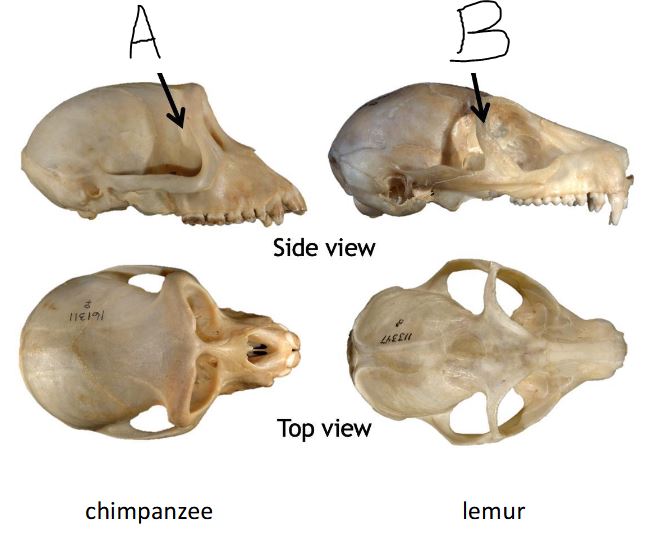
A
Post orbital plate
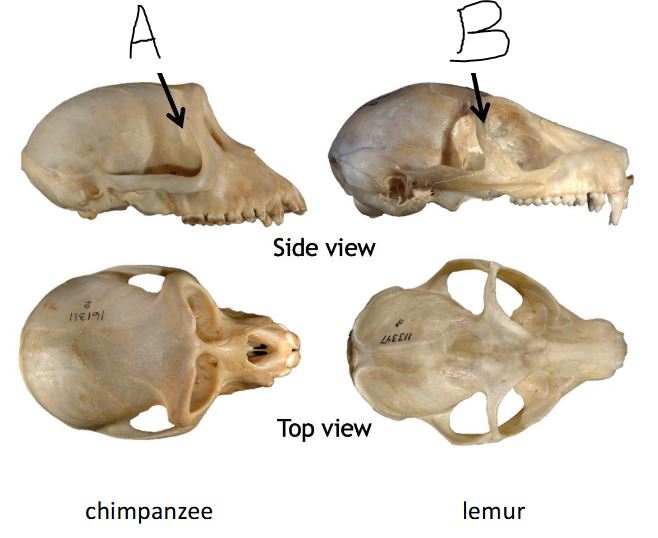
B
Post Orbital Bar
Order Primates contains 2 suborders: _______________ and ______________
Strepsirhini Haplorhini
Suborder _____________ characteristics:
post orbital plate
shorter rostrum
continuous upper incisors (no gap in middle)
Haplorhini
Suborder _____________ characteristics:
post orbital bar
longer rostrum
gap in upper incisors
Strepsirhini
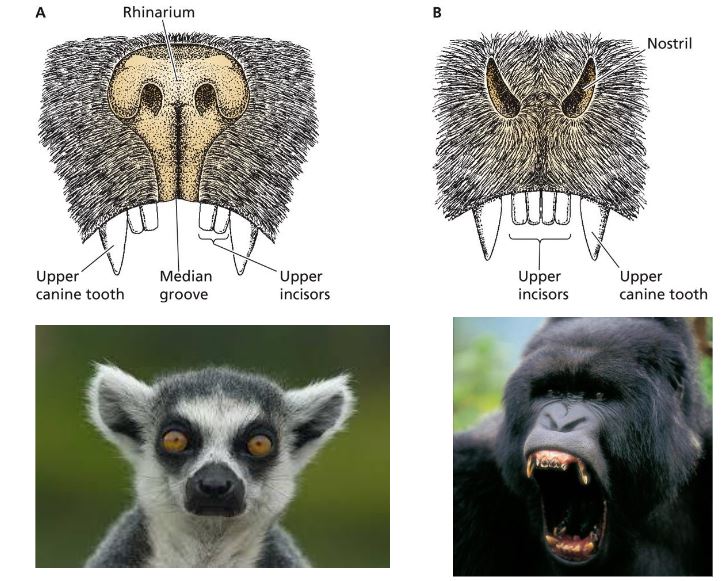
A is a species from Primate suborder _________________
Strepsirhini
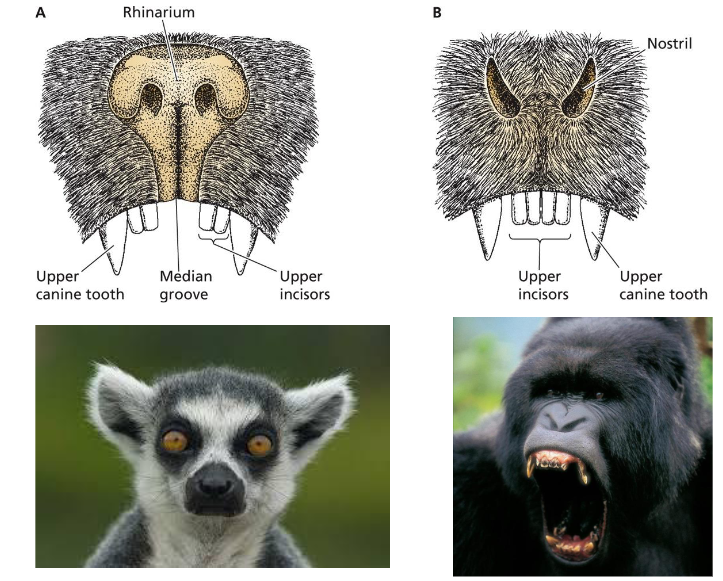
B is a species from Primate suborder _________________
Haplorhini
Tarsiers, Monkeys and Apes are part of suborder
Haplorhini
Lemurs, lorises, and aye-ayes are part of suborder
Strepsirhini
Group containing Monkeys and Apes (excludes Tarsiers)
Simiiformes
Order ____________ characteristics:
worldwide distribution except Antarctica and N.Z.
most are born altricial
single pair of upper/lower incisors
Diastema
anterior of incisors coated with enamel, creates chisel shape
largest mammalian order
Rodentia
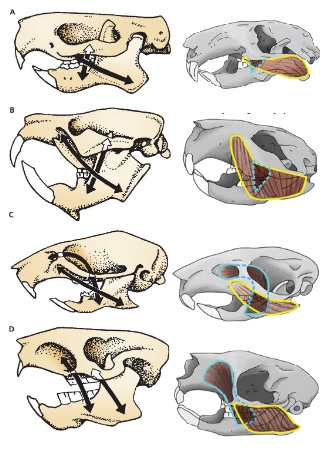
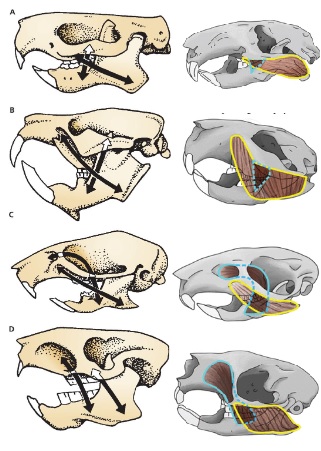
A
Protrogomorph
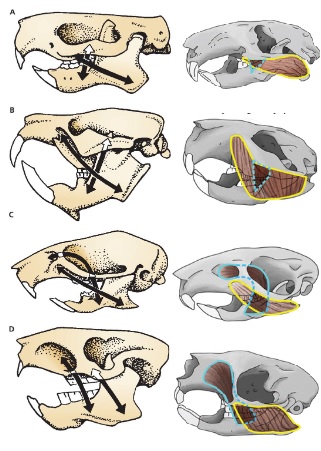
B
Sciuromorph
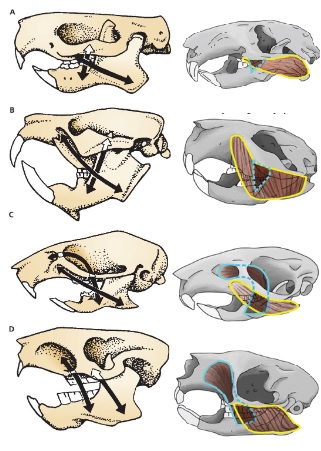
C
Myomorph
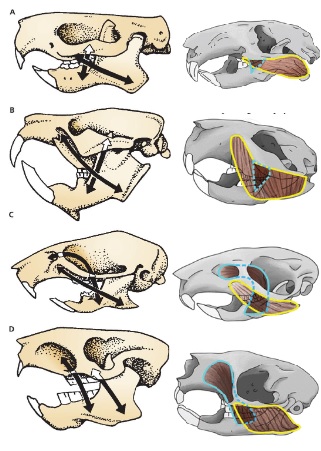
D
Hystricomorph
Species with morphology A
Mountain Beaver
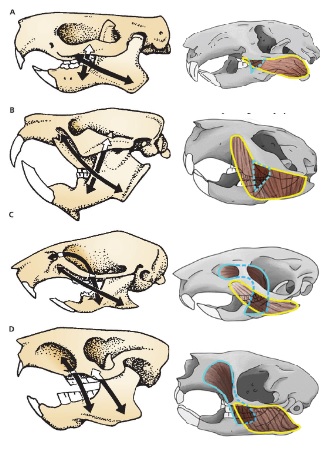
Suborders with morphology B
Sciuromorpha Castoromorpha
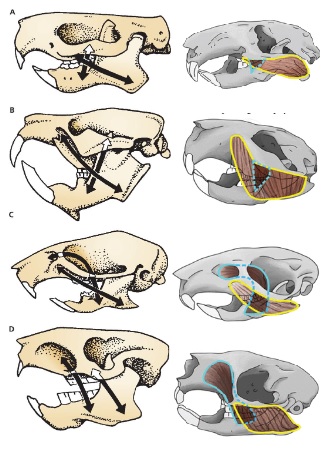
Suborder with morphology C
Myomorpha
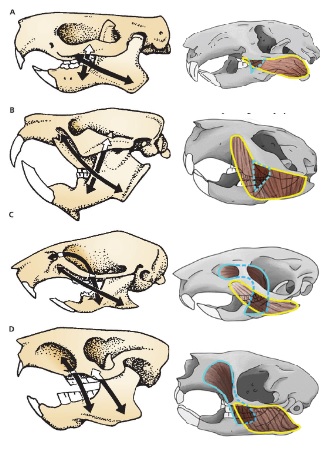
Suborders with morphology D
Hystricomorpha Anomaluromorpha
Rodentia suborder ____________ contains Beavers, gophers, kangaroo rats and kangaroo mice
Castorimorpha
Rodentia suborder ____________ contains mice, rats, gerbils, hamsters, lemmings, voles
Myomorpha
Rodentia suborder ____________ contains squirrels, chipmunks, mountain beaver
Sciuromorpha
Rodentia suborder ____________ contains “square-faced rodents” (porcupine)
Hystricomorpha
Rodentia suborder ____________ contains scaly-tailed squirrels and springhares
Anomaluromorpha
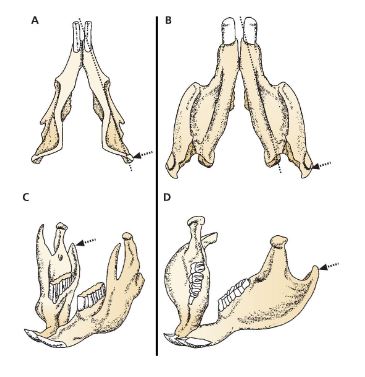
A and C mandible morphology
Sciurognathous
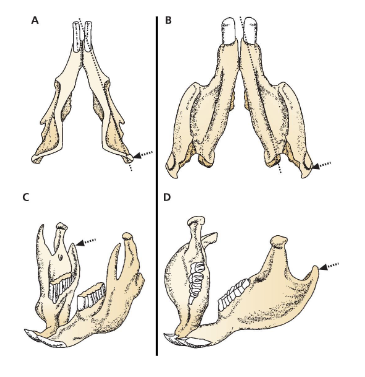
B and D mandible morphology
Hystricognathous
__% of Rodentia species are at risk
20
Order __________ characteristics":
92 species
mostly found worldwise (except Australia, N.Z, Antarctica, Philippines, Madagascar)
Herbivorous and coprophagus
hindgut fermenters
second set of incisors behind main set
Lagomorpha
Hares give birth to _______ young
precocial
Pika and rabbits give birth to _______ young
altricial
__% of Lagomorphs are at risk
24
Characteristics of Order ____________:
300 species
all diet types
highest size diversity of any order
Carnivora
The two Carnivora suborders are: ______________ and ______________
Feliforma Caniforma
Suborder _____________ contains:
Felidae (cats)
Hyaenidae (Hyenas)
Nandiniidae (Palm Civet)
Viverridae (Civet)
Prionodontidae (Linsangs)
Herpestidae (Mongooses)
Eupleridae (Madagascar Mongooses, fossa)
Feliforma
Suborder _____________ contains:
Canidae (dogs)
Ursidae (bears)
Mustelidae (weasels)
Procyonidae (raccoons)
Mephitidae (skunks)
Ailuridae (red panda)
Phocidae (earless ‘true’ seals)
Otariidae (eared seals)
Odobenidae (walrus)
Caniforma
Family _______ characteristics:
2 subfamilies (Pantherinae, Felinae)
40 species
almost global
obligate carnivores
stalking/stealth predator
Felidae
Family _______ characteristics:
•13–14 genera
• 33–37 diverse species
• distributed across tropical and subtropical habitats in Africa, Asia and Middle East
• carnivorous, omnivorous, frugivorous, scavengers.
• diurnal or nocturnal
• solitary or social
• terrestrial, semiaquatic, or arboreal
• small to medium body size
Viverridae
Family ______________ characteristics:
• 13–16 genera
• 35–36 species
• Distributed across Africa, the Middle East, and Asia
• Small, slender bodies and long tails and snouts
• Inhabit grasslands, savanna, and forested habitats
• Dietary generalists (small vertebrates, insects, vegetation, carrion)
• Solitary or social
Herpestidae
Family _______ characteristics:
• 13 genera
• 37 species
• Most widely distributed family of carnivores; occur on all continents except Antarctica
• Red fox (Vulpes vulpes) and gray wolf (Canis lupus) most widely distributed mammal
• Habitats range from hot, dry deserts, grasslands, savannas, forests, arctic ice, to urban landscapes
• Primarily carnivorous but will consume plants, fruits, insects
Canidae
Family ___________ characteristics:
• 6 genera
• 12–14
• restricted to North and South America from Canada to Argentina
• inhabit temperate and tropical forested
• typically have long, bushy tails with alternating light
and dark rings (except in the kinkajou [Potos flavus]), and black facemasks or facial marks.
• least carnivorous of the carnivores; dentition is generalized and adapted for an omnivorous diet
Procyonidae
Group containing:
− Phocidae (earless ‘true’ seals)
− Otariidae (eared seals)
− Odobenidae (walrus)
Pinnipedia
_______________ characteristics:
• Thought to have evolved from an otter-like ancestor
• Short, broad humerus and femur (arrows)
and elongated foot bones for ‘flippers’
• Diet consists of fish, octopus, penguins, and more
• Many threatened by overfishing
• Historically threatened by over hunting; fur/hide, blubber, meat
Pinnipedia
Subfamily _______________ characteristics:
• the “big cats”
• The structure of the larynx enables them to roar
Pantherinae
Subfamily __________ characteristics:
• the “small cats”
• Bony hyoid enables them to purr but not roar
Felinae
Species in subfamily ________________:
lion
tiger
jaguar
leopard (regular, clouded, snow)
Pantherinae
Species in subfamily _____________:
Bay cat
Caracal
Ocelot
Lynx
Puma
Leopard
domestic cat
Felinae
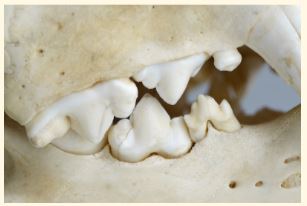
These are __________ teeth
carnasial
__________ characteristics:
• Light, streamlined body – for short, explosive bursts of speed (only about 30secs)
• Large nasal passages increased oxygen - due to the smaller size canines
• Enlarged heart and lungs allow enrichment of oxygenated blood
• Tail is a rudder-like means of steering that enables them to make sharp turns, to out- flank antelopes
• The protracted claws increase grip over the ground
• Longer limbs than what is typical for other cats of this size
Cheetah
Superorder ___________ contains Orders Perissodactyla and Cetariodactyla
Euungulata
_____________ characteristics:
• Walk on tips of their toes, which end in
keratinized hoofs
• Reduced number of toes (<5)
• Heel bone (calcaneum, shaded) articulates with the astragalus (a) rather than fibula like in other mammals
• Perissodactyls (odd-toed; 1, 3)
• Cannon bone (b) found in Equidae
• Cetartiodactyls (even-toed; 2, 4)
• Digits 2, 5 are vestigial and form “dew claws”
Ungulate
Order ___________ characteristics:
• Three extant families, ~ 17 species
• Equidae
• Rhinocerotidae
• Tapiridae
• Upper incisors
• Lophodont molars
• Long upper jaw; diastema
• Herbivorous
• Cecal (hindgut) fermentation
Perissodactyla
Family _______ characteristics:
• 7-9 species
• Originated and diversified in Great Basin of North America
• Modern distribution across Africa and Eurasia
• Most species are threatened or endangered
Equidae
Family _________ characteristics:
• 2 genera, 4 species
• Distributed across the tropics of South America and SE Asia
• Inhabit dense forest, mixed feeders
• Proboscis like rostrum
• 4 toes on front foot, 3 toes on back
• all threatened or endangered
Tapiridae
Family _________ characteristics:
• 4 genera, 5 species
• “nose horn”
• Characteristic horn(s) on rostrum, which have no bony core or keratinized sheath, simply a mass of keratinized fibers
• All species threatened or endangered
• Occupy tropical rainforests, floodplains, grasslands, and scrublands
Rhinocerotidae
Family __________ characteristics:
• “Even-toed ungulates”
• 10 extant families
• ~205 species (much more diverse than Perissodactyla)
• Horns and antlers (except Suids, Hippos)
• Mostly ruminants (except Suids)
• No upper incisors (except Suids)
• Distributed globally, except Antarctica and Australia
• Most economically important group of mammals
Cetartiodactyla
Suborder __________ characteristics:
• Largest group of ungulates, 6 families
• Cervidae (deer, moose, elk, caribou)
• Bovidae (sheep, antelope, buffalo)
• Antilocapridae (pronghorn)
• Giraffidae (giraffes)
• Tragulidae (chevrons, mouse deer)
• Moschidae (musk deer)
• All have horns or antlers
• Globally distributed
• Most economically important group
• domestication
• sustenance hunting
Ruminantia
Suborder __________ characteristics:
• Two families
• Pigs/hogs (Suidae) & peccaries (Tayassuidae)
• Most primitive group of ungulates
• Globally distributed except Antartica
• Habitat generalists
• Omnivorous
• Monogastric digestion
• Upper incisors, bunodont molars
• Tusks
• Large litter size
Suina
Suborder ____________ characteristics:
• Camels, alpacas, llamas, guanacos, vicunas
• Three-chambered stomach, “simple ruminants”
• Originated and diversified in Great Basin of North America
• Modern distribution across South American and Eurasian deserts/arid grasslands
• Soft hooves with nails (unlike other ungulates), adaptation for walking in sand, soft surfaces
Tylopoda
Suborder ______________ characteristics:
• “River horse”, aquatic
• Two genera, two species (common hippopotamus, pygmy hippotamus)
• Diverged from cetaceans around 55 mya
• Common hippo ~ 3,000 lb, second largest land mammal after elephants
• Used to be grouped with pigs because bunodont molars
• Herbivorous, feed on land
• Hydrodefecator
• Large tusk-like canines
• Used to be much more speciose
Whippomorpha
Order ______________ characteristics:
• Sister group to family Hippopotamidae
• Transitioned from land to sea during Eocene (50 mya)
• Earliest fossils from Indo-Pakistan region
• Toothed
• Semi-aquatic
• Foraged in shallow water
• Astragalus present in hind limbs
• Fusiform body type
• Dense bones allow for diving
• Blubber
• “Telescoped” skull
Cetacea
Posture similar to reptiles, larger eggs/ovaries, brood patches, and cloaca are all characteristics of:
Monotremes
Reduced pectoral girdle, smaller uteruses, forked genitalia, and pouches are characteristics of:
Marsupials
Orders Paucituberculata, Microbiotheria, Dasyuromorphia, Peramelemorphia, Notoryctemorphia are all:
Marsupials
Afroinsectiphilia and Paenungulata are both clades within:
Afrotheria
Orders Macroscelidea, Afrosoricida and Tubulindentata are part of clade:
Afroinsectiphilia
Orders: Sirenia, Hyracoidea, and Proboscidea are all part of clade:
Paenungulata
Lemurs, aye-ayes, and lorises are all part of suborder:
Strepsirhini