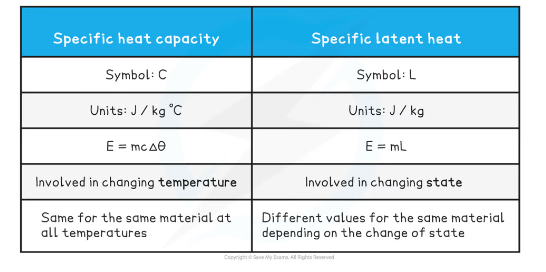
specific latent heat
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/21
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
1
New cards
What happens to the temperature of a substance whilst it changes state?
The temperature remains constant
2
New cards
what happens when boiling
When a substance changes state from a liquid to a gas, it's called boiling. During boiling, heat energy is used to break the forces holding the particles together.
3
New cards
specific latent heat
the energy required to change 1kg of a particular substance from one state to another, without a change in temperature.
4
New cards
specific latent heat of fusion
The thermal energy required to convert 1 kg of solid to liquid with no change in temperature
5
New cards
specific latent heat of vaporisation
The thermal energy required to convert 1 kg of liquid to gas with no change in temperature
6
New cards
What is the formula for specific latent heat
Energy = mass x specific latent heat
E=mL
E=mL
7
New cards
energy when melting and evaporating
is abosrbed
8
New cards
energy when freezing and condensing
released
9
New cards
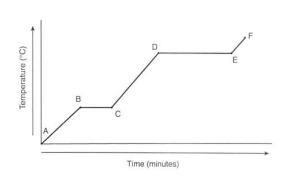
explain the trends of this graph
At A it is Solid.
- At B, reaches 0°C .
- From B to C there is no temperature change because the
energy is used through melting.
- From C to D it is in liquid state.
- From D to E the water is boiling. This takes longer,
because evaporation takes more energy
- From E to F the gas is heating.
- At B, reaches 0°C .
- From B to C there is no temperature change because the
energy is used through melting.
- From C to D it is in liquid state.
- From D to E the water is boiling. This takes longer,
because evaporation takes more energy
- From E to F the gas is heating.
10
New cards
Specific Heat Capacity
- The amount of energy required to raise the temperature of 1kg of a substance by 1°C.
11
New cards
Specific Heat Capacity equation
change in thermal energy = mass × specific heat capacity × temperature change
∆𝐸 = mc∆T
∆𝐸 = mc∆T
12
New cards
If the temperature of the system increases, the increase in temperature of this system depends on:
The mass of the substance heated
The type of material
The energy input to the system
The type of material
The energy input to the system
13
New cards
Different substances have different specific heat capacities
If a substance has a low specific heat capacity, it heats up and cools down quickly (ie. it takes less energy to change its temperature)
If a substance has a high specific heat capacity, it heats up and cools down slowly (ie. it takes more energy to change its temperature)
If a substance has a high specific heat capacity, it heats up and cools down slowly (ie. it takes more energy to change its temperature)
14
New cards
conductor
Good electrical conductors, such as copper and lead, are excellent conductors of heat due to their low specific heat capacity
On the other hand, water has a very high specific heat capacity, making it ideal for heating homes as the water remains hot in a radiator for a long time
On the other hand, water has a very high specific heat capacity, making it ideal for heating homes as the water remains hot in a radiator for a long time
15
New cards
The latent heat comes in two types depending on the change of state:
Latent heat of fusion
Latent heat of vaporisation
Latent heat of vaporisation
16
New cards
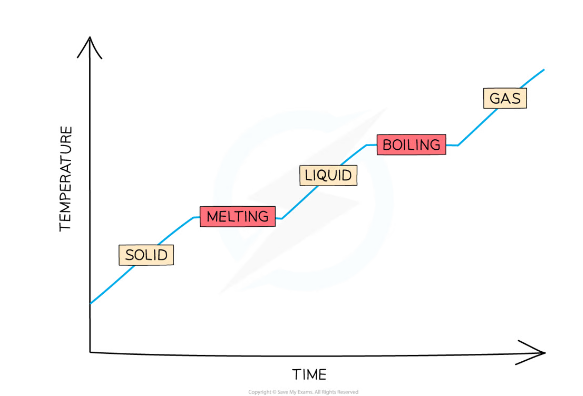
This means that only when changing state (e.g. from liquid to gas), the temperature of the substance remains constant, despite the fact that energy is still being added to the substance
This is because
This is because
the energy is being used to break the bonds between the molecules instead of increasing the kinetic energy of the molecules (and hence the temperature)The temperature remains constant when melting and boiling, despite energy being added, as shown in the graph below:
17
New cards
what happens during Latent Heat of Vaporisation
When a liquid substance is heated, at its boiling point, the substance boils and turns into vapour
The latent heat of vaporisation is the energy needed by the particles to break away from their neighbouring particles in the liquid
If the substance in its gas state is cooled, it will condense at the same temperature as its boiling point
Therefore, latent heat is transferred to the surroundings as the substance condenses into a liquid and its particles form new molecular bonds
The latent heat of vaporisation is the energy needed by the particles to break away from their neighbouring particles in the liquid
If the substance in its gas state is cooled, it will condense at the same temperature as its boiling point
Therefore, latent heat is transferred to the surroundings as the substance condenses into a liquid and its particles form new molecular bonds
18
New cards
what happens during Latent Heat of evaporation
This is used when melting a solid or freezing a liquid
When a solid substance is melted, its temperature stays constant until all of the substance has melted
The latent heat of fusion is the energy needed to break the bonds between the molecules
If the substance in its liquid state is cooled, it will solidify at the same temperature as its melting point
When this happens, the particles bond together into a rigid structure
Latent heat is transferred to the surroundings as the substance solidifies and the particles form stronger bonds
When a solid substance is melted, its temperature stays constant until all of the substance has melted
The latent heat of fusion is the energy needed to break the bonds between the molecules
If the substance in its liquid state is cooled, it will solidify at the same temperature as its melting point
When this happens, the particles bond together into a rigid structure
Latent heat is transferred to the surroundings as the substance solidifies and the particles form stronger bonds
19
New cards
heating
Heating is when the heat is added and the kinetic energy of the molecules increases (red arrows to the right)
When heat is added to a solid, the temperature starts to increase as the particles vibrate and gain kinetic energy
At a substance's melting point, the heat energy added goes into breaking the intermolecular bonds and there no more increase in kinetic energy or temperature
This is melting and the substance is now a liquid
As heat is continually added, the temperature of the liquid continues to increase as the particles gain more kinetic energy
At a substance's boiling point, the heat energy added goes into breaking the intermolecular bonds further and there is no more increase in kinetic energy or temperature
This is evaporation or vaporisation and the substance is now a gas
When heat is added to a solid, the temperature starts to increase as the particles vibrate and gain kinetic energy
At a substance's melting point, the heat energy added goes into breaking the intermolecular bonds and there no more increase in kinetic energy or temperature
This is melting and the substance is now a liquid
As heat is continually added, the temperature of the liquid continues to increase as the particles gain more kinetic energy
At a substance's boiling point, the heat energy added goes into breaking the intermolecular bonds further and there is no more increase in kinetic energy or temperature
This is evaporation or vaporisation and the substance is now a gas
20
New cards
cooling
Cooling is when heat is removed (or goes to the surroundings) and the kinetic energy of the molecules decreases (blue arrows to the left)
The process is repeated backwards for cooling as heat is taken away
A gas turns back into liquid through condensation
A liquid turns back into a solid through freezing
The process is repeated backwards for cooling as heat is taken away
A gas turns back into liquid through condensation
A liquid turns back into a solid through freezing
21
New cards
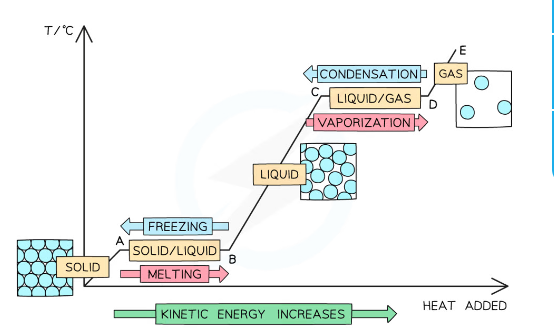
Heating/cooling curve of a substance showing the energy changes as temperature is increased/decreased
The different sections of the graph show:
ORIGIN to A: Added heat energy is being used to increase the kinetic energy of the particles while it is a solid
A to B: Added heat energy is being used to break the bonds between the solid molecules, increasing the potential energy and melting the substance
B to C: Added heat energy is being used to further increase the kinetic energy of the particles while the substance is a liquid
C to D: Added heat energy is being used to break the bonds between the liquid molecules, further increasing the potential energy and boiling the substance
D to E: Added heat energy is being used to further increase the kinetic energy of the particles while the substance is a gas
The different sections of the graph show:
ORIGIN to A: Added heat energy is being used to increase the kinetic energy of the particles while it is a solid
A to B: Added heat energy is being used to break the bonds between the solid molecules, increasing the potential energy and melting the substance
B to C: Added heat energy is being used to further increase the kinetic energy of the particles while the substance is a liquid
C to D: Added heat energy is being used to break the bonds between the liquid molecules, further increasing the potential energy and boiling the substance
D to E: Added heat energy is being used to further increase the kinetic energy of the particles while the substance is a gas
22
New cards
Specific Heat Capacity vs. Specific Latent Heat Table