Coordination and Response (2.45-2.53)
- Coordination is acheived by the endocrine system and nervous system
Nervous system
- Nervous system allows us to make sense of surrounding and respond and to coordinate and regulate body function
Nervous System consists of
- Central Nervous system (CNS): Brain and Spinal Cord
- Peripheral nervous system (PNS): Nerves/neurons and carries impulses to and from the CNS
- Nerve Impulse: Electrical signals pass along nerve cells called neurons
- Receptors detect a change (stimulus)
- Message carried from receptor to CNS through Sensory neuron
- Message sent from CNS to Effector (response organ) by motor neuron
Types of Neurons:
- Sensory Neurone: Send nerve impulses from sense organs (receptors) to CNS
- Motor neurone: From CNS to effectors
- Relay neurone: Inside CNS. Connect motor and sensory neurons
Adaptations of Neurons:
- Neurons have long fibre axon
- Less time wasted transferring impulse
- Insulated with fatty sheath with small uninsulated sections NODES
- Impulse jumps from node to next
- Dendrites allow them to connect other neurones
Reflex Arc
- Stimulus detected by receptor
- Sensory neurone sends electrical impulses to spinal cord (CNS)
- Passed on to relay in spinal cord
- Motor neurone carries to effector
- Muscle contacts (response)
Stimulus→Receptor→Sensory→Relay→Motor→Effector→Response
Synapse: Junction between 2 neurones
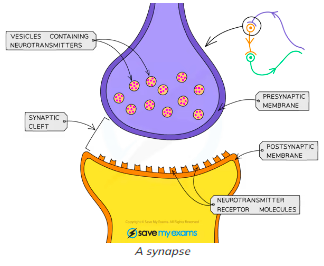
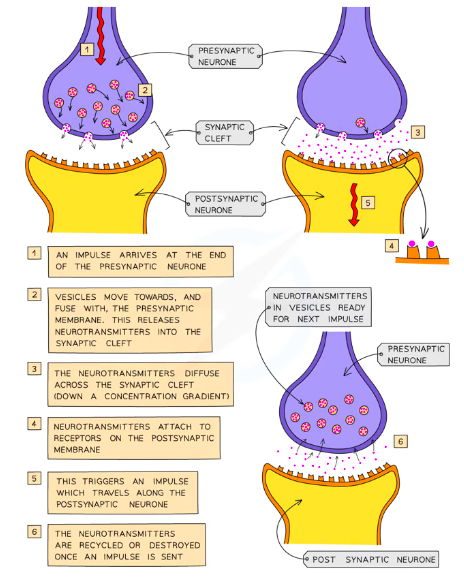
Electrical impulse travels down te first axon
Neurotransmitters diffuse across cleft
Attach to receptor molecules in postsynaptic membrane
2nd neurone generates impulse
Neurotransmitters destroyed to avoid same impulse to be sent twice
Sense organs: Group of receptor cells responding to specific stimuli
Detect a change im envronment and stimualte electrical impulses in response
- Skin- touch, temperature and pain
- Tongue- taste (chemicals in food)
- Nose- Chemicals in air/ smell
- Ear- Sound, balance and movement
- Eye- light and color
Eyes are sense organs containing receptor cells sensitive to light (rods) and color (cones)

| Structure | Function |
|---|---|
| Cornea | Refracts light - bends it as it enters the eye |
| Iris | Controls how much light enters the pupil |
| Lens | Focuses light onto the retina |
| Retina | Contains the light receptors |
| Optic nerve | Carries impulses between the eye and the brain |
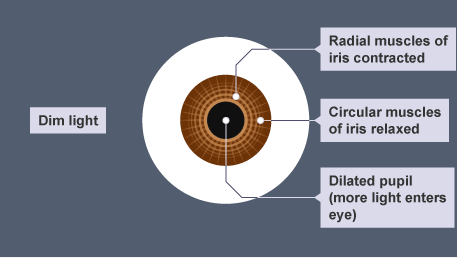
Light enters the light through the pupils
- Too much light can damage the retina and too little light makes it very difficult to see.
The pupil reflex controls the level of light that enters the eyes

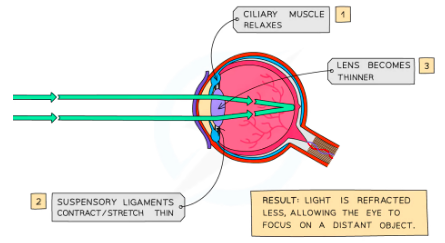
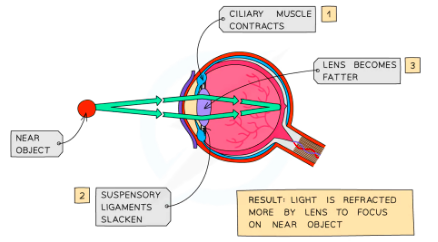
Accomodation
Close object needs to be refracted more so a stronger lense is needed
- Lense is Short and Fat
Distant object doesnt need to be strongly refracted
- Lense is short and thin
Cilirary muscles and suspensory ligament are responsible

Homeostasis and Endocrine System
- Hormone: Chemical substance produced by glands and carried by blood to alter activity of target organs
- Chemicals that transmit info. from one part of an organism to another to bring about change
- Endocrine system: Group of glands producing hormones
Endocrine Glands
Pituitary gland: ‘master gland’ FSH, LH,GH
Thyroid gland: Thyroxide
Pancrease: Insulin and Glucagon
Adrenal Gland: Adrelanine
Ovaries: Oestrogen Testes: Testosterone
Endocrine glands have a good blood supply to get hormones in the blood stream as soon as possible to reach target organ
- Hormones only affect cells with target receptors that the hormone can bind to
- These are either found on the cell membrane, or inside cells. Receptors have to be complementary to hormones for there to be an effect.

Adrelanine:
Fight or flight hormone
Produced when body is in danger
Increaseed blood glucose concentration and increased respiration
Increased pulse rate and breathing rate
Dilated pupils so more information reaches the brain
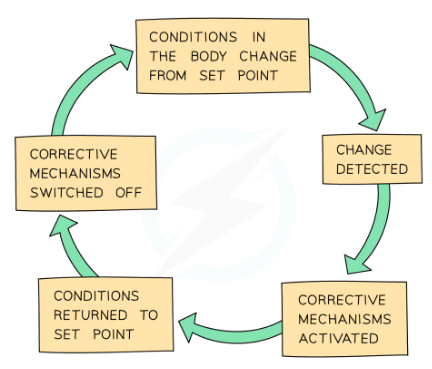
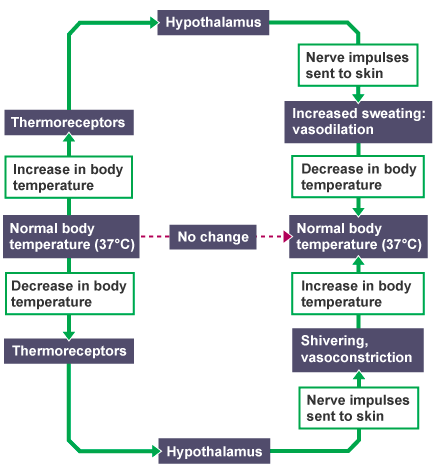
Homeostasis: Maintaining constant internal environment
Internal conditions kept within set limits
Negative feedback: If conditions deviate from normal, body will not function properly
Conditions change from ideal and return to set point
- If levels RISE they are REDUCED
- If levels FALL they are RAISED
Blood sugar levels are controlled by two hormones that are secreted by the pancreas
- Insulin – Causes liver to use blood glucose and covert it to glycogen for storage inside liver cells
- Glucagon – Causes the liver to convert glycogen to glucose and release it into the blood
Insulin causes blood sugar levels to fall and glucagon causes blood sugar levels to rise.
When glucose levels are too high, negative feedback will reduce it back down
- Pancreas secretes insulin
- Liver converts blood glucose to glycogen
- Blood sugar levels fall
When glucose levels fall too low, positive feedback will increase it back up
- Pancreas secretes insulin
- Liver converts blood glucose to glycogen
- Blood sugar levels fall

Type 1 diabetes: Caused by insufficient insulin production
Leads to a very high blood glucose level.
Symptoms:
- Increased hunger
- Frequent urination
- Blurred vision
- Tiredness & fatigue
- Unexplained weight loss
Treatment:
Controlling sugar intakes
Monitoring sugar levels
Insulin injections
If you become too hot or too cold, there are ways in which your body temperature can be controlled.
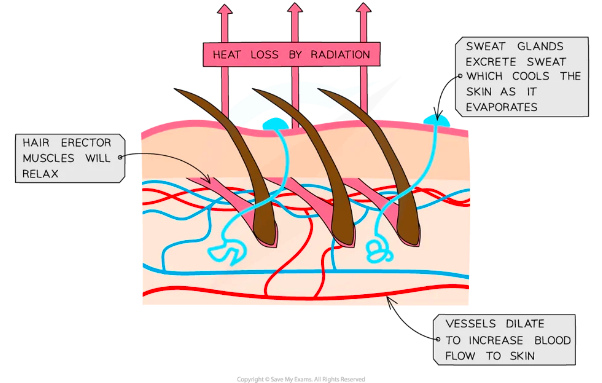
When we get too hot:
- Sweat glands in the skin release more sweat. The sweat evaporates, removing heat energy from the skin
- Hairs lay flat on skin
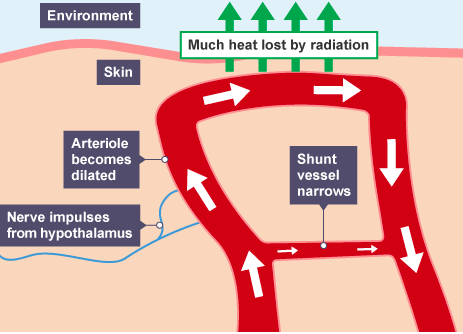
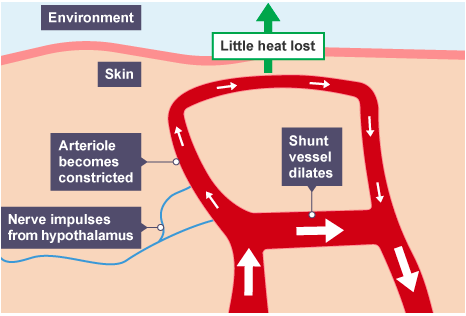
- ==Vasoconstriction==
- Heat is carried in the blood
- If blood goes near the skin surface, then heat radiates out of the body
- Constriction of the skin arterioles reduce the amount of blood flowing near the skin surface to retain heat in the blood
When we get too cold:
- Muscles contract rapidly - we shiver and release heat
- Hairs rise to trap air and provide insulation
- ==Vasodilation==
- Dilation of skin arterioles increase the amount of blood flowing near the skin surface to allow more heat to radiate out of the body

Tropic Responses
There are two main types of tropisms:
positive tropisms – the plant grows towards the stimulus
negative tropisms – the plant grows away from the stimulus
Phototropism: is a response where the stimulus is light
Geotropism: (also called gravitropism) is a response where the stimulus is gravity
%%Auxins%%%%: plant growth hormones.%%
Produced by the tips of root shoots and plants.
Auxins will always move away from sunlight and towards gravity
Geotropism:
If a shoot is placed horizontally, then auxins will accumulate on the lower side due to gravity.
The lower side of the shoot will grow quicker the top. This results in the shoot bending away from the ground.
- %%In shoots, the auxins promote cell growth%%
In the absence of light, if a root is placed horizontally, then auxins will accumulate on the lower side due to gravity.
This uneven cell growth causes the root to bend towards the ground.
- %%In roots, the auxins inhibit cell growth.%%

Phototropism:
When light is exposed to one side of a shoot, auxins move away and accumulate on the shaded side
The shaded side grows quicker than the exposed side
%%This results in the shoot bending towards the light%%

When light is exposed to one side of a root, again, accumulate on the shaded side.
The shaded side grows slower than the exposed side.
%%This results in the root bending away from the sun%%
\n