week 1 lecture 2 neuron
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
76 Terms
neuron (nerve cell)
excitable cell in the nervous system that processes and transmits information by electrochemical signaling
axon
sends messages to other neurons by making connections
synapses
junction between 2 nerve cells
how do neurons talk to each other
releasing chemicals called neurotransmitters at the synapse
about how many neurons are in the brain
86 billion
how many connections could the brain neurons have
over 10000
camillo golgi
developed staining pattern called golgi stain
golgi stain
took tissues, placed in potassium dichromate then did the same with silver nitrate to get staining to various tissues. stains only a few cells at a time making them visible under the microscope
reticular theory
nervous system is a single network (turned out to be wrong)
santiago ramon y cajal
used golgi stain with parts of brain, drawing all the different types of cells noticing similar structural components, proposed the neuron doctrine
neuron doctrine
nervous system is made up of discrete individual cells, which shifted framework from thinking about the nervous system as a continuous network to a cellular circuit-based network
sensory neuron
neuron that detects changes in the external or internal environment and sends information about these changes to the central nervous system
motor neuron
neuron located within the central nervous system that controls the contraction of a muscle or the secretion of a gland
interneuron
neuron located entirely within the central nervous system
membrane function
encloses the cell in a double layer of lipid
cytoplasm function
fluid inside the cell
nucleus function
cell center that contains DNA
mitochondria function
supplies energy from nutrients
ribosomes function
protein synthesis
lysosomes function
recycling center
smooth ER function
produces lipids
rough ER function
has ribosomes for making proteins
golgi apparatus function
packaging and storage
microtubules function
protein filaments for transporting substances within the cell
why do neurons care about mitochondria more than other cells
high energy demand for ion gradients and neurotransmitter release
why do neurons care about cytoskeleton more than other cells
axonal transport over long distances
why do neurons care about rough ER more than other cells
neurotransmitter receptor synthesis
neuroglia
nerve glue, supporting cells of the central nervous system
functional types of neurons
sensory, motor, inter
types of glial cells
schwann cell, oligodendrocyte, astrocyte, microglia
schwann cell
cell in peripheral nervous system that is wrapped around myelinated axon, providing one segment of its myelin sheath
oligodendrocyte
forms myelin sheaths
most abundant cell of human brain, contributes to the blood-brain barrier
astrocyte
microglia
specialized immune cells of the brain and spinal cord acting as the central nervous system’s resident immune cells to monitor the brain’s environment, defend against pathogens, clear cellular debris through phagocytosis, support neural development, prune unnecessary neuronal connections
Oligodendrocytes vs. Schwann Cell
One oligodendrocytes can myelinate many axons; one Schwann cell myelinates one axon segment
blood-brain barrier
semi-permeable barrier between the blood and the brain produced by the cells in the walls of the brain’s capillaries
how is blood-brain barrier formed
endothelial tight junctions
how is blood-brain barrier regulated
astrocytic end-feet
blood-brain barrier function
protect the brain, tightly regulates what substances can pass from the blood to the brain
what can pass through the blood-brain barrier
glucose, fat-soluble molecules, oxygen, carbon dioxide, anesthetics, alcohol, viruses, amino acids
what can’t pass through the blood-brain barrier
most large hydrophobic molecules, proteins, ions, bacteria, antibiotics
epilepsy
blood-brain barrier breaks down which trigger chronic or acute seizures
multiple sclerosis
an autoimmune and neurodegenerative disorder in which the immune system attacks the myelin. blood-brain barrier breaks down allowing T-lymphocytes to cross and attack the myelin
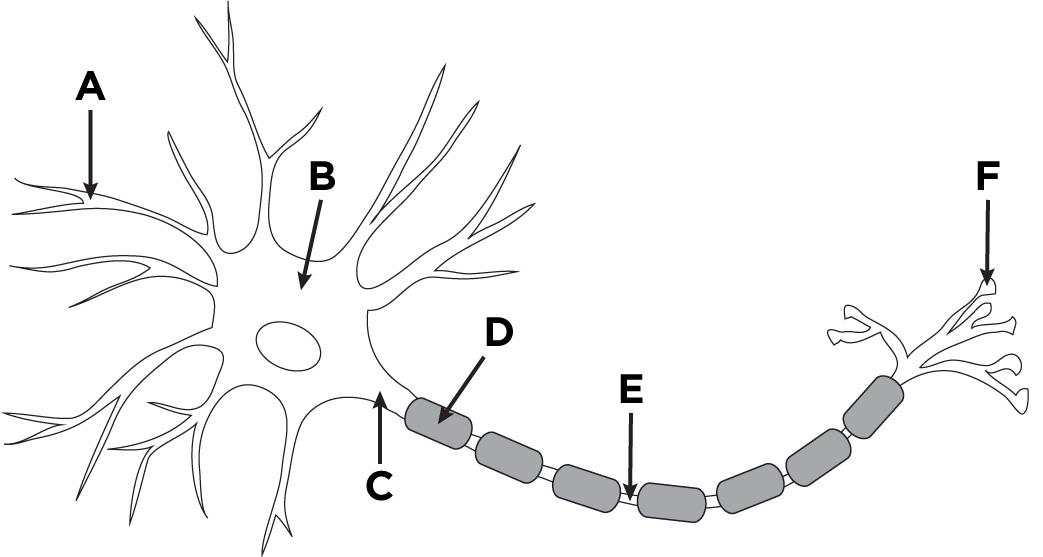
A
dendrites
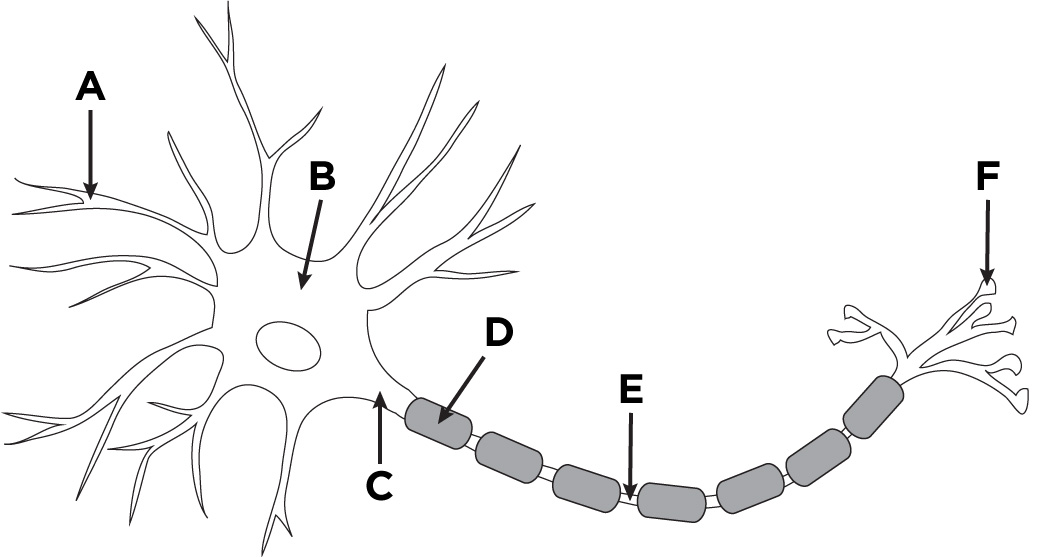
B
nucleus
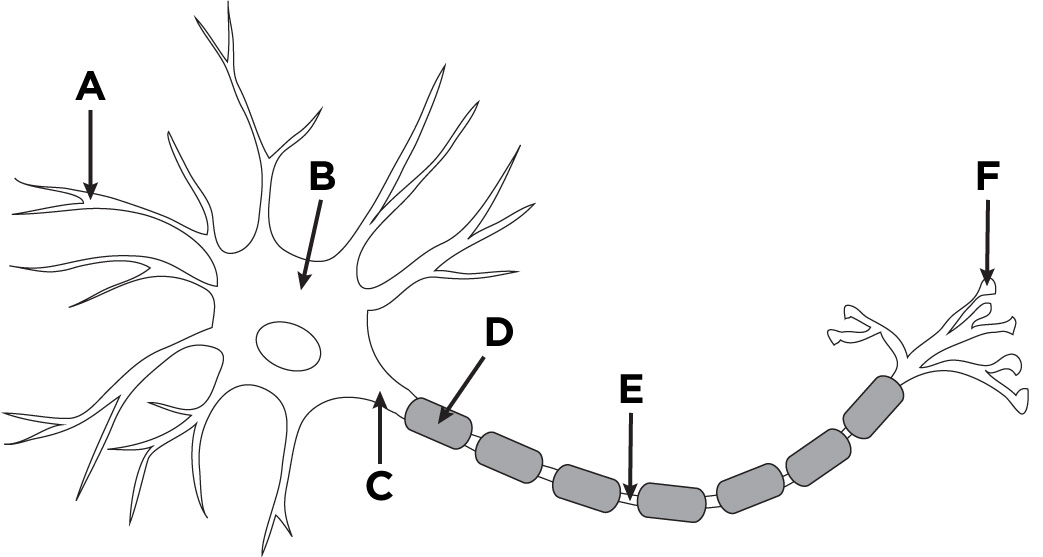
C
cell body (soma)
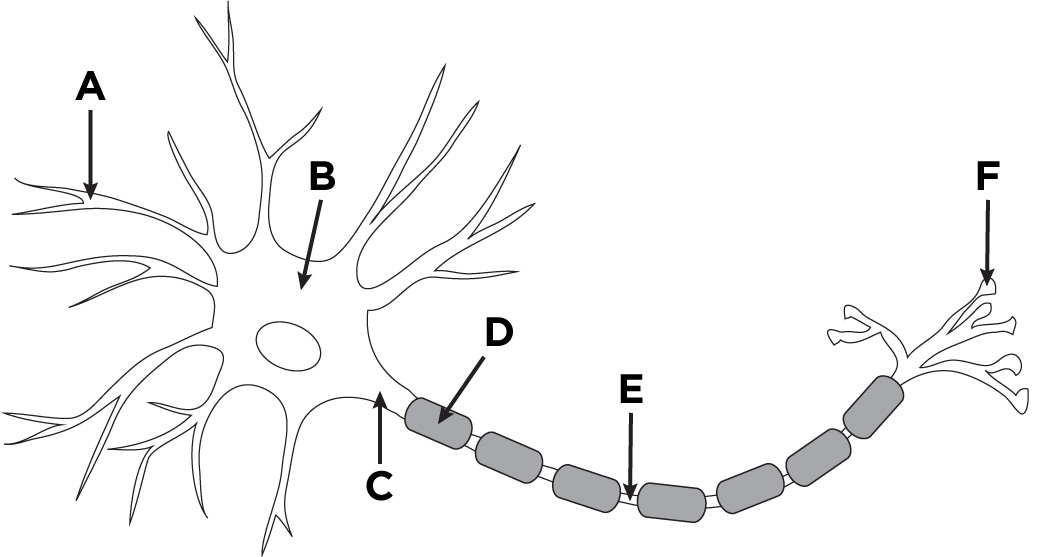
D
glial cell
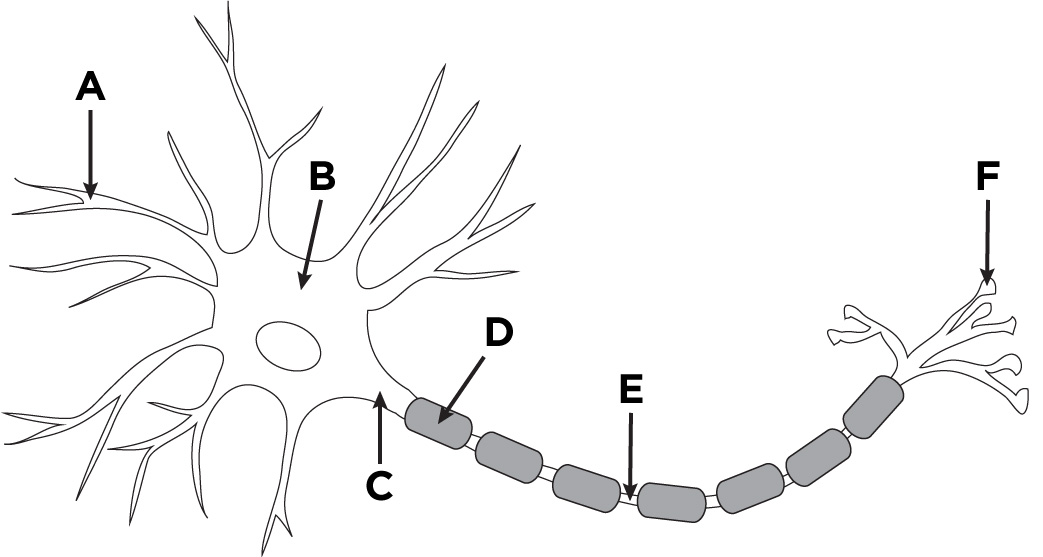
E
axon
F
axon terminal
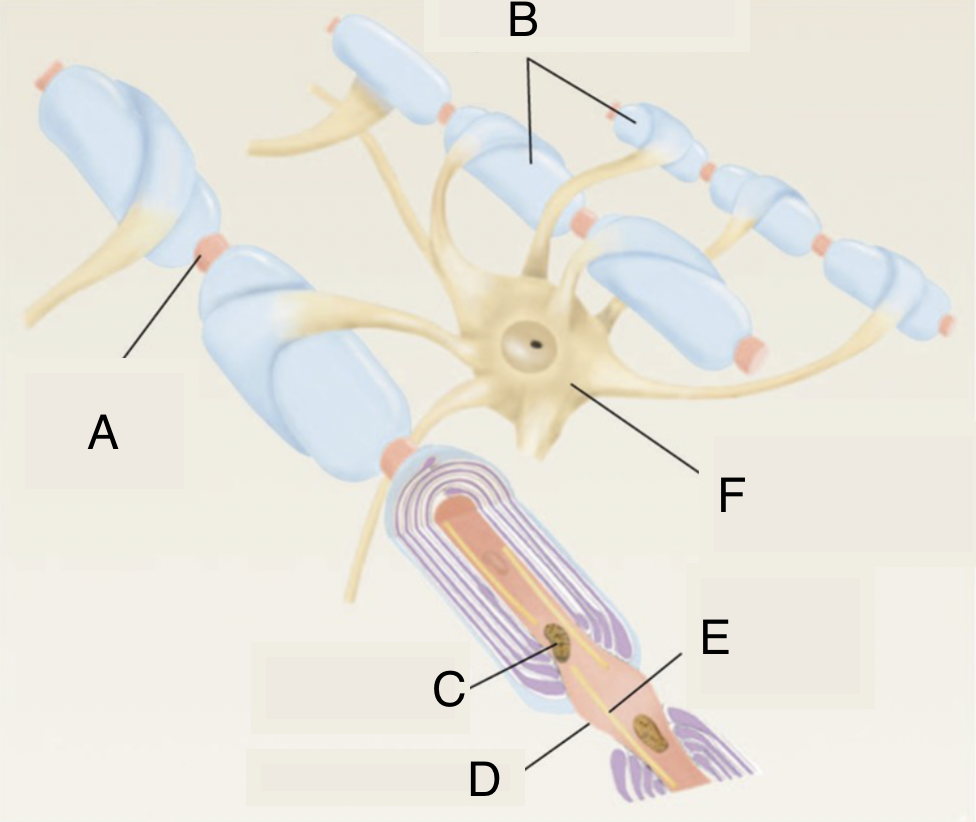
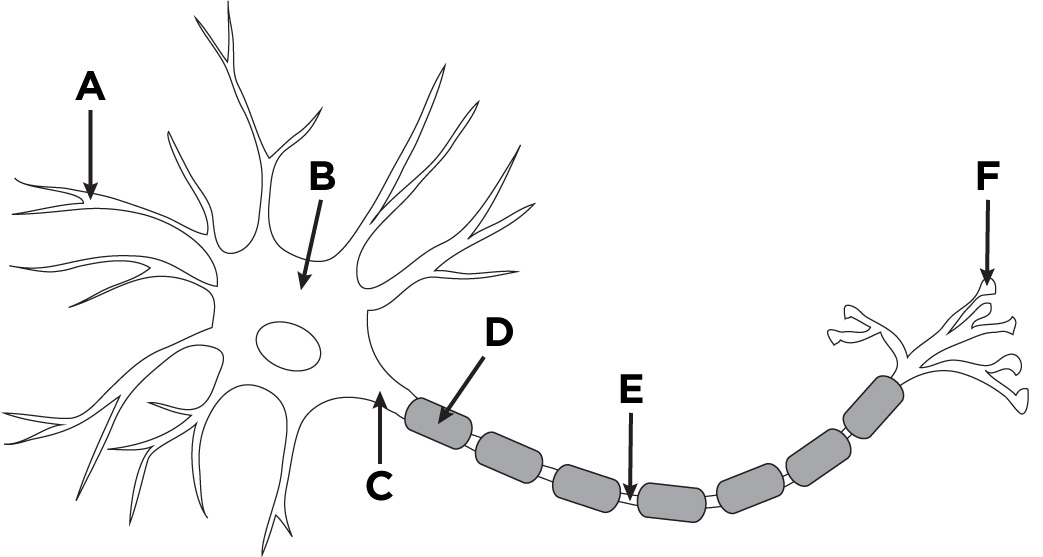
A
node of ranvier
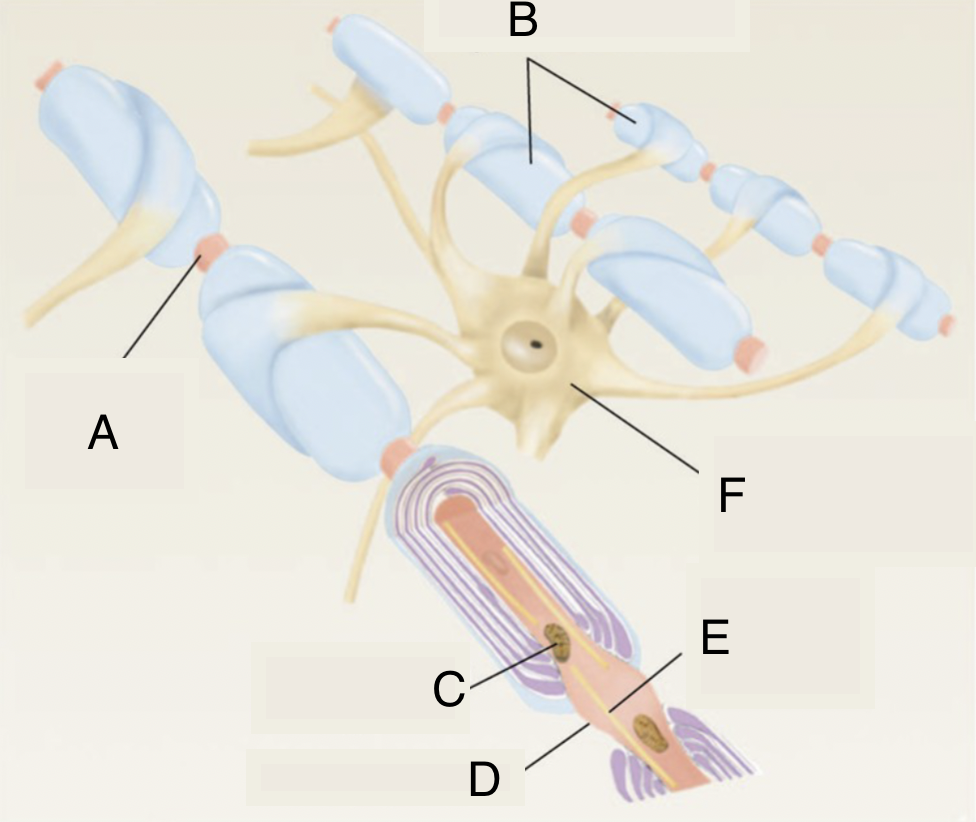
B
myelinated axons
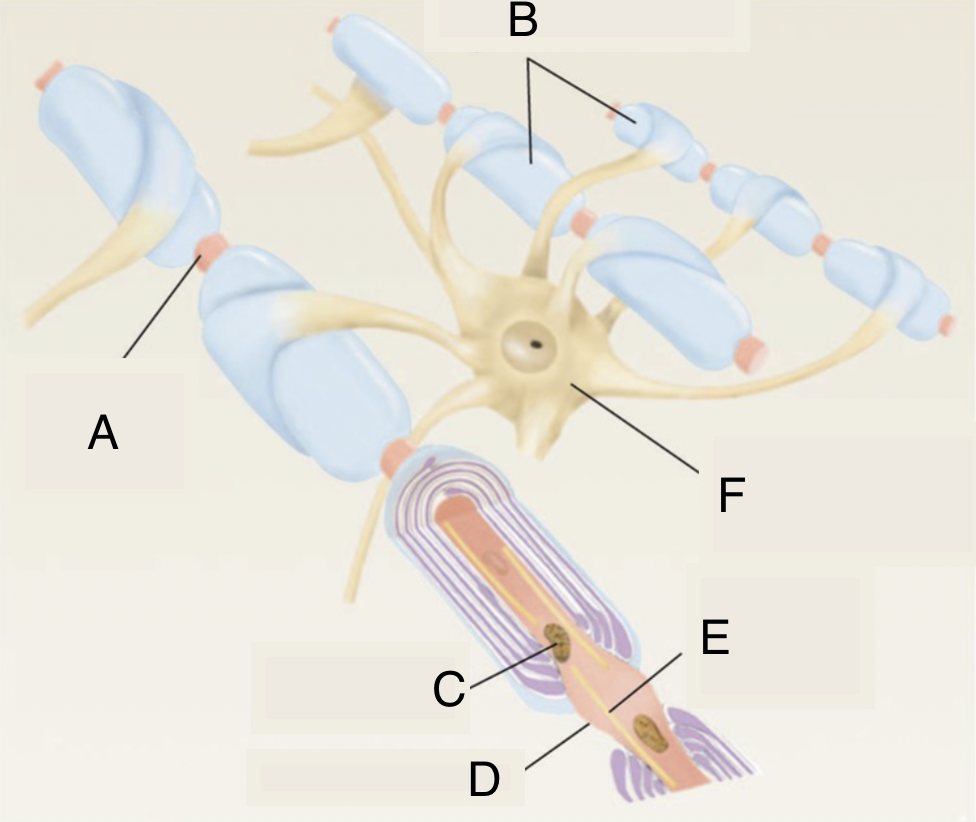
C
mitochondrion in axoplasm
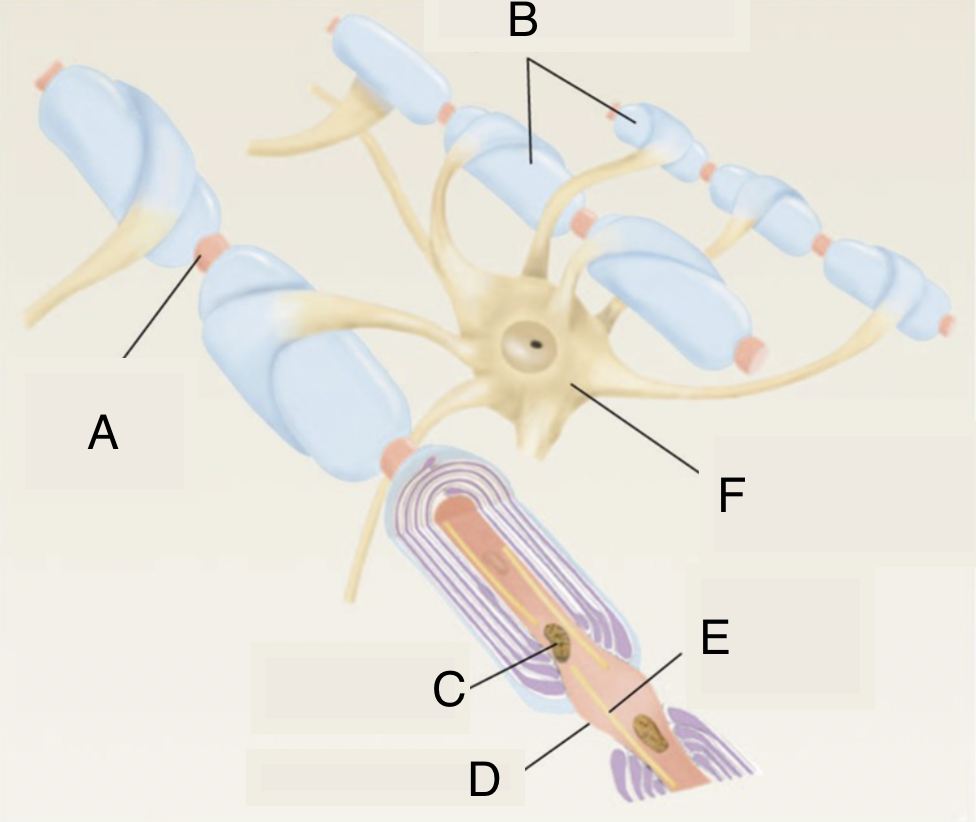
D
node of ranvier
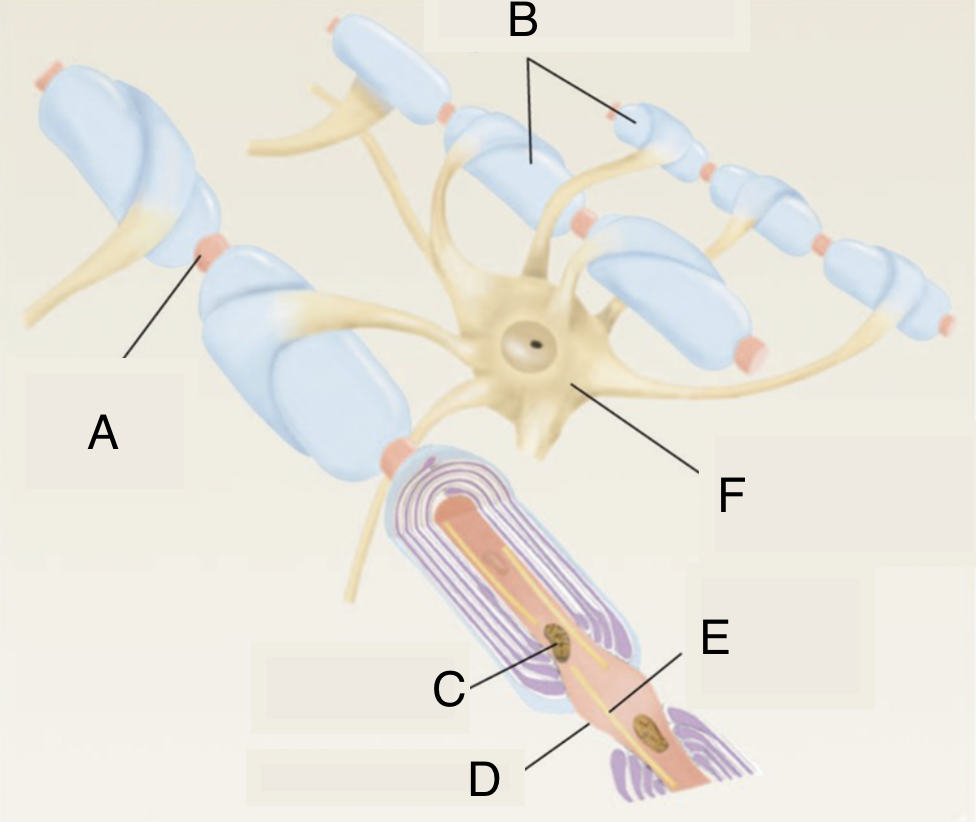
E
microtubule
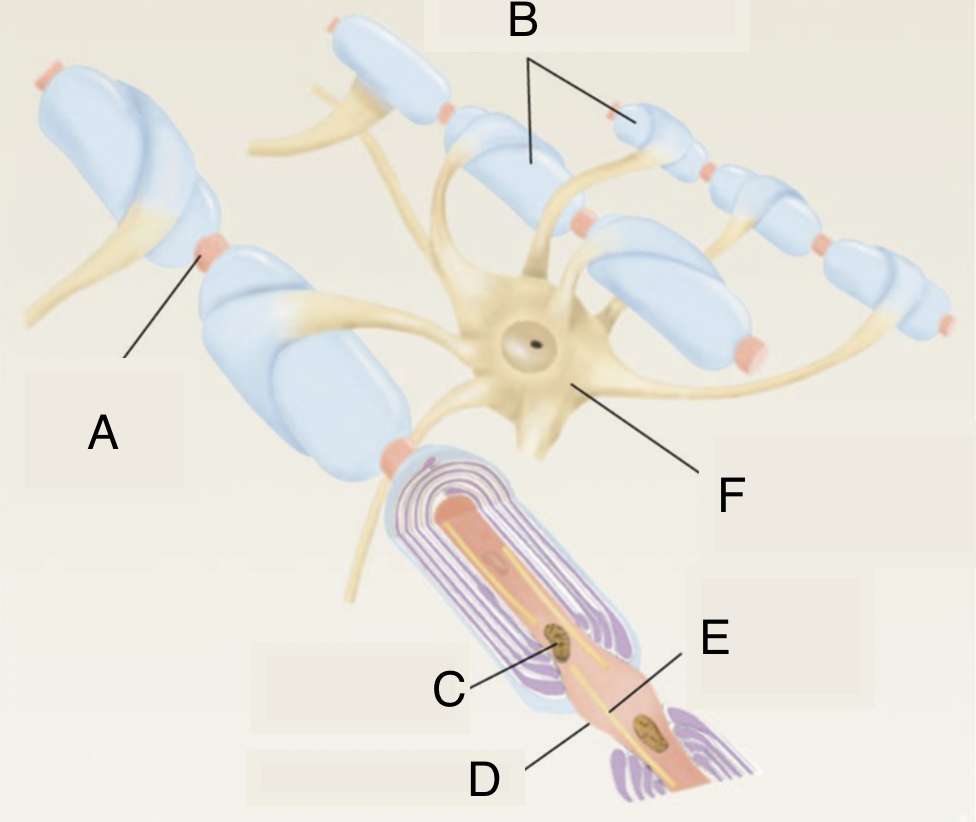
F
soma of oligodendrocyte
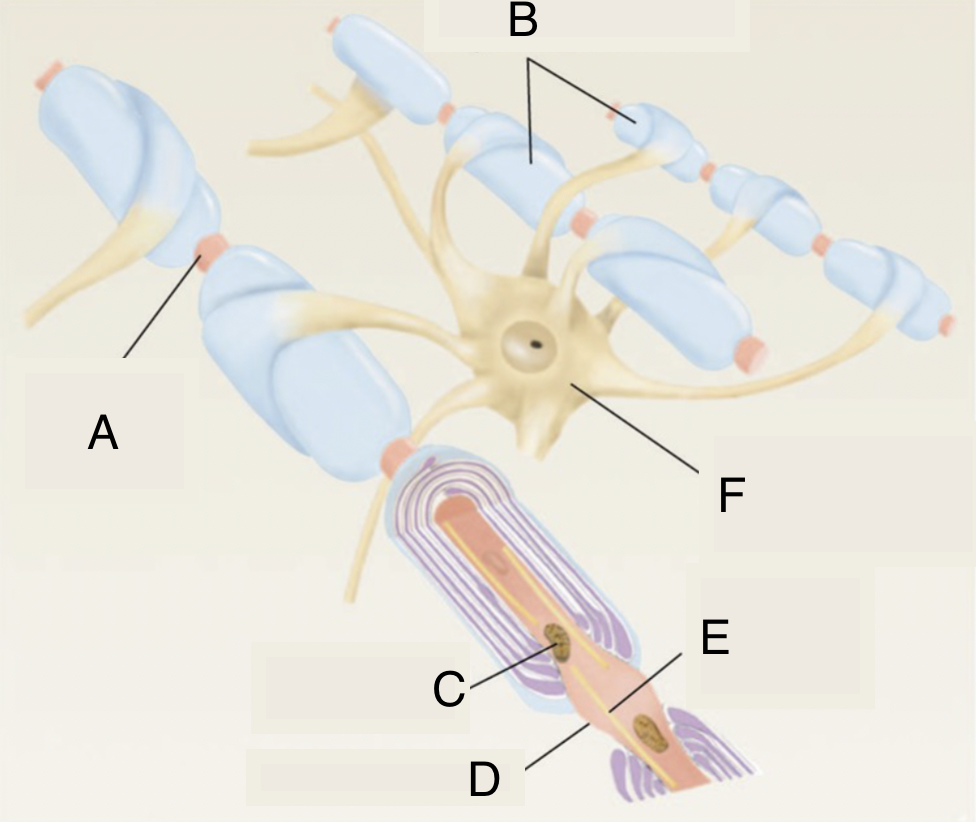
what is this structure
oligodendrocytes (central nervous system)
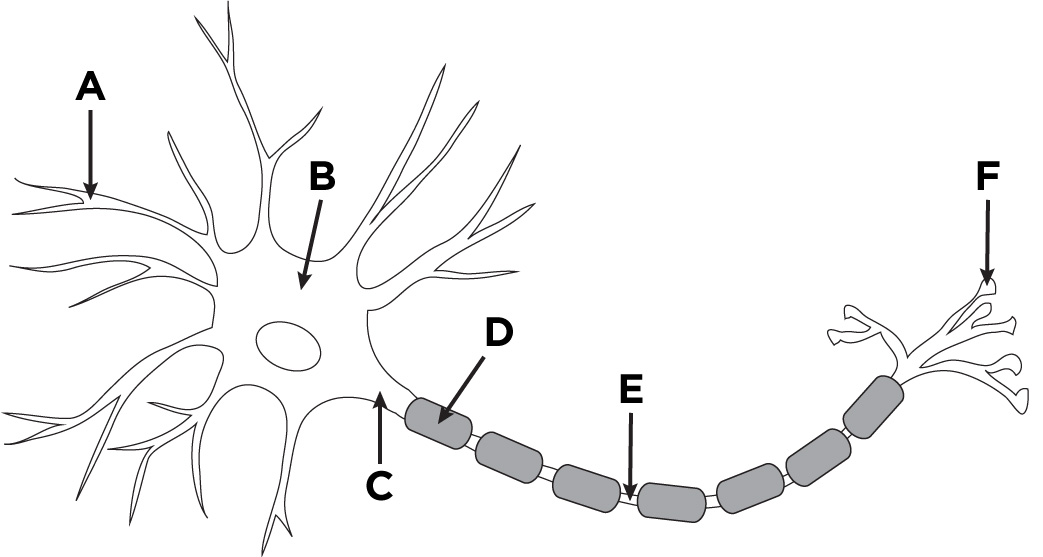
what is this structure
neuron
what are the major intracellular organelles relevant to neurons
nucleus, mitochondria, ribosomes, lysosomes, ER, golgi apparatus
soma
central region of the neuron containing the nucleus
dendrites
neurite specialized to receive synaptic inputs from other neurons
dendritic spine
small sac of membrane that protrudes from the dendrites of some cells and receives synaptic input
axon hillock
swelling of the axon where it joins the soma
terminal bouton
axon terminal, end region of an axon usually a site of synaptic contact with another cell
synapse
region of contact where a neuron transfers information to another cell
neurotransmitter
chemical released by a presynaptic element upon stimulation that activates postsynaptic receptors
presynaptic neuron
nerve cell that sends a signal to the postsynaptic neuron across a synapse
postsynaptic neuron
nerve cell that receives signals from the presynaptic neuron at a synapse
myelin
membranous wrapping or sheath around axons provided by oligodendroglia in the central nervous system and Schwann cells in the peripheral nervous system
node of Ranvier
space between two consecutive myelin sheaths where an axon comes in contact with the extracellular fluid
extracellular fluid
all the fluid in the body outside of cells
extracellular fluid function
crucial internal environment for cells, deliver nutrients, remove waste, transport substances like oxygen, hormones, and electrolytes
intracellular fluid
water and dissolved substances found inside every body cell
ion channel
membrane-spanning protein that forms a pore that allows the passage of ions from one side of the membrane to the other
concentration gradient
difference in concentration from one region to another. Ionic concentration gradients across the neuronal membrane help determine the membrane potential
electrical gradient
separation of positive and negative charges across the cell membrane
resting membrane potential
membrane potential or membrane voltage maintained by a cell when it is not generating action potentials; also called resting potential. Neurons have a resting membrane potential of about -65 mV