Chapter 5 - Neo Freudian Psychoanalytic Approach
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
Theorists rejected the idea that personality is formed
by experiences in the initial years of life
Freud failed to recognize
the importance of social and cultural forces in shaping individual personality
Alfred Adler
Developed the approach of individual psychology
Contributions to understanding of personality
Birth Order!
Pampering
Robs the child of independence and adds to feelings of inferiority
Neglect
Children who receive little attention from their parents:
Firstborn children
Subjected to excessive attention from parents
Arrival of second child ends the pampering
Strong perception of inferiority
Among firstborn we often find problem children, neurotics, criminals, drunkards, and perverts
Middle-born children
Develop a strong superiority striving
Highest achievers
Try hard to catch up with their older siblings
Last-born children
Pampered throughout their childhood
Vulnerable to strong inferiority feelings
According to Adler, second-born children
will spend a lifetime trying to catch up with their older siblings.
Carl Jung
First president of the International Psychoanalytic Association
Disagreement with Freud’s theory, resulted in resignation from the association in 1914 (THOUGHT MORE OF THE CONCIOUS MIND)
Established analytic psychology
Collective Unconscious
Part of unconscious mind
Constitutes of thoughts, images, and psychic characteristics that are difficult to bring into awareness
Anima
Feminine side of the male
Animus
Masculine side of the female
Shadow
Negative side of personality
Evidence for the Collective Unconscious
Is based on examination of mythology, cultural symbols, dreams, and the statements of schizophrenics
Erik Erickson
Believed that ego is a relatively powerful, independent part of personality
Ego psychology
Erikson’s approach to personality
Identity crisis
Confusion and despair we feel when we lack a strong sense of who we are
Crises
Turning points encountered by people in personality development
Personality Development Throughout the Life Cycle
Infancy - Old Age
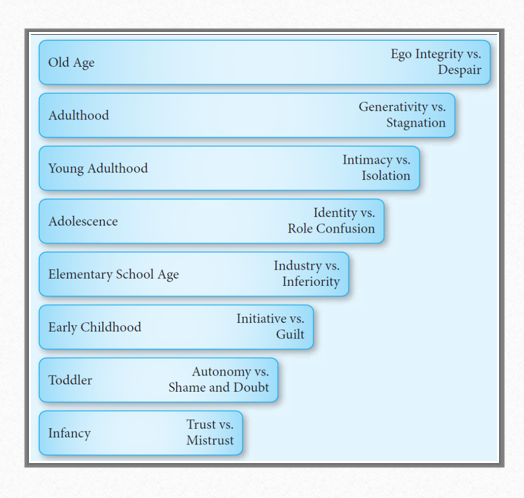
Autonomy
Allowing children to manipulate and control what they encounter
Over protection of children hinders
development and lead to shame and doubt
Industry
Belief in one’s strengths and abilities
Inferiority
Lack of appreciation for one’s talents and skills
People with a sense of identity
make decisions about personal values and religious questions
Middle aged individuals develop a concern
for guiding the next generation
Adults who fail to develop sense of
generativity suffer from a sense of stagnation
Karen Horney
Studied Freud’s work and taught psychoanalysis
Founded American Institute for Psychoanalysis
Important contributions
•Neurosis and feminine psychology
Neurotic
People who are trapped in a self-defeating interpersonal style
Interaction styles adopted
by neurotics to avoid anxiety-provoking experiences
Moving against people
People deal with anxiety differently: some seek comfort in others, while others fight it. Some kids use aggression and hostility to cope with a tough home life.
Moving away from people
Some children facing anxiety may employ a third strategy: withdrawing from others and seeking solitude to become self-sufficient and independent.
Feminine Psychology
Introduced the concept of womb envy
In a society where men and women are free to become whatever they desire girls would not want to be boys, or vice versa
Personal narratives
Narration of one’s own life story, that requires describing turning point scenes from one’s life
Strengths Neo-Freudian Theory
Freud's oversight of important concepts, recognition of social influences on personality, a positive view of humanity, and the introduction of new ideas like identity crises, introverts, and inferiority complexes.
Criticism Neo-Freudian Theory
Neo-Freudian theories lack strong evidence and overlook crucial aspects.