chemistry - fuels (8.1 - 8.17)
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
8.1 what are hydrocarbons?
compounds that contain carbon & hydrogen only
8.2 what is crude oil?
a complex mixture of hydrocarbons
contains molecules in which carbon atoms are in chains/rings
an important source of useful substances (fuels & feedstock for petrochemical industry)
a finite resource
8.3 separation of crude oil by fractional distillation - why?
crude oil not runny enough/ignited easily enough to be used as fuel
separated into simpler, more useful mixtures
fractional distillation - different hydrocarbons have different boiling points
8.3 separation of crude oil by fractional distillation - how?
in tall metal fractionating column
crude oil heated strongly to evaporate it & hot vapours pipped into bottom of column
column is hottest at bottom & coldest at top
vapours condense when reach part of column below their boiling point
liquid falls into tray & piped away
vapours with lowest boiling points don’t condense - leave top as mixture of gases
bitumen has highest boiling point - leaves at bottom as hot liquid
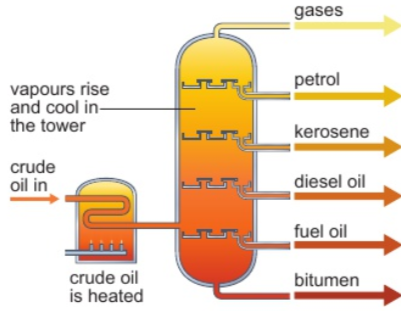
8.4 names & uses of fractions: gases
domestic heating & cooking
8.4 names & uses of fractions: petrol
fuel for cars
8.4 names & uses of fractions: kerosene
fuel for aircraft
8.4 names & uses of fractions: diesel oil
fuel for some cars & trains
8.4 names & uses of fractions: fuel oil
fuel for large ships & in some power stations
8.4 names & uses of fractions: bitumen
surface roads & roofs
8.5 properties of fractions
compounds in crude oil fractions are mostly from alkane homologous series
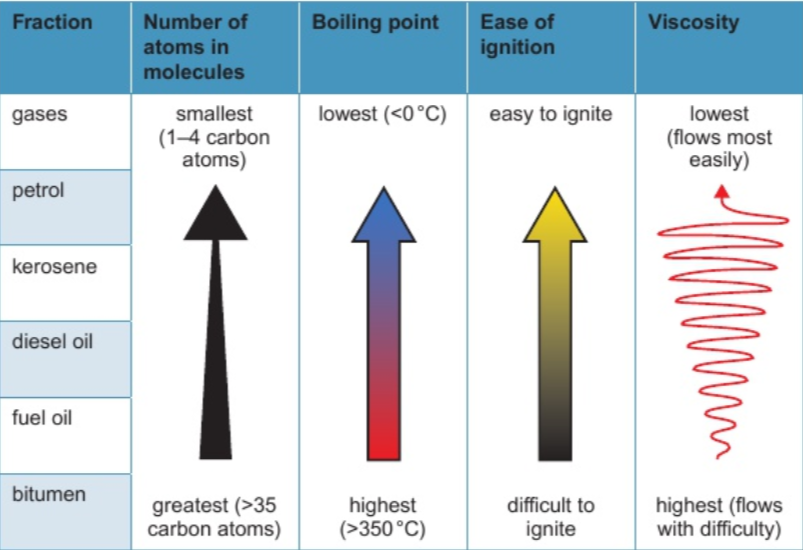
8.6 a homologous series is a series of compounds which…
have same general formula (e.g. alkanes = CnH2n+2)
differ by CH2 in molecular formulae from neighbouring compounds
show gradual variation in physical properties (shown in boiling points)
have similar chemical properties (e.g. alkane + oxygen → carbon dioxide + water)
8.7 complete combustion of hydrocarbon fuels
carbon dioxide + water produced
energy given out
8.8 why can incomplete combustion of hydrocarbons produce carbon & carbon monoxide?
some carbon atoms in hydrocarbon may be:
fully oxidised to carbon dioxide
only partially oxidised to carbon monoxide
released as smoke & soot
incomplete combustion of hydrocarbon fuels
happens when limited supply air/oxygen
carbon dioxide + carbon monoxide + water produced
energy given out (less than complete combustion)
8.9 how does carbon monoxide behave as a toxic gas?
combines with haemoglobin in RBCs - prevents oxygen combining
reduces amount of oxygen carried in bloodstream - makes people sleepy/unconscious/can cause death