Lecture 1- Foundations and Introduction to Anatomy
1/77
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
78 Terms
Anatomy
the study of internal and external body structures and relationships between them
Physiology
study of how the body functions
Microscopic anatomy
the study of structures that can’t be seen w/o magnification
cytology
study of cells
histology
study of tissues
cells make tissues which make organs
what is the relationship of microscopic anatomy to gross anatomy
gross anatomy
The study of structures that can be seen without magnification
surface anatomy
study of general anatomical form, or morphology; refers to the superficial anatomical markings
regional anatomy
refers to all structures in a specific area of the body
systemic anatomy
study of the organ systems in the body
developmental anatomy
examines structural changes over time
embrology
the study of early developmental changes
comparative anatomy
Considers anatomical similarities and differences in different types of animals
Clinical Anatomy
Studies anatomical changes that occur during pathological illnesses
surgical anatomy
Studies anatomical landmarks important for surgical procedures
radiographic anatomy
Using x-rays or ultrasound scans to study anatomy
cross-sectional anatomy
Using radiographic techniques (CT, MRI, and spiral scans) to study cross sections of the body
chemical/molecular, cellular, tissue, organ, organ system, organism
list the levels of anatomical organizations from smallest to largest
hydrogen, carbon, oxygen, nitrogen
what 4 elements make up 99 percent of the body?
water, proteins, lipids, carbohydrates
what 4 major classes of compounds are found in the body?
cellular level
-The smallest living organizational unit in the body
• Consists of organelles
tissue level
made up of many cells and some surrounding material
epithelial, muscular, connective, neural
4 tissue types found in the human body
organ level
combination of tissues
organ system level
Combination of various organs
11
how many organ systems make up the human body?
responsiveness, reproduction, growth/differentiation, movement, metabolism, excretion
what vital functions do the organ systems of the human body carry out?
anabolism
the synthesis of complex molecules
cataboliam
the breakdown of complex molecules
absorption
the process of bringing material into the body.
respiration
the absorption, transport, and use of oxygen by cells
excretion
the removal of waste
latin and greek
what types of words are the basis of most anatomical terms?
superficial anatomy
what are anatomical landmarks, anatomical regions, and anatomical directions part of?
Sectional anatomy
Electronic imaging allow us to see inside the body. Key to illustrate the anatomy of 3D objects.
standing with feet flat on the floor, hands at side, palms facing forward
what is the anatomical position?
supine
lying down (face up) in the anatomical position
prone
lying down (face down) in the anatomical position
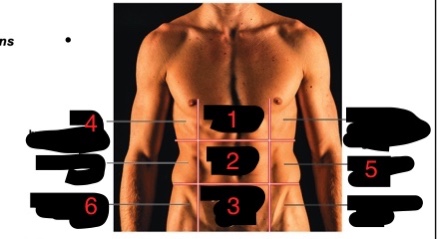
abdominopelvic quadrants
The abdomen and pelvic regions can be subdivided into four sections called _____________
abdominopelvic regions
The abdomen and pelvic regions can be subdivided into nine sections called _____________
liver, gallbladder, right kidney
What is found in the RUQ
Cecum, appendix, right ureter, right ovary or spermatic cord
what is found in the RLQ
stomach, pancreas, left kidney, spleen
What is found in the LUQ
left ureter, left ovary or spermatic cord
what is found in the LLQ?
epigastric, umbilical, hypogastric, right hypochondriac, left lumbar, right inguinal
name the six numbered abdominopelvic regions
medial
located towards the midline
lateral
located away from the midline
proximal
located towards an attached base
distal
located away from an attached base
cranial
toward the head
caudal
downward towards the tail or coccyx
anterior
refers to the abdominal side of the human body
ventral
the abdominal side in non-humans, equivalent to anterior
dorsal
the back side in non-humans, equivalent to posterior
posterior
the backside of the human body
sagittal plane
Separates the tissue/body into left and right sections
midsagittal
plane that separates equal left and right sections
parasagittal
a parallel section to the midline
transverse plane
Separates the tissue/body into upper and lower sections
frontal plane
Separates the tissue/body into anterior and posterior sections
serial reconstruction
A series of sections at small intervals
diaphragm muscle
what separate the abdominal and thoracic cavities?
thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities
what are the two major divisions of the anterior body cavity?
pleural and pericardial cavities
what makes up the thoracic cavity?
abdominal cavity, pelvic cavity, peritoneal cavity
what makes up the abdominopelvic cavity?
cranial and spinal cavities
what makes up the posterior cavity?
visceral layer
inner membrane layer that lines organs
parietal layer
outer membrane layer that lines cavities
clinical anatomy
Which specialty focuses on anatomical features that may undergo recognizable pathological changes during illness?
• comparative anatomy
• developmental anatomy
• clinical anatomy
• radiographic anatomy
microscopic anatomy
The study of anatomy that cannot be seen without magnification is _____.
• regional anatomy
• pathological anatomy
• gross anatomy
• microscopic anatomy
organ system level
The “lymphatic” level is representative of which level of organization?
• tissue level
• organ system level
• organ level
• cellular level
nervous system
Which organ system directs immediate responses to environmental stimuli, usually by coordinating the activities of other systems?
• lymphatic system
• endocrine system
• nervous system
• muscular system
patella
What is the anatomical term for the anterior region of the knee?
• popliteal
• patella
• sura
• crus
femoral
Which of the following anatomical landmarks is the most proximal of those listed?
• tarsal
• crural
• patellar
• femoral
mediastinum
What is the name of the region located between the right and left lungs?
• pleural cavity
• mediastinum
• epigastric
• thoracic cavity
right lower quadrant
The appendix is located in the _____.
• right upper quadrant
• right lower quadrant
• left upper quadrant
• left lower quadrant