Ch 13 Monetary Theory: the Impact of Money on the Economy
1/40
Earn XP
Description and Tags
TopHat Assessment 13.1, 13.2, 13.3
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
If the money supply (M) is $750, the price level (P) is 1.5, and real GDP (Q) is $2,000, then, the velocity of money (V):
a. is 4.
b. is 2.67.
c. is 5.
d. cannot be determined from the information given.
a. is 4.
According to the Monetarist model, if real GDP increases by 2%, a 7% increase in the money supply leads to an increase in the price level of approximately ______%. For the price level to stay the same, the increase in the money supply should be ______% when real GDP increases by 2%.
5%, 2%
Which of the following statements is NOT associated with the Monetarist school of thought?
a. Inflation is always a monetary phenomenon.
b. The velocity of money is not stable in the short run.
c. The key to long-run economic stability is stable money growth.
d. Fiscal policy may be ineffective due to crowding out.
b. The velocity of money is not stable in the short run.
If the nominal interest rate is 8% and the inflation rate is 3%, the real interest rate is ______%. A lender who demands a 6% real interest rate and expects inflation to be 3% charges a nominal interest rate equal to ______%.
5%, 9%
Ceteris paribus, if the Fed pursues contractionary monetary policy:
a. the money supply increases and the interest rate decreases.
b. the money supply decreases and the interest rate increases.
c. the demand for money increases and the interest rate increases.
d. the demand for money decreases and the interest rate decreases.
b. the money supply decreases and the interest rate increases.
Increase in the money supply
Increase in investment spending
Increase in aggregate demand
Decrease in the interest rate
Increase in the money supply
Decrease in the interest rate
Increase in investment spending
Increase in aggregate demand
Horizontal portion of the money demand curve
Liquidity Trap
A change in the money supply changes the interest rate which changes investment spending which then changes aggregate demand
Keynesian Monetary Transmission Mechanism
Cash balances held to meet expected spending such as paying rent and buying groceries
Transactions demand for money
People increase the quantity of cash balances they hold when the interest rate decreases and vice-versa
Asset demand for money
Reason why investment spending may not increase even when there is a substantial decrease in the interest rate
Pessimistic business expectations
The equation of exchange is:
a. MV = PQ.
b. RR = r(D).
c. MP = VQ.
d. Y = (G)(1/MPS).
a. MV = PQ.
According to the equation of exchange, if nominal GDP is $5,000 billion and the money supply is $1,000 billion, the velocity of money is:
a. 0.20.
b. 10
c. 5
d. impossible to estimate.
c. 5
Using the equation of exchange, if V and Q are both constant, then a 10% increase in the money supply leads to a 10% increase in:
a. real GDP.
b. the money supply.
c. the velocity of money.
d. the price level.
d. the price level.
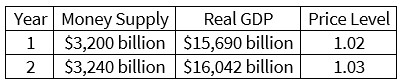
According to the data in the table, the velocity of money in year 2 is approximately:
a. 4.8.
b. 4.9.
c. 5.0.
d. 5.1.
d. 5.1.
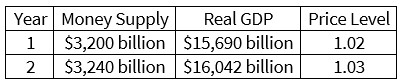
According to the data in the table, aggregate spending, or nominal GDP, in year 1 is approximately __________ and is approximately _________ in year 2.
a. $15,690 billion; $16,042 billion
b. $16,004 billion; $16,523 billion
c. $16,004 billion; $16,042 billion
d. $15,690 billion; $16,523 billion
b. $16,004 billion; $16,523 billion
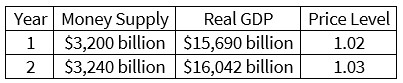
According to the data in the table, the money supply ________ and the economy ________ between year 1 and year 2.
a. increased; grew
b. increased; contracted
c. decreased; grew
d. decreased; contracted
a. increased; grew
The Monetarist model is based on the work of:
a. John Maynard Keynes.
b. Adam Smith.
c. Milton Friedman.
d. Karl Marx.
c. Milton Friedman.
According to the Monetarists, historically inflation is a result of:
a. insufficient aggregate demand.
b. insufficient economic growth.
c. excessive money growth.
d. excessive production of goods and services.
c. excessive money growth.
The Monetarist model concludes that a 10% increase in the money supply when real GDP increases by 2.5% leads to an approximate:
a. 7.5% increase in the price level.
b. 10% increase in the price level.
c. 2.5% increase in the price level.
d. 12.5% increase in the price level.
a. 7.5% increase in the price level.
Which of the following statements is not associated with the Monetarists?
a. Fiscal policy is often ineffective or counterproductive for stabilizing the economy.
b. The key to long-run stability in the economy is stable money growth.
c. Government policy-makers are unnecessary; complete laissez-faire is the most appropriate policy approach.
d. Policy rules, such as a monetary growth rule, yield better outcomes than discretionary policy.
c. Government policy-makers are unnecessary; complete laissez-faire is the most appropriate policy approach.
The money demand function:
a. slopes downward to the right indicating that people always want more money.
b. illustrates the inverse relationship between the quantity of money balances demanded and the interest rate.
c. is a vertical line implying that the Federal Reserve exerts significant control of both money demand and money supply.
d. represents the demand for income and wealth.
b. illustrates the inverse relationship between the quantity of money balances demanded and the interest rate.
All of the following are true with respect to the money market EXCEPT:
a. the transactions demand for money is independent of the interest rate.
b. the opportunity cost of holding cash balances is higher at higher rates of interest than at lower rates of interest.
c. when the interest rate is above the equilibrium interest rate, people are likely to move into of cash and out of interest-bearing assets.
d. the downward-sloping money demand curve represents the asset demand for money.
c. when the interest rate is above the equilibrium interest rate, people are likely to move into of cash and out of interest-bearing assets.
If the nominal interest rate is 8% and the inflation rate is 3%, then the real interest rate is:
a. 3%.
b. 5%
c. 8%.
d. 11%.
b. 5%
A lender that demands a 4% increase in purchasing power as compensation for making a loan charges a nominal interest rate of ______ if the lender expects inflation to be 2.5%.
a. 1.5%.
b. 2.5%.
c. 4%.
d. 6.5%.
d. 6.5%.
An increase in the money supply, ceteris paribus, leads to a(n):
a. decrease in the interest rate and an increase in the demand for money.
b. decrease in the interest rate and an increase the quantity demanded of money.
c. increase in the interest rate and a decrease in the demand for money.
d. increase in the interest rate and a decrease in the quantity demanded of money.
b. decrease in the interest rate and an increase the quantity demanded of money.
Ceteris paribus, if the Fed sells bonds in the open market:
a. money demand will shift to the right, causing interest rates to rise.
b. money demand will shift to the left, causing interest rates to fall.
c. money supply will shift to the left, causing interest rates to rise.
d. money supply will shift to the right, causing interest rates to fall.
c. money supply will shift to the left, causing interest rates to rise.
The Keynesian perspective of the impact of money on the economy suggests that an increase in the money supply will result in a(n) __________ in interest rates, a(n) __________in investment spending, and a(n)_________ in aggregate demand.
a. increase; increase; increase
b. decrease; decrease; decrease
c. decrease; increase; increase
d. increase; decrease; decrease
c. decrease; increase; increase
The liquidity trap:
a. is the horizontal portion of the money demand curve.
b. occurs when investors believe interest rates have bottomed out and hoard cash.
c. implies that an increase in the money supply has no impact on interest rates.
d. All of the above true regarding the liquidity trap.
d. All of the above true regarding the liquidity trap.
According to Keynes, monetary policy may be ineffective if:
a. investment and consumer spending are not sensitive to changes in short-term interest rates.
b. the money demand curve slopes downward to the right.
c. the money market is in a liquidity trap.
d. Both a. and c. are true.
d. Both a. and c. are true.
If investors are very pessimistic regarding future sales and profits:
a. even a relatively large decrease in interest rates may lead to little or no increase in investment spending.
b. investment spending will only increase if interest rates fall when the economy is in a liquidity trap.
c. lower interest rates lead to substantial increases in investment spending which increases aggregate demand.
d. a change in the money supply leads to no change in interest rates.
a. even a relatively large decrease in interest rates may lead to little or no increase in investment spending.
Using the equation of exchange, if nominal GDP is $5,000 billion and the money supply is $1,000 billion, the velocity of money is:
a. 0.20.
b. 10
c. 5
d. impossible to estimate.
c. 5
The Monetarists contend that the most important determinant of inflation in U.S. history has been:
a. decisions by Congress to raise income tax rates.
b. decisions by the Fed to allow the money supply to grow too quickly.
c. supply shocks such as OPEC activity leading to higher energy prices.
d. attempts by labor unions to raise wages.
b. decisions by the Fed to allow the money supply to grow too quickly.
Monetarists argue that increasing the growth rate of the money supply will:
a. cause real GDP to continuously rise substantially in the long run.
b. cause nominal GDP to decrease in the long run because velocity is so erratic and unstable.
c. ultimately increase the price level in the long run and have no effect on real GDP.
d. have no effect on nominal GDP.
c. ultimately increase the price level in the long run and have no effect on real GDP.
The notion that the Fed should adhere to a policy of steady and predictable expansion of the money supply represents:
a. the monetary rule advocated by the Monetarists.
b. the fiscal rule advocated by the Monetarists.
c. the monetary rule advocated by the Keynesians.
d. the fiscal rule advocated by the Keynesians.
a. the monetary rule advocated by the Monetarists.
If the nominal rate of interest is 9% and the inflation rate is 5%, then the real rate of interest is:
a. 14%.
b. 9%.
c. 5%.
d. 4%.
d. 4%.
Expansionary monetary policy:
a. increases the money supply and lowers interest rates.
b. increases the money supply and raises interest rates.
c. decreases the money supply and lowers interest rates.
d. decreases the money supply and raises interest rates.
a. increases the money supply and lowers interest rates.
Which of the following summarizes the Keynesian Monetary Transmission Mechanism in response to contractionary monetary policy?
a. Increase in the money supply leads to lower interest rates, an increase in investment spending , and an increase in aggregate demand
b. Increase in the money supply leads to lower interest rates, a decrease in investment spending , and a decrease in aggregate demand
c. Decrease in the money supply leads to higher interest rates, a decrease in investment spending, and a decrease in aggregate demand
d. Decrease in the money supply leads to higher interest rates, an increase in investment spending, and an increase in aggregate demand
c. Decrease in the money supply leads to higher interest rates, a decrease in investment spending, and a decrease in aggregate demand
According to Keynes, monetary policy may be ineffective if:
a. investment and consumer spending are insensitive to changes in short-term interest rates.
b. investment spending increases when the interest rate decreases.
c. the money market is in a liquidity trap.
d. Both a. and c. are true
d. Both a. and c. are true
According to many non-Keynesian Schools of Thought, macroeconomic policy:
a. should not be implemented and continually changed at the discretion of current policymakers.
b. is the best tool for achieving the goals of full employment and price level stability so long as it is highly discretionary.
c. eliminates the concern over the growing national debt because policymakers tend to focus on balancing the budget rather than influencing the macroeconomy.
d. is best conducted at the discretion of the members of Congress.
a. should not be implemented and continually changed at the discretion of current policymakers.
Two economists, Greene and Johnson, are discussing the currently high unemployment rate. Greene says that the Fed should lower interest rates quickly in order to increase borrowing and spending. Johnson says that it is better for the Fed to not immediately lower interest rates or allow the money supply to grow too fast in order to avoid inflation in the future. Which of the following is most likely to be true?
a. Greene and Johnson are both Keynesians with a few differences of opinion.
b. Greene and Johnson are both Monetarists with a few differences of opinion.
c. Greene takes a Keynesian view and Johnson takes a Monetarist view.
d. Greene takes a Monetarist view and Johnson takes a Keynesian view.
c. Greene takes a Keynesian view and Johnson takes a Monetarist view.