1.2.1 - Carbohydrates 1 - monosaccharides and disaccharides
1/22
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
What do carbohydrate molecules consist of?
Carbon, Hydrogen and Oxygen
What are long chains of sugars called?
saccharides
What are the three type of saccharides?
Monosaccharides, Disaccharides, Polysaccharides
Monosaccharide
single sugar molecule
Disaccharide
Two monosaccharides
Polysaccharide
Many monosaccharides
How do monosaccharides join together to form disaccharides and polysaccharides?
by glyosidic bonds formed in condensation reactions
What is the difference between alpha glucose and beta glucose
The orientation of the hydroxyl (-OH) group on carbon 1.
What is the structural formula of glucose alpha + draw
C6H1206
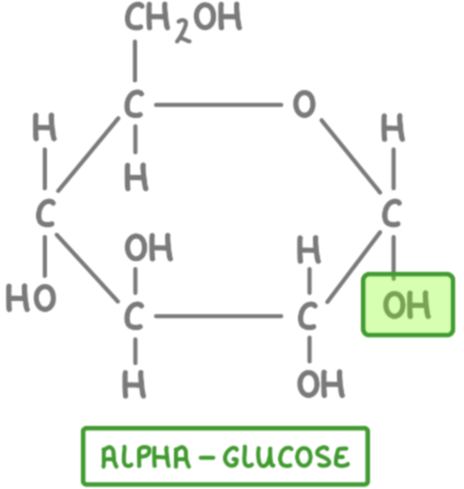
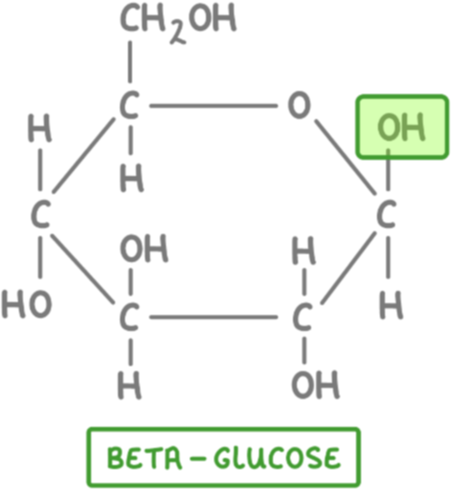
What is the structural formula of beta glucose + draw
C6H1206
Ribose
A monosaccharide containing five carbon atoms.
A pentose sugar and a component of RNA.
What is the structural formula of ribose + draw
C5H10O5
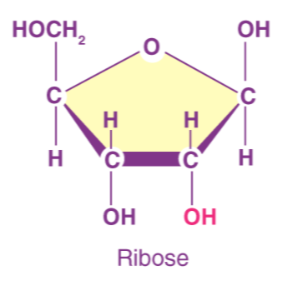

What is the structural formula of deoxyribose + draw
C5H10O4
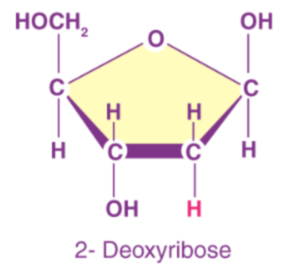

Name a ribose isomer and its feature(s) and where it’s found
deoxyribose, lacks the OH group on the second carbon of the sugar ring, found in the DNA
Maltose
a disaccharide formed by condensation of two glucose molecules
Sucrose
Sucrose is a disaccharide formed by condensation of glucose and fructose
Lactose
Lactose is a disaccharide formed by condensation of glucose & galactose
What are some glucose units polysaccharides are made of?
Glycogen and starch which are both formed by the condensation of alpha glucose
Cellulose formed by the condensation of beta glucose
Glycogen
the main energy storage molecule in animals and is formed from many molecules of alpha glucose joined together by 1, 4 and 1, 6 glyosidic bonds .
has a large number of side branches meaning that the molecule can be hydrolysed and energy can be released quickly.
It is a relatively large, but compact molecule thus maximizing the amount of energy it can store.
What is two polysaccharides is starch a mixture of?
Amylopectin and Amylose
Amylose
An unbranched chain of glucose molecules joined by 1, 4 glycosidic bonds .
As a result, amylose is coiled
Very compact molecule meaning it can store a lot of energy.
● Amylopectin is made up of glucose molecules joined by 1,4 and 1,6 glycosidic bonds, making it a branched molecule. Due to the presence of many side branches, it is rapidly digested by enzymes, therefore, energy is released quickly. It is also a compact molecule, although not as compact as amylose.
Amylopectin
is made up of glucose molecules joined by 1,4 and 1,6 glycosidic bonds, making it a branched molecule.
Due to the presence of many side branches, it is rapidly digested by enzymes,
therefore, energy is released quickly. It is also a compact molecule, although not as compact as amylose.
Cellulose
a component of cell walls in plants and is composed of long, unbranched chains of beta glucose monomers which are joined by 1,4 glycosidic bonds.
Microfibres and microfibrils are strong threads which are made of long cellulose chains joined together by hydrogen bonds and they provide structural support in plant cells.