MUSCULAR SYSTEM
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
MUSCULAR SYSTEM
composed of muscle cells and tissues that brings about movement of an organs or body party
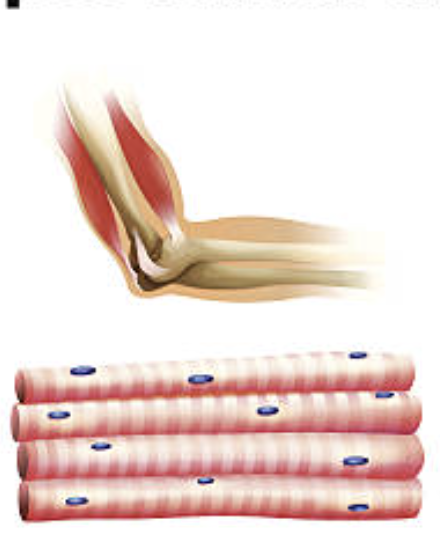
SKELETAL MUSCLE
attached to the bone. voluntary movements. striated. Moves skeleton, maintains posture
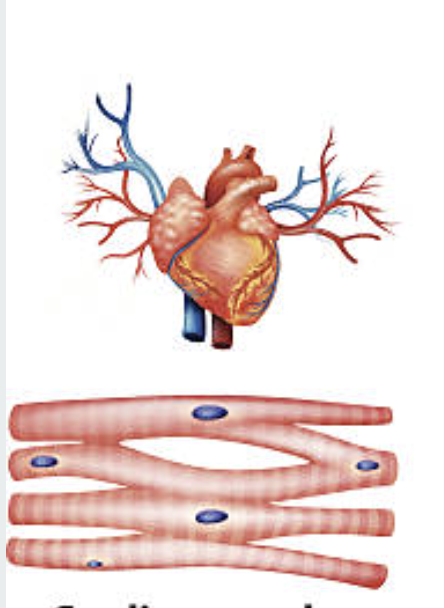
CARDIAC MUSCLE
only exist in the heart. involuntary movement. Striated with intercalated discs. Pumps blood
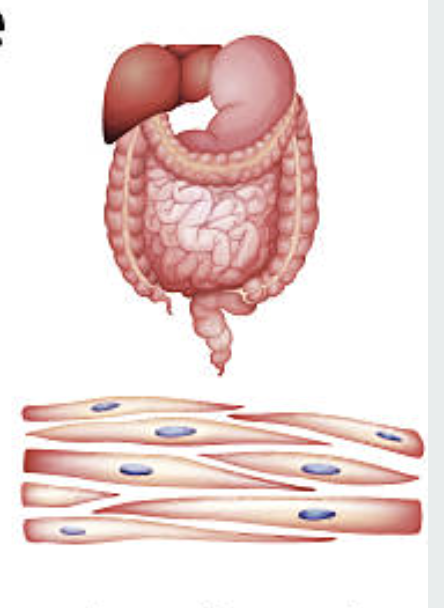
SMOOTH MUSCLE
Walls of organs (stomach, intestines, blood vessels). Involuntary. Nonstriated. Moves substances through organs
MUSCLE FIBER CELL
a single long muscle cell inside the muscle

MYOFIBRIL
long thread-like structures inside each fiber
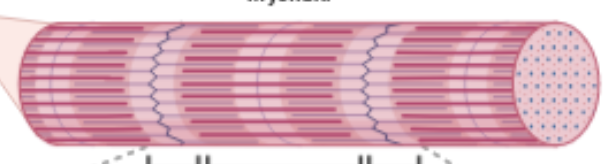
SARCOMERES
the function unit inside a myofibril. this is where contraction happens
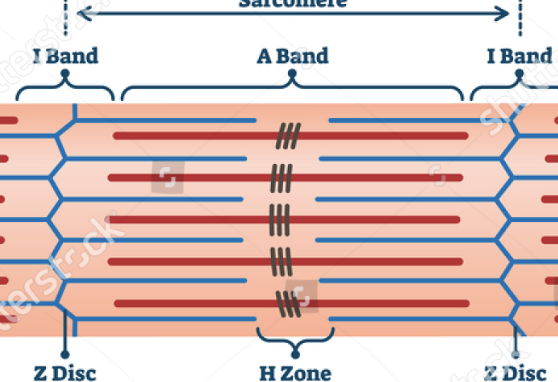
ACTIN
thin filament

MYOSIN
thick filament

NEVER ACT CALMLY, APES MIGHT ALWAYS RELAX
(NACA MAR)
nerve impulse, acetylcholine, calcium, actin and mysin bind, atp, relax
NERVE IMPULSE
Brain sends a nerve impulse down a motor neuron.
ACETYCHOLINE
tells the muscle fiber to contract by triggering calcium release from a storage area inside the cell called the sarcoplasmic reticulum.
CALCIUM
Calcium binds to troponin (a protein on actin), which moves tropomyosin out of the way → myosin can now grab actin.
TROPOMYOSIN
Troponin shifts tropomyosin so myosin can bind actin.
ACTIN & MYSIN BIND
Myosin and actin slide past each other to shorten the sarcomere
ATP
The energy molecule muscles need for contraction and relaxation.
RELAX
Relaxation when calcium returns
MUSCULAR SYSTEM
responsible for movement, posture, and heat production.
It works closely with the skeletal system (to move bones) and the nervous system (to control contractions).