PSYC1030 - QUIZ 2
1/107
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
108 Terms
What is the nomothetic approach?
Involves trying to understand personality by identifying general rules that govern the behaviour of all individuals.
What is the idiographic approach?
Used when people are interested in understanding personality by identifying the unique configuration of characteristics and life history within the individual person.
What factors cause personality?
Genetic factors
Shared environmental (e.g. sibilings)
Non-shared environmental (e.g. diff schools)
How do we research the causes of personality?
Twin studies
The studies suggest that genes are a bigger contributor to personality than shared environment.
Nature vs nurture.
genes are not ONLY factor
What does personality refer to?
character traits that identify what makes a person who they are, and a particular pattern of behaviour and thinking that prevails across time and situations.
What are the three core principals of psychoanalytic theory?
(Sigmund Freud)
- Psychic determination: We are not free to choose our own actions. Everything driven by unconsciousness
- Symbolic meaning: No action is meaningless
- unconscious motivation: We rarely understand what we do
What does psychic determination refer to?
All psychological events have a cause.
Most of our behaviour is driven by unconscious processes and not by conscious thoughts.
What does symbolic meaning refer to?
No action is meaningless.
What does unconscious motivation refer to?
We rarely understand what we do, even if we are able to explain it after the fact.
What are the levels of awareness?
Unconscious level (Id): most primitive instinctive component operating on pleasure principle - immediate gratification
Preconscious level (ego) and Conscious level (ego): aware of at conscious level. 'boss of personality'. Decision making component. Seeks delayed gratification bc reality is a thing
Superego is present at all levels. It represents societies moral standards: all levels of awareness. Deeloped 3-5yo. Moral component
How does the ego deal with anxiety from conflict between the superego and Id?
Defence mechanisms e.g. repression, denial, projection, rationalisation etc
What is the psychosexual theory?
Personality development involves passing through the different psychosexual stages of development.
diff stages of psychosexual stages of development
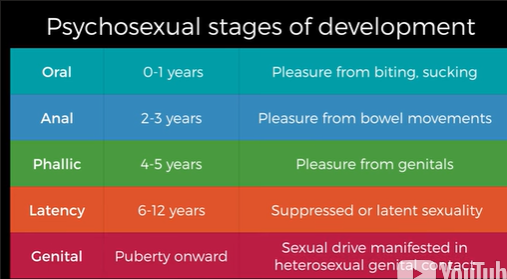
criticism of psychosexual theory
sexist, limited evidence for defence mechanisms, limited supporting evidence, non falsifiable
What is the behavioural approach?
(B.F. Skinner)
The idea that personality is under the control of genetic factors and environmental reinforcers and punishers.
It is deterministic (we don't choose how we behave).
What is Albert Bandura's social theory of personality? What does it rely upon?
Personality is the interaction between a person's traits, their thoughts and the environment that their behaviour is expressed in.
It relies upon expectations.
requires reciprocal determinism
What is reciprocal determinism?
The idea that behavioural cognitive and environmental variables interact to produce personality.
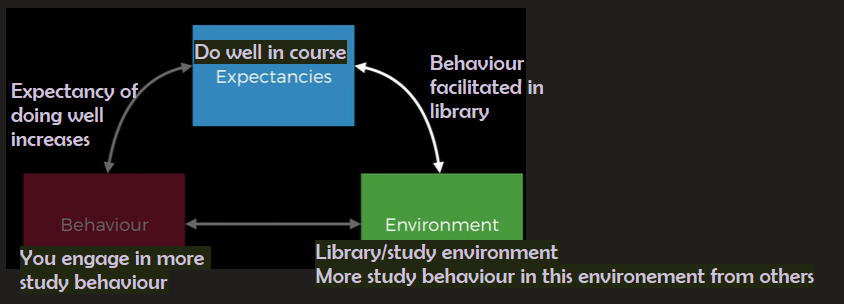
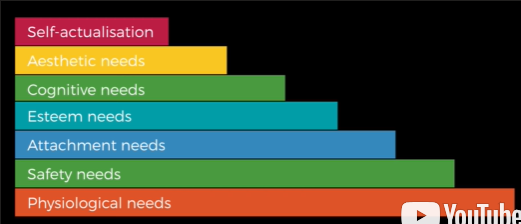
What is the positive motivation theory of personality?
(Maslow)
Defined personality as the expression of the tendency to strive for self-actualisation (the idea that people want to fulfil their potential).
What is Roger’s theory of personality
personality development would be fully expressed in world w/ no expectancies of what we should be
An idealised world with no conditions of worth
What are the barriers to positive personality development?
(Rogers' theory?
Personality is a function of the organism.
The self (self-concept)
Conditions of worth → expectations or rules that society puts on our behaviour.
What was the Humoral theory of personality traits? What was a limitation of this theory?
The idea that you could characterise a person's personality based on what sort of humor, or fluid, they had in excess in their body. choleric, melancholic, phlegmatic, sanguine
There is no biological evidence.
type theorists (typists)
categorisation into distinct types. divisive (e.g. humoral theory)
What are trait theorists?
They think that traits are the factors that are responsible for causing patterns of behaviour. They think that traits are things that reside in our brains. traits are thought of in dimensions
What is a factor analysis?
Tells us statistically what the minimum number of things are that we need to summarise the data
that minimum number of things is a way to find the dimensions of personality.
how many dimensions of personality are there
3-16
What is Raymond Cattell's 16PF measure of personality traits>
The thought that there there were 16 source traits that produce what we observe in behaviour.
What are the 5 primary dimensions of personality according to the Big 5 theory? (NEOPI)
- Neuroticism
- Extraversion
- Openness
- Agreeableness
Conscientiousness
What are the three bipolar dimensions used to explain personality in Eynenck's theory?
Extraversion to introversion.
Neuroticism to emotional stability.
Psychoticism to self-control.
What are the four key traits or the Chinese Personality Assessment Inventory (CAPI)?
- Dependability
- Interpersonal relatedness.
- Social potency.
- Individualism.
What is the overlap between the Big 5 and the CAPI?
- Neuroticism is correlated with dependability
- Extraversion with social potency.
- Agreeableness with individualism.
What did Jeffery Gray propose about the biopsychological theory of personality?
Proposed the behavioural inhibition system (BIS) and the behavioural approach system (BAS) are the two systems that control our behaviour.
Our arousal system is affected by both.
What is the behavioural inhibition system (BIS)?
related to the individual's sensitivity to punishment and motivation for avoidance.
What is the behavioural approach system (BAS)?
related to the individual's sensitivity to reward as well as their motivation for approach.
What is Phrenology?
idea that the brain has got all these undulations, and these are reflected by bumps on people's heads.
thought that you could map these bumps into different aspects of personality.
What is Physiognomy?
Facial features are correlated with certain types of personality. Certain facial shapes might predispose people to commit crimes.
What is the Minnesota Multiphasic Personality Inventory (MMPI)?
objective test
Test is designed to detect deception and social desirability bias, but people can still influence the scores on it. It is useful for diagnosing psychological disorders. designed for clinical settings
What is the Thematic Apperception Test?
projective test
Presents ambiguous stimuli and asks people to describe what's going on in the image.
The explanation reflects our unconscious personality desires or traits onto the ambiguous stimuli. e.g. roscharch
What is a Rorschach inkblot test?
a projective technique in which respondents' inner thoughts and feelings are believed to be revealed by analysis of their responses to a set of unstructured inkblots. low reliability + validity but good for establishing rapport
what are goals of social psychology
understand how ppl think and behave in socialsettings by systematically testing theories in groups. NB. group-related phenomena do not mean groups have same effects on everyone
What is impression formation?
the process by which people combine information about others to make overall judgements.
What does the algebraic model of impression formation refer to?
impressions are formed on the basis of the mechanical combination of information that we know about a person.
What are the 3 models of algebraic impression formation?
all use assumption that we can ‘score’ attributes based on importance to us
Summative model: total sum of traits. neg or pos number tells us whether good or bad
Averaging model: average of traits.
Weighted averaging model: considers importance of attribute in situation. to get score multiply situational importance by importance to us. then average
What is the configurational model of impression formation?
based on gestalt principles (the whole is greater than just the sum of its parts). In this model, ppl combine info received abt person into an overall impression. Diff from just summing up the quantification of individual attributes. e.g. oh wow theyre rlly nice to homeless ppl all the time and mean to bullies
What are the two types of traits that influence impression formation in the configurational model?
central traits and peripheral traits. central traits are most influential but peripheral traits take on diff meanings in the context of central traits
What are schemas? How are they formed?
cognitive structures that represent our knowledge about a concept or type of stimulus.
Formed on the basis of past experiences.
why things are they way they are
What are event schemas?
generalised representations of activities and events.
Tell us what to expect in a particular situation. e.g. in restaurant u expect to be cooked for
What are role schemas?
the roles or parts that people are expected to play in a particular setting. e.g. that u expect cook to cook in a restaurant
What are person schemas?
represent our individualised knowledge structures about specific types of groups of people, as well as individuals.
what is a stereotype (schema)
person schema associated w/ a social category e.g. ethnicity, gender etc
Lippman (1992): Pictures in Our Head
What is the implicit personality theory?
What we believe to be the characteristics that go together to form certain types of personality.
person schema about a particular type of person.
What does heuristics refer to?
use of mental shortcuts that are less time-consuming strategies to get a quick solution to a problem.
What does the availability heuristic refer to?
when people judge an event's frequency by the ease with which they can bring examples of the event to mind. e.g. what kills more? smoking or car accidents. availability heuristic means we r more likely to say car accident bc we can think of more examples
What is the representativeness heuristic?
Estimation of the likelihood that someone belongs to a group by comparing the features of that person to the prototype for that group. e.g. if someone loves maths and numbers we think they are more likely an accountant than a writer
What is attribution theory?
an attempt to determine whether an individual's behaviour is internally (dispositional) or externally (situational) caused. inferring cause of behaviour
What are the three types of information in the covariation model?
Consensus information.
Distinctiveness information.
Consistency information.
What is the covariation principle
Theory that states to form an attribution about what cause a person's behaviour -- we attribute a behvaiour to the cause with which it covaries (happens with) over time
What is consensus information?
whether other people perform the same behaviour or not.
What is distinctiveness information?
whether the behaviour is only performed towards the particular target or person, or whether it is performed to other targets as well.
What is consistency information?
whether the behaviour is performed all the time or not.
What is person attribution?
when we attribute the cause of the behaviour to the person performing the behaviour. Low consensus.
What is target attribution?
when there’s information that the behaviour is highly distinctive.
What is situational attribution?
when the behaviour is due to something in the context or situation, when there’s low consistency in performing the behaviour (behaviour is formed in some contexts or situations, but not others).
What is the actor-observer bias?
the tendency to blame our actions on the situation and blame the actions of others on their personalities. only apprent under certain conditions e.g. explaining neg events
What is the fundamental attribution error? (correspondence bias)
The tendency to attribute another person’s behaviour to dispositional qualities. overestimation of internal attributes. person attrivution over situation attribution
What is self-serving bias?
tendency to attribute success to stable, internal factors and failure to temporary external factors.
What is the purpose of the self-serving bias
make us look better to other people (self-presentation effect)
enhances self esteem
What is prosocial behaviour?
any voluntary behaviour performed with the intention of benefitting another person.
What is myopia?
short-sightedness or lack of intellectual insight.
alcohol myopia
Developed to explain the effects that alcohol causes on an individual's perceptual and cognitive functioning.

how many global deaths are caused by harmful alc use
5.9% (3.3 million)
between 2000-2006 how many homicides in aus hae been alc related
~47%
what did Provenzo 1991 find
85% of most pop video games consisted of violence
73% boys and 59% girls preferred to play video games w/ violence
what is the correlation between media violence and aggression
between 0.11 and 0.31 (tobacco usage and lung cancer is 0.4)
What does observational learning suggest in regards to aggression?
Suggests that we learn to be aggressive (media consumption, video games, social media).
What is the Werther effect?
Refers to the phenomenon where a sharp increase in the rate of suicide occurs following the release of a high profile suicide story.
What is the copy-cat effect?
People are so inspired by a story in the media, that they themselves copy the person from the story.
e.g. After columbine massacre 1999, school shootings have become more common. Following this there was a lot of imitation of behaviour and sometimes even competition between kill numbers
What is the cognitive argument for aggression?
suggests that some people just think a particular way that leads them to be more aggressive.
What is the social cognitive explanation for aggression?
people develop aggressive tendencies because of maladaptive thinking patterns. same thing—> two responses
What happens to violence in crowds?
Deindividuated → we lose ourselves in crowds, and the superego melts away, and our id is left to go rampant. less accountability
Effects of deindividuation depends on context and situation we r sesnsitive too.
e.g. ppl in nurse outfit will be nicer even tho theyre deindivduated.
Anonymity and deindividuation assist ppl in taking on the role that is implied by a situation
what is the effect of ostracism
regardless of WHO the ostraciser is (friend, stranger, enemy etc) we respond in a way which aims to get us reintegrated
What are the factors that determine if someone will be altruistic?
when they have seen another person be altruistic modelling this behaviour.
Whether or not people are in a rush
What is the dependency theory?
Biological need satisfied by caregiver, then biological satisfaction bc relief from discomfort.
What is imprinting?
the process by which an individual forms a strong and often irreversible emotional connection to another individual or object
What is attachment theory?
A baby loves their mother, not because of the stuff she provides, but because of a feeling of security.
What is the goal of the attachment behavioural system?
proximity to the caregiver.
What are Mary Ainsworth's dual motivations in children?
Exploration and security.
If infant is sensing danger it will go to mother but will want to explore when safe
Primary caregiver becomes secure base from which to explore
What is the purpose of exploration in the dual motivation theory?
serves the purpose of learning and equipping them for independent survival
What are the major classifications in the patterns of attachment?
A → anxious avoidant (20%)
B → secure (60%)
C → anxious ambivalent (20%
What are some characteristics of the secure (B) child?
children show distress when caregiver leaves but is easily comforted at reunion. trust and security in relo w/ caregiver
What are some characteristics of an anxious avoidant (A) child?
children seem indifferent to departure/return of caregiver. tendency to avoid seeking comfort from them
What are some characteristics of of a anxious ambivalent (C) child?
children highly distressed upon separation and not easily comforted upon reunion. ambivalence and resistance to contact and comforting. paradigm often has to end early due to distress levels in this group
What is Genetic epistemology
the study of how we develop knowledges
What is the Constructivist theory?
based on the idea that children actively construct knowledge as they manipulate and explore their world. driven by assimiliation and accomodation
What are the 4 stages of the constructivist theory (Jean Piaget)
Sensorimotor stage
pre-operational
Concrete operation
Formal operation
When does disequilibrium occur?
occurs when our basic knowledge or schema differs from the new experiences.
What are the 2 ways to deal with disequilibrium?
ASSIMILATION
We deal with this by assimilating the new experience → fit the new experience into our knowledge.
ACCOMODATION
we accommodate it → create a new concept to accommodate that new experience.
What occurs during the sensorimotor stage?
Infants explore the world through their senses and motor abilities, beginning with reflexes. (birth to 2yo) object permenance, cause/effect (8-12 mos
What is mental representation?
ability to form images about the world inside their heads. occurs by end of sensorimotor period
What does the deferred imitation task allow us to realise? What age do children pass it?
allows us to know infants have developed mental representation.
Pass this at 18 - 24 months of age.
What occurs in the preoperational stage? What is most important in this stage?
(2-7yo)Develop ability to engage in representational activity or symbolic activity. still intuitive and egocentric. Egocentrism; centrism; symbolic function (e.g. dolls represent people). Focused on ONE thing
Language (symbolic tool)