L5 Soil Cations/Anions
1/14
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Physical and chemical
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
Physical properties of soils
Texture
Structure
Density
Porosity
Permeability
Soil colour
Temperature of soil
Soil plasticity, Compressibility and Erodibility
Soil texture
A relative amount of sand, silt and clay
Sand: Gritty
Silt: Floury when dry, silky when wet
Clay: Velvety
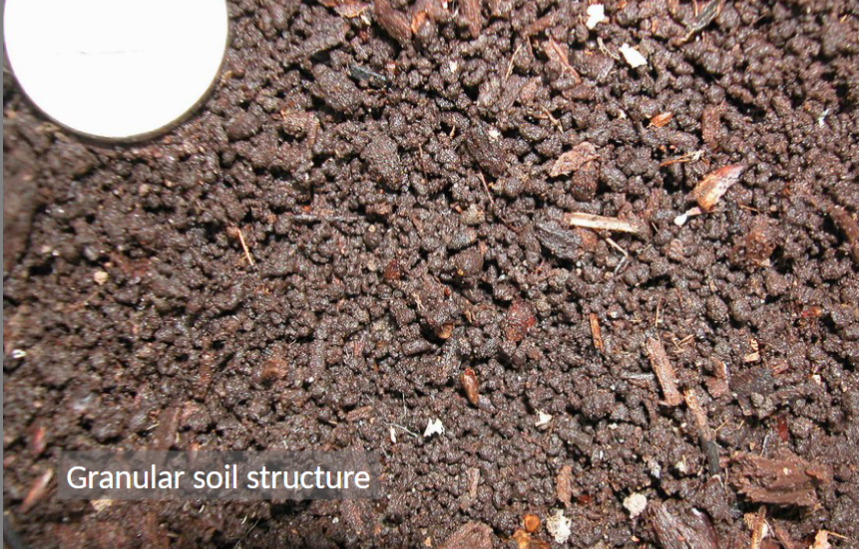
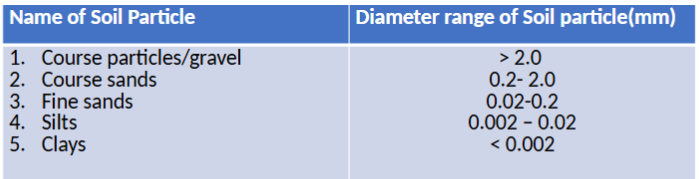

Soil structure
Arrangement of soil particles into aggregates (peds)
Granular
Blocky
Platy
Columnar and prismatic
Massive (non-structure)
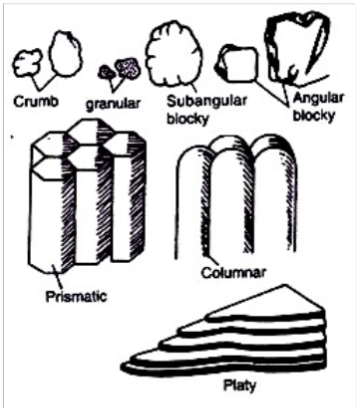
Effect of Soil structure on water permeability
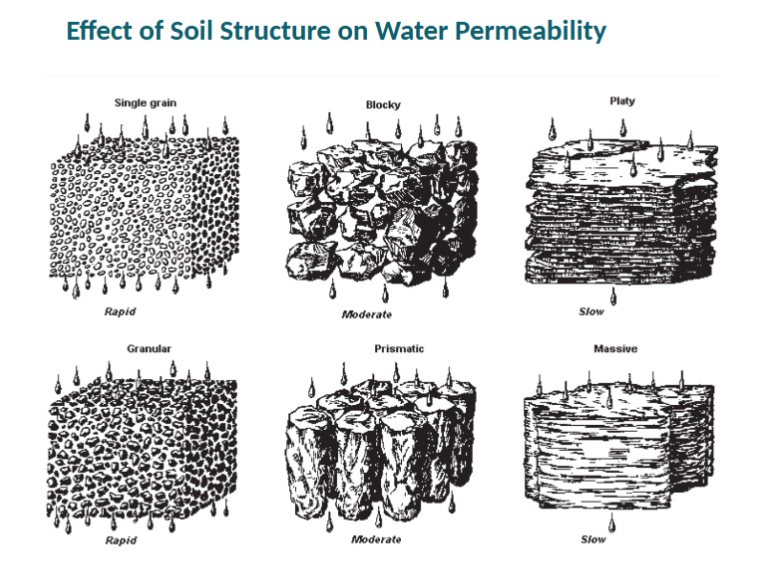
Soil Density and Pore Space
Loose, well-aggregated, porous soils and those rich in organic matter have lower bulk density
Soil colour
Inherited from parental material or due to soil forming processes
Organic substances impact - black or geryish-black colour.
Iron compounds → brown, red and yellow coloured soil
Iron oxide in combo with organic substances → brown colour which is the most common soil colour
Silica, lime → white and grey tinges to soil
Chemical properties of soil
Inorganic matter composition
Organic matter composition
Cation Exchange Capacity of Soils
Buffering Capacity of Soils
Inorganic matter composition
Aluminosilicates and oxides, because surface electrochemical properties these minerals control the adsorption and transformation and behaviour of other chemical constituents.
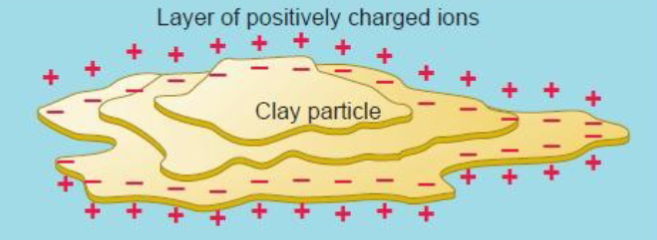
Aluminosilicates → clay particles, colloidal in nature
Colloids
Thin, plate-like shape that reflect their layered chemical crystal structure
Colloid surfaces are negatively charged because of their molecular structure.
They attract and hold positively charged ions that include nutrient bases like calcium and magnesium.
Ion
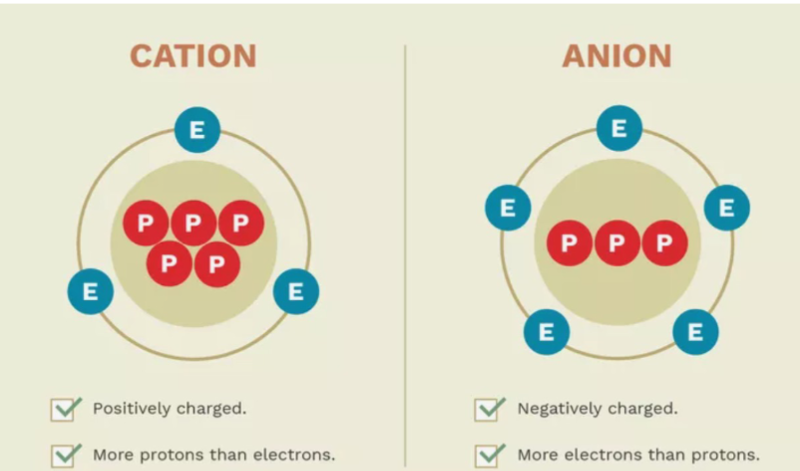
An ion is an atom with positive or negative charge
Cation
Positively charged ion that has more protons than electrons, meaning it has lost one or more electrons.
Common +2 cations include mg and ca
Anion
Negatively charged ion that has more electrons than protons, meaning it has gained one or more electrons
Cation Exchange Capacity (CEC)
The total capacity of soil to hold exchangeable cations
Clay and organic matter have negative charges that hold and release positively charged nutrients. (Cations absorbed onto the surface of the clay or humus)
The static charge keeps the nutrients from being washed away and holds them so they are available to plant roots and soil microorganisms.

Buffer capacity
The amount of acid or base buffered solution can soak up before its pH will start to change significantly.
Bioavailablity
Available to Biological Organisms
May refer to ingestion or uptake of a given compound
May also refer to biological or physiological effects
By definition → chemical measurements remain proxy and mist be linked to a biological organism