Comparing Planets
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
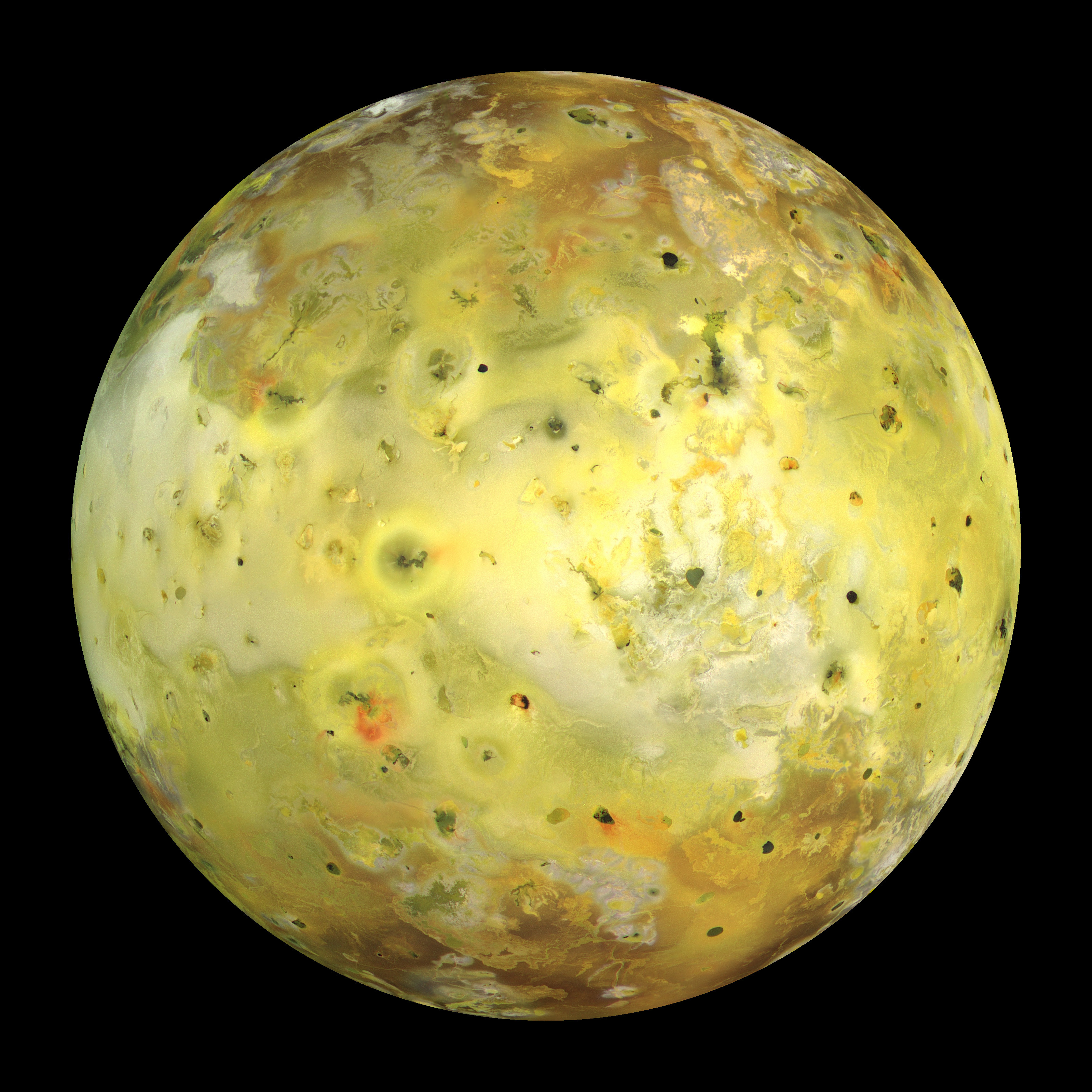
Io
closer to Jupiter
active volcanism (it is the innermost moon)
tidal heating
young
tectonically active
warmest
has an eccentric, elliptical orbit

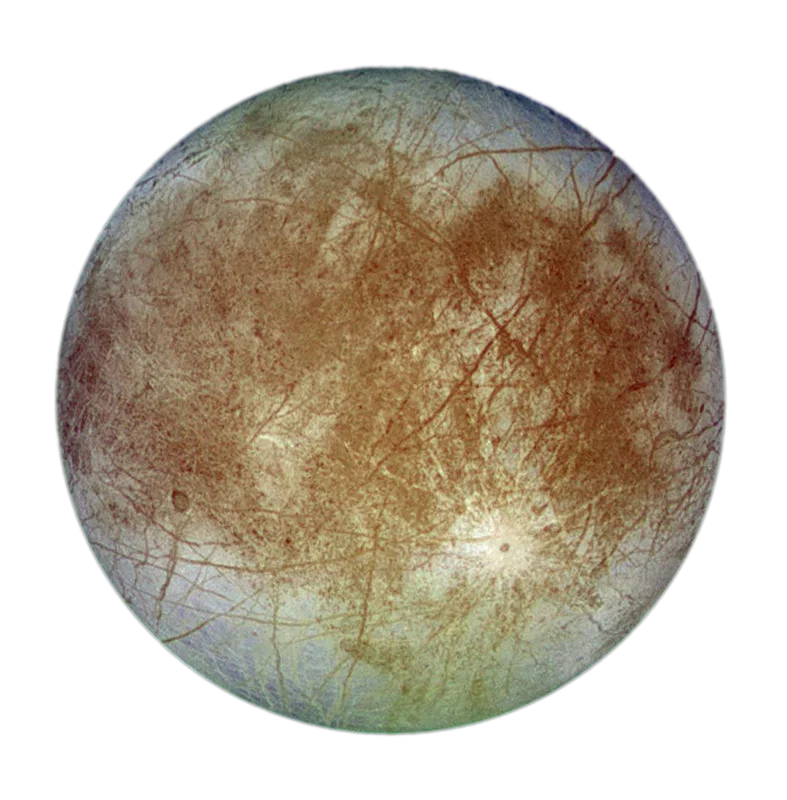
Europa
tectonic fractures dominate icy surface
most likely place to find liquid water near surface
young
lots of active tectonism
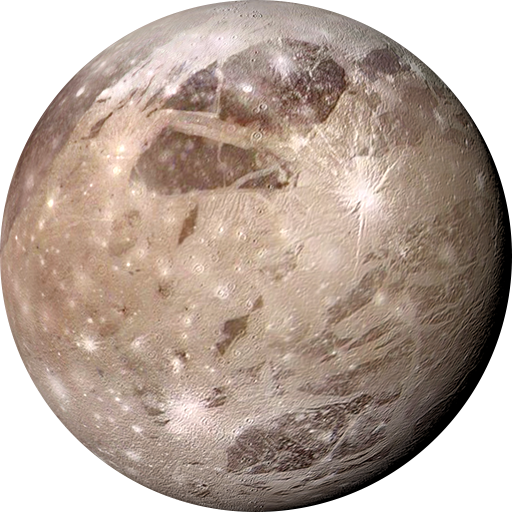
Ganymede
grooved terrain from tectonic disruptions of cratered surface
largest satellite
has its own magnetic field

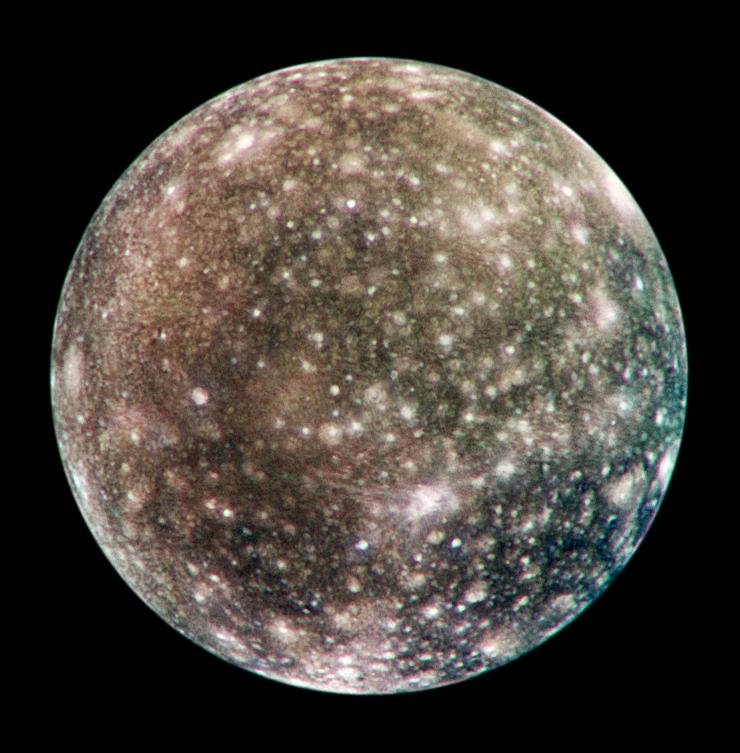
Callisto
tectonically inactive
oldest surface (most cratered)
greater thickness of ice
coldest surface

Triton
small
rich in nitrogen ice
has a water ice lithosphere
has a rocky core
is in retrograde
too cold for liquid nitrogen
neptune’s moon
its orbit is distinctive because it is in retrograde
most like Pluto
Uranus
has a magnetic field that is tilted with respect to the axis of rotation
thought to have water in its interior
it has an unexpected orientation
it is irregular and may be experiencing a reversal
condensation in a thermal gradient
blue color from methane
planetary rings
large body impacts
cooling and satellite expansion
too small and the internal temperature and pressure are not high enough for metallic hydrogen
its spin axis is tipped from vertical by over 90 degrees

Neptune
has a magnetic field that is tilted with respect to the axis of rotation
thought to have water in its interior
orbital evolution
tidal heating
icy volcanism
low surface temperatures
methane ice clouds

Titan
has an atmosphere rich in nitrogen and methane
the only satellite known to have a substantial atmosphere
the biggest moon of Saturn
has liquids that flow on its surface- hydrosphere!
the only moon with dunes
Moon
planetary body that has the oldest surface
small planet
impact cratering processes
geologic time
volcanic processes
tectonic processes

rocky surface
Mercury
Venus
Earth
Mars
Gas until very deep
Jupiter
Saturn
Uranus
Neptune
Pluto
Earth
ideal for the rise of life
resides in the habitable zone where water is abundant and liquid on the surface
larger moon stabilizes the tilt, preventing climate extremes and creating tidal zones where life could form
large planet
long history with young surfaces
plate tectonics
flow of surface fluids (air and water)
biosphere
effect on atmosphere and tectonics
modest temperature!
carbon dioxide was removed from atmosphere and life evolved and added oxygen

challenges in finding extrasolar planets
planets don’t produce light on their own
they are very far away
they are lost in the blinding glare of the star
radial velocity
swaying of star due to planet’s gravity
transit
planet crosses in front of star
gravitational lensing
stars bend light around
the gravity of a massive object bends and distorts the path of light from a distant object behind it
direct imaging
taking actual pictures of planets orbiting other stars
there is a planet around
just bout every star
asteroids
small planets
short histories
condensation in solar nebula
collisional histories
planetary differentiation
Mercury
heat and the strength of the lithosphere
warm and weak
cooling and contraction
iron rich planet
planet can stay warm enough to maintain a magnetic field
thrust faults across the surface
lots of craters

Mars
larger planet
has an atmosphere
eolian processes
fluvial processes
tectonism
mantle plumes
volcanism
lots of lava flows

Venus
large planet
long history with young surfaces (no heavily cratered terrains)
tectonics
mantle plumes
counterplumes
atmosphere evolution
greenhouse effect
hgh surface temperatures and pressures
makes it hard for us to explore
Jupiter
condensation in a temperature gradient
so large because ice was stable
Io, Europa, Ganymede, and Callisto variations
composition differences in “mini” accretion disk
icy lithosphere
tidal heating
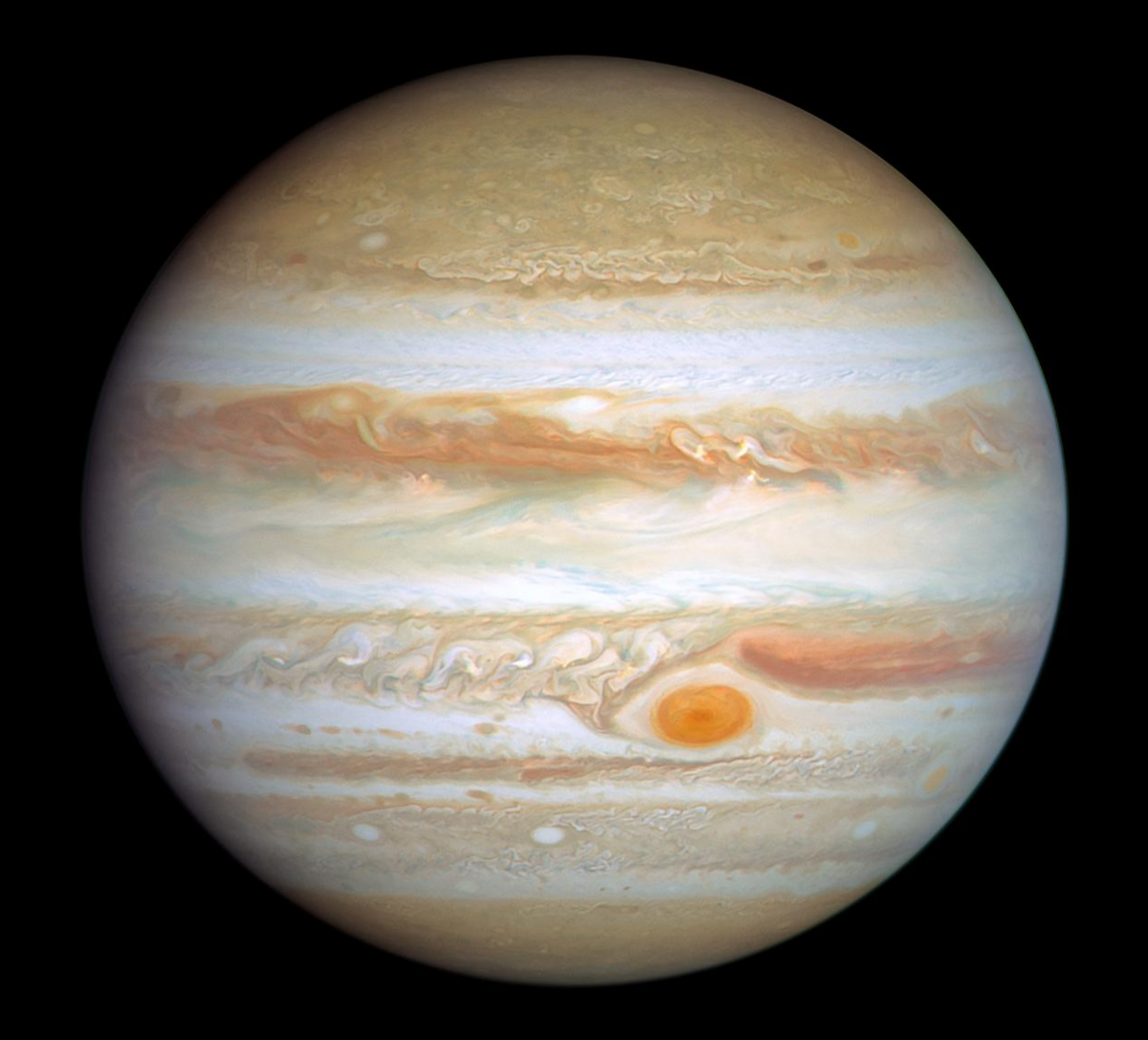

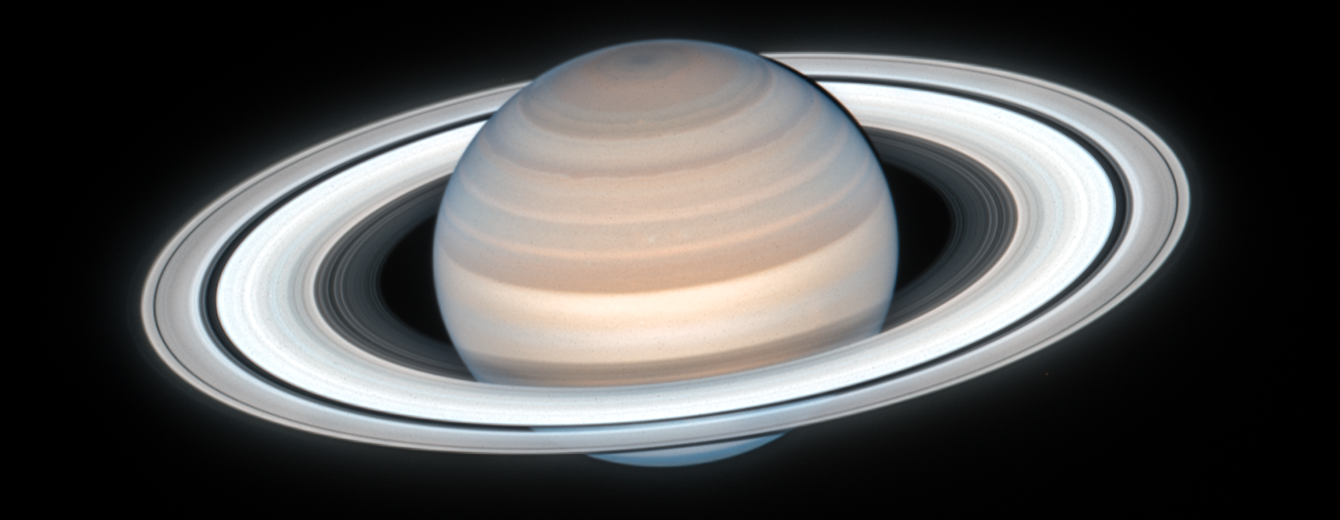
Saturn
planetary rings (are the biggest and brightest here!)
tidal heating on moons
icy lithospheres on moons
cooling and satellite expansion (which may lead to cracks)
contains global rifts caused by expansion because of ice
driven by heat released from the interior
Hydrogen is the MOST ABUNDANT GAS!
most similar in composition and internal structure to Jupiter
has a yellowish tint because of crystals of ammonia ice in the clouds
magnetic field formed by convection in a shell of metallic hydrogen

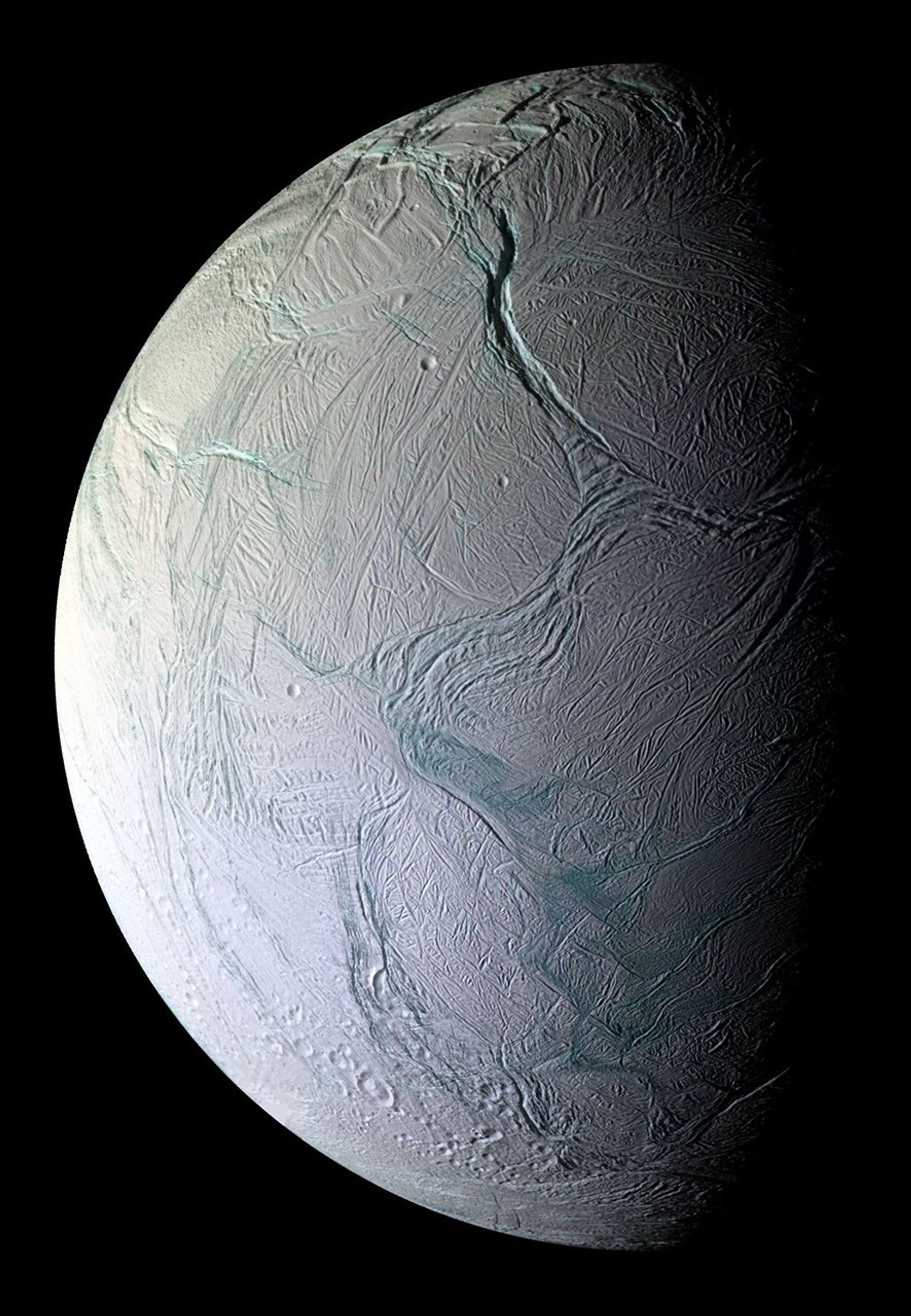
Enceladus
saturn’s small, but still active, moon must be heated by tidal forces

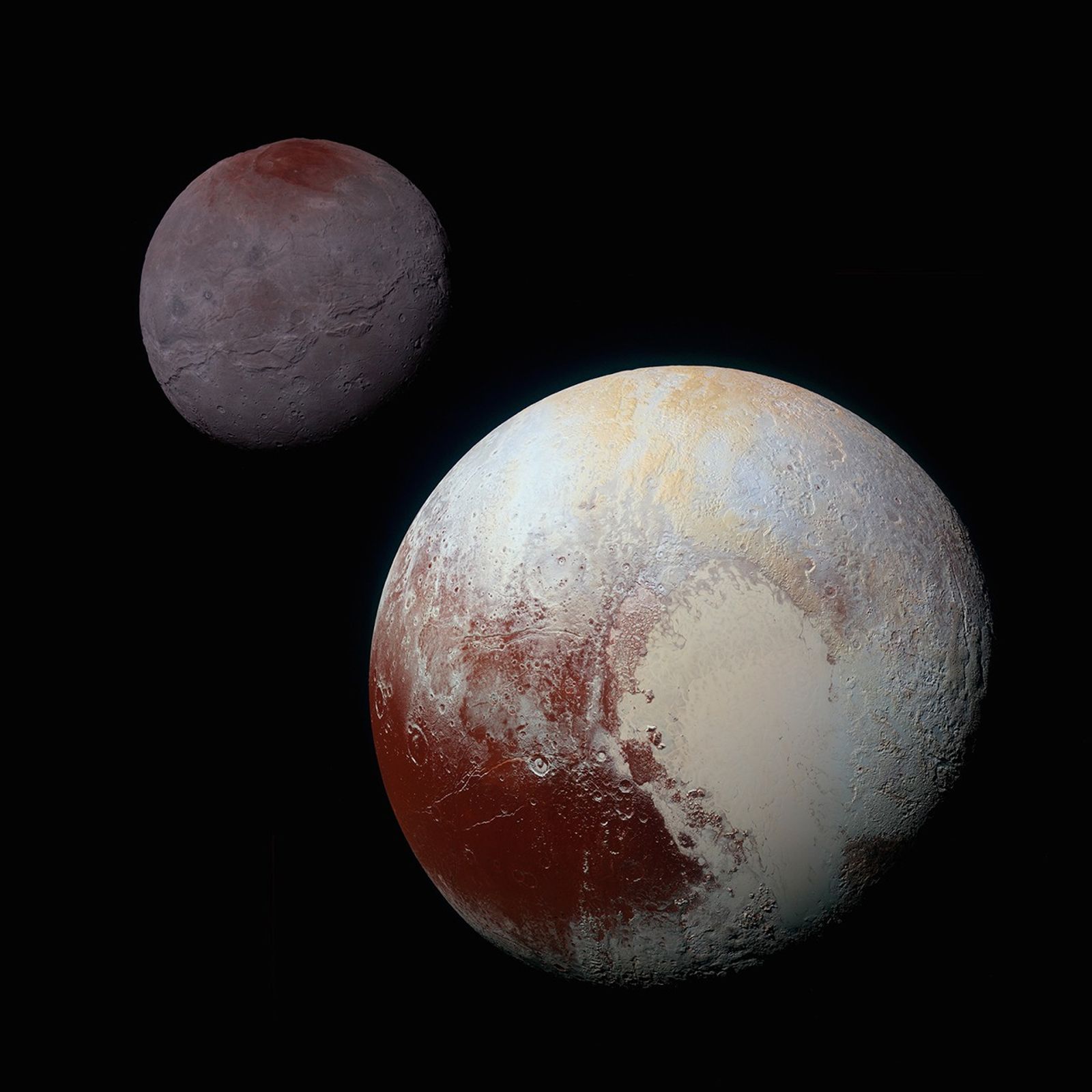
pluto and charon
condensation in a temperature and mass gradient
glacial flow
ice tectonics
lots of heavy impact craters
tall mountains are made from WATER ice
nitrogen and methane are in its atmosphere

comets
orbital evolution
condensation in a thermal gradient
sublimation
planets from smallest to largest
Asteroid, Pluto, Mercury, Mars, Venus, Earth, Neptune, Uranus, Saturn, Jupiter
planets from closest to sun to farthest to sun
mercury, venus, earth, mars, jupiter, saturn, uranus, neptune, pluto, asteroid
My Very Educated Mother Just Served US Nine Pizzas Ah!