ISP 205 Exam 3
1/48
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
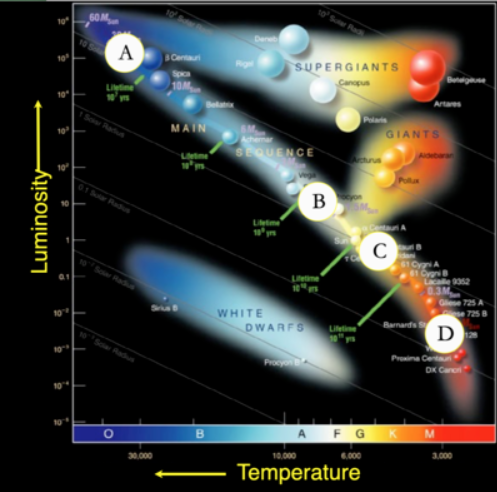
Which Star is the brightest?
A
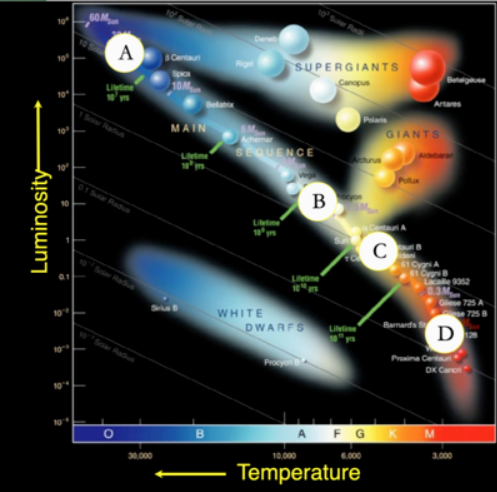
Which star will change the Least over the next 10 billion years?
D
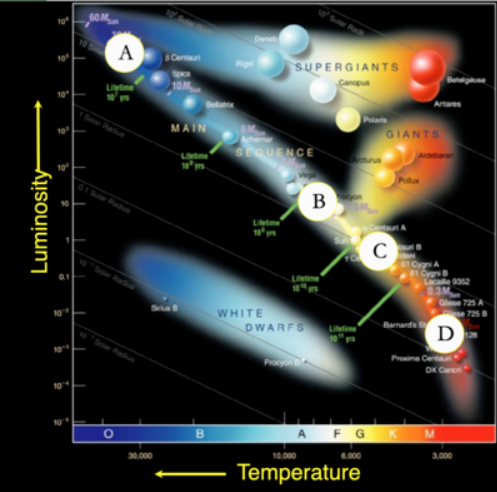
Which star can be no more than 10 million years old?
A
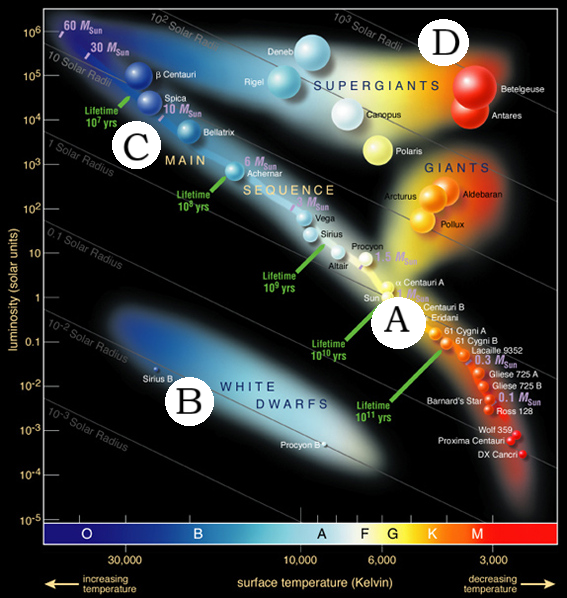
Which star is the biggest?
D
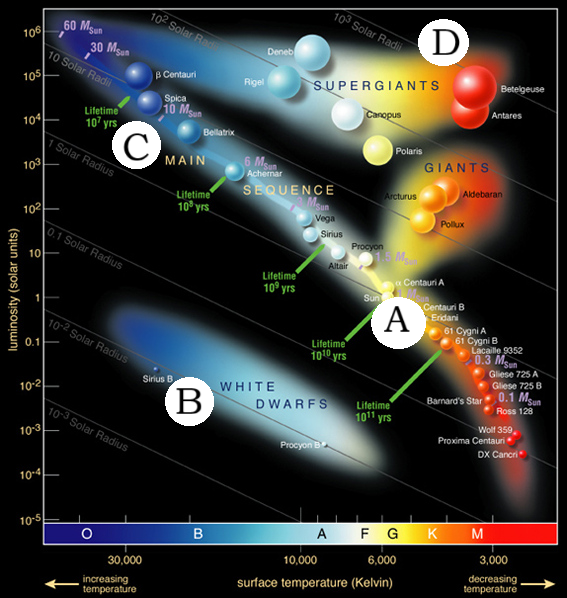
Which star is Most like our sun?
A
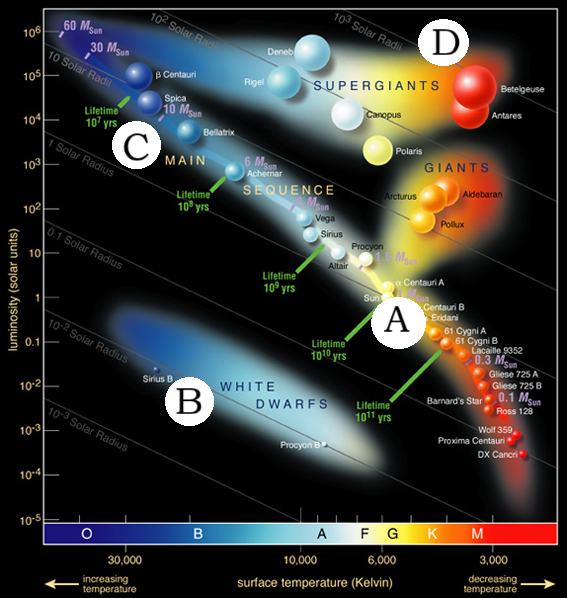
Which star is the Hottest?
C
What is the spectral type of our Sun?
G

Which star cluster is the youngest?
C. just blue stars
What color of star is the Hottest
Blue Stars
When does a protostar become a main-sequence star?
when the rate of hydrogen fusion becomes high enough to balance the rate at which the star radiates energy into space
Approximately what core temperature is required before hydrogen fusion can begin in a star?
10 million K
gravitational equilibrium
A state of balance where the force of gravity pulling inward is counteracted by an opposing outward pressure
Energy Balance
Net energy produced by a fusion reaction is the difference between the fusion power generated and the power required to maintain the reaction.
When the core of a star like the sun uses up its supply of hydrogen for fusion, the core begins to _____.
Shrink and Heat
Hydrogen Shell Fusion
High Mass Star
A star that is more than 8 times the mass of the Sun. Hot enough to make all elements possible.
Low Mass Star
A star that is less than 2 times the mass of the Sun. Only hot enough to make carbon and some oxygen.
Intermediate Mass Stars
A star that can make heavier elements, by is eventually stopped by degeneracy pressure.
What happens to a stars surface during core contraction?
Larger, Redder, and Brighter
What type of stars end as a planetary nebula and white dwarf?
Low-to-average mass stars
What type of stars explode in a supernova and leave behind a neutron star or black hole?
Massive stars
7 main types of stars in order.
OBAFGKM
Stars are born in
Cold, dense clouds of gas whose pressure cannot resist gravitational contraction.
Molecular clouds
Cool, dense interstellar clouds in which the low temperatures allow hydrogen atoms to pair up into hydrogen molecules
What happens to the core of a star if its fusion rate is too low to replace the energy it radiates from its surface?
It contracts and heats up
Degeneracy pressure
A type of pressure unrelated to an object’s temperature
Thermal pressure
The ordinary pressure in a gas arising from motions of particles that can be attributed to the object’s temperature.
Brown dwarfs are supported against gravity by _____________, which does not weaken with decreasing temperature.
Degeneracy Pressure
A high-mass star’s death is imminent when what element piles up in its core?
Iron
What happens when a main-sequence star exhausts its core hydrogen fuel supply?
The core shrinks while the rest of the star expands.
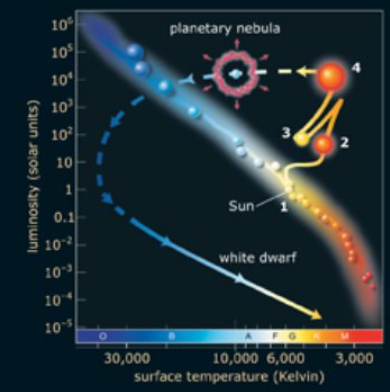
This H-R diagram shows the life track of a 1 M Sun star from the time it first becomes a main-sequence star. Which numbered point represents the star when it has both hydrogen-fusing and helium-fusing shells around an inert carbon core?
Point 4
Stars that are fusing hydrogen in their cores are
Main Sequence Stars
A star that is expanding (into a subgiant and then a giant) has a(n)
Inert Helium Core
When it dies, a high-mass star explodes as a
Supernova
When it dies, a low-mass star expels a
Planetary Nebula
A typical neutron star is more massive than our Sun and about the size (radius) of _________.
a small asteroid (10 km in diameter)
Pulsars are thought to be _________.
rapidly rotating neutron stars
What do we mean by the event horizon of a black hole?
It is the point beyond which neither light nor anything else can escape.
Imagine that our Sun were magically and suddenly replaced by a black hole of the same mass (1 solar mass). What would happen to Earth in its orbit?
Nothing. Earth’s orbit would stay the same.
The Schwarzschild radius of a black hole depends on ________.
the mass of the black hole
Gravitational waves were first detected directly in 2015. According to models, the source of these gravitational waves was __________.
the merger of two black holes
A white dwarf can remain stable in size because of
Electron Degeneracy Pressure
Pulsar
Rapidly rotating Neutron Star
Nova
occurs when fusion ignites on the surface of a white dwarf.
The Singularity
The place to which all of a black hole's mass is in principle located within the black hole.
Event Horizon
The boundary between the inside and outside of a black hole.
Escape Velocity
The minimum speed needed for an object to escape from contact with or orbit of a primary body.
Neutron Degeneracy Pressure
A quantum-mechanical force that prevents neutrons from being compressed further. It is a counter-force to gravity in objects like neutron stars.
Electron degeneracy Pressure.
Quantum mechanical force that prevents the collapse of very dense matter.