1. Foodborne illnesses
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
What kind of foods have the highest chance to have foodborne ilness?
Mainly food of animal origin, such as: meat, poultry, raw milk, eggs, (shell)fish
Intoxication vs Infection
Intoxication: toxin in the food
Infection: invasion in gastrointestinal tract (by microbes)
Time range intoxication vs infection
Intoxication: toxin production in food, ill after 0-6 hours
Nausea, vomiting, duration ~1 day
Infection: Caused by microbes
Ill after 8- 24 hours
Nausea, diarrhea, stomach ache, duration of a few days
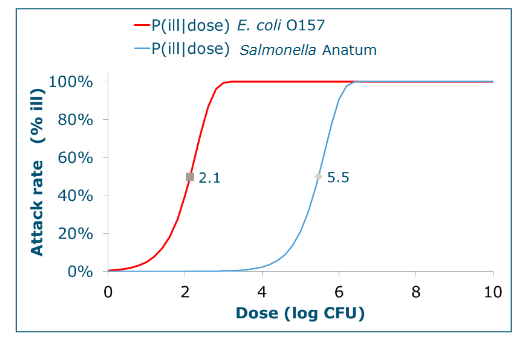
Dose response relation (D/R)
Graph that describes attack rate, how ill someone is, compared to the dose they had.
host susceptibility
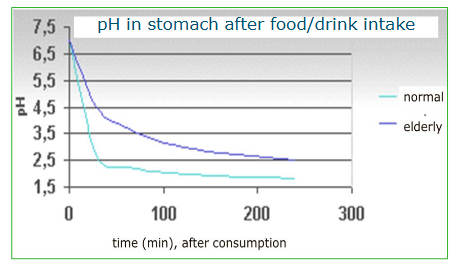
Older people have higher pH meaning that microbes can survive more easily in their stomach and can effect them.
Transmission of foodborne diseases
Dependent on ecology of m.o./reservoir
Environment
Spread via faeces
Direct: host to host (human, farm-/pet animals)
Indirect: vector*/fomites/water/food
Kitchen
vector: like a vehicle to transport microbes e.g. cutlery
Example of spreading of disease through animal gut
Chickens are healthy carriers of Campylobacter in their gut
These bacteria can be spread via feces into the environment.
Cross contamination
The transfer of microbes from one food to another, specifically from raw to cooked products.
Are foodborne illnesses always reported enough?
No they are underreported, making its true incidence difficult to ascertain.
What are the major contributing factors to foodborne illness?
Temperature and time mismanagement
Inadequate cooling
Prolonged storage at ambient temperatures
Insufficient heating
Undercooking and cross contamination
Why are elderly more susceptible to microbes
The pH in their stomach goes down slower than in a young adult. Therefore the pH might not be as low.
What are vectors?
Vectors are organisms that carry and transmit an infectious pathogen to another living organism or food.
What are fomites?
Inanimate materials that can transmit pathogens.