motion
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
motion
occurs when an object changes changes position reative to a referance point
scarlars
have size only, no direction
scalars examples
Length, Time, Speed
scalars size represented
by number e.g speed (55m/s)
vectors
have size and direction
vector examples
Displacement, Velocity, Force, Momentum
vectors size represented
by number w/ a unit e.g velocity (33m/s, west)
vectors direction represented
N/S/E/W or an arrow
how they relate to motion
measurements such as force momentum, speed and time define how much motion occurs
distance
symbol: d
how far apart two objects are
units: m and km
always positive number
distance example
You swim an 100 meter lap in a race. You then swim another 100 meter lap, back to where you started, the distance you’ve travelled is 200 meters.
displacement
symbol: s
a straight line from start point to end point
can be positive or negative
units: m and km
vector: include direction
displacement example
You swim an 100 meter lap in a race. You then swim another 100 meter lap, back to where you started, the displacement is zero.
speed
symbol V
rate at which an object moves over a distance
scalar
m/s or km/m
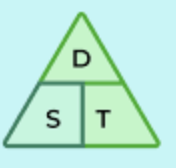
speed formula: as well as distance + time
speed form: s:d/t
d= distance
s: speed
t: time
if you have a distance in m and a time in s then speed with be
m/s
if you have a distance in km and a time in hr than speed will be
km/h
average speed
average speed of an object throughout journey
average speed calculated for speed
using V= d/t
( does not count for changing speed, starting or stopping)
instantaneous speed
speed at particular instant
e.g speed camera
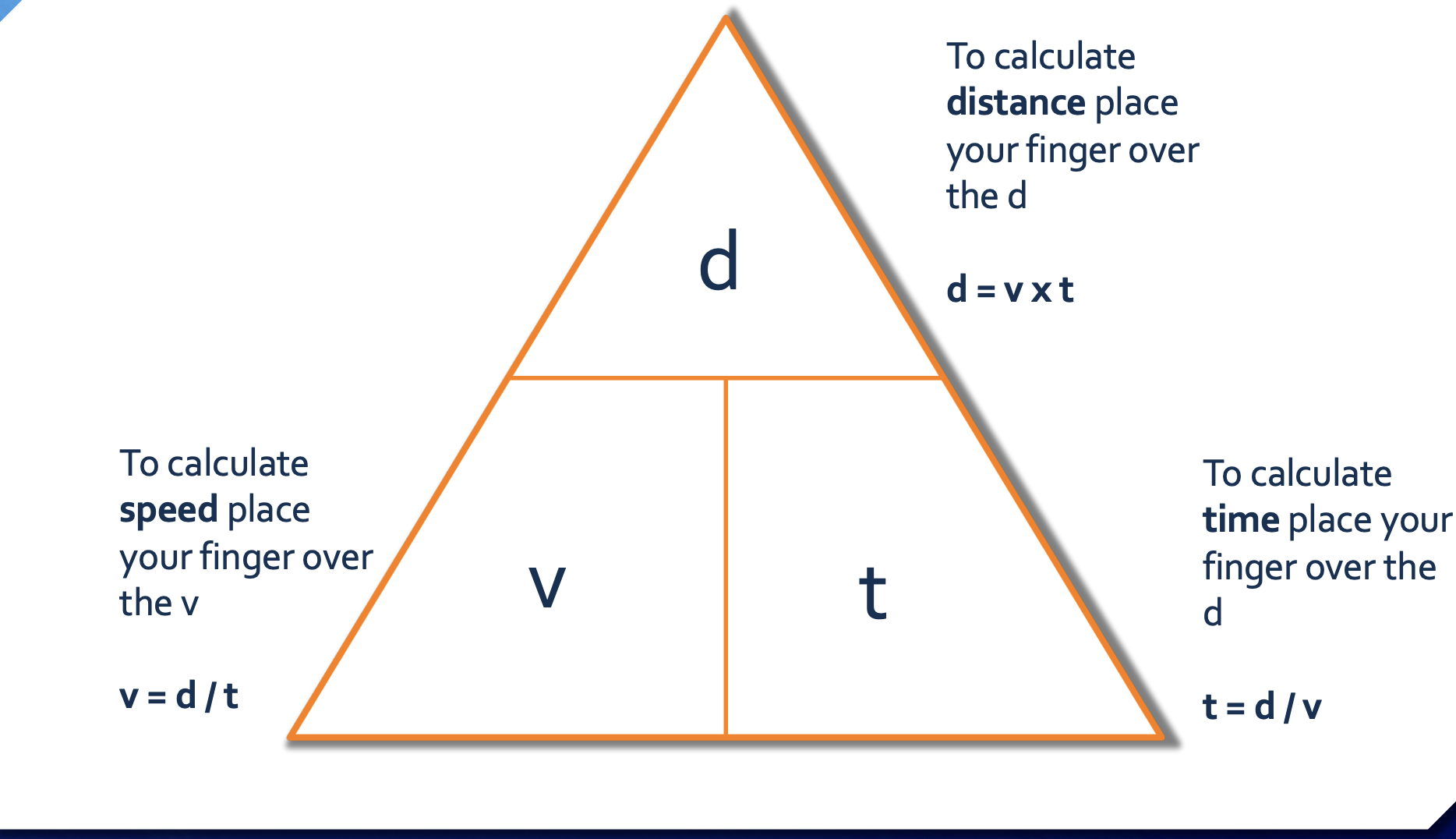
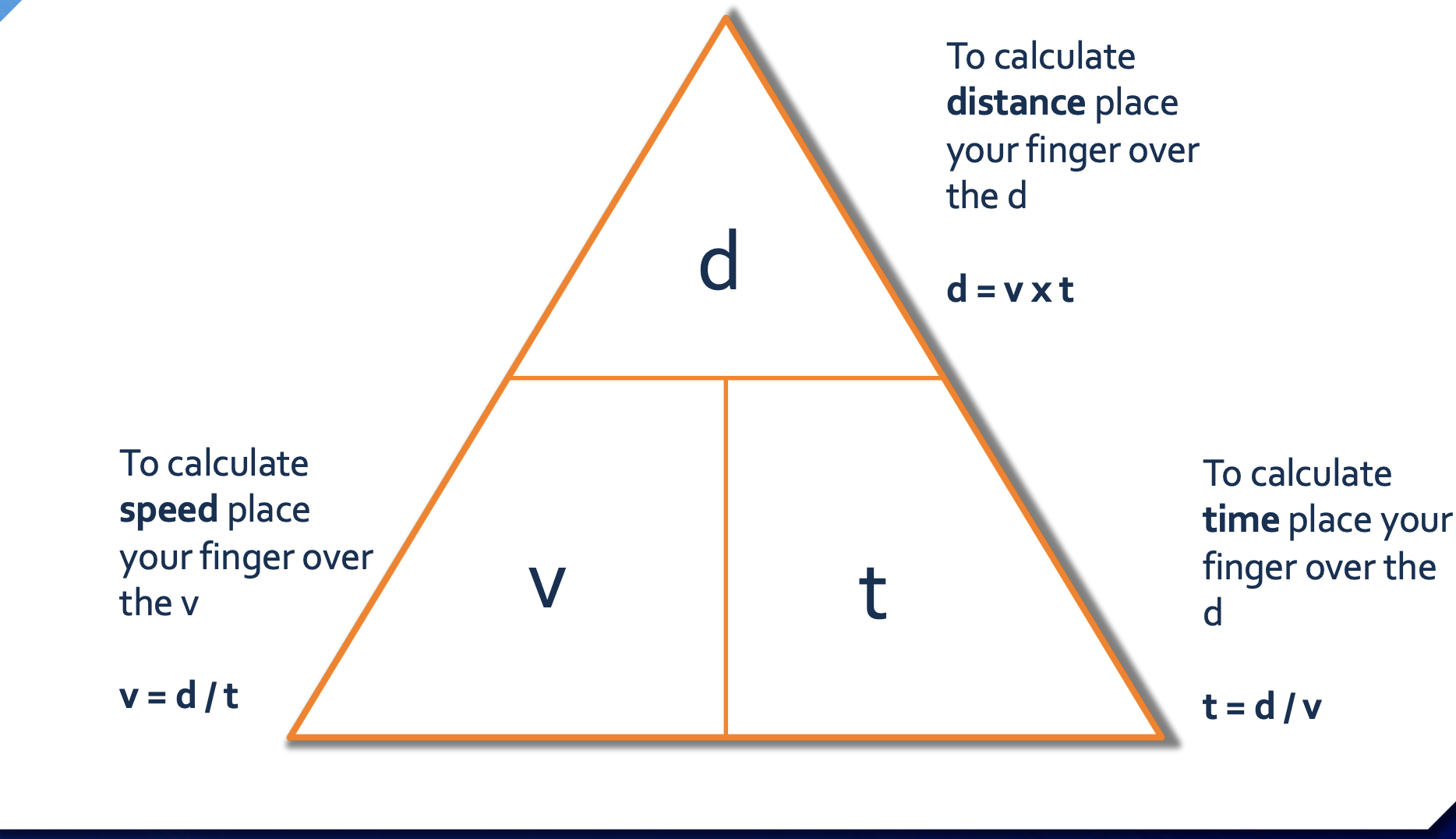
triangle formula ofIDK
d= v x t
d= distance
v= velocity/speed
t= time
acceleration definition
rate of change in velocity over time
can be both positive or negative
why is acceleration a vector
has both a direction and magnitude
acceleration units
units: m/s/s, m/s2, ms-2 OR km/h/s
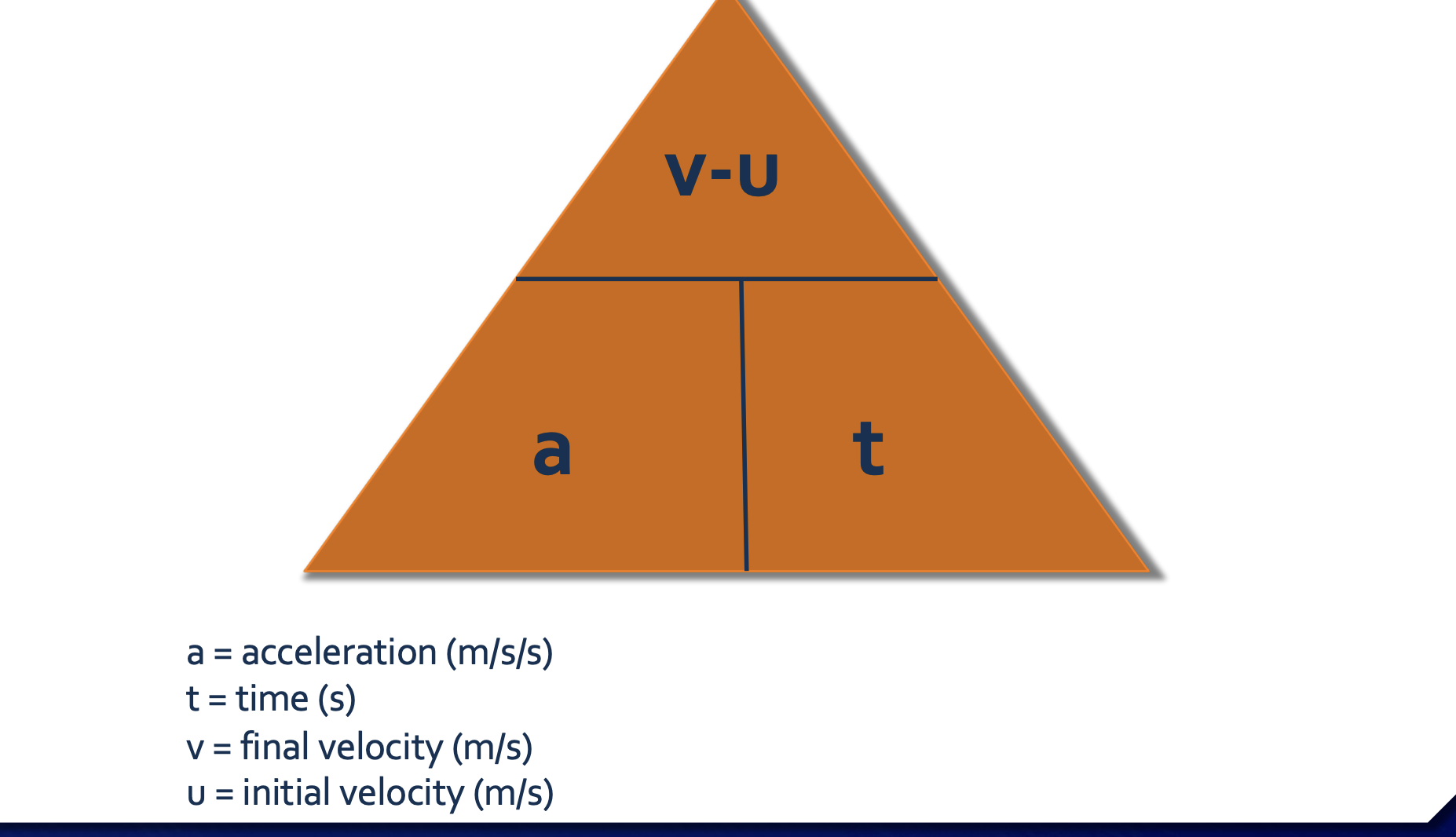
acceleration formula
a= v-u / t
a= acceleration
v= velocity
u= initial velocity
t= time
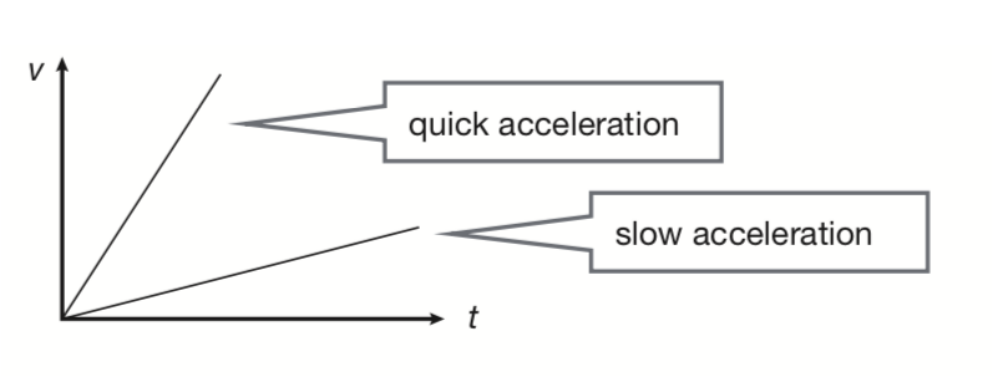
graphing acceleration- quick + slow
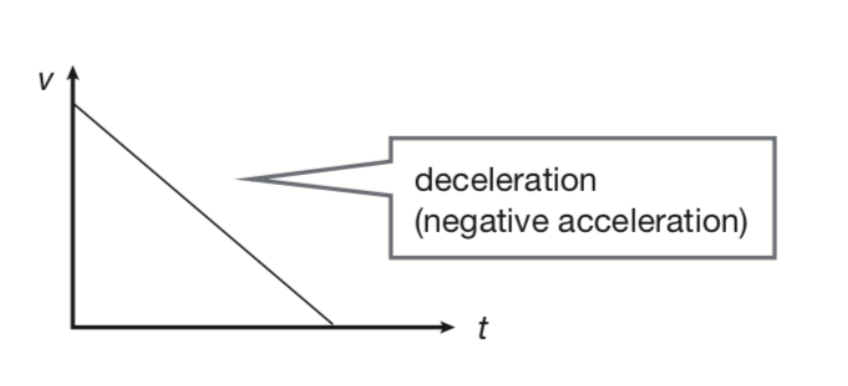
graphing acceleration- deceleration
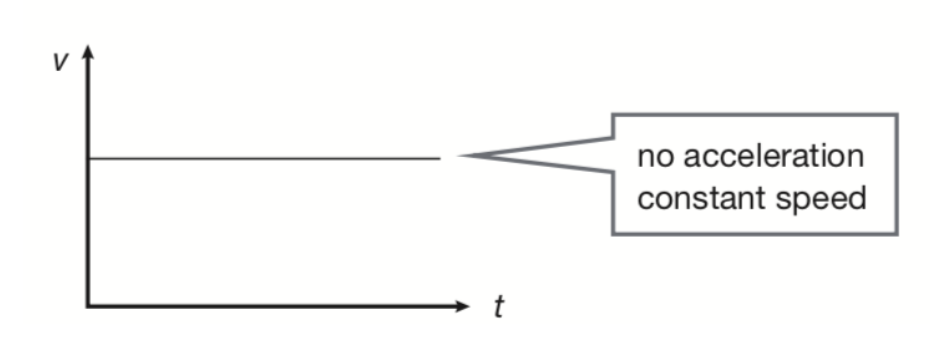
graphing acceleration- no acceleration
acceleration due to gravity (9.8m/s2)
every second an object is in free fall, gravity will cause the velocity of the object to increase 9.8 m/s. (each second +9.8)
The maximum speed it can reach will be affected by
air resistance
How much force a human can tolerate depends on:
how big the force is
how long it lasts
the direction in which it acts
the part of the body that is affected
(vertical drop dangerous as blood flow to the brain can be disrupted)
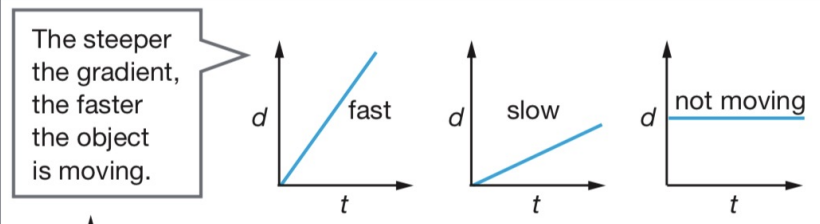
distance time graphs
steeper slope= faster
less steep= slower
flat line= stationary
finding gradient will find speed
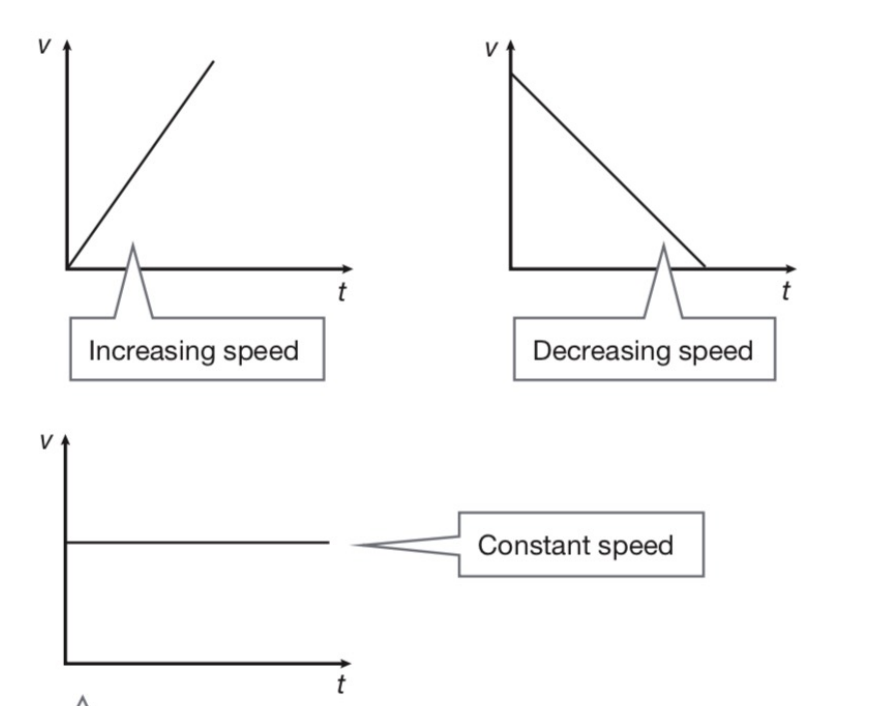
speed time graphs (velocity)
upwards: speed increasing
downwards: speed decreasing
flatline: constant speed
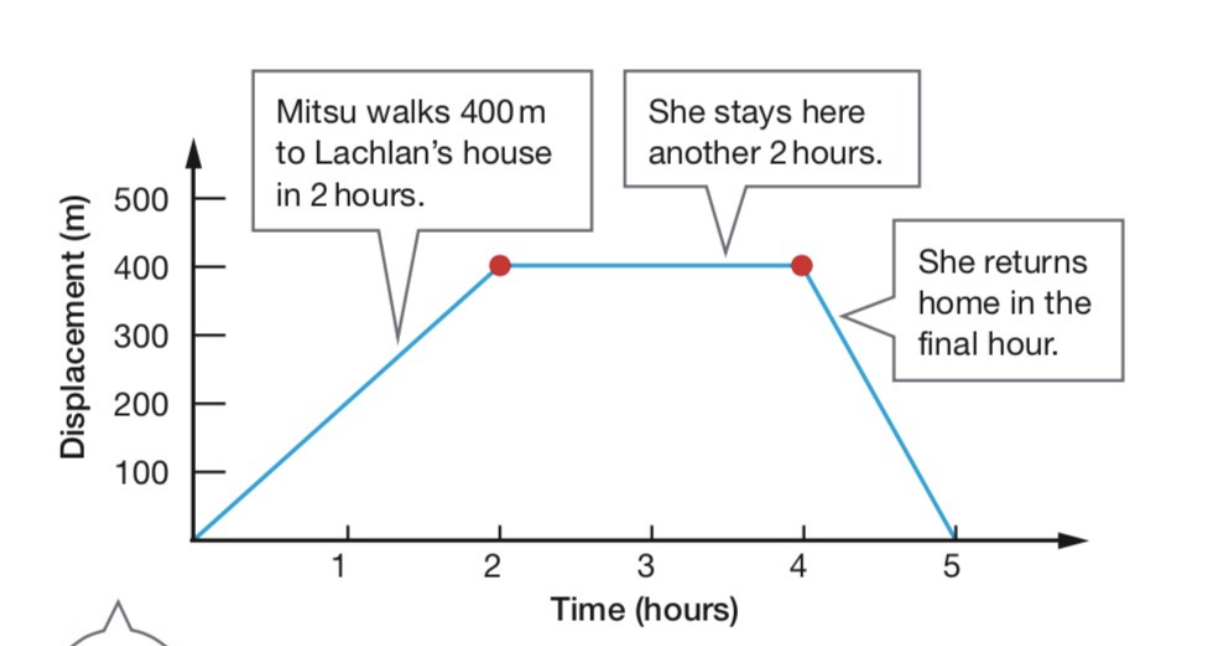
displacement time graphs
slope up: moving away from start
slope down: moving back to start point
flatline: stationary
force
a push or pull motion that alters an object
e.g speeding it up
symbol: F
unit: N (newtons )
vector
newtons first law
an object at rest will remain at rest unless it is acted upon by a force
also applies to moving objects
will keep going at same speed and same direction until a force acts
first law- inertia
an objects tendency to resist any chance in motion e.g on a moving train
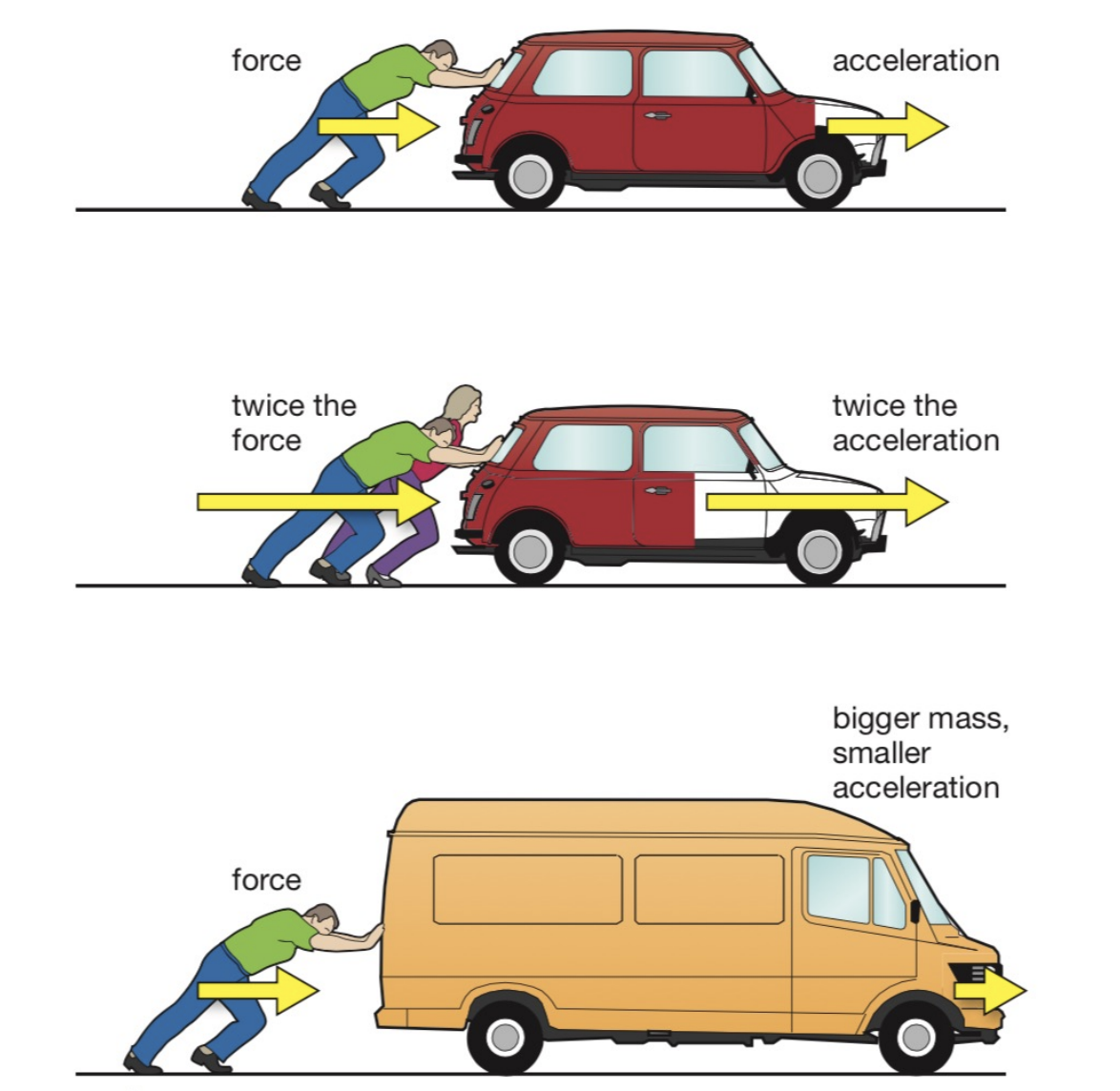
newtons second law
an object will accelerate in the direction of an unbalanced force acting upon it
the acceleration will depend on mass of object + size of force
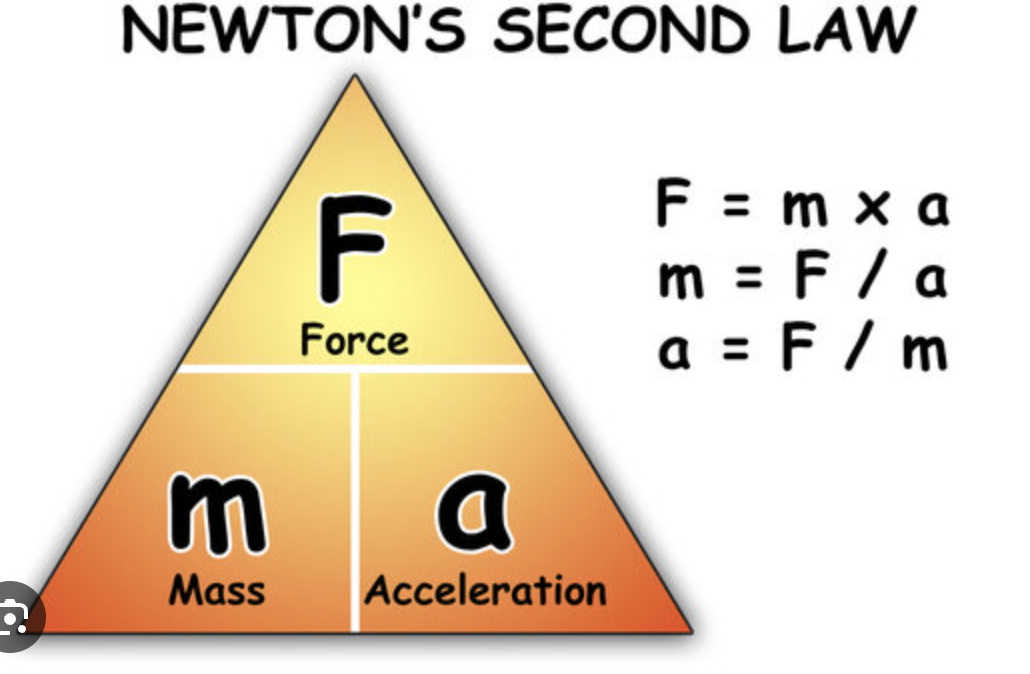
F= m x a
f=m x a
F= force in newtons
m= mass in kg
a= acceleration m/s2
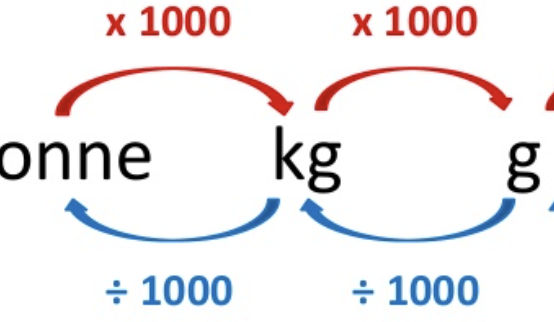
grams → kg → t
1000
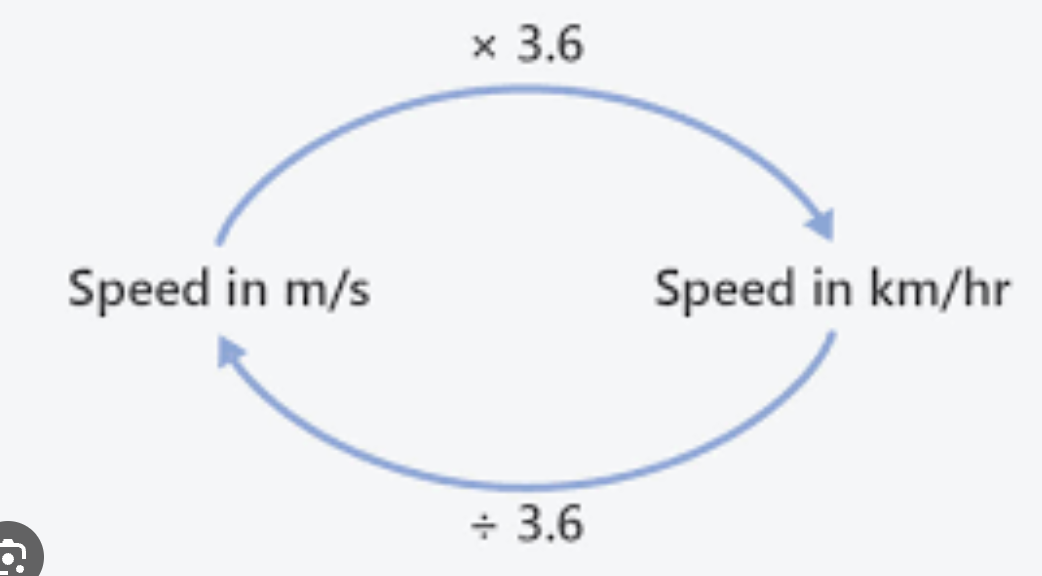
m/s → km/h
3.6
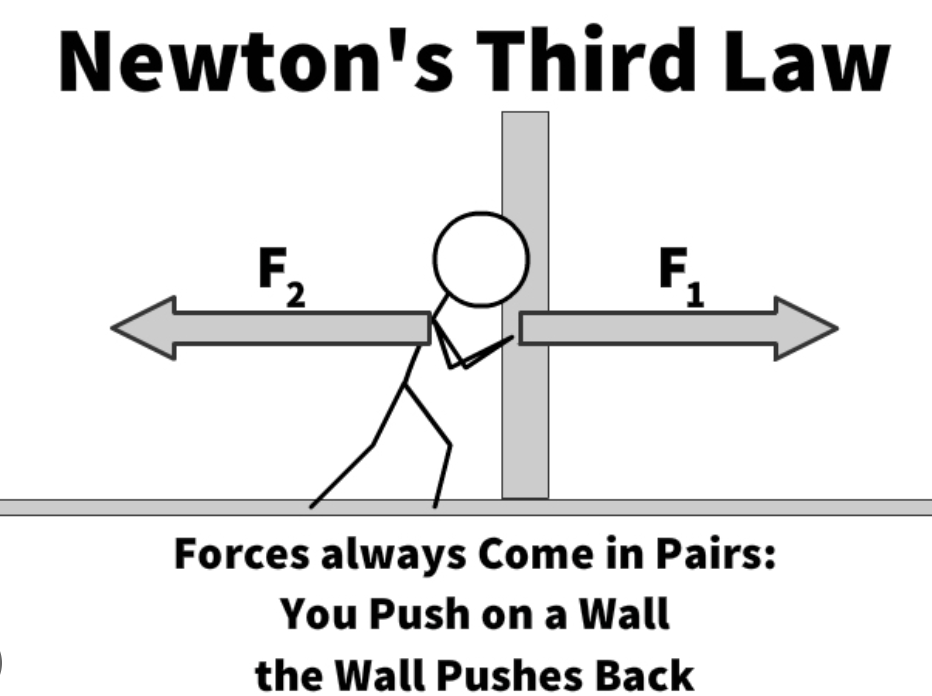
newtons third law:
for every force there is an equal and opposite reaction force
example of force- same direction
add the numbers together
example of force- opposite direction
subtract the numbers from each other
if arrow same direction: add
if arrow opposite: subtract
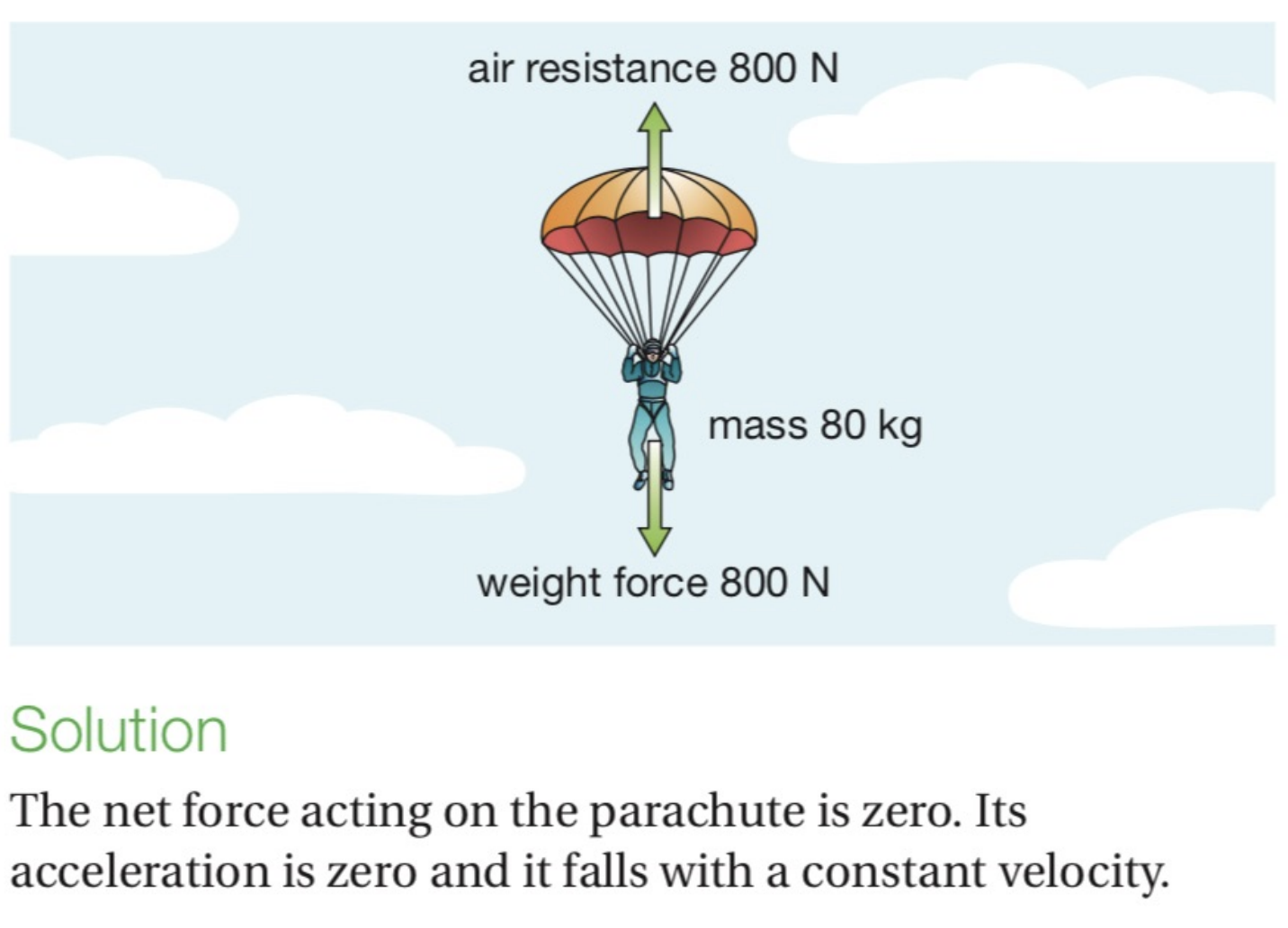
balanced force
equal and opposite forces acting on an object
• will not result in any change of movement
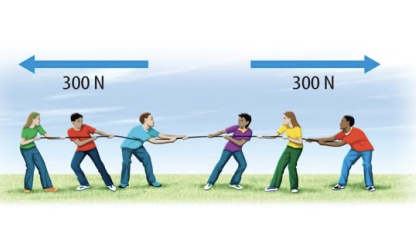
unbalanced force
unequal forces acting on an object
• will result in change of speed, change of direction, change of shape, stopping or starting to move
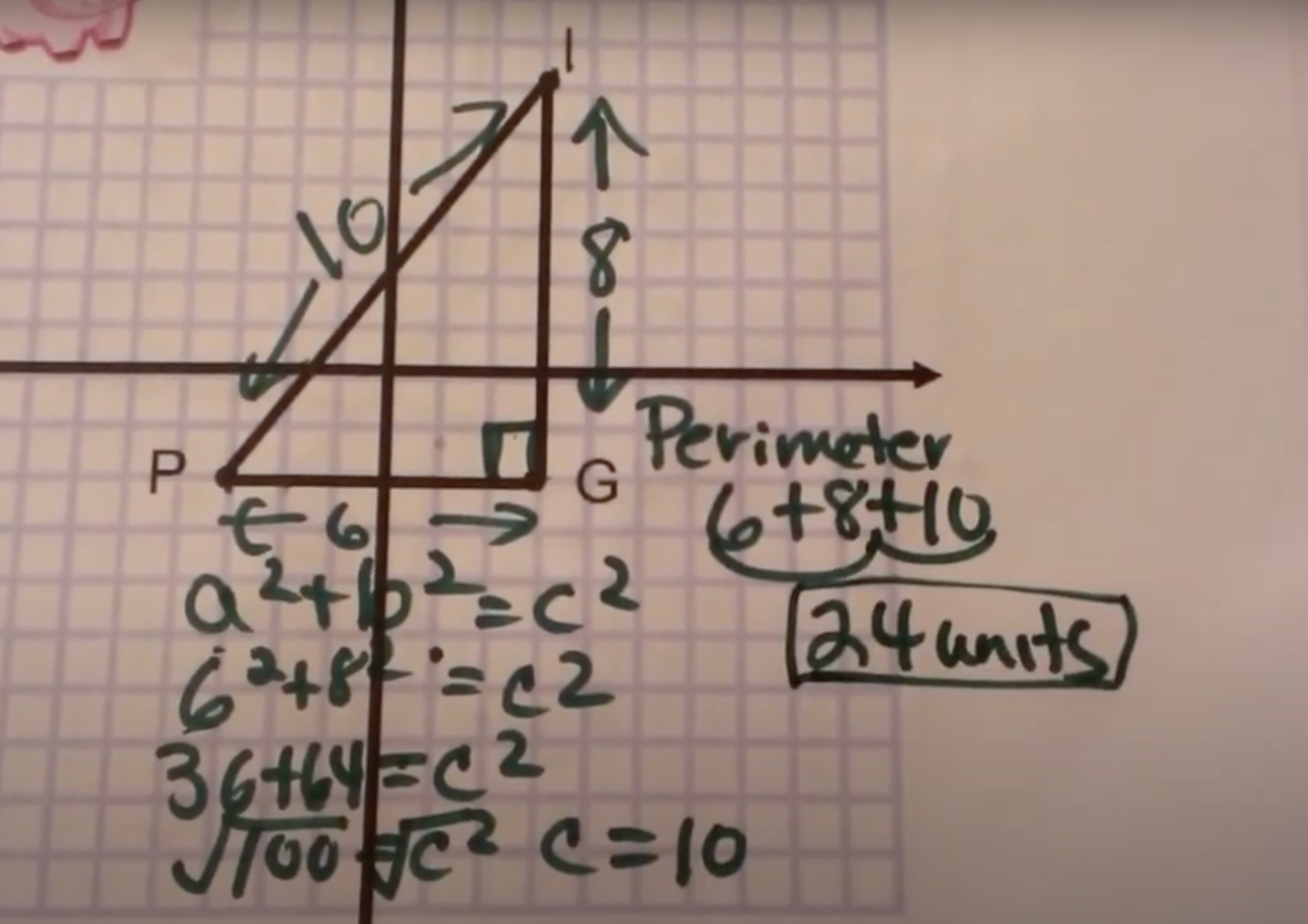
finding distance using
Pythagoras a2+b2=c2
motion graph example
net force
the total force acting on an object, calculated as the vector sum of all individual forces