Chem 8LC
1/73
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
The solids obtained by vacuum filtration is mostly pure. Which of the following statements is false?
the product is a solid that can be isolated by filtration
most unreacted indene should pass through the filter because it is a liquid
acetonitrile and indene are possible impurities contaminating the product
formation of a diastereomeric product is possible, which can contaminate the major product
vacuum filtration is capable of removing impurities because it is similar column chromatography
vacuum filtration is capable of removing impurities because it is similar column chromatography
You will be "rotovapping" a 1:1 mixture of acetonitrile/water. It is unlikely that all of the solvent will evaporate. Which solvent will remain and why?
acetonitrile will remain because it has a higher boiling point
acetonitrile will remain because it has a lower boiling point
acetonitrile will remain because it is organic and organic solvents are harder to evaporate
water will remain because it was a higher boiling point
water will remain because it has a lower boiling point
water will remain because it has a higher boiling point
What is Oxone?
O2
O3
KHSO5
KHSO4
a 2:1:1 mixture of KHSO5/KHSO4/K2SO4
a 2:1:1 mixture of KHSO5/KHSO4/K2SO4
How many mL of indene should you measure out if 2.15 mmol is required for the experiment? The density, ρ, of indene 0.997 g/mL.
0.233mL
2.33mL
0.025mL
0.25mL
2.5mL
0.25 mL
Oxone consists of a 2:1:1 molar mixture of KHSO5 (152.20 g/mol), KHSO4 (136.17 g/mol), and K2SO4 (174.26 g/mol). KHSO4 and K2SO4 act to stabilize the active oxidant. Based on their molecular weights, approximately 49.5% of the Oxone reagent measured out will correspond to the active oxidant. How many mmol of KHSO5 is present in 1 gram of Oxone?
3.29 mmol
Which of the following is not a vicinal halohydrin?
A
B
C
D
E
D
Which of the following atoms or groups are arranged in a vicinal relationship?
OH and CH3
Cl and H
OH and Ph
OH and F
Cl and CH3
OH and CH3
Will this reaction be successful in producing an iodonium ion?
Yes: NaI is a good source of iodine
Yes: NaI is a good electrophile
No: the alkene is a poor nucleophile
No: iodonium ions are unstable
No: NaI is not an electrophilic iodine source
No: NaI is not an electrophilic iodine source
Which is the correct chloronium ion formed in the following reaction?
A
B
C
D
E
B
Why does the nucleophile attack the halonium ion? [select multiple]
the halonium ion is electron-rich and likes electrons
the halogen is electronegative and renders the adjacent carbon atoms electrophilic
attacking the halonium ion opens the 3-membered ring to produce a molecule with less strain
the nucleophile is electron-poor and therefore interacts with the electron-rich halonium ion
the halogen is electropositive and renders the adjacent carbon atoms nucleophilic
the halogen is electronegative and renders the adjacent carbon atoms electrophilic
attacking the halonium ion opens the 3-membered ring to produce a molecule with less strain
Which of the following are true regarding alkenes?
alkenes contain a triple bond
alkenes and olefins refer to different functional groups
alkenes are C=N bonds
alkenes are C=O bonds
alkenes are C=C bonds
alkenes are C=C bonds
How many alkenes are in palbociclib?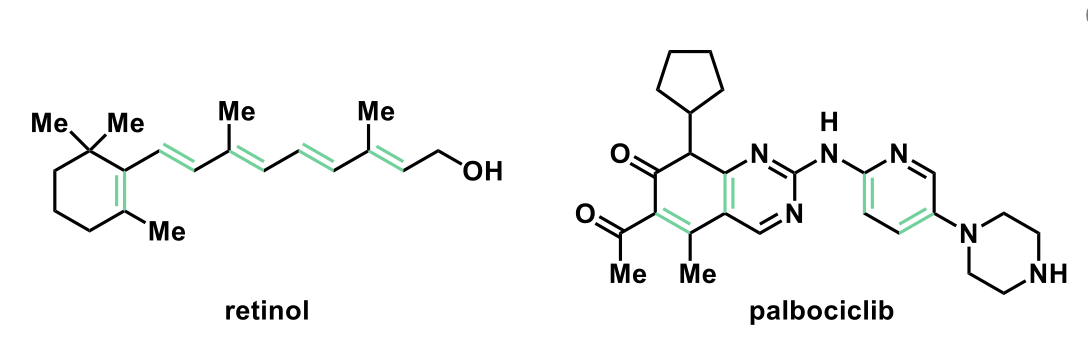
2
3
4
5
6
7
4
Which of the following statements are FALSE regarding carbonyl compounds?
aldehydes and ketones are carbonyl compounds
carbonyl compounds have C=O bonds
carbonyl compounds have triple bonds
amides and esters are carbonyl compounds
none of the above
carbonyl compounds have triple bonds
Is the product of this reaction a stabilized or unstabilized ylide?
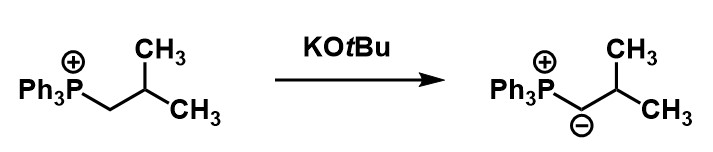
stabilized ylide
unstabilized ylide
neither stabilized nor unstabilized
not enough information to determine
unstabilized ylide
Which of the product is correct for this reaction?
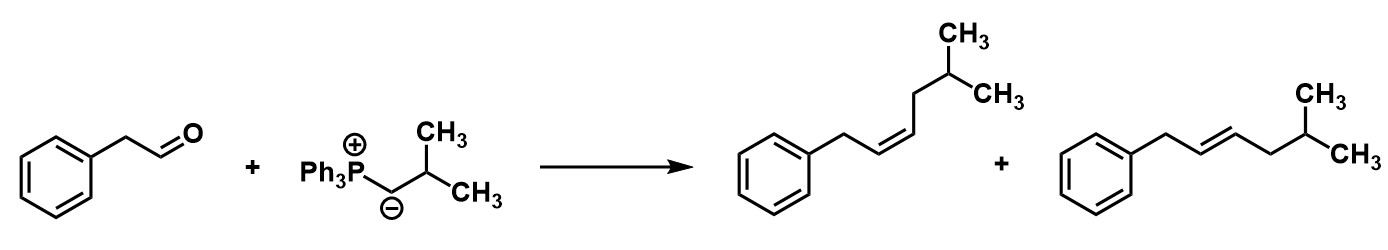
Z-alkene
E-alkene
both are correct
both are incorrect
Z-alkene
How many hydrogens are on each of the indicated carbons?
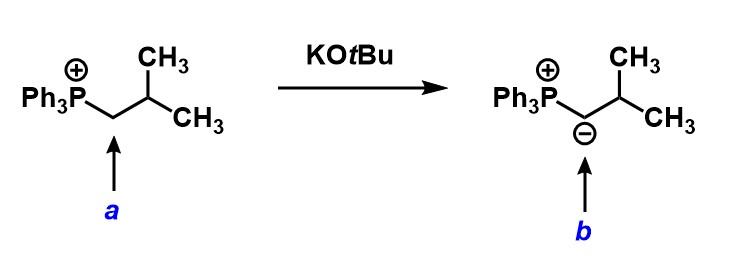
a=2 b=2
a=1 b=2
a=1 b=1
a=2 b=0
a=2 b=1
a=2 b=1
Select all that is true regarding Nafion resin 417.
it is a solvent for Fischer esterification
it protonates the carboxylic acid
it is a superacid
it is a catalyst
it is a superbase
it protonates the carboxylic acid
it is a superacid
it is a catalyst
The molecular ion, M+, is
an ionized fragment of the molecule that is smaller than the molecular weight
a positively charged molybdenum ion
the ionized form of the molecule with a mass that corresponds to the molecular weight of the molecule
the largest peak in the NMR spectrum
always the tallest signal in the mass spectrum
the ionized form of the molecule with a mass that corresponds to the molecular weight of the molecule
The molecular ion for an unknown carboxylic acid has m/z = 122. Using the Rule of 13, determine a possible molecular formula. Hint: consider how many oxygen atoms a carboxylic acid should have.
C9H14
C9H5
C8H10O
C7H6O2
C6H2O3
C7H6O2
Which of the following molecules has 2 degrees of unsaturations?
cyclohexane
cyclohexene
cyclopentane
benzene
cyclohexadiene
cyclohexene
How many degrees of unsaturation does the compound with molecular formula C6H12O6 have?
0
1
2
3
4
1
Which signal in the above 13C NMR spectrum is characteristic of the ester carbonyl carbon?
δ14
δ19
δ22
δ31
δ65
δ171
δ171
Which is true of the signal at δ1.4?
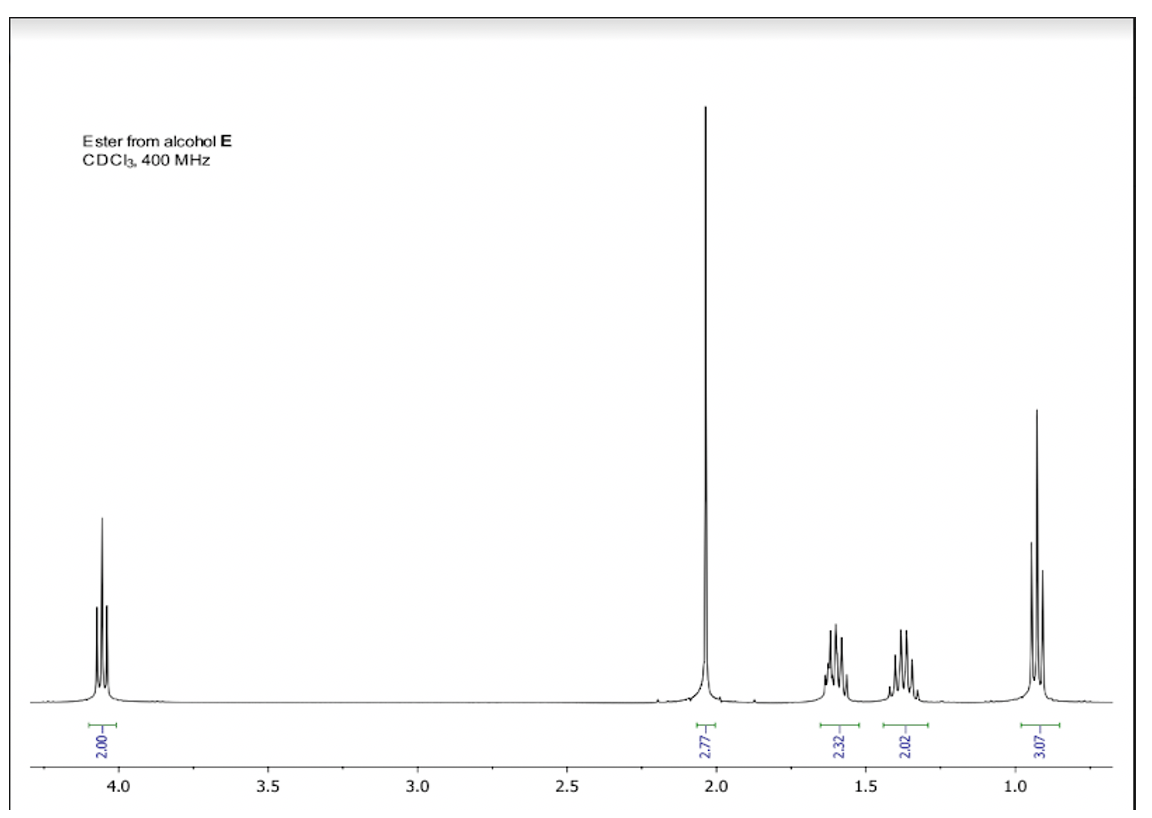
triplet representing 2 hydrogens
singlet; hydrogens have 2 hydrogen neighbors
triplet representing 3 hydrogens
quintet; hydrogens have 4 hydrogen neighbors
sextet; hydrogens have 5 hydrogen neighbors
sextet; hydrogens have 5 hydrogen neighbors
What is glacial acetic acid?
acetic acid that contains minimal water
regular vinegar
acetic acid extracted from glaciers
acetic acid with ice
a specific brand of acetic acid
acetic acid that contains minimal water
When extracting water with diethyl ether, which of the follow statement(s) are correct?
Diethyl ether is more dense than water
Water is more dense than diethyl ether
Water is the bottom layer
Diethyl ether is the bottom layer
The organic and aqueous layers are completely miscible
Water is more dense than diethyl ether
Water is the bottom layer
What important information can be derived from IR spectroscopy?
the total number of carbons in the molecule
the total number of hydrogens in the molecule
the shape of the molecule
the melting and boiling points of the sample
key functional groups present in the sample
key functional groups present in the sample
What is a heterocycle?
a molecule that contains two different rings
any cyclic ring structure
a cyclic ring structure that contains only carbons and hydrogens
a cyclic ring structure that contains any element(s) outside of carbons and hydrogens
a non-cyclic molecule that becomes a cyclic molecule
a cyclic ring structure that contains any element(s) outside of carbons and hydrogens
Which of the follow molecules represent an unsubstituted amine(s)?

A
B
C
D
E
A, C, and E
A
Which of the following molecules represent a disubstituted amine?
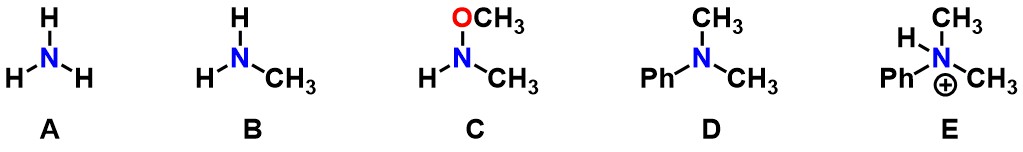
A
B
C
D
E
C
In Figure 2 above, why is the SN2 reaction a poor choice for synthesizing substituted amines?
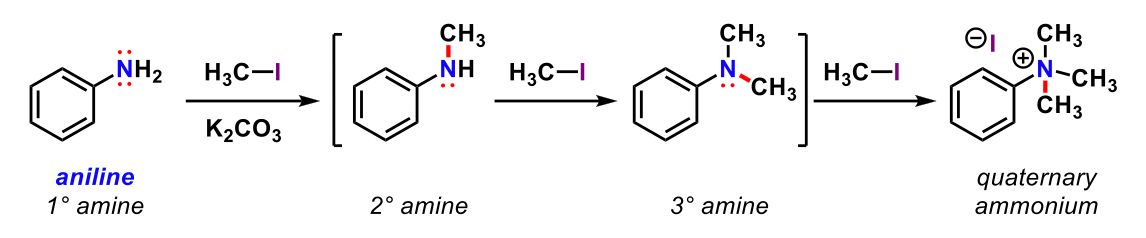
only 1 product can be formed from an SN2 reaction
amines do not participate in SN2 reactions
the primary amine is too nucleophilic
amines' nucleophilicities increase with increasing substitution, which leads to multiple products
the quaternary ammonium salt is not nucleophilic enough to react further
amines' nucleophilicities increase with increasing substitution, which leads to multiple products
Which of the following are true regarding the mechanism of imine formation? [select multiple]
The aldehyde attacks the amine
the amine attacks the carbonyl
formation of the hemiaminal is reversible
formation of the imine is reversible
the hemiaminal is more stable than the starting aldehyde and amine
the amine attacks the carbonyl
formation of the hemiaminal is reversible
formation of the imine is reversible
![<p>Predict the product of the following reaction. [free response]</p><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/217f164a-ae8d-4c49-a9aa-a2a5045a5e53.png)
Predict the product of the following reaction. [free response]
C
Predict the product for the following reaction:
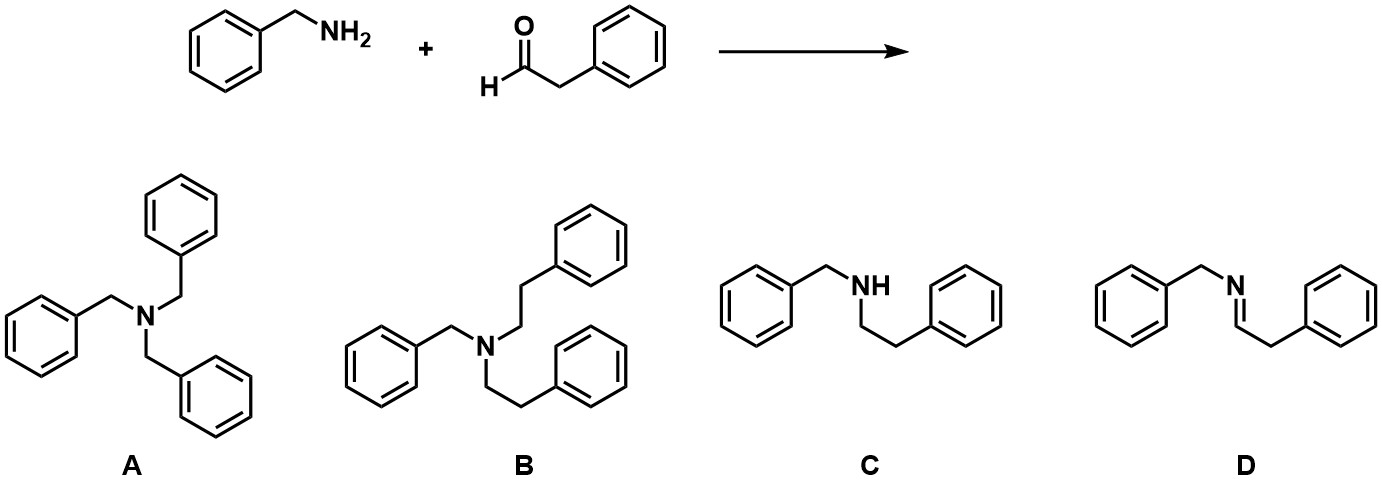
A
B
C
D
C and D
D
The synthesis of compound X requires 2 steps. The first step was accomplished in 80% yield and the second step in 90% yield. What is the overall yield of the 2-step synthesis?
80%
90%
81%
64%
72%
72%
What is the purpose of mixing the 2 solids with a stirring rod?
to prepare the substances to react at a later stage
to purify the two solids
to recrystallize the two solids
to induce a chemical reaction between the two solids
it doesn't accomplish anything
to induce a chemical reaction between the two solids
What can happen if too much hexanes is used in the recrystallization?
the recrystallization yield can be low or even no crystals may form
hexanes is a non-polar solvent so there is no consequence for using too much
hexanes is a polar solvent so it can absorb water and complicate the recrystallization process
the yield will be >100%
the product may decompose
the recrystallization yield can be low or even no crystals may form
What is the most important piece of information that we can obtain from the IR spectrum at this step?
product formation can be distinguished by looking at the C-H stretches between 2850-3150 cm-1
product formation can be distinguished by looking for a new C=O stretch at approximately 1700 cm-1
product formation can be distinguished by the presence of an O-H stretch between 3200-3400 cm-1
product formation can be distinguished by looking for new C=C stretches at approximately 1600-1650 cm-1
product formation can be distinguished by the disappearance of the C=O stretch at approximately 1700 cm-1
product formation can be distinguished by the disappearance of the C=O stretch at approximately 1700 cm-1
Is p-toluidine or o-vanillin expected to be more polar?
they are both equally polar
p-toluidine
o-vanillin
p-toluidine is more polar only in polar solvents
it is impossible to distinguish
p-toluidine
Ethanol - Is the highlighted atom best described as a hydrogen, proton, or hydride?
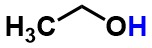
proton
hydride
hydrogen
All of the above
None of the above
proton
LiAlH4 - Is the highlighted atom best described as a hydrogen, proton, or hydride?

proton
hydride
hydrogen
all of the above
none of the above
hydride
Acetic acid - Is the highlighted atom best described as a hydrogen, proton, or hydride?
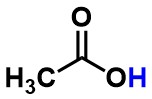
proton
hydride
hydrogen
all of the above
none of the above
proton
Methyl acetate - Is the highlighted atom best described as a hydrogen, proton, or hydride?
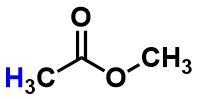
proton
hydride
hydrogen
all of the above
none of the above
proton
Benzene - Is the highlighted atom best described as a hydrogen, proton, or hydride?
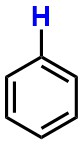
proton
hydride
hydrogen
all of the above
none of the above
hydrogen
Pyridinium - Is the highlighted atom best described as a hydrogen, proton, or hydride?
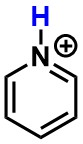
proton
hydride
hydrogen
all of the above
none of the above
proton
Wilkinson's catalyst - Is the highlighted atom best described as a hydrogen, proton, or hydride?
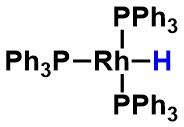
proton
hydride
hydrogen
all of the above
none of the above
hydride
Predict the product of the reaction below:
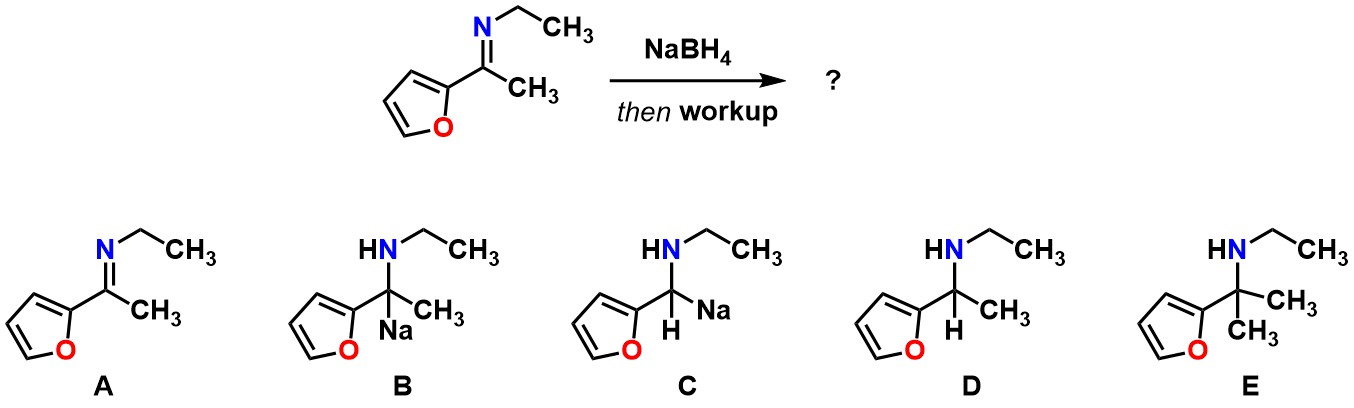
D
What is the purpose of saving some imine for TLC analysis? Select all that apply.
to add to the reaction in case something goes wrong
it helps the solvent elute faster during tlc analysis
to decrease the melting point
to determine reaction progress
to compare the Rf's of the starting material and product
to prevent imine from decomposing
to determine reaction progress
to compare the Rf's of the starting material and product
A gas is formed in this step from the quenching of any unreacted borohydride. What is this gas?
hydrogen gas
helium gas
oxygen gas
air
steam
hydrogen gas
What should be in the organic layer?
ethyl acetate only
ethyl acetate and NaBH4
NaBH4 and amine product
ethyl acetate and amine product
water and byproducts from NaBH4
ethyl acetate and amine product
What is the purpose of washing the organic layer with brine?
it removes NaCl from the organic layer
it removes amine from the organic layer
it removes water from the organic layer
it purifies the organic layer
it purifies both the organic and aqueous layers
it removes water from the organic layer
What structural feature of ethyl acetate will complicate the IR spectrum?
the methyl C-H bonds
the ethyl C-H bonds
the C=O double bond of the ester
the C-O single bond of the ester
both A & B
the C=O double bond of the ester
A TLC analysis using 30% EtOAc in hexanes indicated an Rf = 0.63 for the product. What should you do from here?
Record the Rf and proceed with the experiment according to the procedure
Repeat the TLC analysis using a solvent mixture with greater polarity (50% EtOAc in hexanes) to increase the Rf further
Repeat the TLC analysis using a solvent mixture with lower polarity (15% EtOAc in hexanes) to decrease the Rf to about 0.3
Repeat the experiment entirely because something went wrong
Ask TA for help because it is impossible to obtain an Rf = 0.63
Repeat the TLC analysis using a solvent mixture with lower polarity (15% EtOAc in hexanes) to decrease the Rf to about 0.3
Which of the following statements are true with respect to Figure 3?
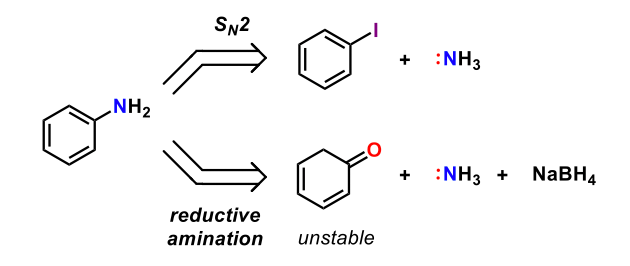
SN2 reactions can proceed with iodobenzene
SN1 reaction can proceed with iodobenzene
SN2 reactions cannot proceed with iodobenzene
Aniline can be synthesized through a reductive amination
Aniline can neither be synthesized from SN2 reactions nor reductive aminations
Aniline can neither be synthesized from SN2 reactions nor reductive aminations
Which of the following statements are true for household bleach? (Select all that apply.)
bleach contains 5.25%-5.75% sodium hypochlorite
bleach is mainly chlorine gas
bleach is mainly sodium hydroxide
sodium hypochlorite is in equilibrium with chlorine gas and sodium hydroxide
sodium hypochlorite is safe when dilute
bleach contains 5.25%-5.75% sodium hypochlorite
sodium hypochlorite is in equilibrium with chlorine gas and sodium hydroxide
sodium hypochlorite is safe when dilute
What is the role of bleach in this experiment?
to disinfect glassware
to kill bacteria that would interfere with the Hofmann rearrangement
to be used as a clean source of water
to be used as a convenient source of chlorine
to be used as a source of strong acid
to be used as a convenient source of chlorine
How much sodium hypochlorite (in grams) is in 9.0 mL of 5.75% bleach solution?
5.2g
9.0g
52g
5.75g
0.52g
0.52g
What is the purpose of adding sodium bisulfite solution?
it is a strong acid to react with sodium hydroxide
it is a strong base to react with 3-nitrobenzamide
it is a reducing agent to neutralize unreacted chlorine
it helps to cool the reaction mixture
it is an oxidant to neutralize unreacted chlorine
it is a reducing agent to neutralize unreacted chlorine
Predict the product of the following reaction.
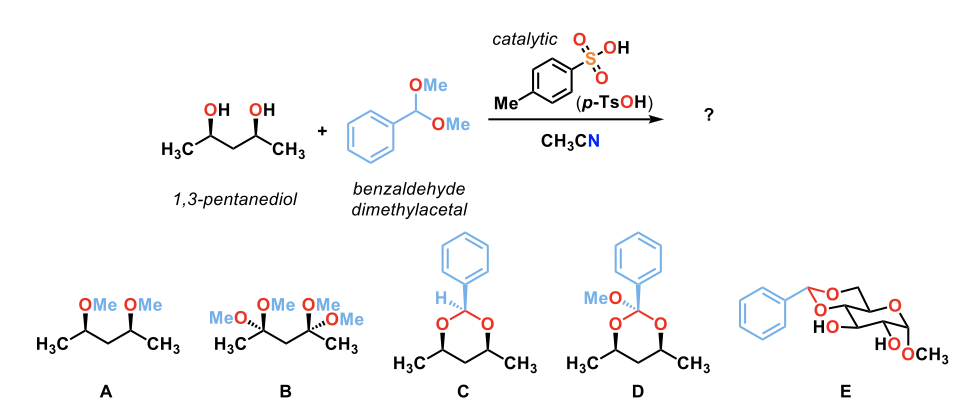
C
Predict the product of the following reaction.
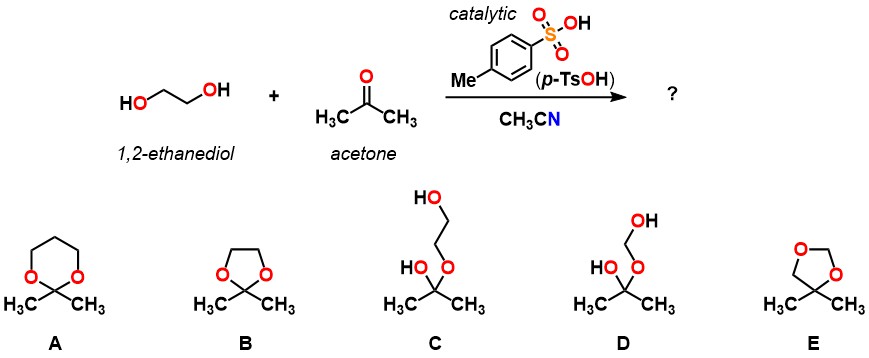
B
Predict the product of the following reaction.
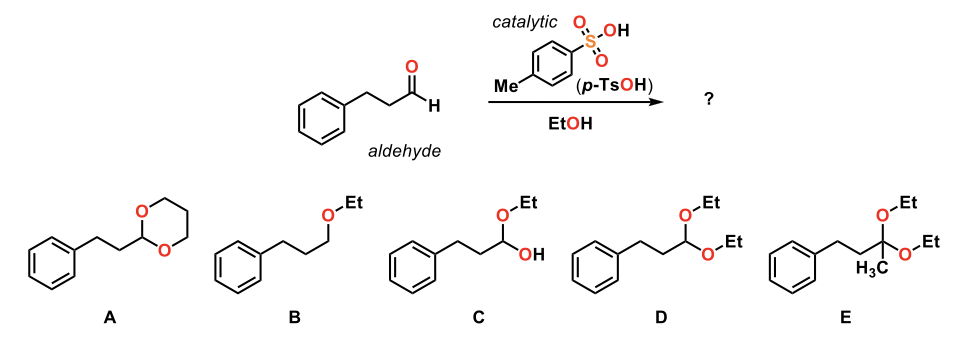
D
How many acetal functional groups are in this molecule?
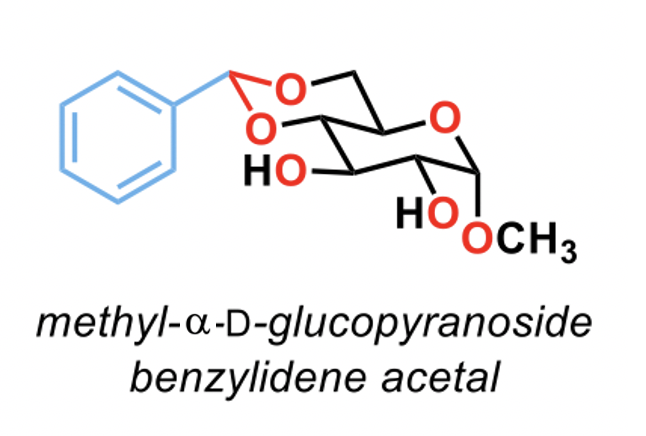
1
2
3
4
5
None
2
What is the role of para-toluenesulfonic acid?
it is the solvent
it is the acid catalyst that reacts with benzaldehyde dimethylacetal
it is the acid catalyst that reacts with acetonitrile
it is the acid catalyst that reacts with the sugar
it removes water from the reaction
it is the acid catalyst that reacts with benzaldehyde dimethylacetal
What is triethylamine reacting with?
acetonitrile
unreacted sugar starting material
unreacted benzaldehyde dimethylacetal
para-toluenesulfonic acid
water
para-toluenesulfonic acid
Which of the following is/are true regarding the organic layer? (select all that applies)
the organic layer is consists of ethyl acetate & acetonitrile & organic product
the organic layer consists of ethyl acetate only
the organic layer is beneath the aqueous layer
the organic layer is above the aqueous layer
the organic layer consists primarily of water
the organic layer is consists of ethyl acetate & acetonitrile & organic product
the organic layer is above the aqueous layer
What happens if one were to use too much DCM?
the yield will increase because more solids will precipitate
the yield will decrease because the product decomposes
the product will revert back to starting material (i.e. deprotection)
the solution will not be saturated and the product will not precipitate as easily or at all
there should be no consequences
the solution will not be saturated and the product will not precipitate as easily or at all
The pKa's refer to the protons highlighted in blue. Select all of the correct statements.
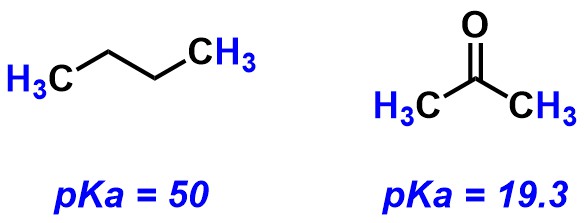
Butane is more acidic than acetone
Acetone is more acidic than butane
Butane can be deprotonated by NaOH (pKa = 15) or LDA (pKa = 35.7)
Acetone can be deprotonated by NaOH (pKa = 15) or LDA (pKa = 35.7)
Butane can deprotonate acetone
Acetone is more acidic than butane
Acetone can be deprotonated by NaOH (pKa = 15) or LDA (pKa = 35.7)
Which of the following statements is false?
The higher the pKa, the harder it is to deprotonate the hydrogens
The higher the pKa, the easier it is to deprotonate the hydrogens
The pKa of a molecule is low when the molecule can form a stabilized carbanion after deprotonation
Deprotonation of acetone forms a stabilized enolate carbanion
Acetone is more acidic than pentane
The higher the pKa, the easier it is to deprotonate the hydrogens
Identify the main electrophile in the reaction depicted in Figure 3?
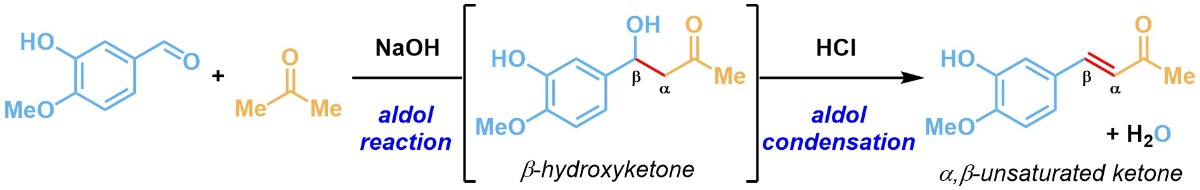
aldehyde
ketone
β-Hydroxyketone
HCl
αβ-Unsaturated ketone
aldehyde
Which of the molecules drawn on the product side of the chemical reaction is incorrect?
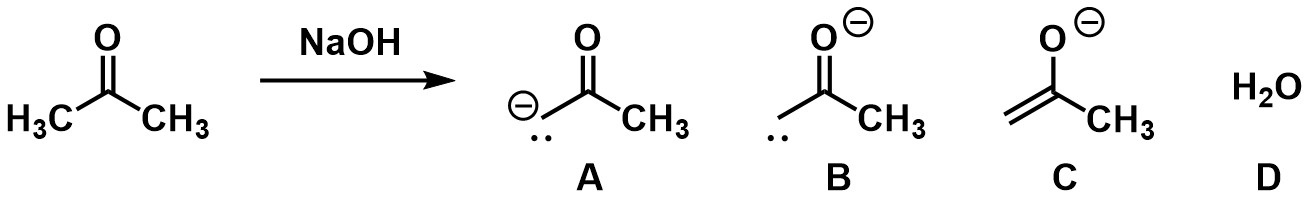
A
B
C
D
B
What is the product of the aldol reaction?
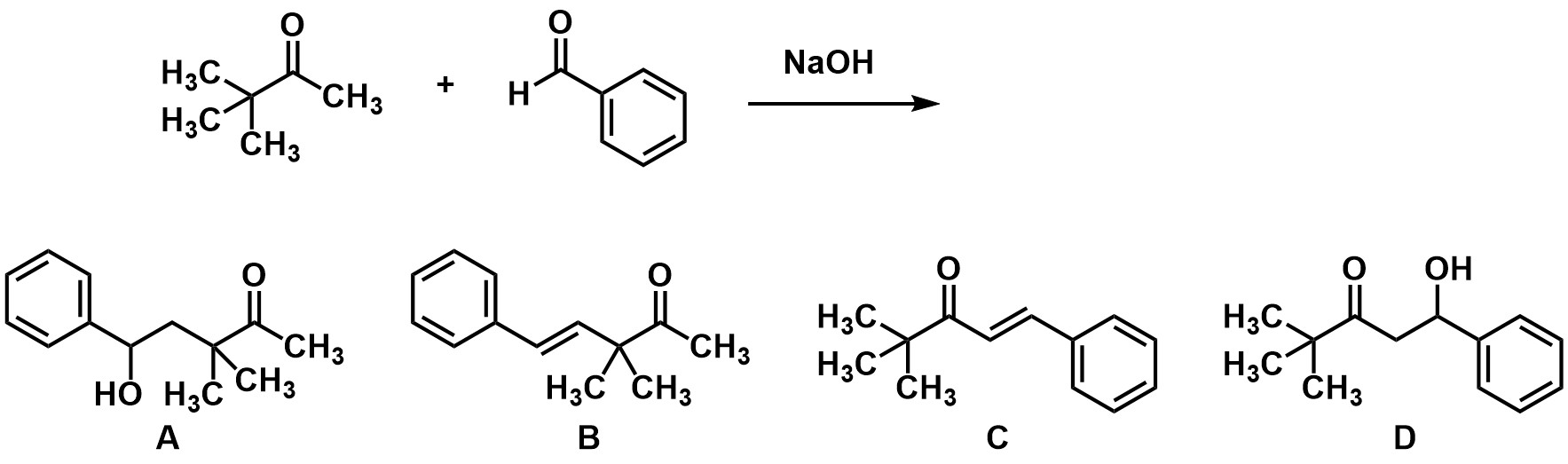
A
B
C
D
This reaction as drawn does not work
D
Why is a reflux condenser needed for this experiment?
It is not really necessary
To prevent dust and dirt in the air from entering the reaction apparatus
It helps to heat the reaction mixture
It prevents the solvent from boiling away by condensing the vapors
It prevents the solvent from boiling away by condensing the vapors
What is the purpose of adding 6 M HCl?
To protonate the aldehyde
To react with acetone
To promote elimination of water in the aldol condensation
To heat up the ice
To promote elimination of water in the aldol condensation
What is the solid precipitate that forms when the mixture is acidified with 6 M HCl?
Hydrogen chloride
The β-hydroxyketone
Sodium chloride
αβ-Unsaturated ketone
Vanillin
αβ-Unsaturated ketone
Which of the following statement is false regarding TLC analysis?
It provides an indication of the progress of the reaction.
It provides information on the purity of the substance.
Silica gel acts as the stationary phase.
Ethyl acetate acts as the mobile phase.
Hexanes acts as the stationary phase.
Hexanes acts as the stationary phase.



