Federalism, Separation of Powers, & Checks and Balances
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
Essential question: How is power shared in U.S. Government?
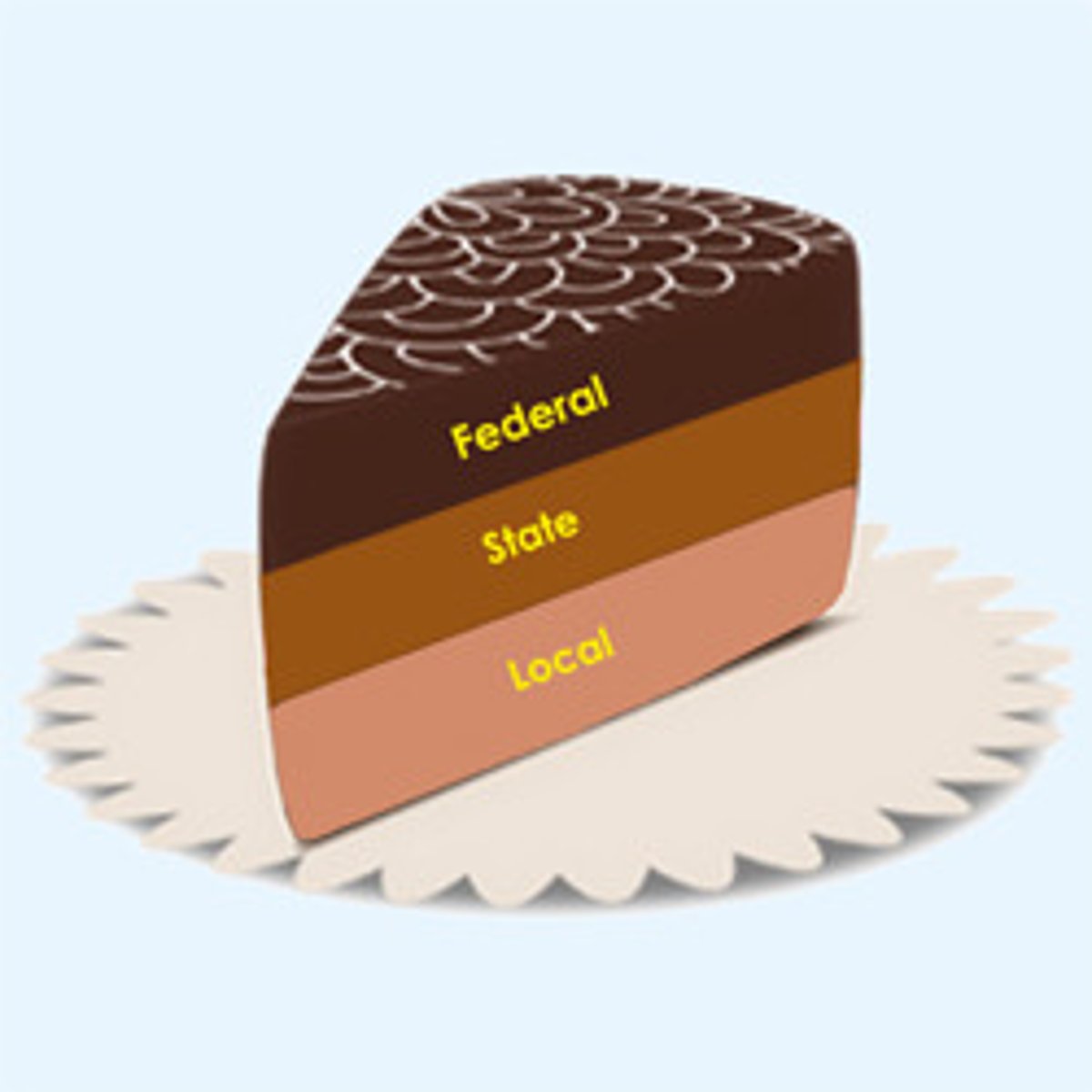
It is divided between the 3 branches (separation of powers) and between national, state, and local government (federalism).
federalism
division of power between levels of government
concurrent powers
shared powers (examples: create laws, raise taxes, build roads, establish banks, borrow money)
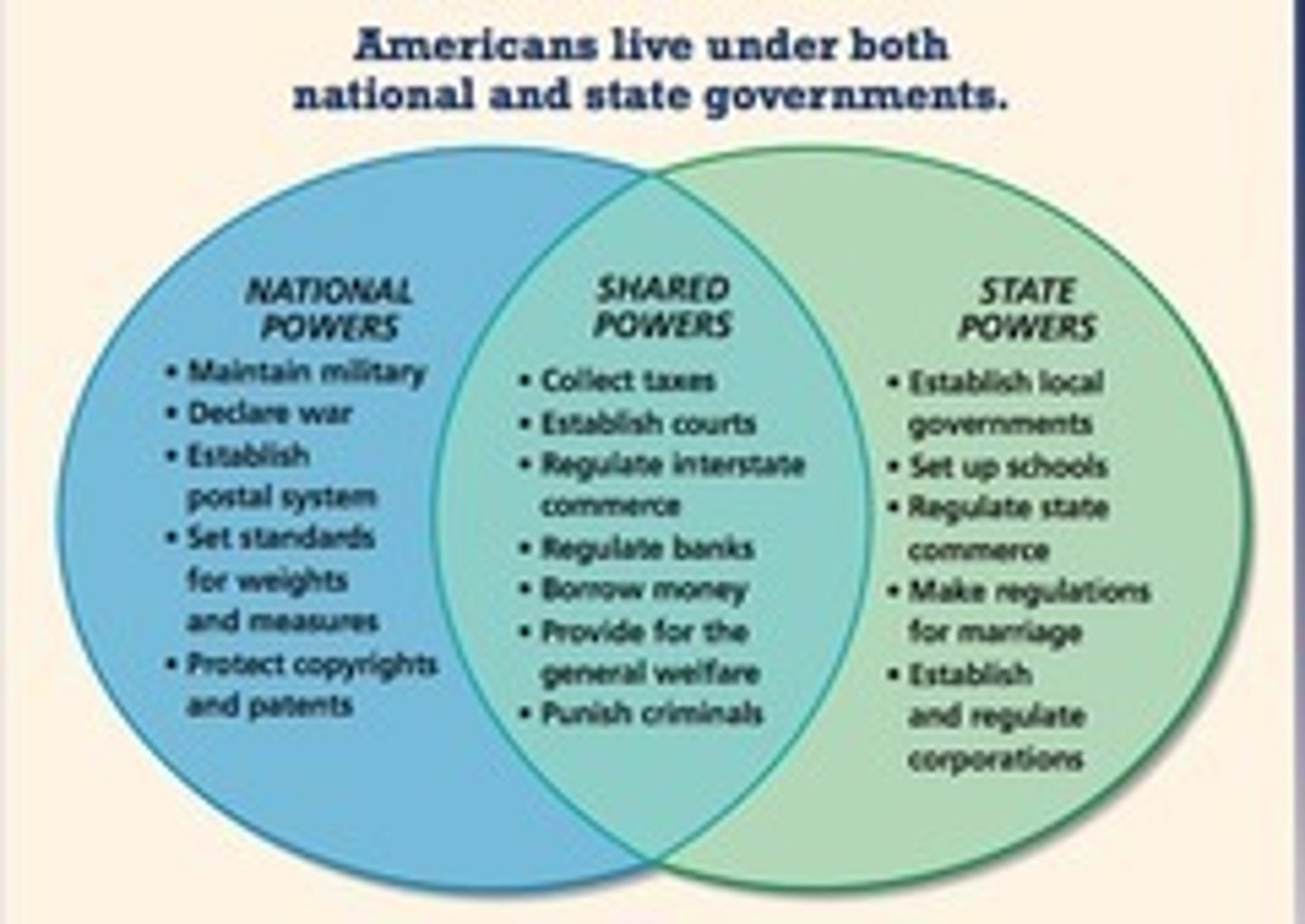
reserved powers
powers granted to the states by the 10th Amendment to the US Constitution (public health, safety, welfare, and education, licensure, and elections)

delegated powers (aka expressed, enumerated powers)
Powers specifically given to the federal government by the US Constitution, for example, the authority to print money.
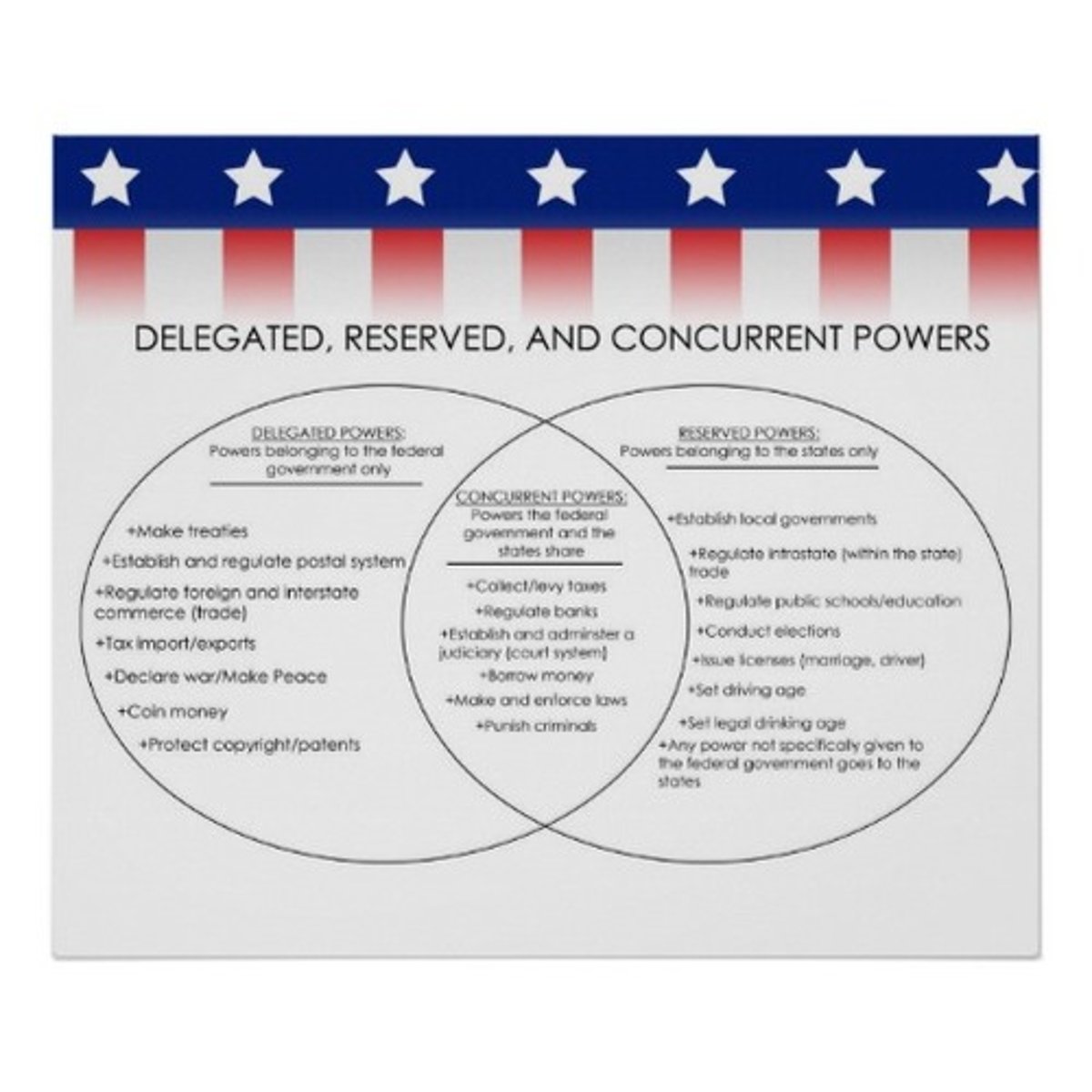
denied powers
powers prohibited by the US Constitution

implied powers
powers not mentioned in the Constitution, but are used to carry out expressed powers

separation of powers
government's power is distributed among three branches of government (legislative, executive, judicial)

legislative branch
makes laws

executive branch
enforces or carries out the law

judicial branch
interprets the law

checks and balances
system that maintains balance between the branches of government; no one branch overpowers the others
impeachment
Congress can formally charge a President or Supreme Court Justice with a crime

judicial review
the US Supreme Court can declare laws or actions unconstitutional

veto
the President can reject a bill passed by Congress

President checks Congress
-Veto laws
-Propose laws, treaties, and appointments
-Create annual budget
-Call special sessions of Congress

Congress checks the President
May override vetoes with a 2/3 vote, may remove through impeachment, senate approves treaties and appointments
President checks Supreme Courtterm-47
President appoints justices to the Supreme Court; pardons criminals
Congress checks Supreme Court
amends Constitution; approves judicial appointments

Supreme Court checks President
declares executive actions unconstitutional

Supreme Court checks Congress
declares laws unconstitutional

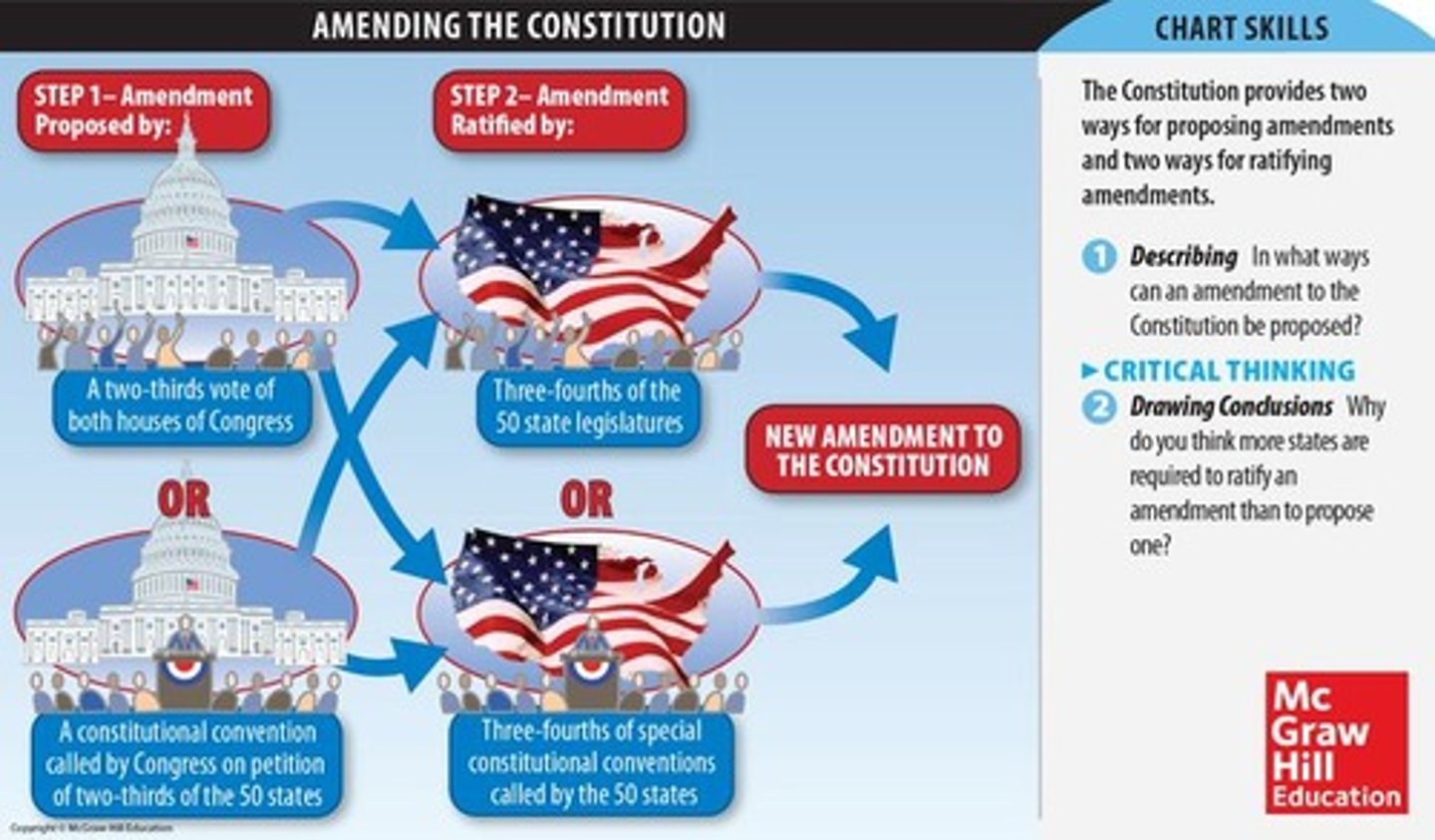
amendment process
proposal by legislative branch or convention; ratification by 3/4 of the states (US) or voters (VA)
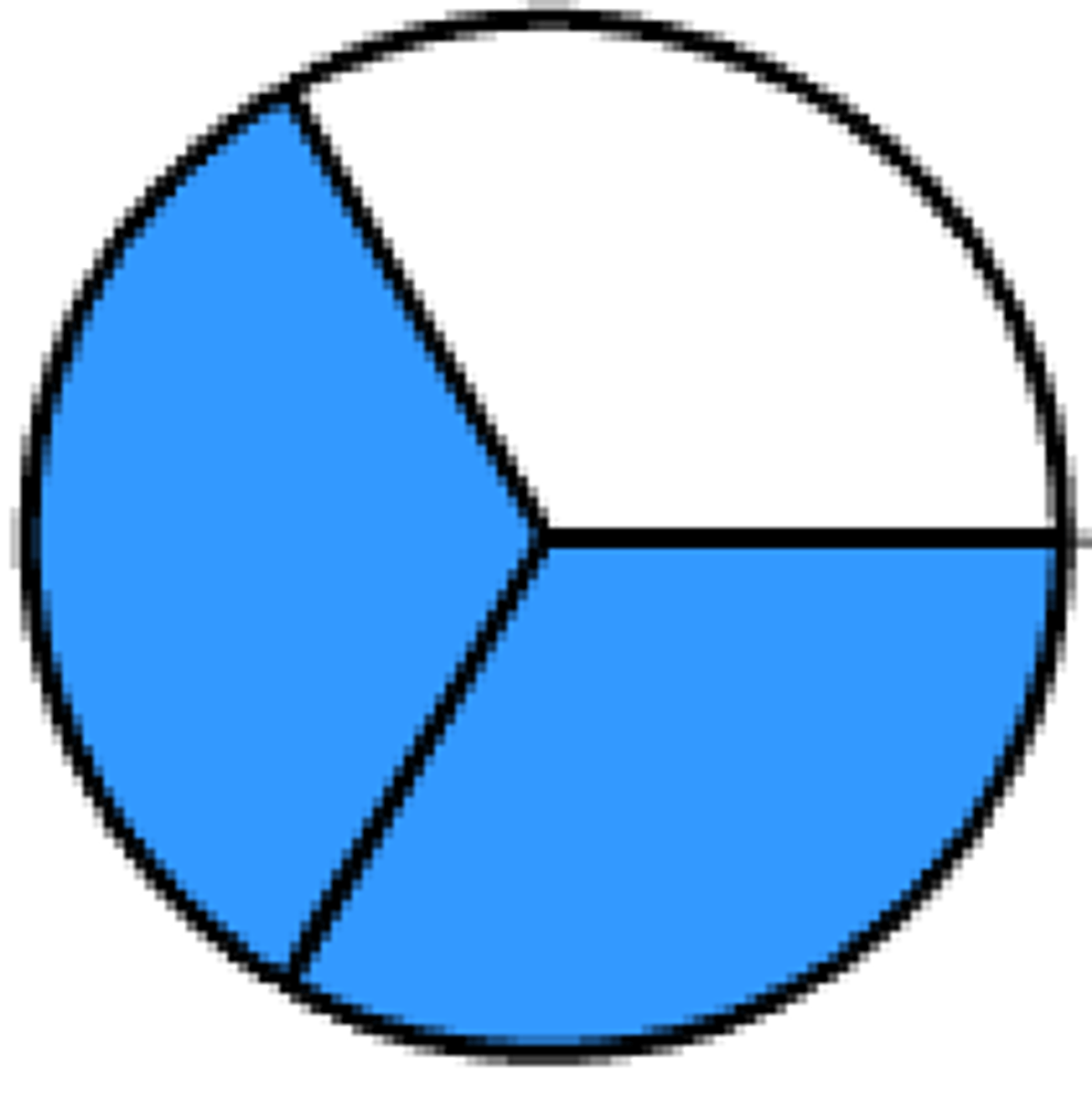
2/3
fraction of votes for legislative approval, law-making, or amending a constitution
appoint
to select aperson for an office or position

ambassador
a government official sent to another country

bicameral
two house legislature
budget
a plan for collecting and spending money, the president prepares it and congress approves

The cabinet officers
a group of senior officials appointed by the president to advise on policy

confirm
to officially select or agree with a person appointed for a job

enforces
to carry out the law- Executive Branches Job

executive agencies
Federal agencies that are part of the executive branch but outside the structure of cabinet departments. Their heads typically serve at the pleasure of the president and can be removed at the president's discretion.

federal bureaucracy
the thousands of federal government agencies and institutions that implement and administer federal laws and programs

execute
to carry out a law

federal law
the law of the national government

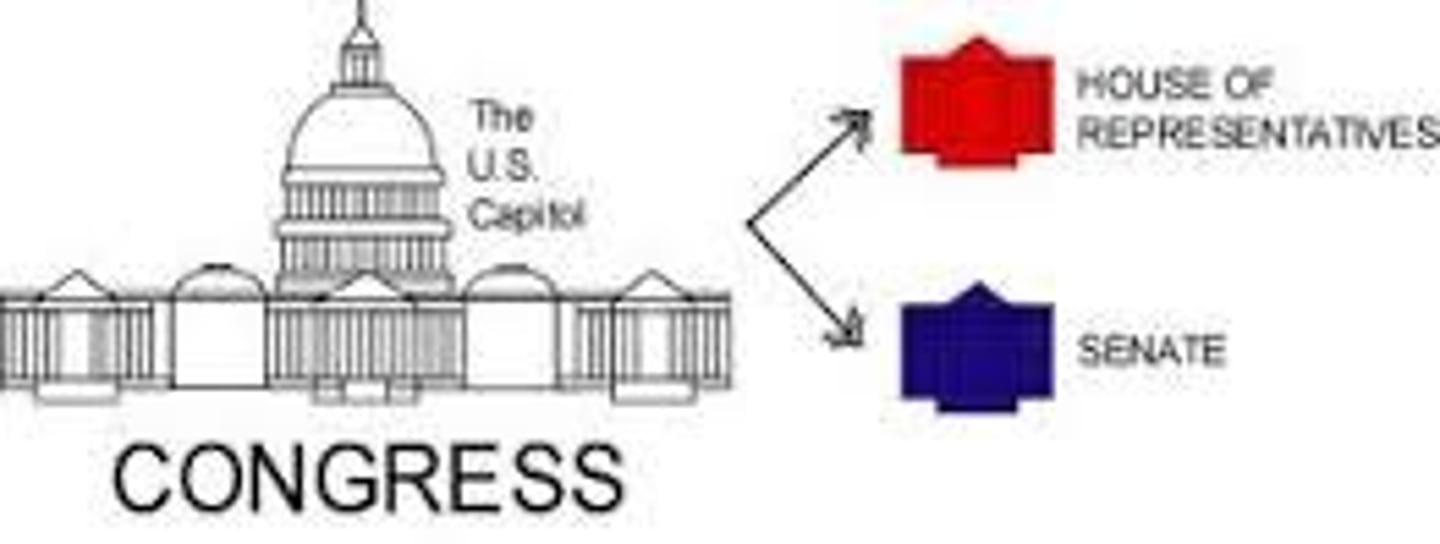
House of Represenatives
the lower house of Congress, consisting of a different number of representatives from each state, depending on the population

Senate
The Upper House in Congress composed of 100 members, 2 senators are elected from each state for 6-year terms

Congress
the legislature of the United States government made up of the House of Representatives and the Senate

Interpret
to explain or give the meaning of- Judaical Branch Power
legislate
to make laws- Legislative Branch Power

President
Chief Executive of the United States, Head of State and Commander and Chief of the US Armed Forces. The President of the United States is elected every 4 years, by the Electoral College. Signs or veto's bills passed to them by Congress.

Judge
a public official appointed to decide cases in a court of law.

Levies Taxes
Collects Money

Tax revenue
the money a government gains from the collection of taxes

interstate
between the states
US Supreme Court
the highest court of the United States; it sits at the top of the federal court system

Confirms Appointments
Power of the Legislative Branch to official check the Presidents picks for jobs

legislature
lawmaking body

Grant-in-aid programs
grants of federal money or other resources to the States and/or their cities, counties, and other local units
