Neuromuscular disorders
1/63
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Anything italitcized is from the 25 charts or uptodate
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
Cerebral Palsy
A group of permanent movement disorders caused by non-progressive disturbances in the developing fetal/infant brain that affects posture, movement, and is often accompanied by sensory, cognitive, communicative, or behavioral challenges
infections during pregnancy, maternal health issues, genetic mutations
What are some prenatal risk factors for Cerebral palsy
birth asphyxia, premature birth, low birth weight
What are some perinatal risk factors for Cerebral palsy
severe jaundice, meningitis, head injuries
What are some postnatal risk factors for Cerebral palsy
Spastic CP
Which type of cerebral palsy is characterized by increased muscle tone, strange looking appearance, and is is most common?
Dyskinetic CP
Which type of cerebral palsy is characterized by involuntary movements including dystonia and choreathetosis (involuntary hand movements)
ataxic CP
Which type of cerebral palsy is characterized by balance and coordination difficulties?
mixed CP
Which type of cerebral palsy is characterized by a combination of spastic, dyskinetic, or ataxic?
Gross motor function classification System (GMFCS)
A 5 level system that categorizes motor function in individuals with CP, focusing on self-initiated movements (sitting, walking, etc) and is age specific
Level I
Which GMFCS level is characterized by the ability to walk without restrictions but limitations in motor skills like running/jumping (typically independent in mobility and daily activities)
Level II
Which GMFCS level is characterized by the ability to walk in most settings, though may have difficulty walking long distances and balancing on uneven terrain and minimal difficulties with balance/coordination - use mobility aids for outdoor distances
Level III
Which GMFCS level is characterized by the ability to walk using a hand-held mobility device for short, indoor distances and may use wheeled mobility for longer distance - may require assistance for transfers
Level IV
Which GMFCS level is characterized by dependence on wheeled mobility for most setting; may be able to use power mobility independently; may walk short distances with support in familiar environments - significant limitations on self-initiate movement
Level V
Which GMFCS level is characterized by severe restrictions in voluntary movements and is dependent on caregiver for all mobility and positioning - limited ability to maintain head and trunk posture
motor impairments, severity levels, onset of symptoms, progression of associated conditions (not CP itself)
What might vary between clinical presentations of cerebral palsy?
child milestones, difficulty in birth/pregnancy
What are we worried about in the Hx of a cerebral palsy work-up?
motor function, gait, posture, ROM, obvious joint deformities, neuro eval (co-existing conditions such as seizures, intellectual impairments)
What are we worried about in the physical exam of a cerebral palsy work-up?
MRI (CT if MRI is not an option)
What imaging are we ordering for cerebral palsy?
early therapeutic strategies (PT, OT) to enhance motor skills and prevent complications, family/caregiver education, resource allocation for adaptive equipment and assistive strategies
If we catch cerebral palsy early this allows us to…
Well child visits (rolling, sitting, crawling, walking, talking), Ages and stages questionnaire (ASQ), Denver developmental screening test
What developmental surveillance can we do for CP?
poor head control, persistent primitive reflex (Moro, tonic neck), asymmetric movements, hypertonia, hypotonia, troubles with suckling, swallowing, or managing solid foods
Red flags for CP in infants
periventricular leukomalacia, cortical malformations, hypoxic ischemic damage
What might we see on MRI for CP
genetic/metabolic testing
If CP is suspected to be part of a broader syndromic condition, what can we run?
PT, OT, Speech to improve function and communication, meds to manage spasticity (baclofen, botox) or seizures, Ortho surgeries and selective dorsal rhizotomy for spasticity, educate on use of aids to maximize independence and participations
Gameplan for cerebral palsy management
PT, OT, possibly orthotics/bracing. No pharmacologic treatment
Mild spasticity or hypertonia (early childhood)
oral baclofen, diazepam (short term), tizanidine
Persistent or Moderate spasticity (Ages 2-5) - spasticity causes pain, contractures, or difficulty with ADLs
BOTOX preferred
Focal spasticity (ages 3-7) - multiple limbs are affected
intrathecal baclofen, selective dorsal rhizotomy
Widespread spasticity in older patients unable to be controlled with oral medications
Trihexphenidyl, Levodopa/carbidopa, deep brain stimulation
Dystonia treatment option in CP
mild motor impairments, early intervention, good cognitive function
Signs of a good prognosis for CP
severe motor impairments, intellectual disabilities, seizures, respiratory and feeding issues
Signs of a bad prognosis for CP
Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
A chronic, autoimmune disease of the CNS characterized by inflammation, demylination, and neurodegeneration → leads to neurological disability
Ts and Bs attack myelin resulting in inflammation, demyelination, and axonal loss leading to sclerotic plaques
Pathophys for MS
woman between 20-40 (the early it pops up the better) in a temperate climate
Typical MS patient
Fam hx, variants in HLA-DRB1, temperate climates, vitamin D deficiency, smoking, obesity, EBV (other viruses, and bacteria), age, gender, other autoimmune disorders, ethnicity, stress, lifestyle
Risk factors for MS
Relapsing-Remitting MS (RRMS)
What is the most common form of MS that has clearly defined episodes of neurological symptoms followed by periods of remission
optic neuritis, numbness, tingling, motor weakness and fatigue
Common symptoms of RRMS
clinically isolated MS syndrome
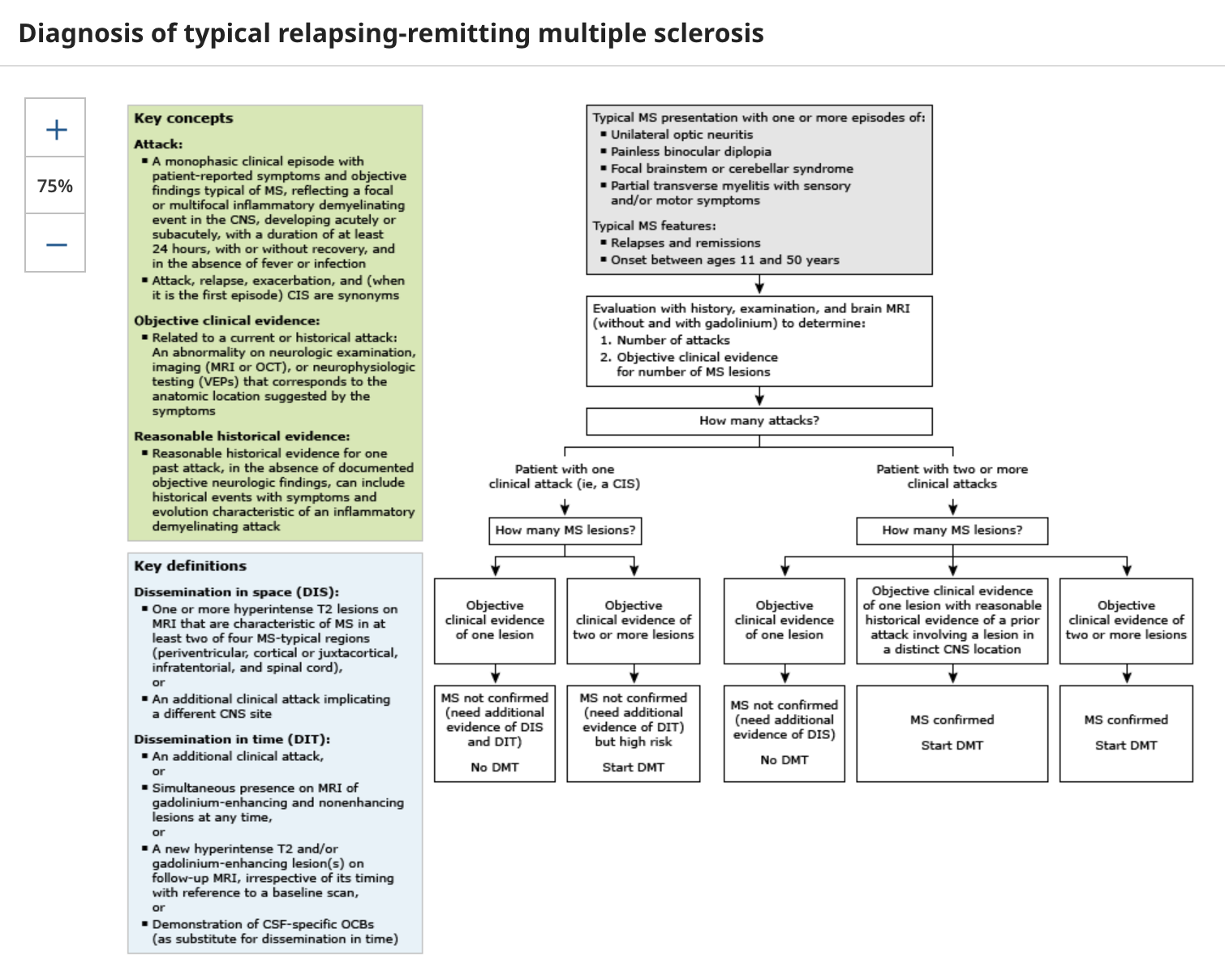
So, fun fact, you cannot diagnose MS based on one MS attack, you need at least two WITH MS lesions on MRI, so until then we are calling it…
Secondary progressive Multiple Sclerosis
A progression of RMSS that shifts from a pattern of relapses/remissions to a more steady and gradual worsening with fewer relapses and the gradual accumulation of a neurological disability and a progressive worsening of neurological function
Primary progressive MS (PPMS)
A form of MS that is characterized by a gradual worsening of neurological onset WITHOUT distinct relapses/remissions, more cortex/spinal involvement (loss of bladder control), increased formation of scar tissue (gliosis), and involves damage of the oligodendroctyes, neurons, and axons
Optic neuritis
An inflammatory condition of the optic nerve associated with demylination and a frequent presentation of MS
MRI (Gd-enhancing lesions for active plaques and apply McDonald criteria), Lumbar puncture (oligoclonal bands or elevated IgG index), High-dose corticosteroids (methylprednisolone)
23 y/o woman presents to the ER for progressive unilateral vision loss over the last 3 days. She also reports extreme fatigue that she just contributed to studying for an extreme psychological torture of a pharm exam, as well as a shooting electric pain that radiates down the spine (lhermitte’s), and heat intolerance that worsens her symptoms. On a physical exam you note BUE weakness and sensory changes, as well as marcus gunn pupil in her affected eye and internuclear opthalmoparesis, What do you want to order?
disease-modifying therapies (DMTs) interferons, glatiramer acetate, natalizumab, ocrelizumab, siponimod
What are the management strategies for MS that slow progression?
Spasticity (baclofen, tizanidine), fatigue (amantadine, modafinil)
What are the management strategies for MS that manage symptoms
early treatment, younger age at onset, RRMS subtype, low lesion burden
What are some signs of a favorable prognosis for MS?
PPMS subtype, older age, male, high lesion burden
What are some signs of a poor prognosis for MS?
Spasticity, optic neuritis, ataxia, cognitive impairment, incontinence, UTIs, depression, anxiety, secondary infections, osteoporosis (steroid use)
Complications of MS
Myasthenia Gravis
What autoimmune disorder is characterized by fluctuating weakness due to dysfunction of the NMJ that typically occurs between the 20-30s for females OR 60-80s for males?
ACh antibodies block Ach receptors and mediate the destruction of said receptors OR MuSK antibodies impair the organization of the membrane
Mechanism of MG
Thymic abnormalities (thymoma, etc)
What is MG (Ach-Ab) often associated with?
Ice pack test, edrophonium test (if you weren’t in the US), AChR Ab, MuSK Ab, autoimmune thyroid labs, CT chest (check for thymoma), Repetitive nerve stimulation studies, single finger electromygraphy
25 y/o female presents to the clinic for generalized weakness that comes and goes and worsens with exercise. She also reports double vision. On a physical exam you note ptosis, an expressionless face (myasthenic sneer) and proximal muscle weakness. Deep tendon reflexes are normal and you find no sensory deficits. What are some test you can order to confirm your diagnosis?

generalized weakness (bulbar, limb), ocular MG
Which symptoms are more common with AChR Ab MG (85%)?
Bulbar weakness (dysphagia, dysarthria), more severe respiratory crisis, focal muscle atrophy, muscle fasciculations
Which symptoms are more common with MuSK Ab MG (15%)?
Fatiguability and weakness of muscles + abnormal diagnostic test
How is the diagnosis of MG made
fluctuating weakness on exam
Hallmark of MG
AChR AB
Thymectomy is more effective in treating which type of MG?
Lambert-Eaton Myasthenic Syndrome, Botulism, thyroid dysfunction, motor neuron disease, muscular dystrophies
DDX for MG
AIRWAY!! ICU admit. intubate and vent - monitor respiratory strength, Plasmapheresis, IV Ig infusion, high dose steroids
77 y/o male presents to the ER for SOB. His daughter states that a week ago he complained of feeling weak and dysphagia, she also doesn’t think he’s been taking his meds. PMHx is positive for MG. What is your treatment plan?
Cholinergic Crisis - atropine
77 y/o male presents to the ER for weakness. His daughter reports that he has been drooling and complaining of stomach cramps. She thinks that he took too much of his meds on accident. PMHx is positive for MG. Vitals are stable with the exception of 90/45, 30 RR (labored), 45 bpm. On a physical exam you note miosis, diaphoresis, and muscle spasms. What is this and what is your treatment plan?
pyridostigmine (AChase inhibitor - monitor dosing to prevent cholinergic crisis), thymectomy in young patients, Steroids
Treatment plan for AChR Ab MG?
rituximab, plasma exchange
Treatment plan for MuSK Ab MG?
Steroids (1st line), azathioprine, mycophenolate mofetil (second)
Immunosuppressants for MG
PT, monitor for aspiration pneumonia (you’ve got dysphagia)
Supportive care measures for MG
Myasthenic crisis (triggered by infection, stress, medication noncompliance), aspiration pneumonia, dysphagia, fatigue, cholinergic crisis (med OD), Osteoporosis/DM/infections from chronic steroid use
Complications of MG