NPTE MSK review
1/224
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
225 Terms
Thumb biomechanics:
Flexion (radial adduction)
extension (radial abduction)
Palmar adduction
Palmar abduction
Flexion: same, ulnar glide
extension: same, radial glide
adduction: opposite, volar/anterior
abduction: opposite, dorsal/posterior
Grades of mobs
Grade one: small amplitude beginning of range
II: large amplitude within range
III: large amplitude from middle to end of range
IV: small amplitude at limit of range and into resistance
V: small, fast at limit of range
Example of firm end feel
shoulder flexion
example of soft end feel
elbow flexion
what is a firm end feel?
capsular/ligamentous stretching
what is a soft end feel?
soft tissue approximating together
what is a boggy end feel?
edema/swelling
what is a rubbery end feel?
muscle spasm
what is a springy end feel?
meniscal displacement
How would you increase flexion at C5/6? extension?
PA glide at C5 to increase flexion and PA glide at C6 to increase extension
How would you increase rotation at C5/6?
PA glide at left C5 or R C6
right rotation: right side closing and left side opening
right side bend: right side opening and left side closing
coupled motions in cervical, thoracic, lumbar spines
cervical/thoracic: rotation and side bending are in the same direction (R side bend and R rotation)
lumbar: side bend and rotation are in opposite directions (r side bend and L rotation)
Lumbopelvic rhythm:
flexion:
extension (from flexed position):
flexion: L spine does 70-60 degrees of flexion, then pelvis rotates anteriorly, then hips flex
extension: hips extend, pelvis moves posteriorly, and spine extends
AC joint tests
cross arm adduction test (horizontal adduction test), resisted extension, painful arc (pain between 170-180 deg), paxinos sign, AC shear test
Paxinos sign
-examiner's thumb placed posterolateral aspect of acromion and index and middle fingers paced superior to mid-clavicle
-thumb applies an anterosuperior pressure and index middle applies an inferior pressure
+=pain at the AC joint
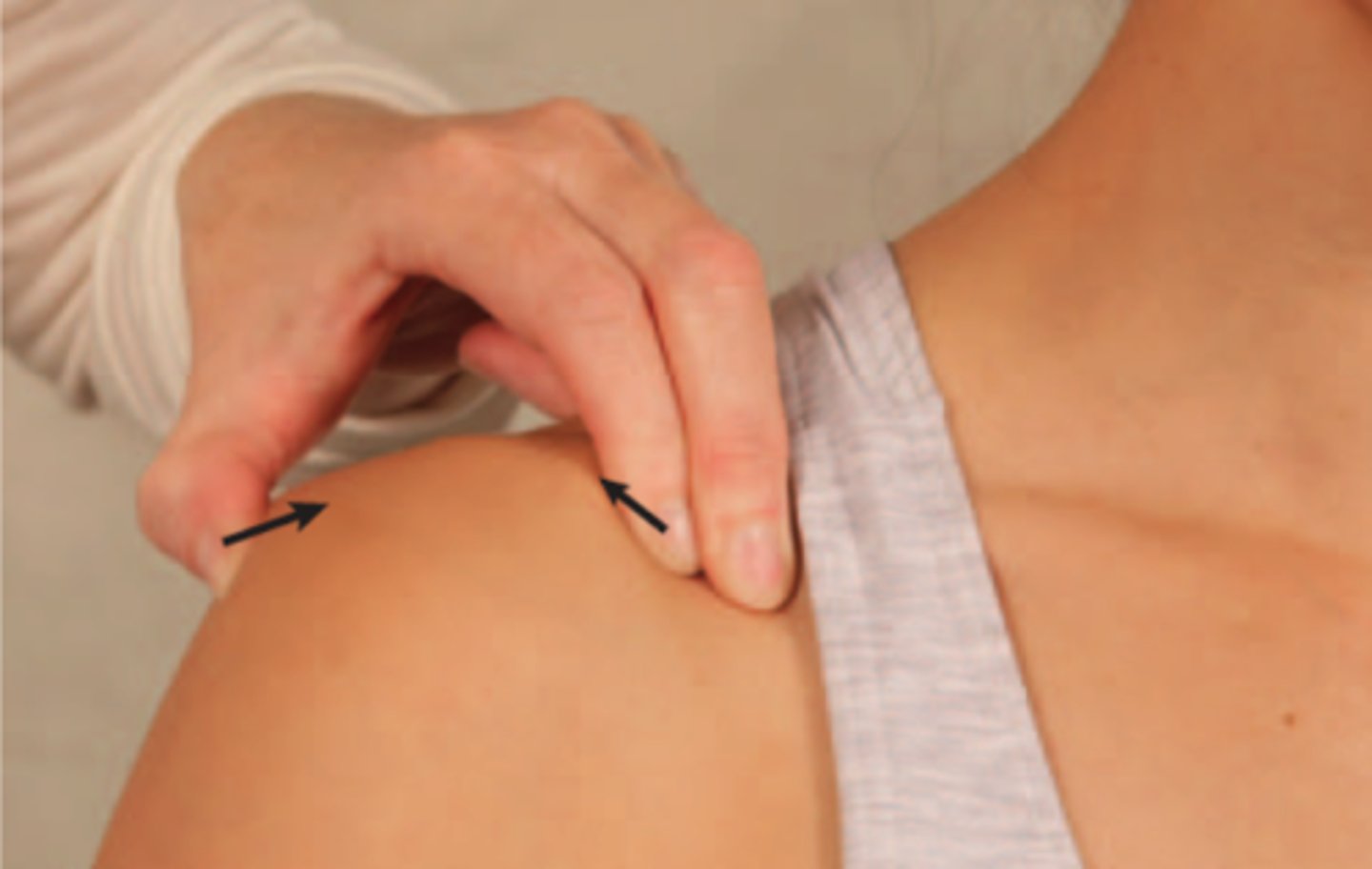
AC shear test
squeeze over deltoid muscle
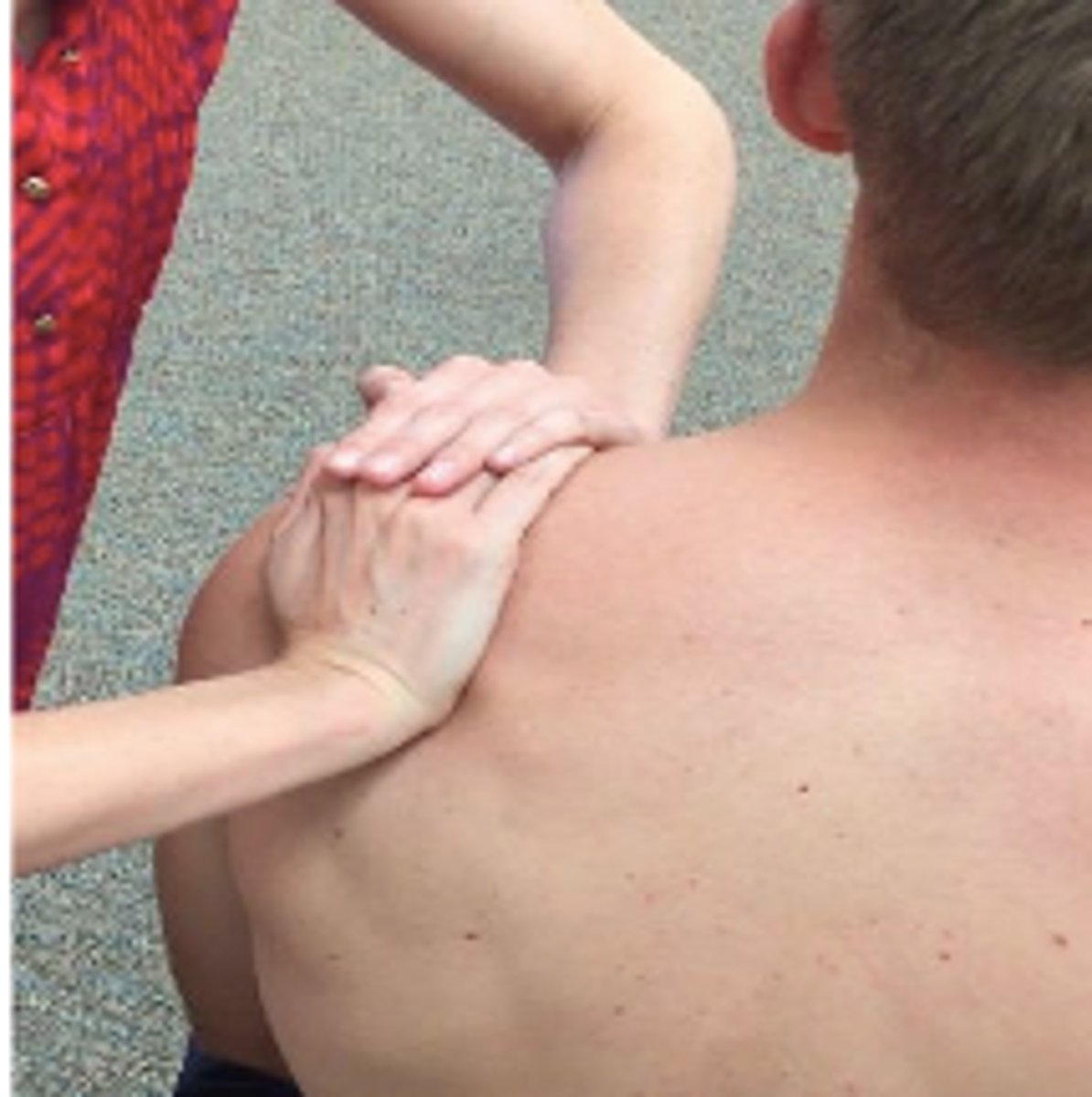
subacromial impingement tests
hawkins kennedy, infraspinatus resisted test, painful arc (60-120), yocum test, neer test, empty can test (jobe test), scapular assistance test
yocum test
modified hawkins kennedy, PT elevates elbow while pts hand is on opposite shoulder
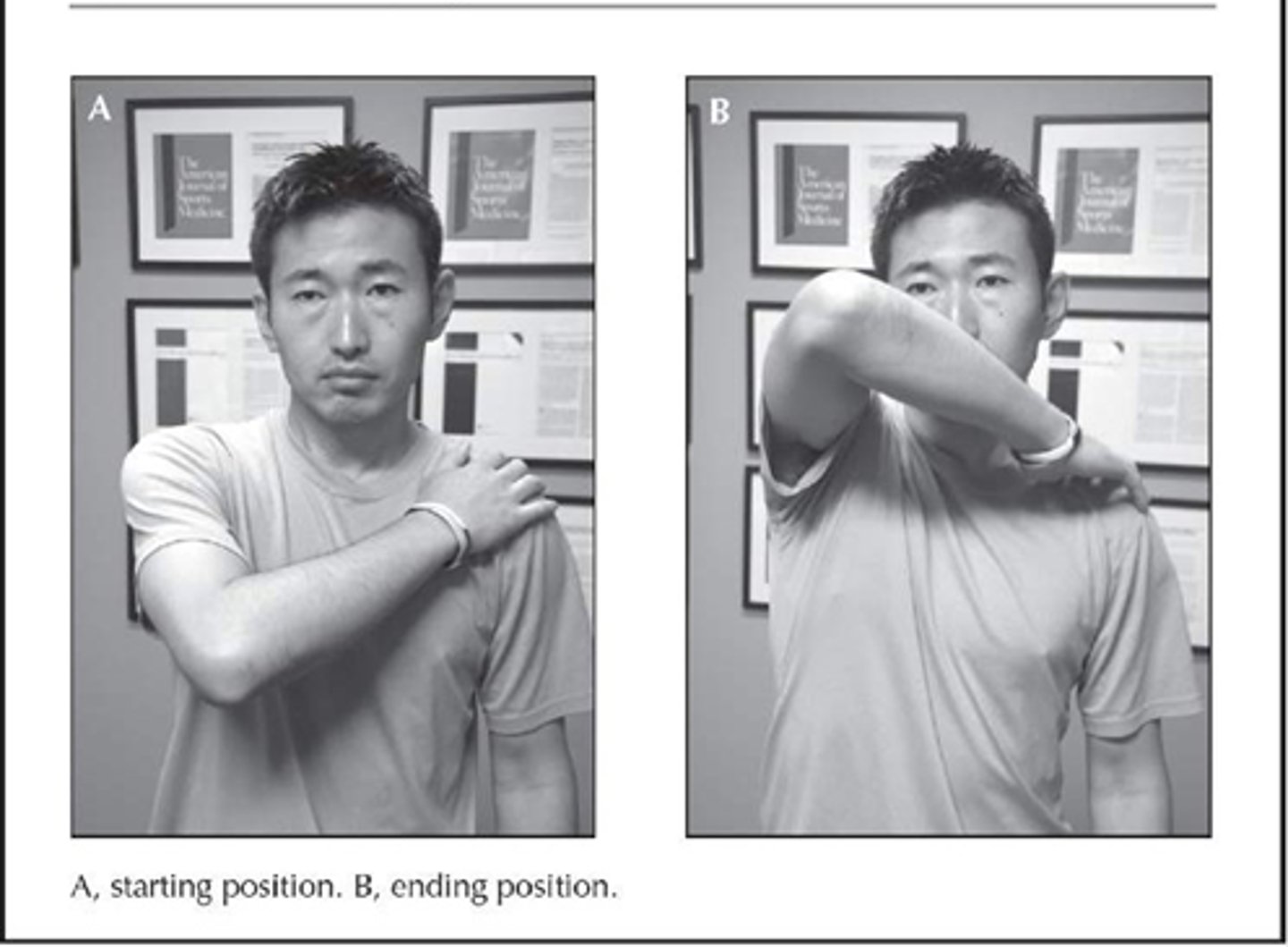
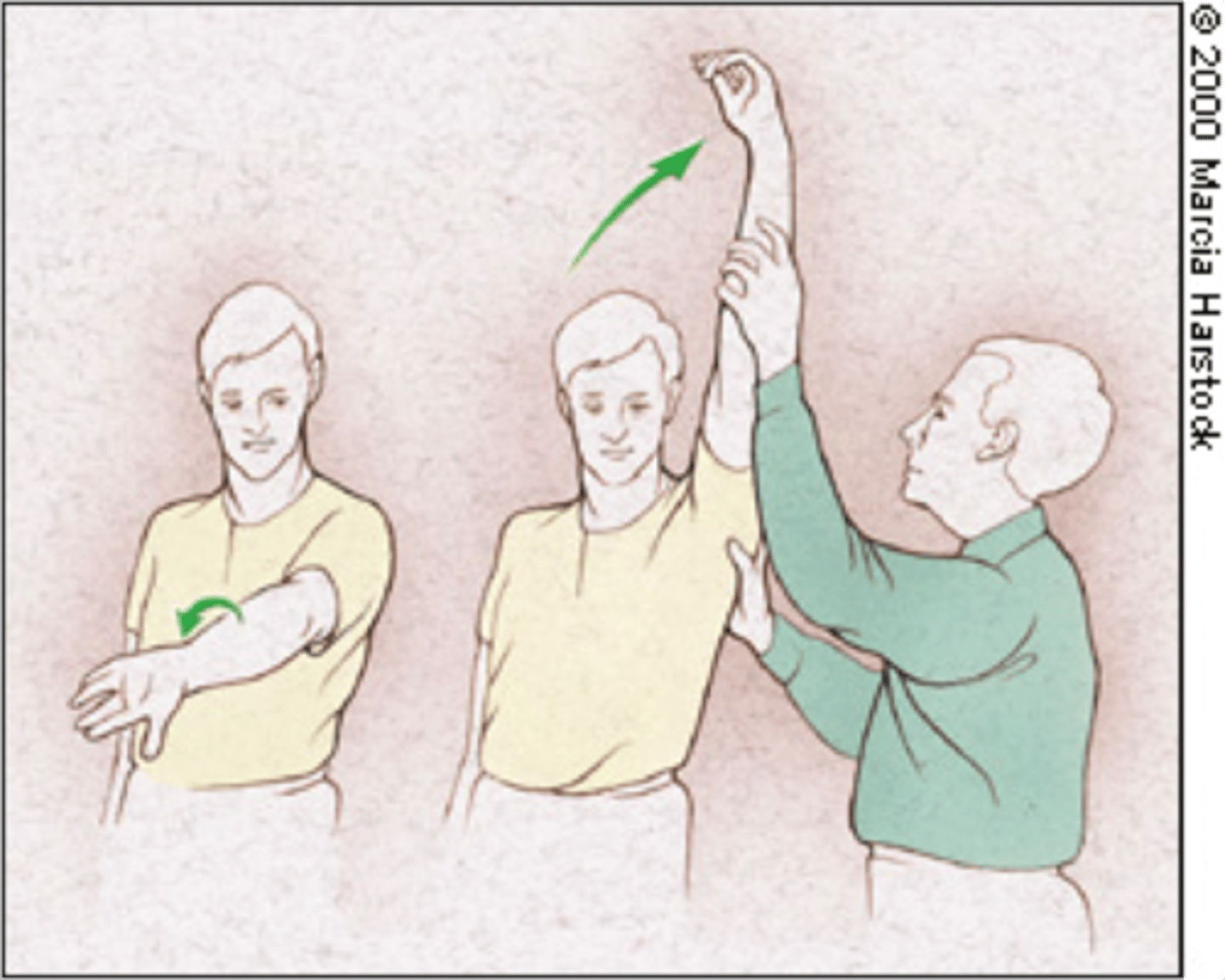
neer test
passive shoulder elevation in scapular plane with IR
RC pathology tests
hornblower sign, ER lag, belly press, lift off, drop arm, infraspinatus resisted
hornblower sign
resisted ER at 90/90 for infraspinatus
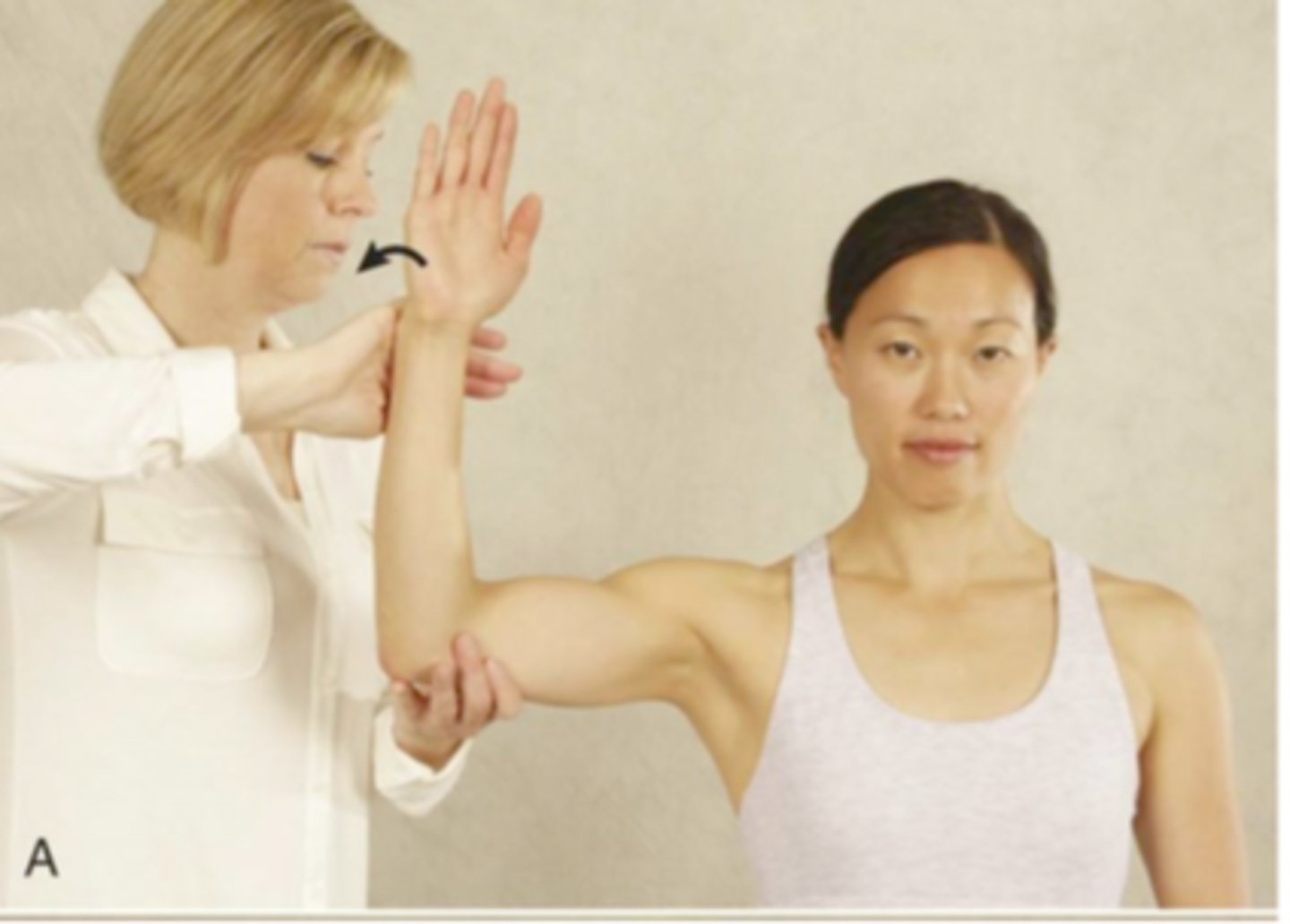

SLAP tests
active compression/obriens test, biceps load II, anterior slide, compression rotation, pain provocation (mimori) test
obriens test
more pain with IR and no pain with ER

biceps load II
pain with resisted elbow flexion
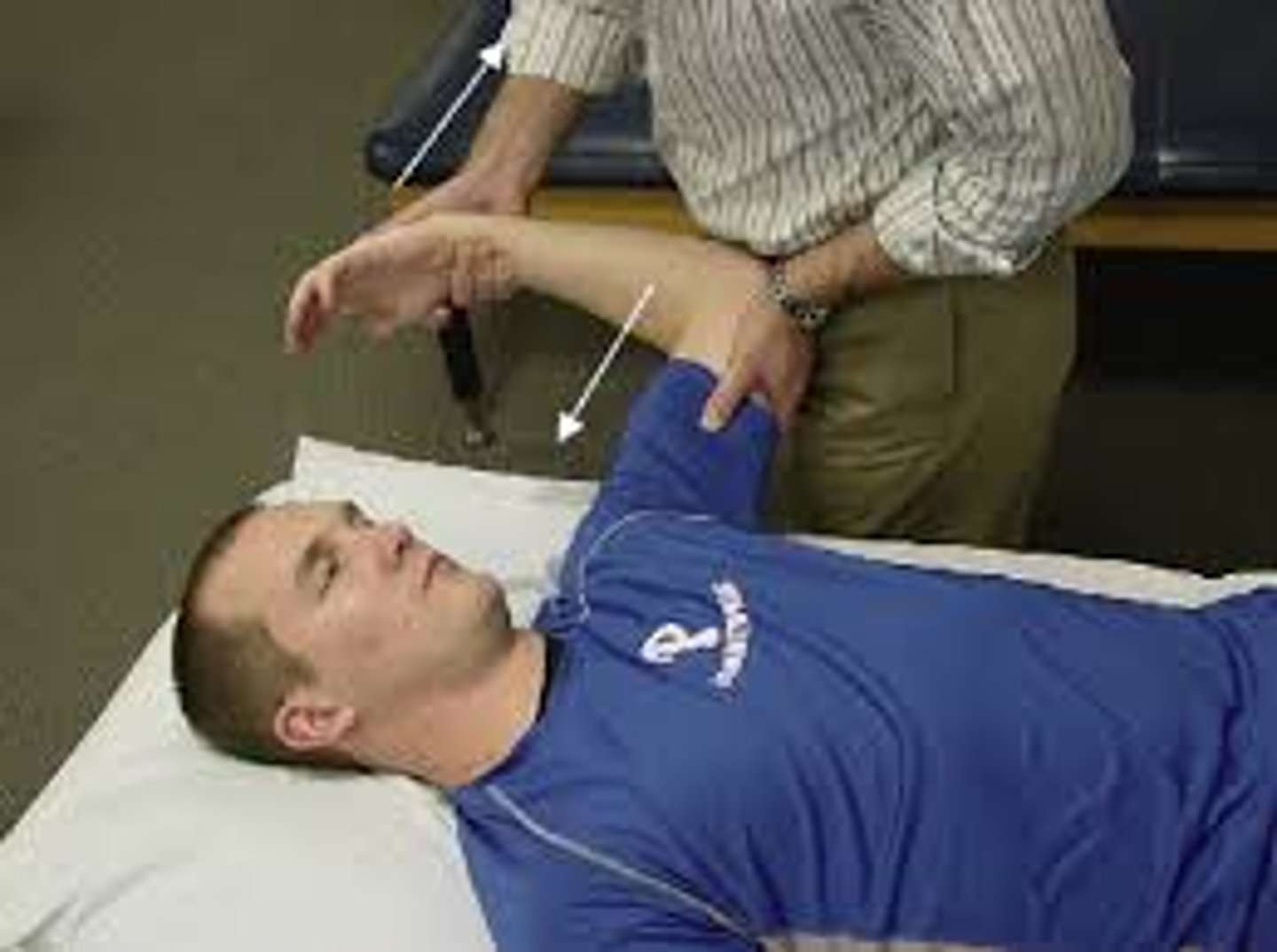
anterior slide test
pain or clicking in deep shoulder
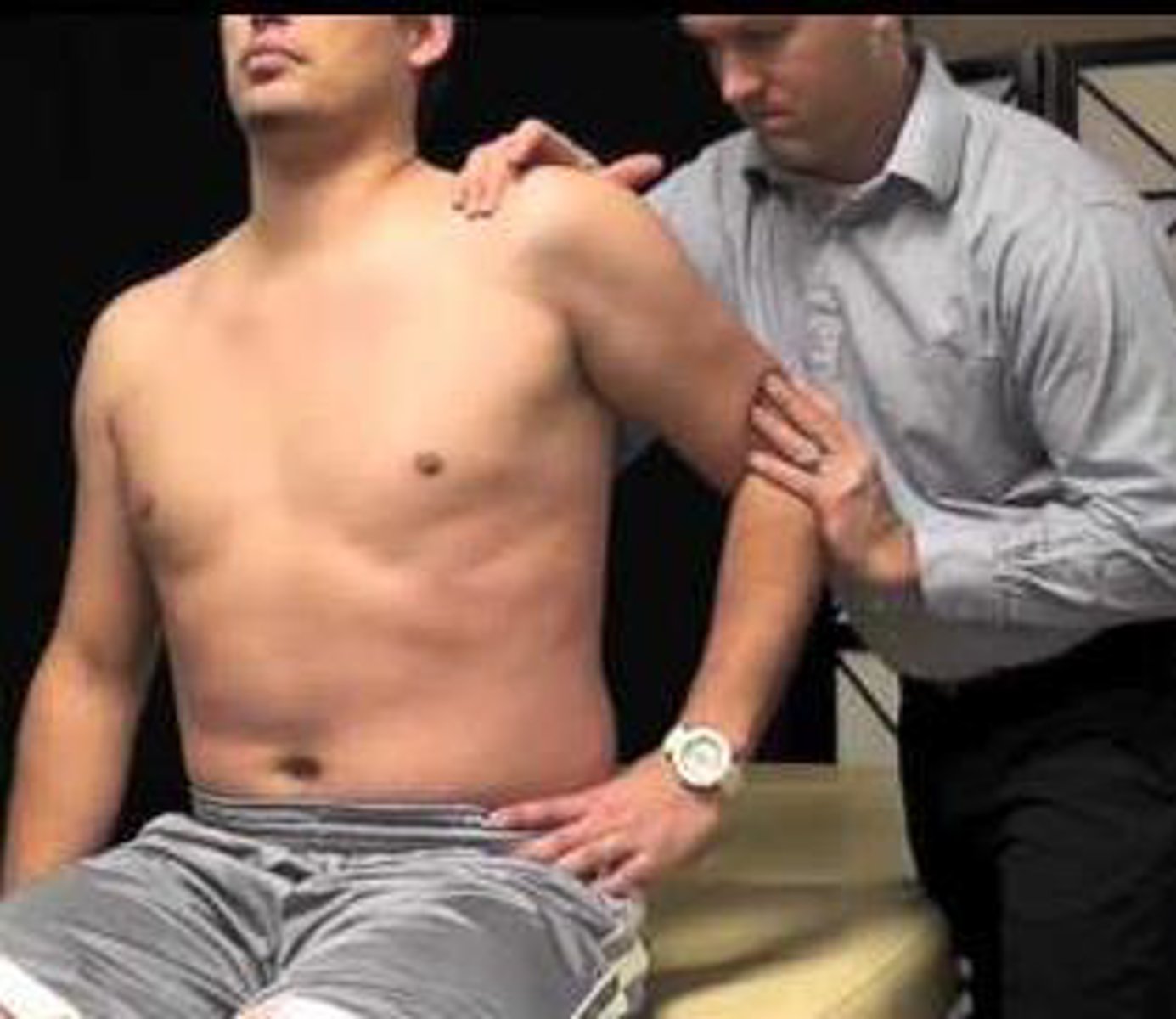
compression rotation test
apply axial compression load with ER and IR
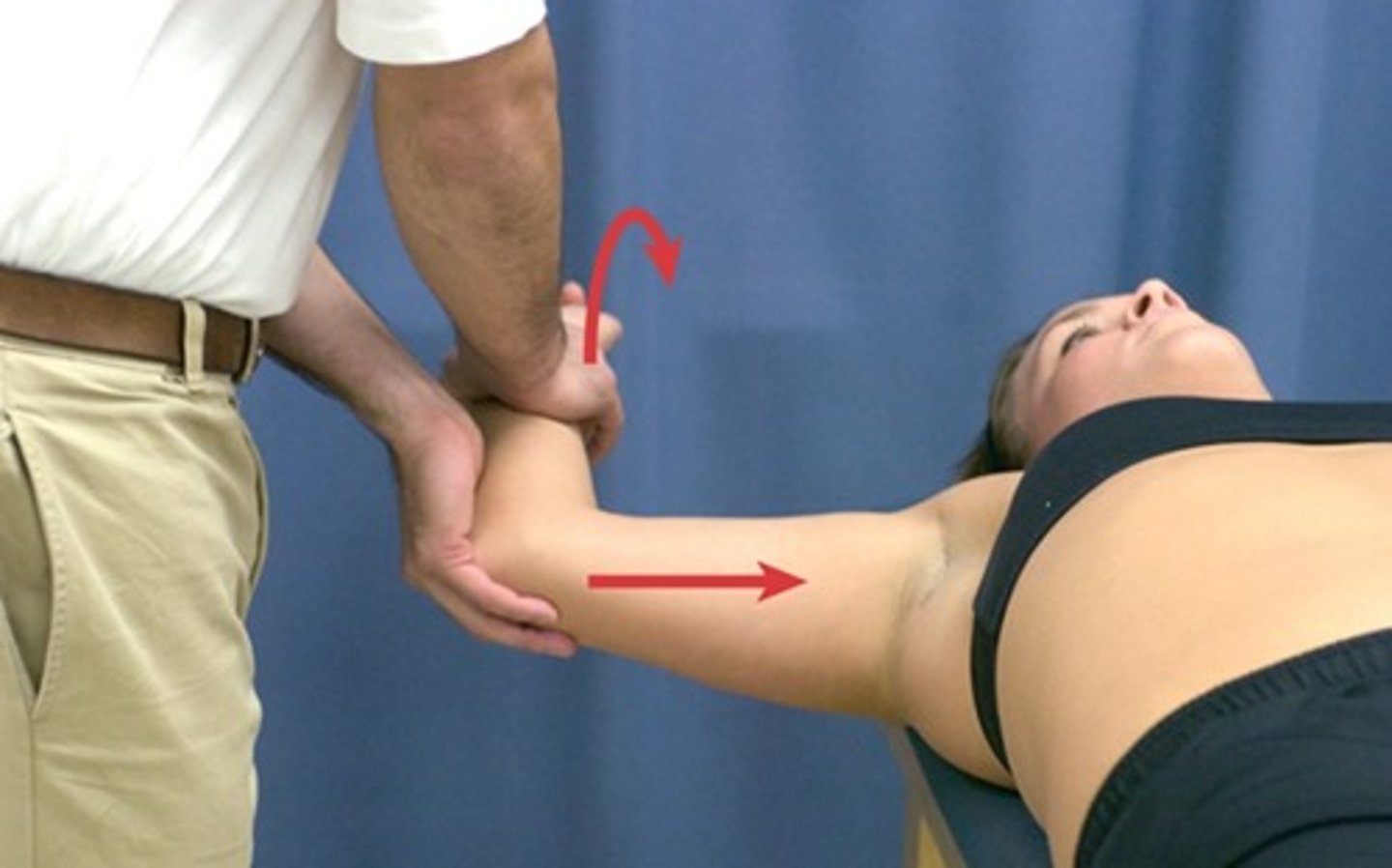
memori/pain provocation test
pain worse in pronated is positive test
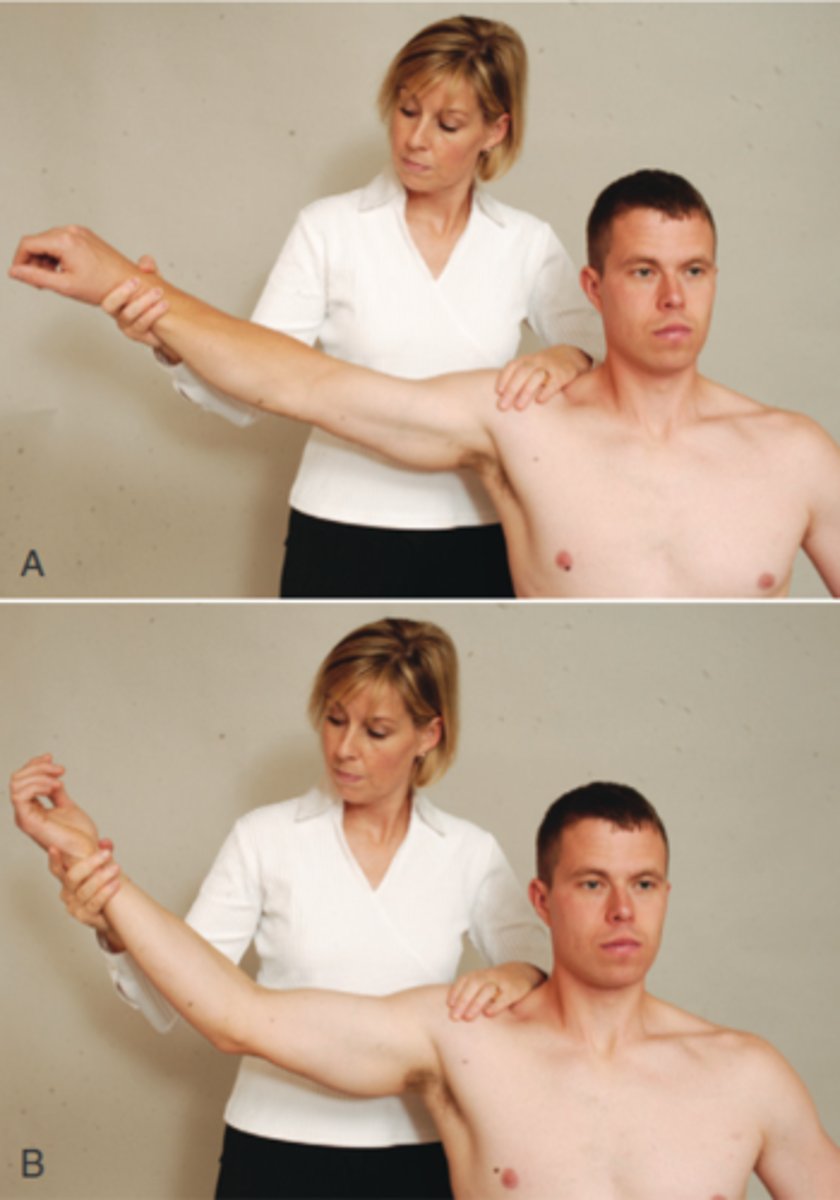
biceps tendonitis test
yergasons, speed test
yergasons
resisted supination and ER
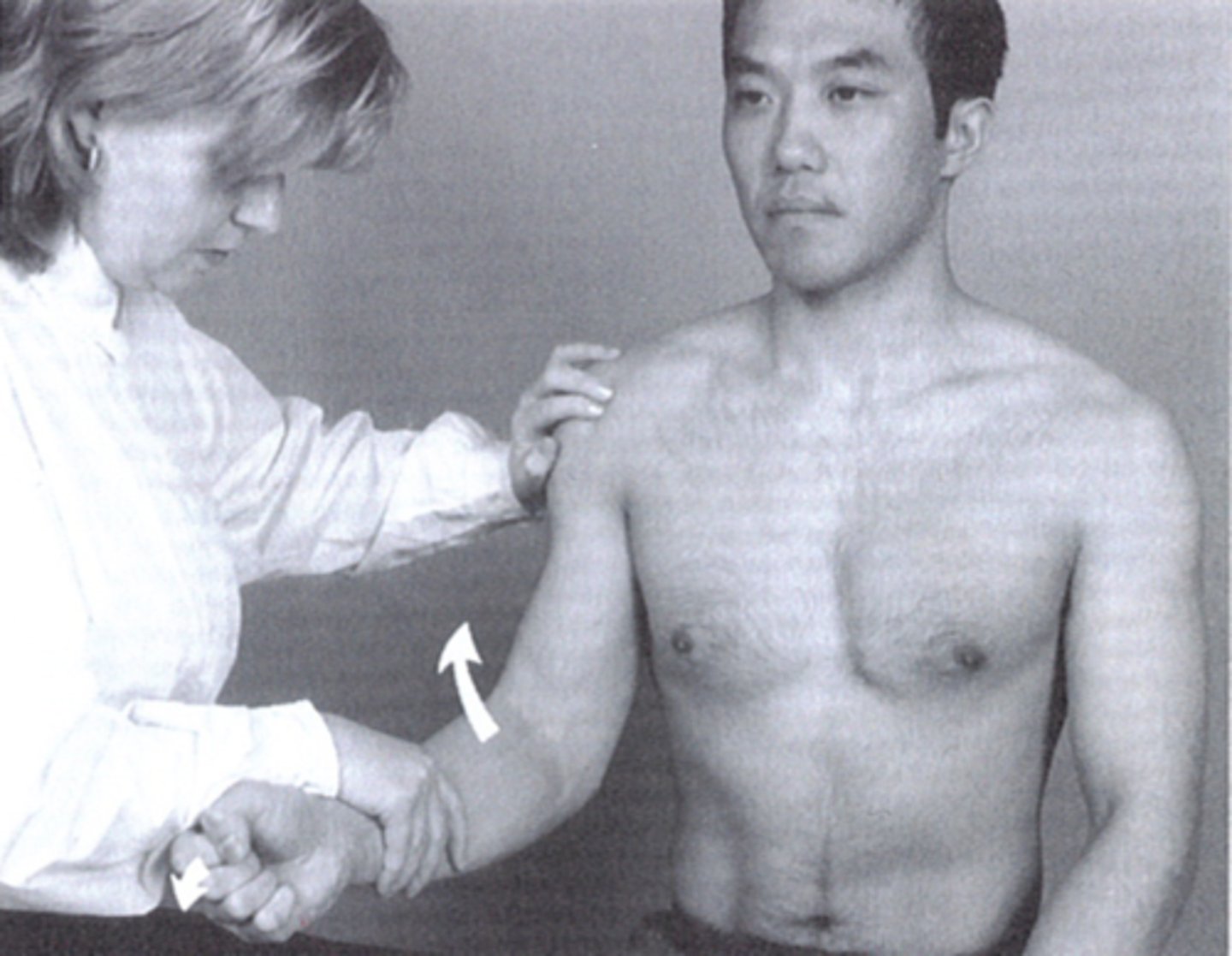
speeds test
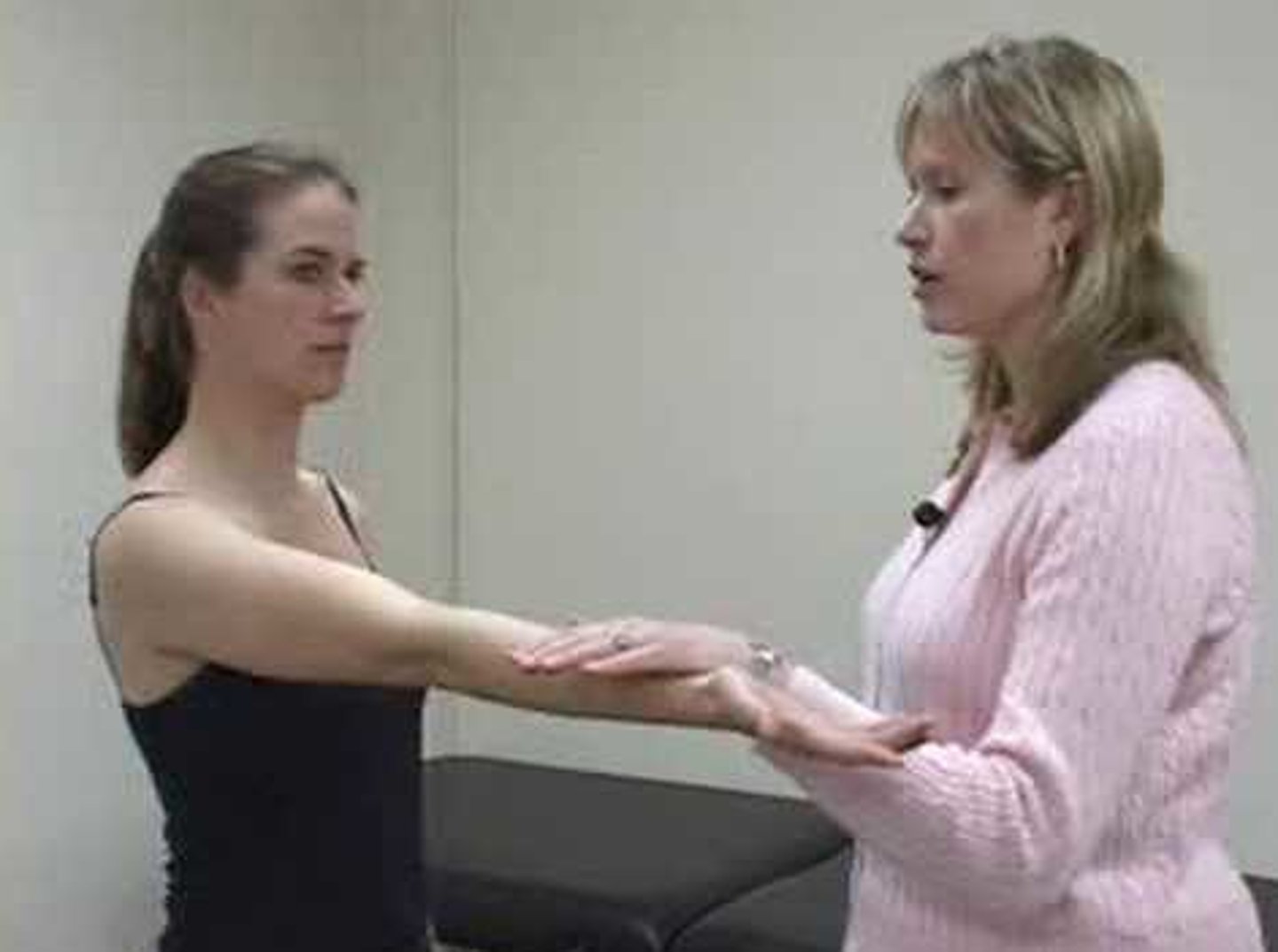

popeyes sign
biceps tendon rupture
anterior instability tests
anterior apprehension test and relocation test
relocation test
after apprehension test, PT stabilizes GHJ posteriorly and the shoulder reduces in apprehension
posterior instability tests
jerk test (posterior-inferior labral), posterior apprehension test
jerk test
sudden jerk with shoulder flexion 90 and IR
TOS tests
adsons, halstead, roos, wright, military brace test
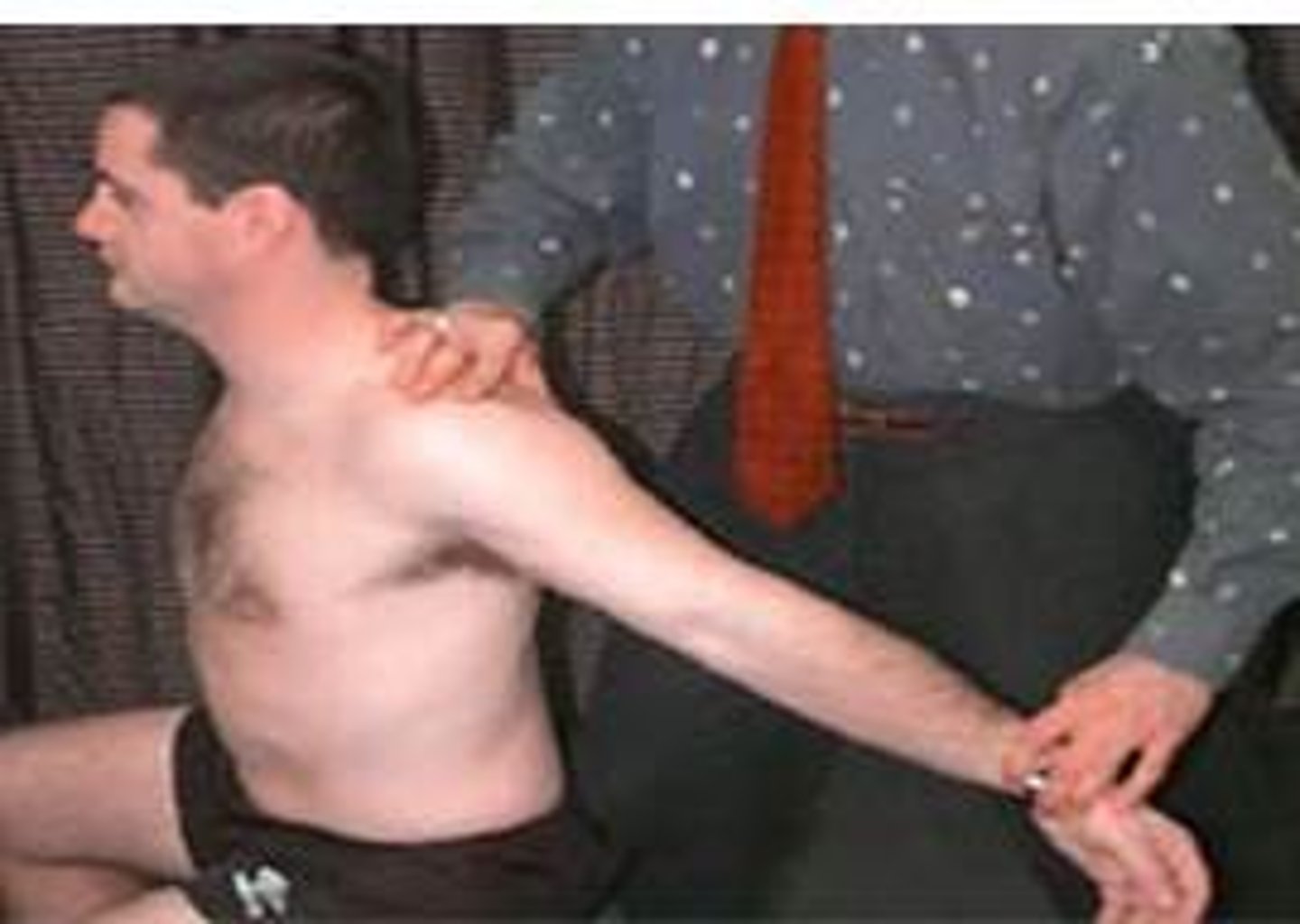
adsons test
rotate toward testing side, ER and extend shoulder and check pulse
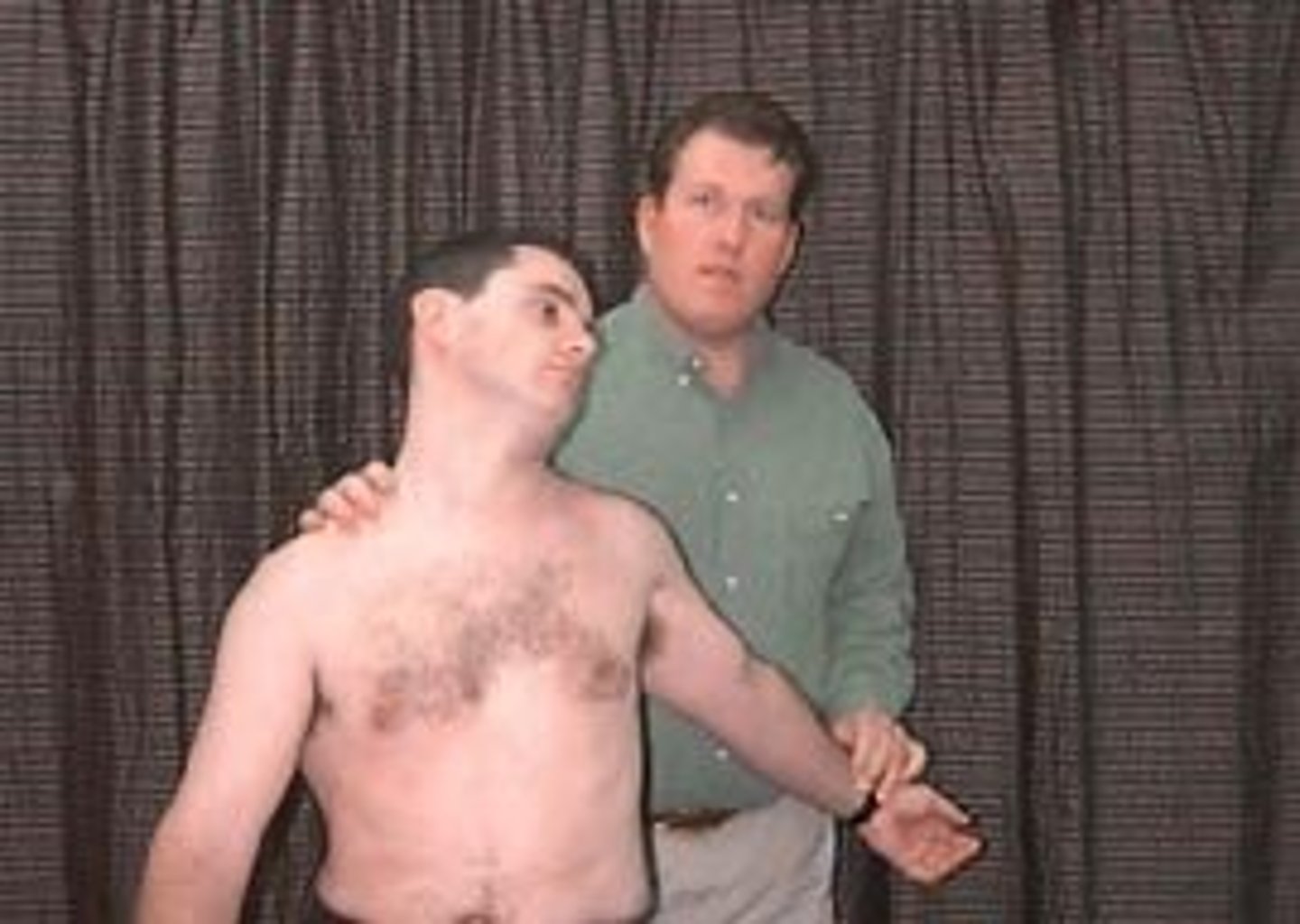
halstead maneuver
applying downward traction on test shoulder
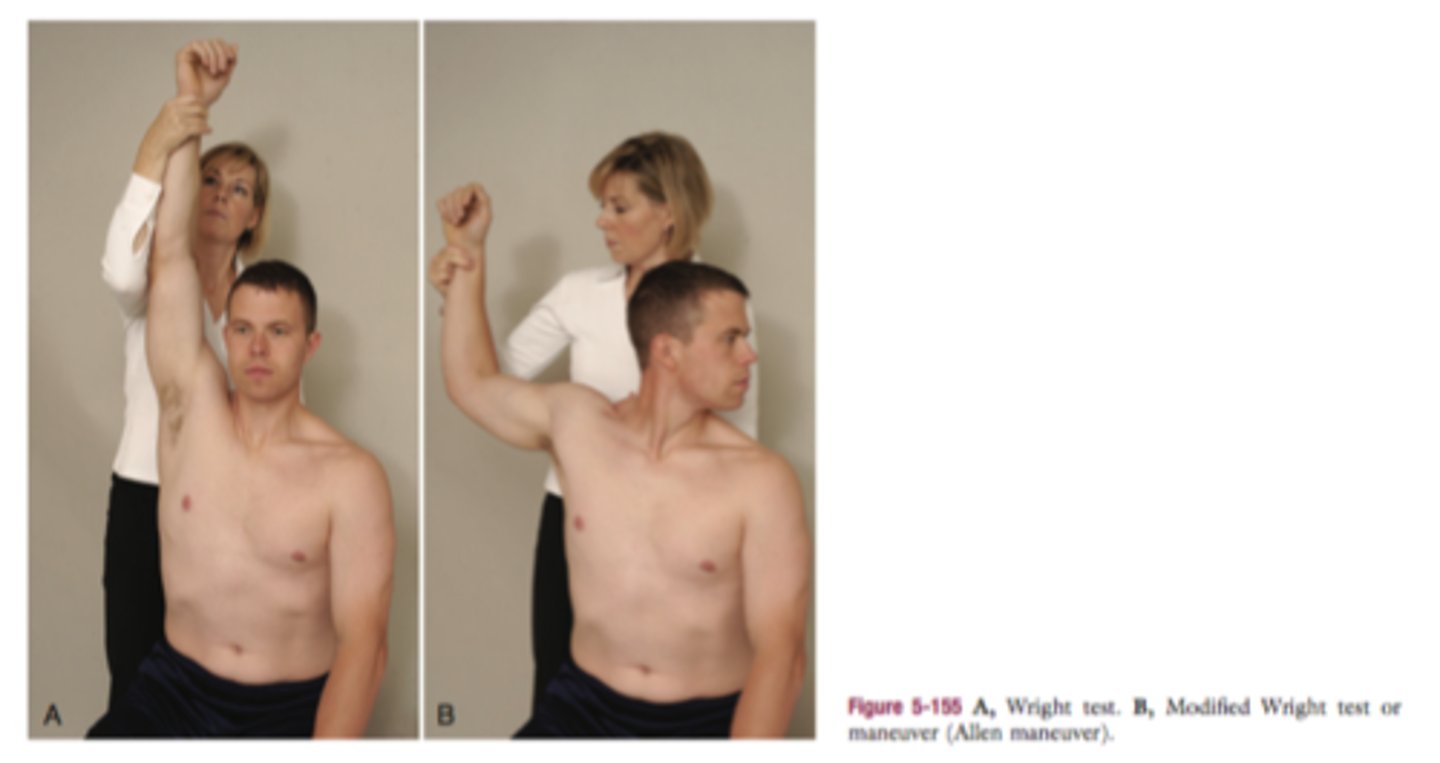
wright test
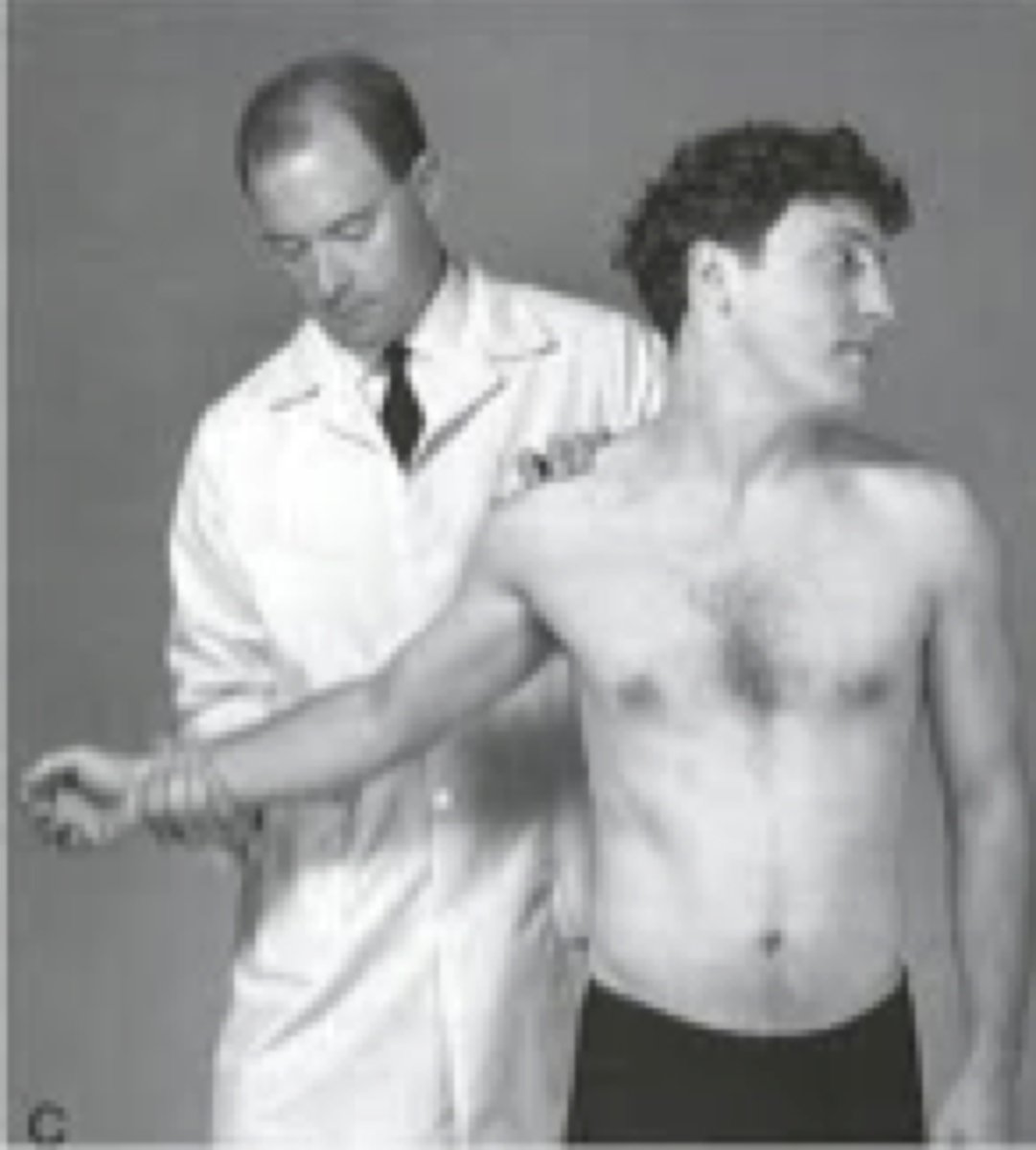
military brace test (costoclavicular syndrome test)
find radial pulse
cubital tunnel special tests
Tinels sign, pinch grib, pressure provocation test, flexion compression test, elbow flexion test
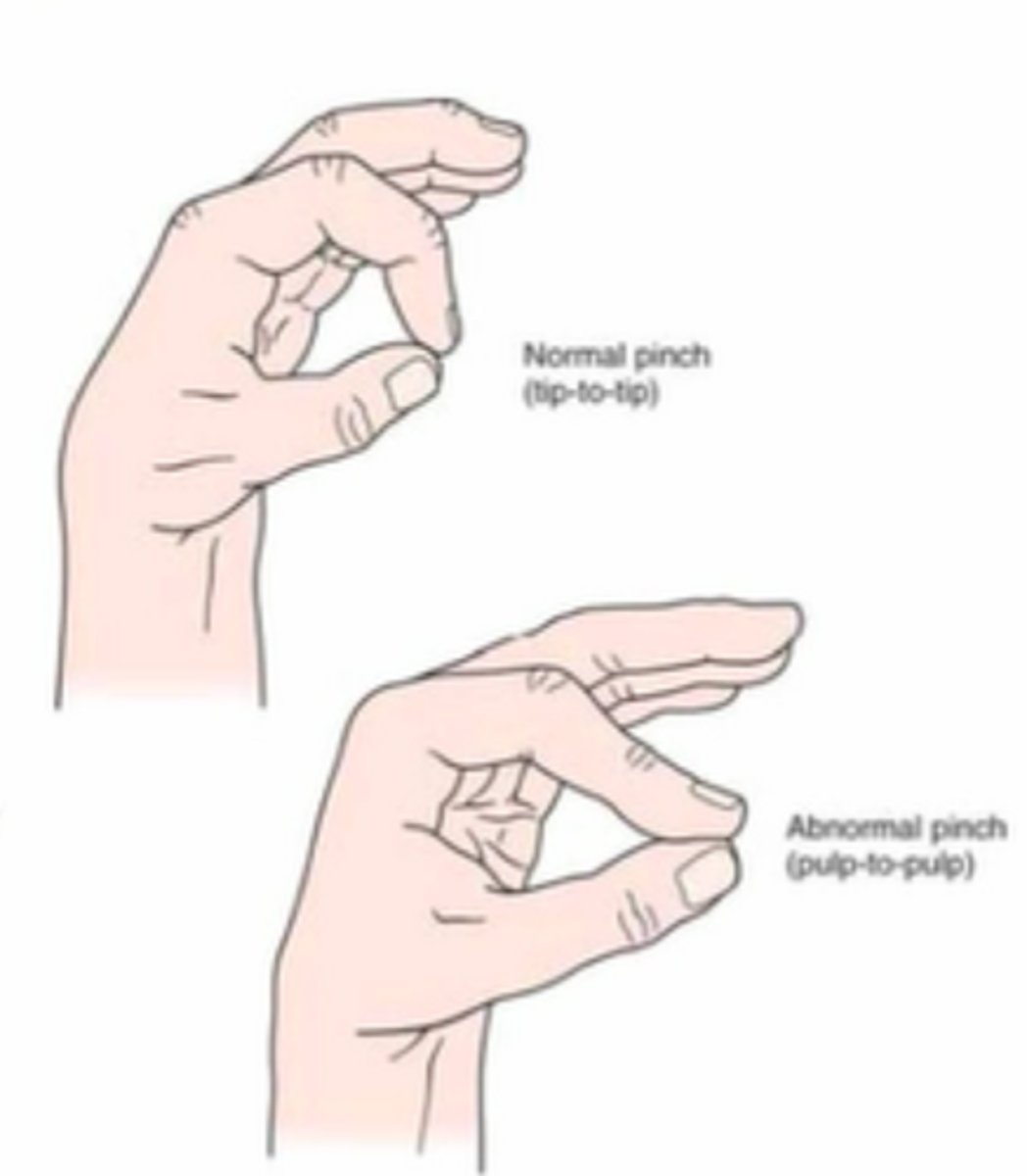
pinch grip
pinch index to thumb (cannot pinch tip to tip--indicates entrapment of AI nerve between pronator teres)
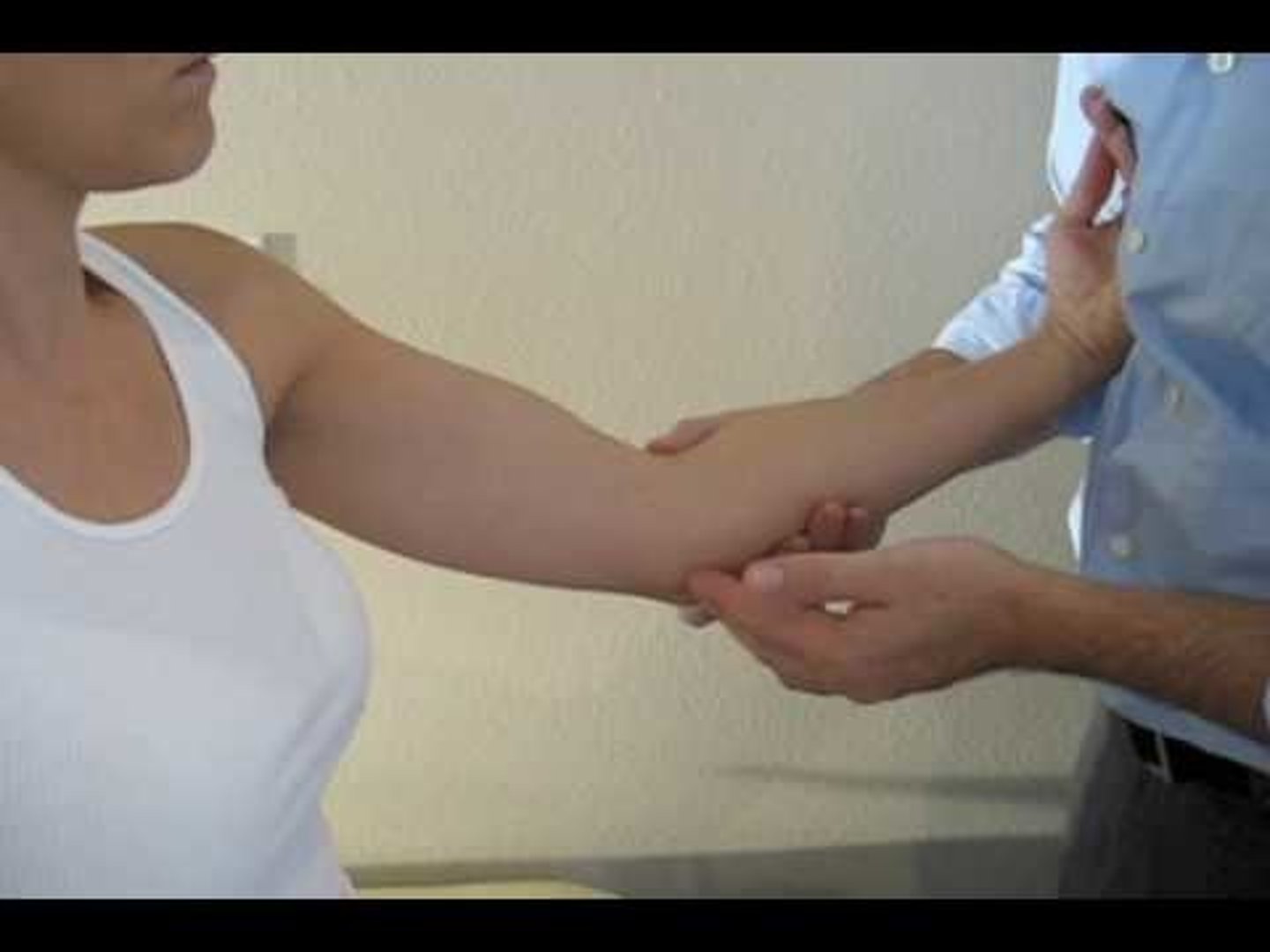
pressure provocation test
flexion compression test
pressure provocation: pressure on ulnar nerve at cubital tunnel --> flexion compression test is the same but add elbow flexion/shoulder abd 90/ER
elbow flexion test
elbow fully flexed with wrist extended and shoulder abducted to 90
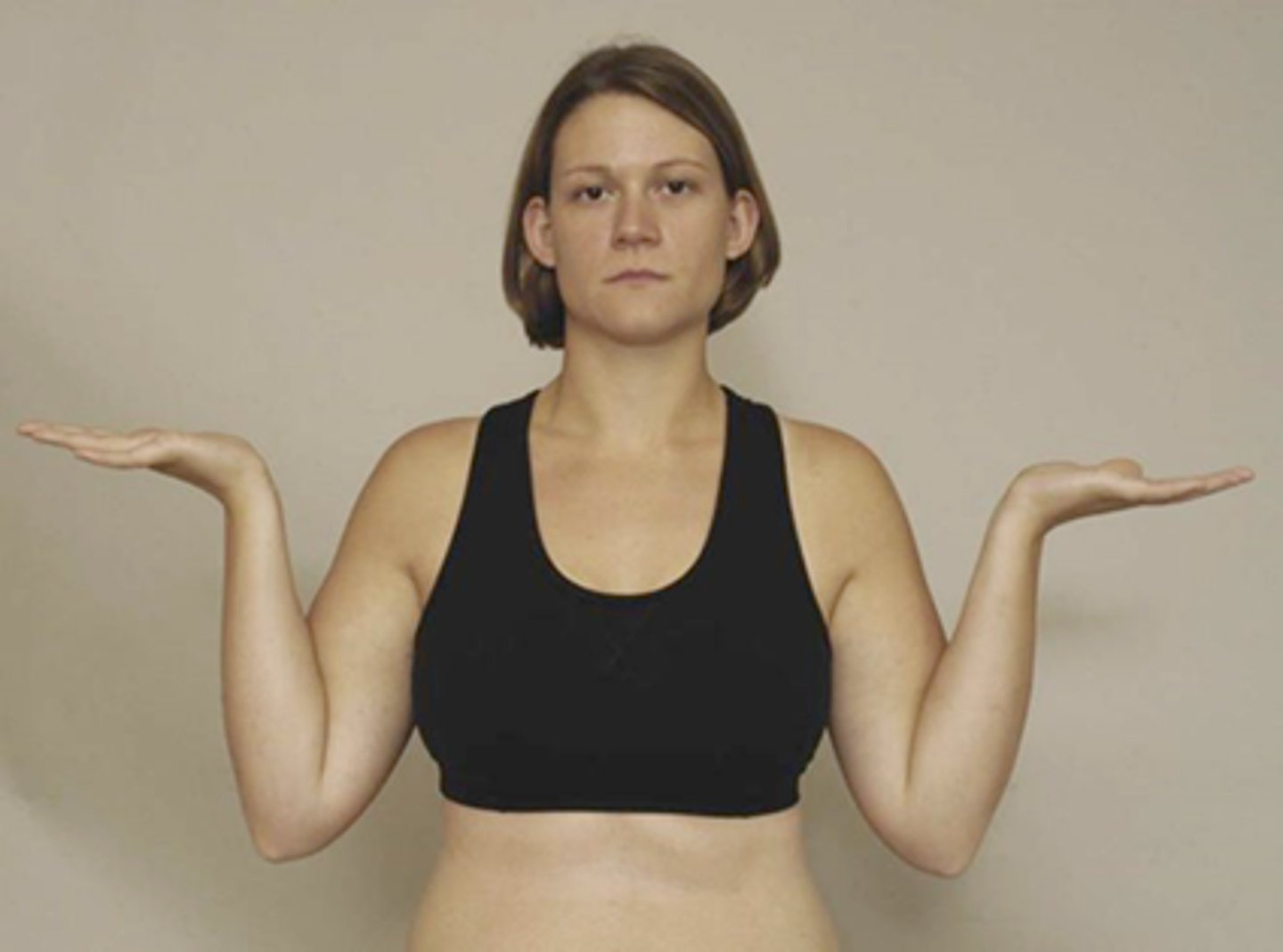

Elbow ligament injury tests
valgus, varus tests
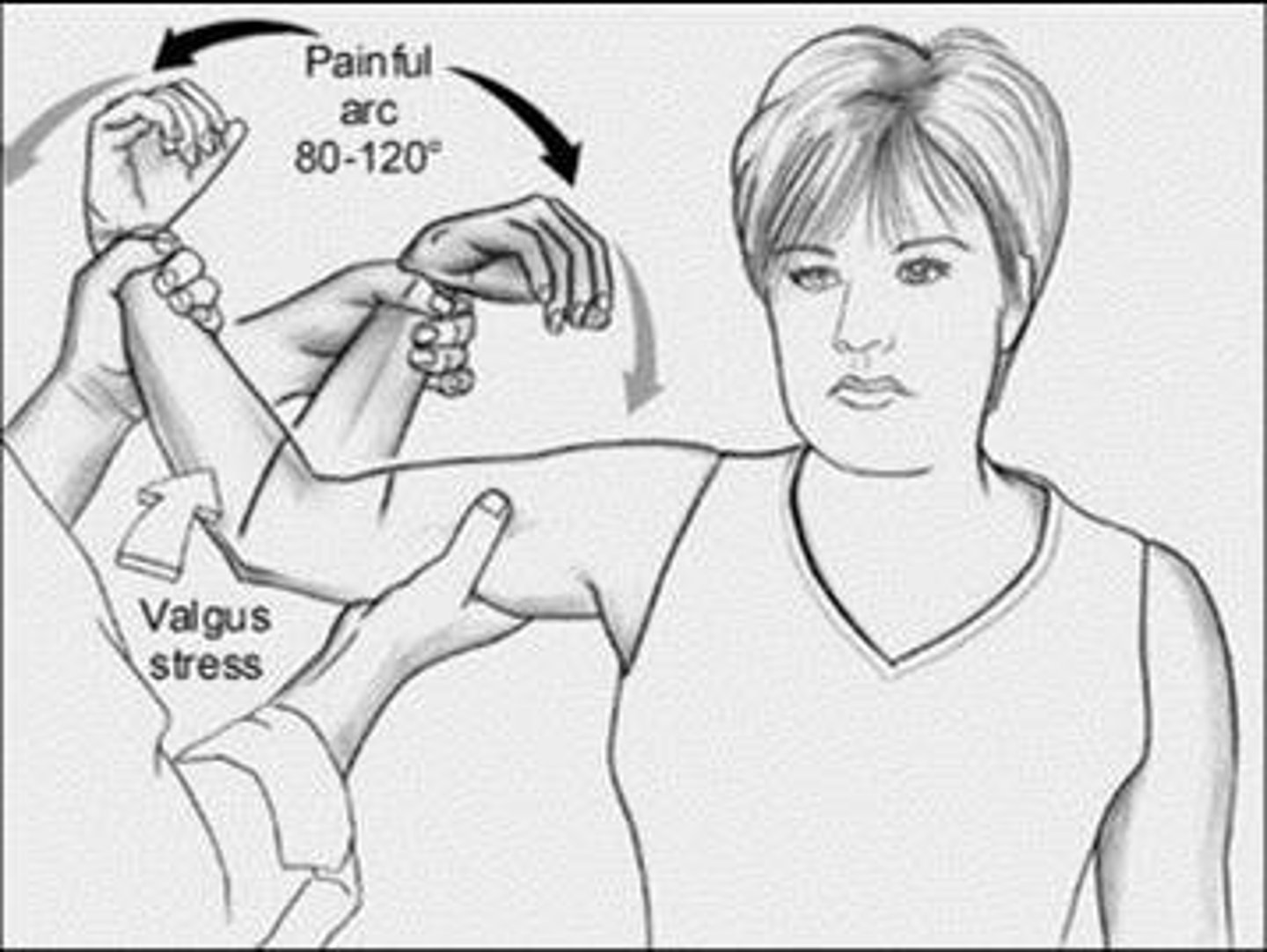
moving valgus
moving valgus test
move elbow from flexion to extension (30 deg)
elbow pain should increase within arc of 120 and 70 deg of flexion if +
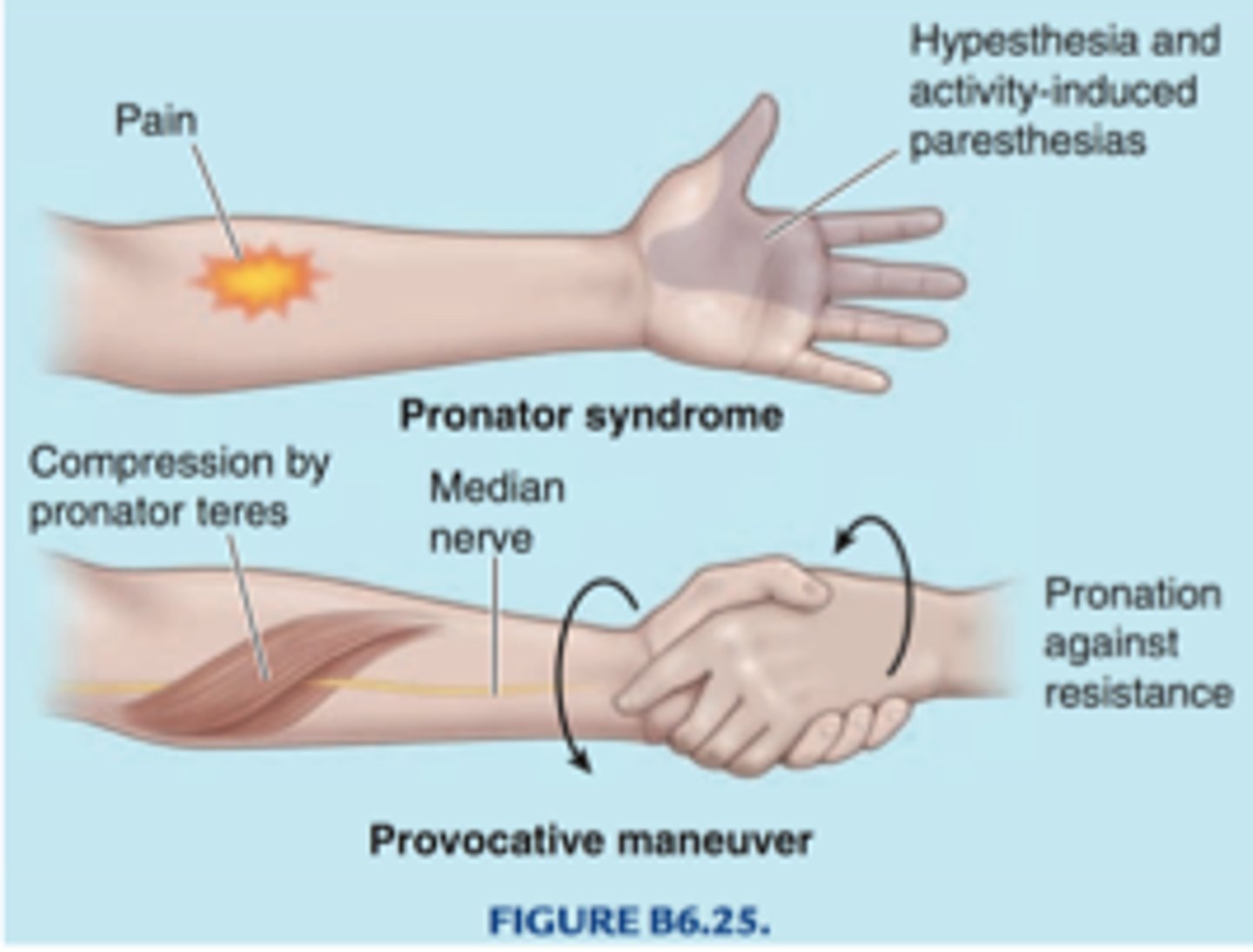
pronator teres syndrome test
identifies median nerve entrapment
lateral epicondylitis test
cozen test
mill test
maudsley test
cozen test
resisted wrist extension
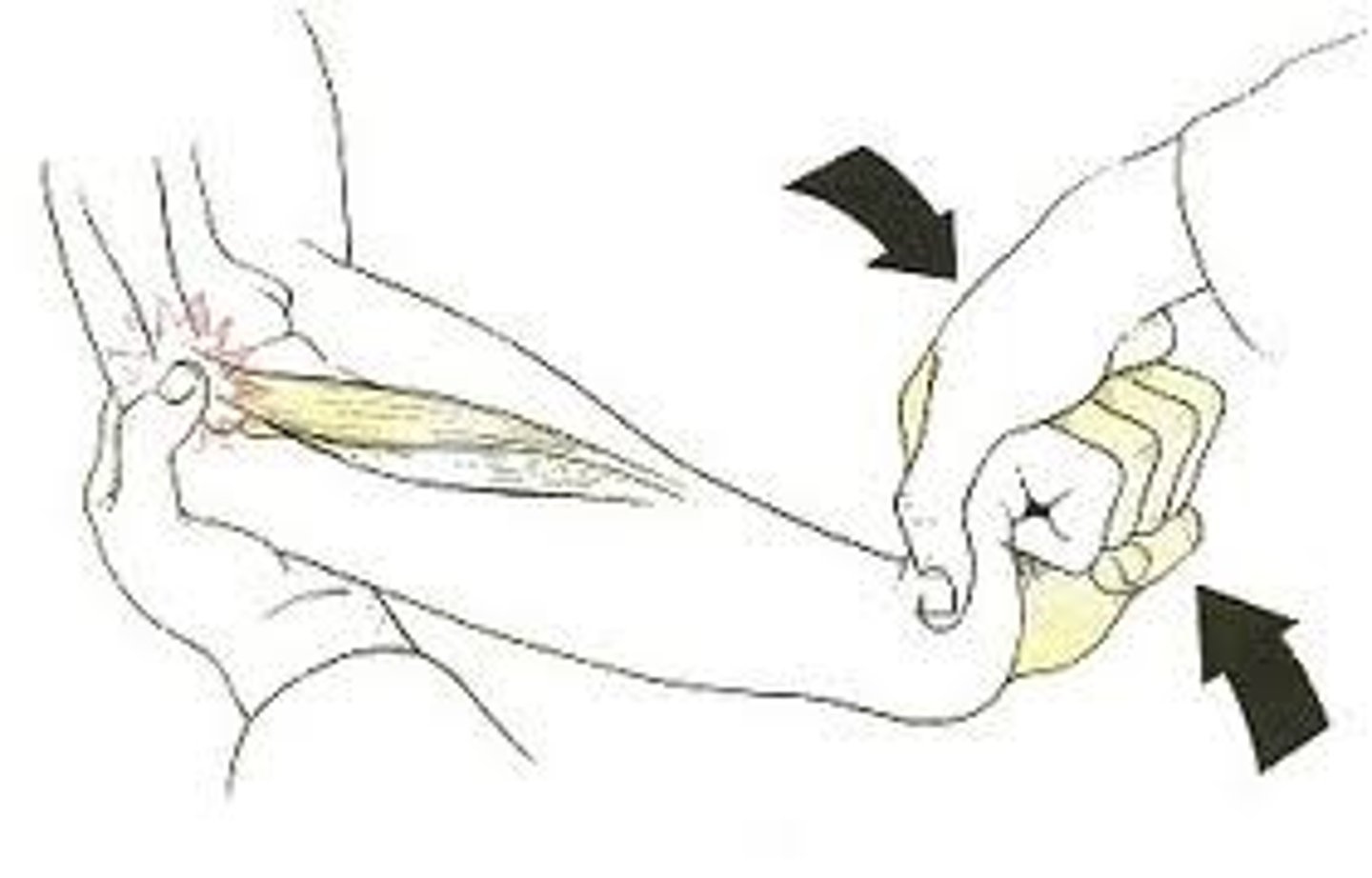
mill test
passive stretching of the wrist extensors
maudsley test
resisted 3rd digit extension (distal to PIP)
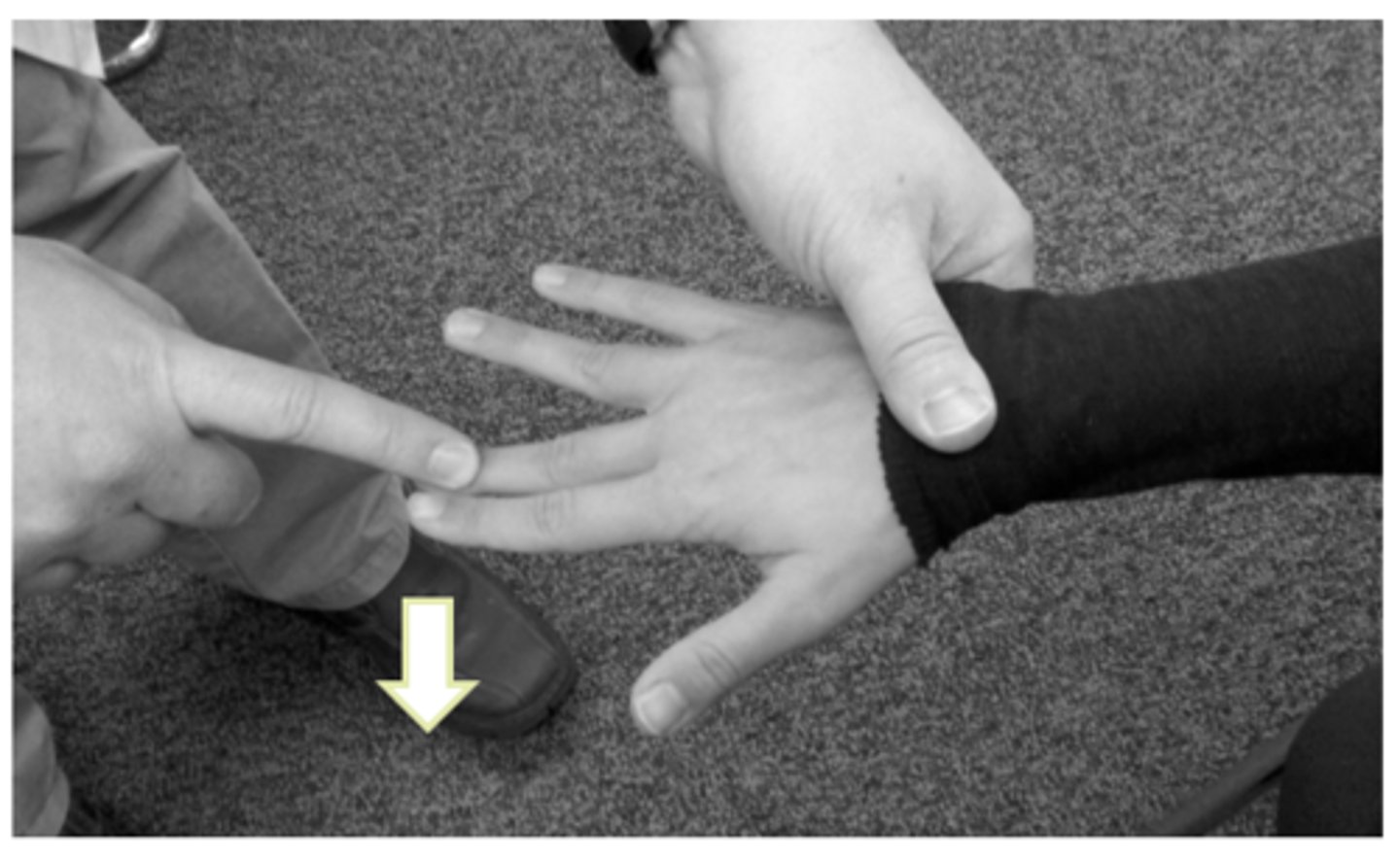

medial epicondylitis test
stretching wrist flexors
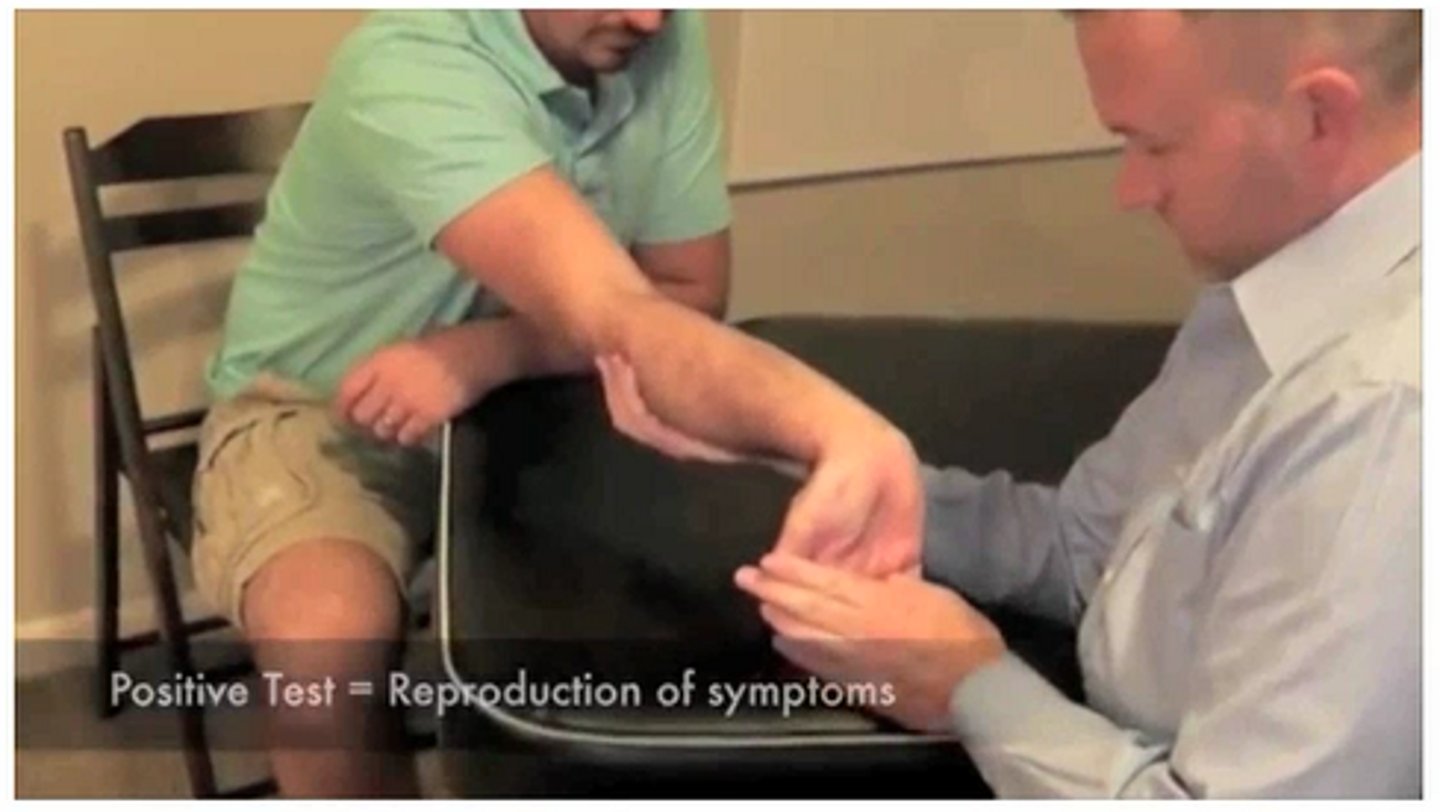

CTS tests
carpal compression test, tinels sign, flick maneuver, sensory testing, phalens test, reverse phalens test
carpal compression test
pressure over median nerve in carpal tunnel
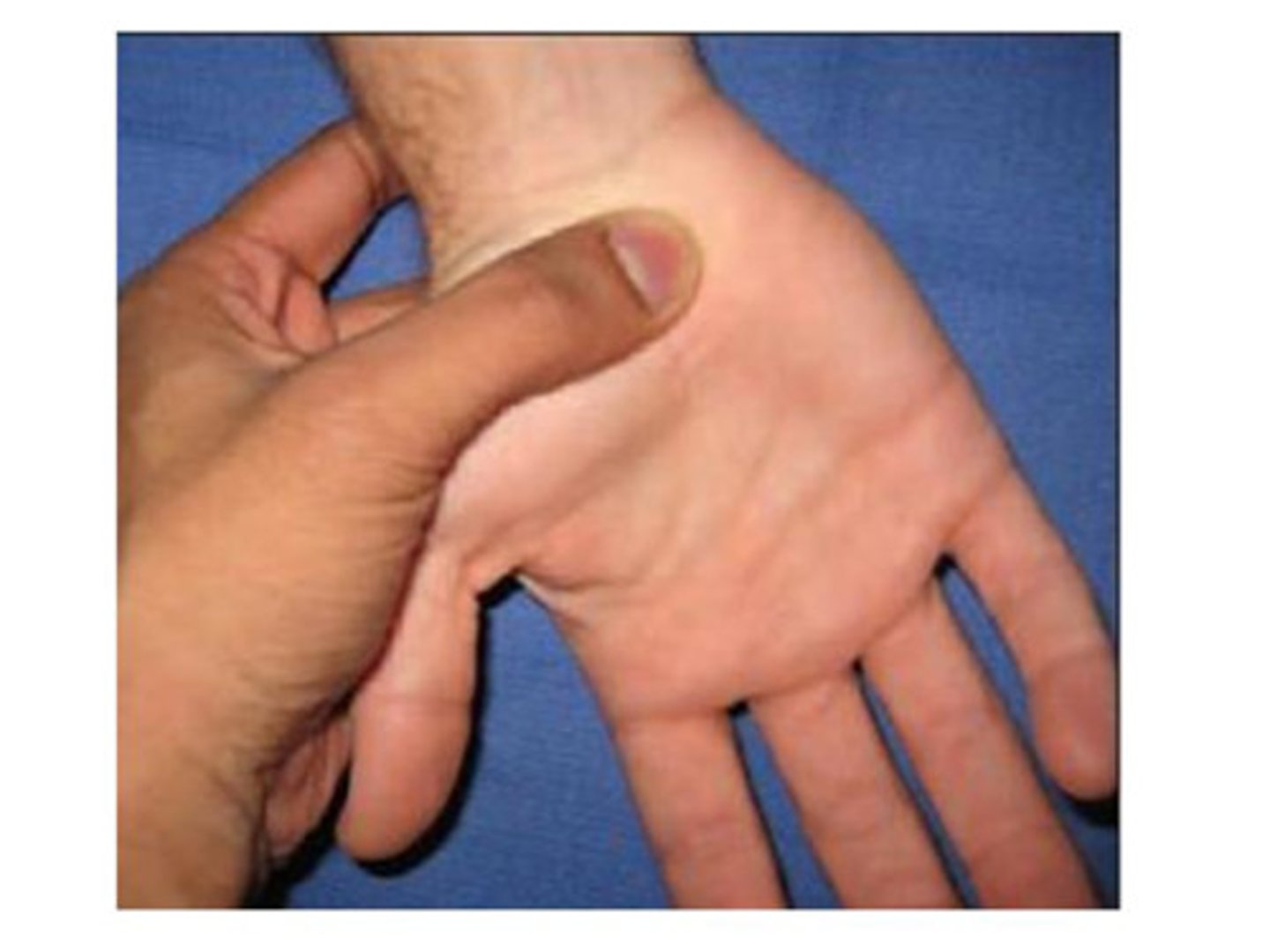
flick maneuver
shaking hands helps the symptoms of CTS
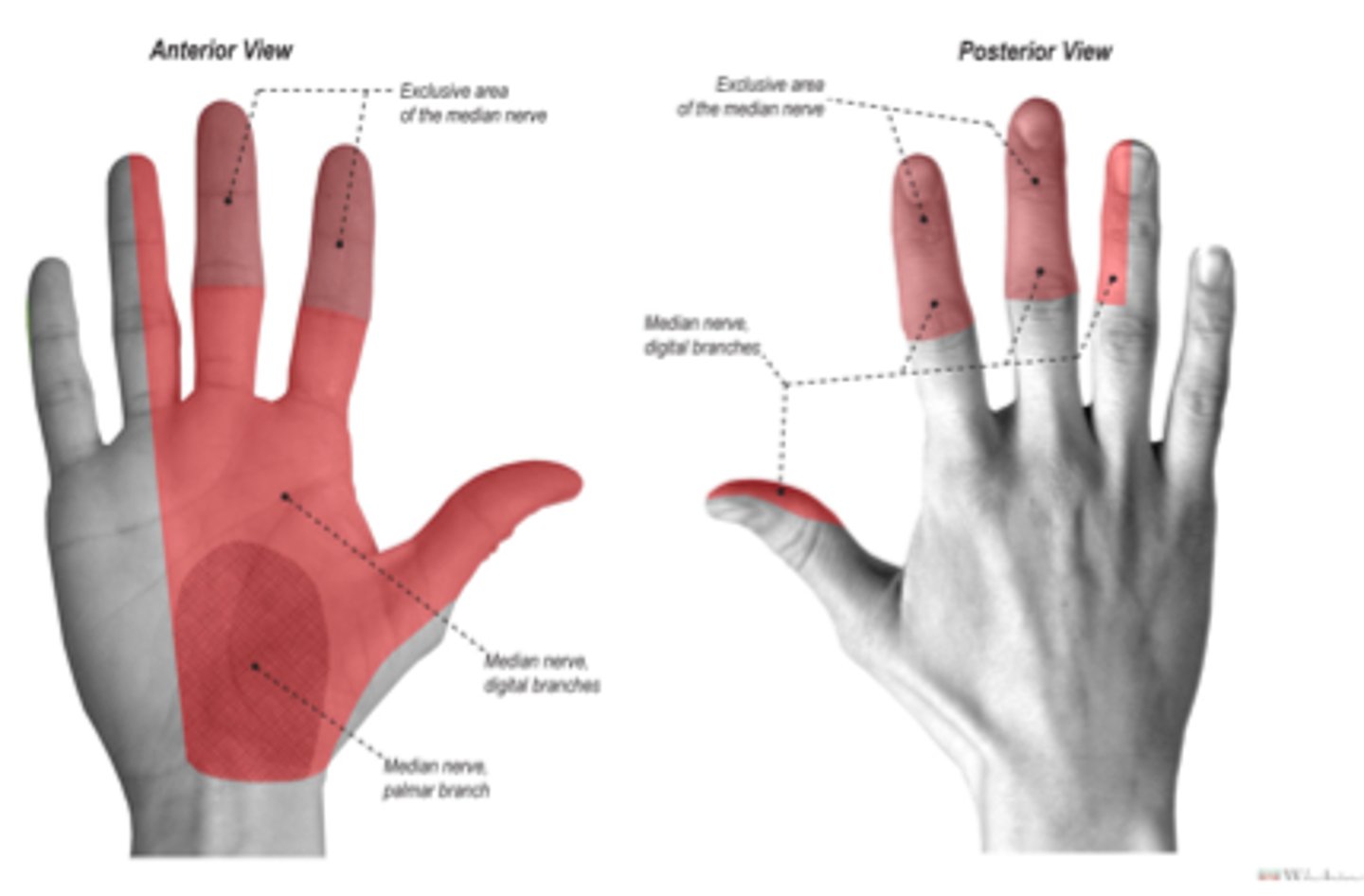
median nerve sensory distribution
reverse phalens test

TFCC tests
supination lift test, TFCC press test, ulnar fovea sign
supination lift test
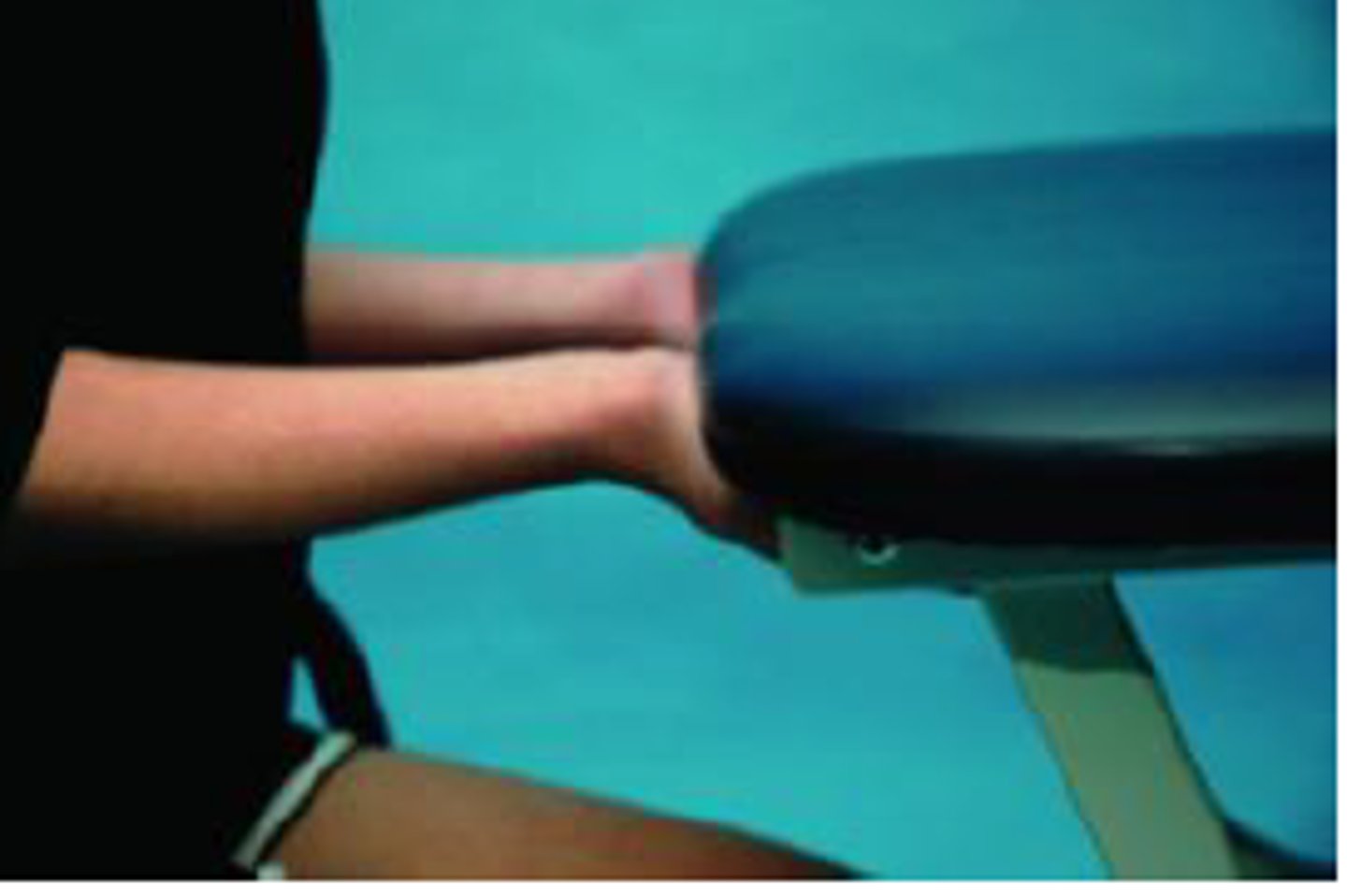

TFCC press test
pushing up from a chair on hand rests
ulnar fovea sign
compression of TFCC in supination
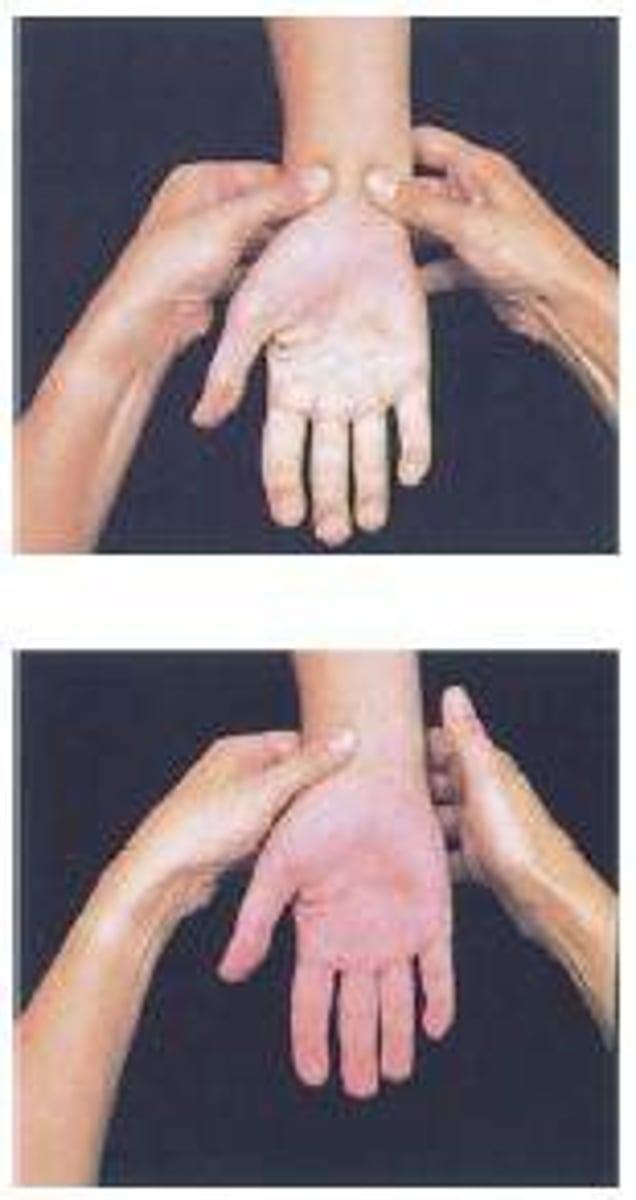
scaphoid fx test
snuff box palpation, thumb grind test (axial load)
watson test
scaphoid shift test --> passive wrist ulnar deviation and slight extension --> press scaphoid --> bring into RD and slight flexion
for scaphoid instability
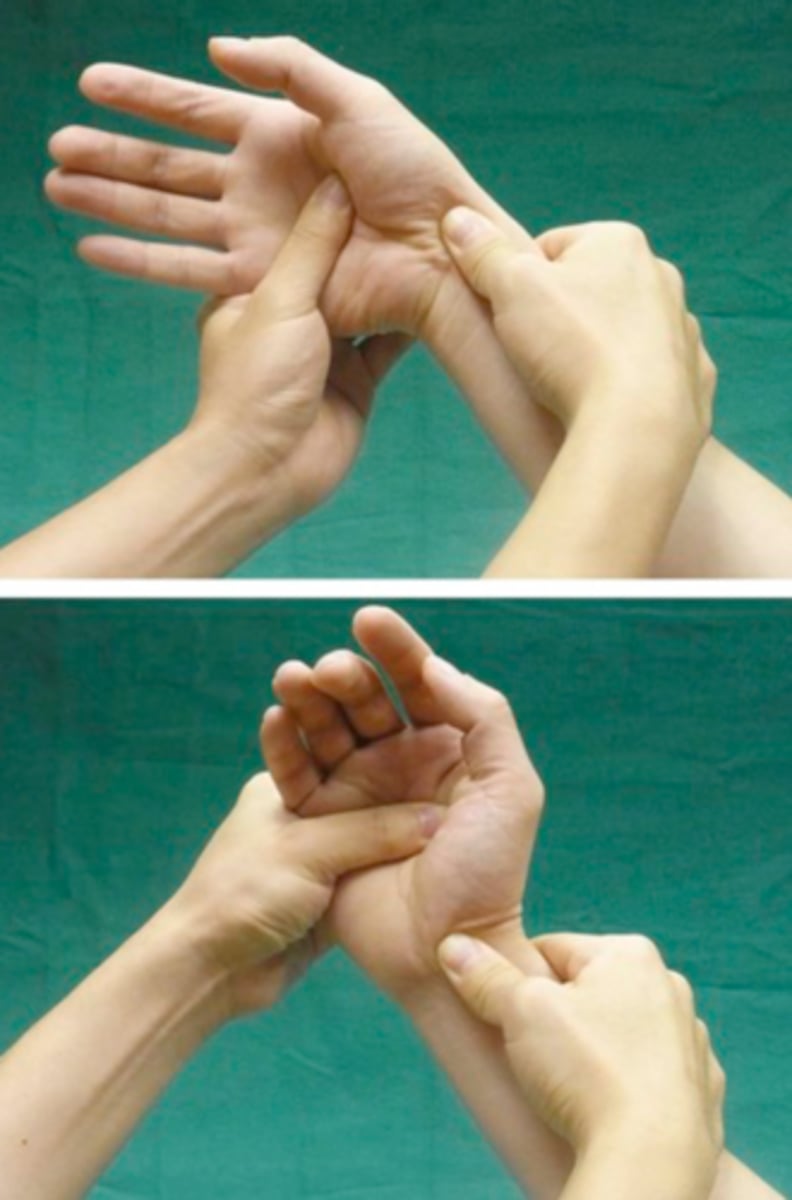
murphy sign
3rd MCP head appears same height as others in a fist

dequervians tenosynovitis tests
finkelsteins, WHAT test
WHAT test
highest sensitivity for DQT
max flexion of wrist and extend and abduct thumb with increasing abduction resistance from therapist to thumb
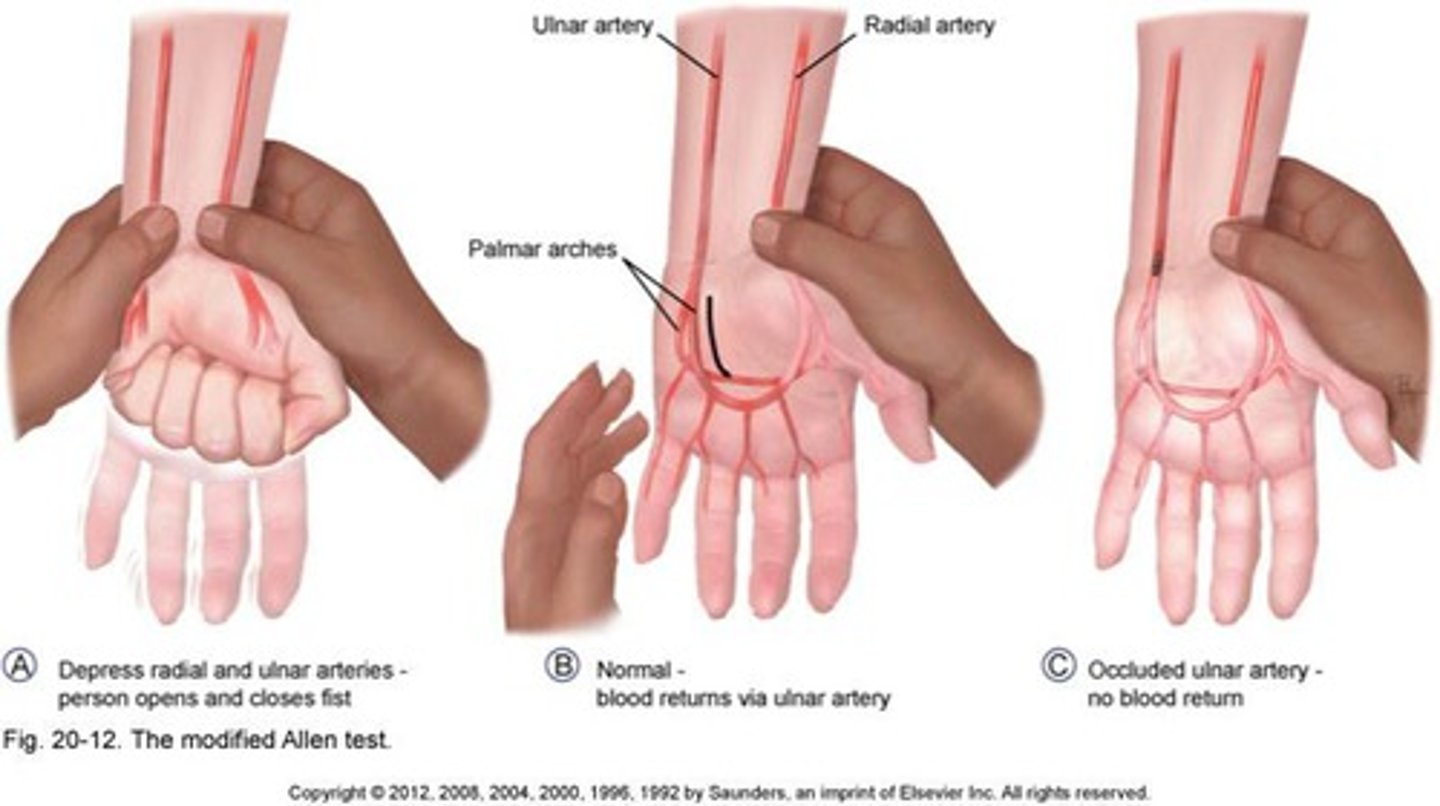
modified allens test
for vascular compromise
open and close fingers and make a fist while compressing arteries and letting go one at a time
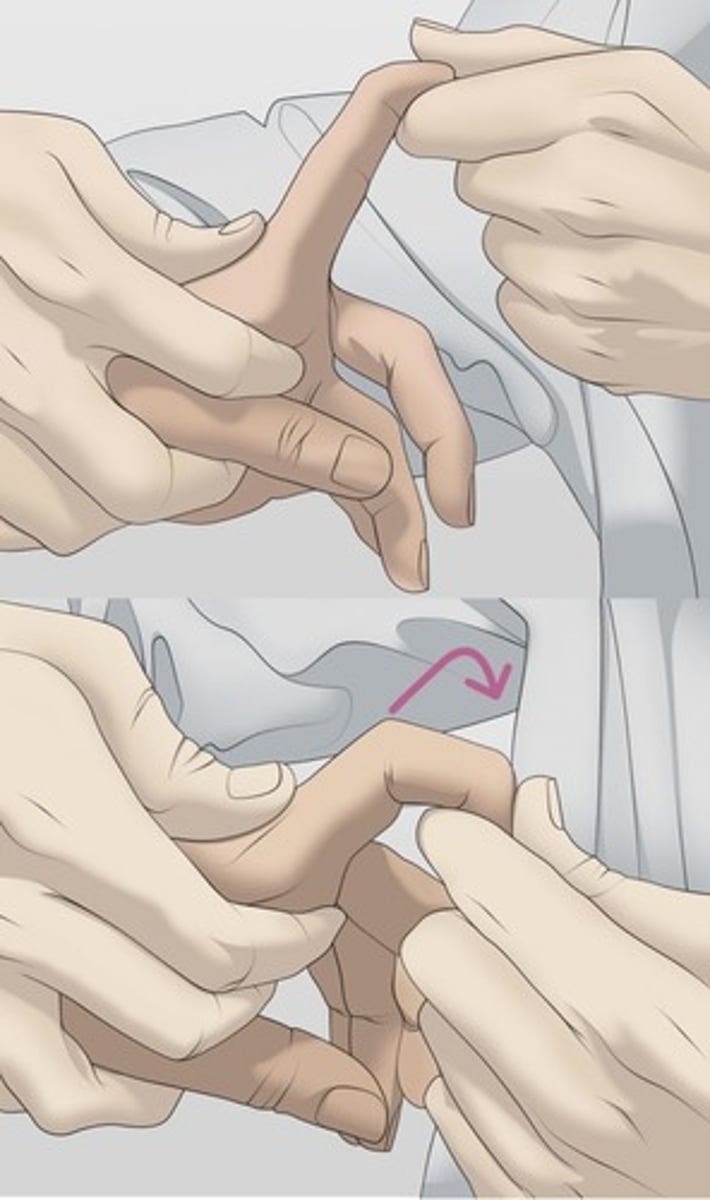
Brunnel-Littler Test
Purpose: Intrinsic Muscle Tightness
Method: Pt is sitting with metacarpophalangeal joint in slight extension. PT moves the PIP joint into flexion
Positive Test: PIP joint does not flex with metocarpholageal joint in slight extension.
harness zancolli test
tight retinacular test
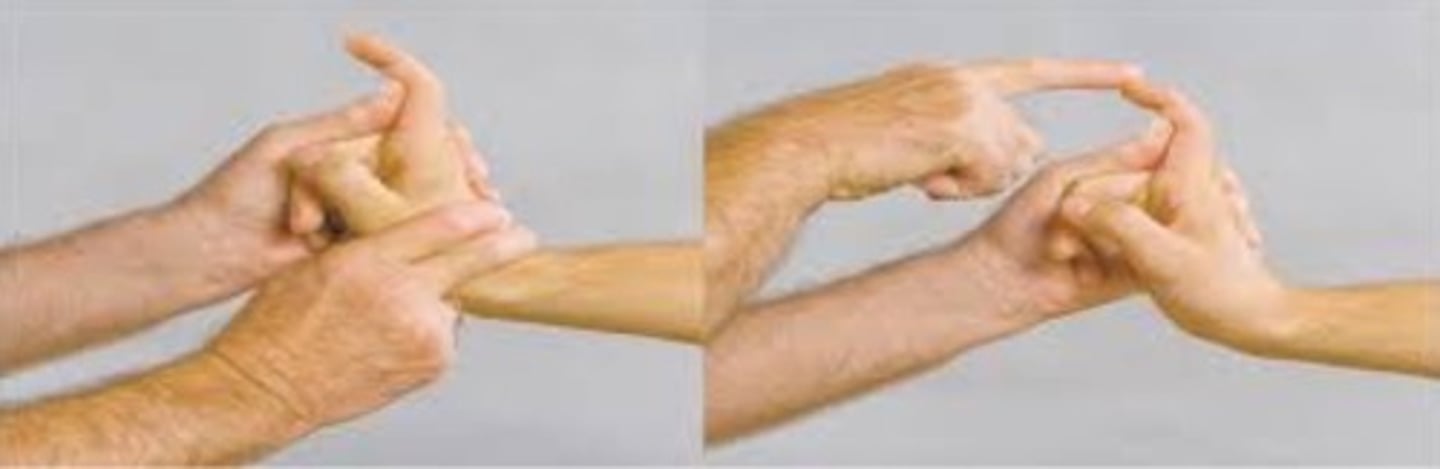

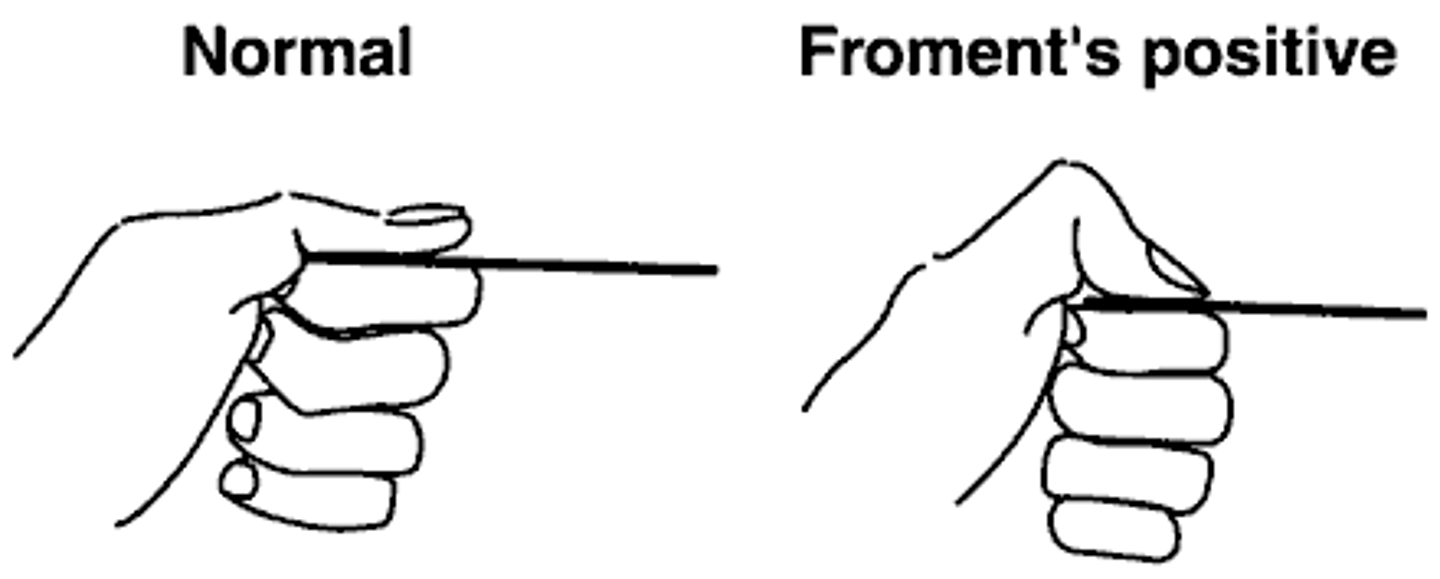
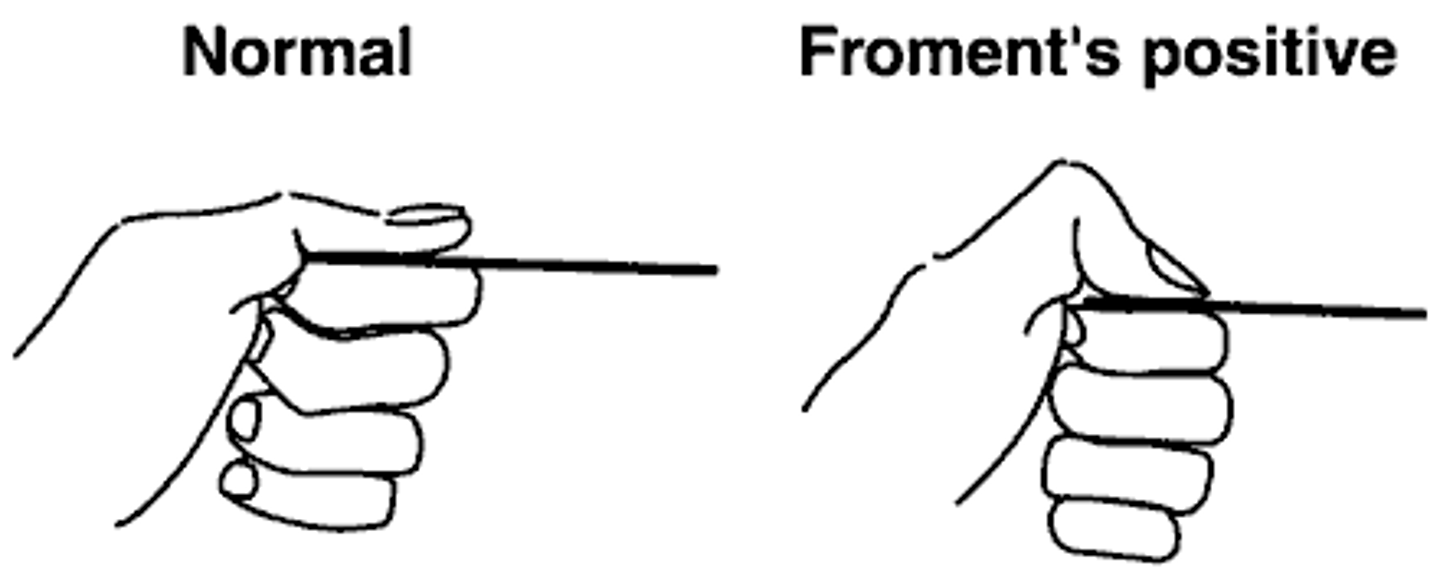
froments sign
grip paper between thumb and finger--> need to utilize flexor pollicus instead of adductor pollicus
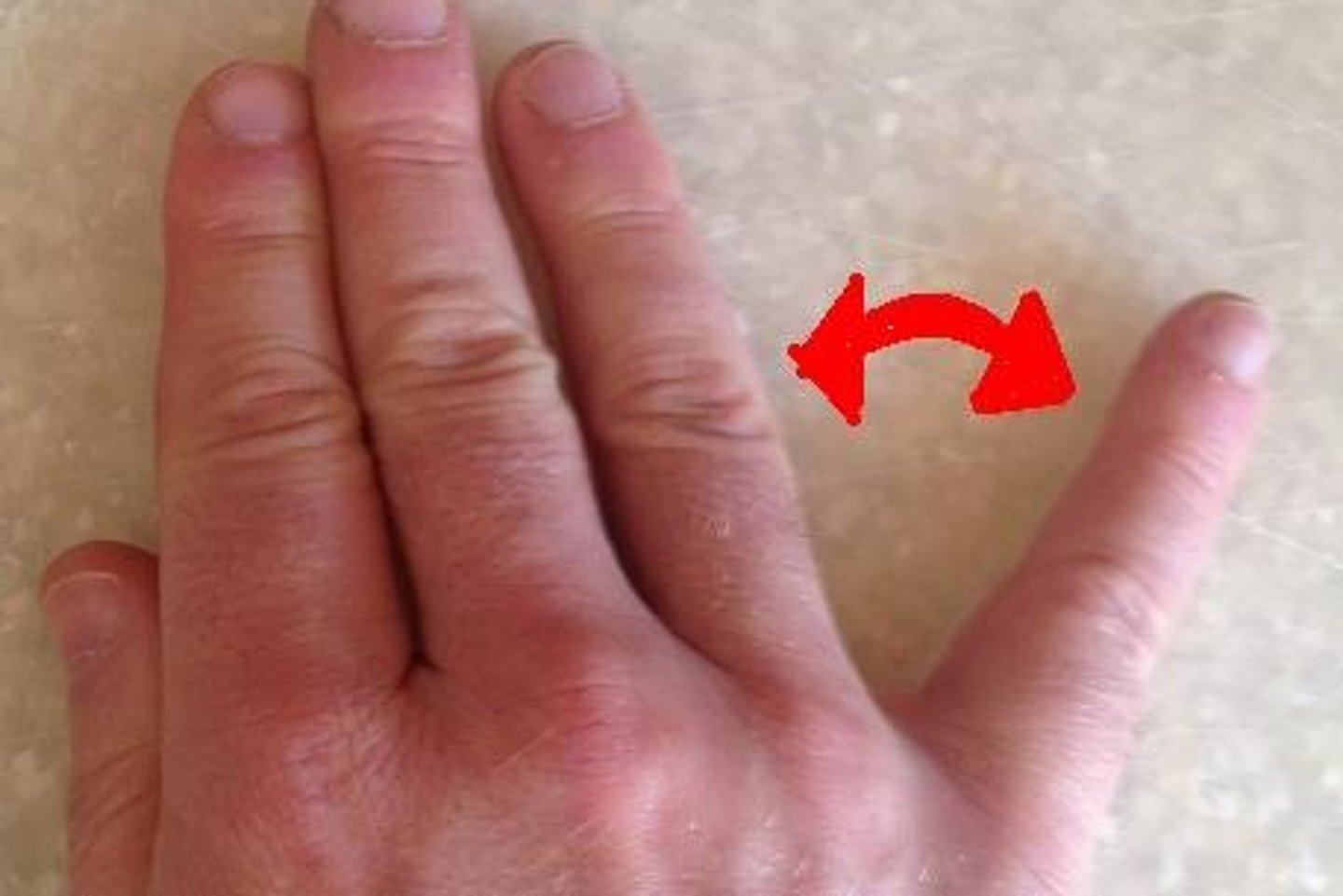
wartenberg sign
cannot adduct little finger back into neutral position
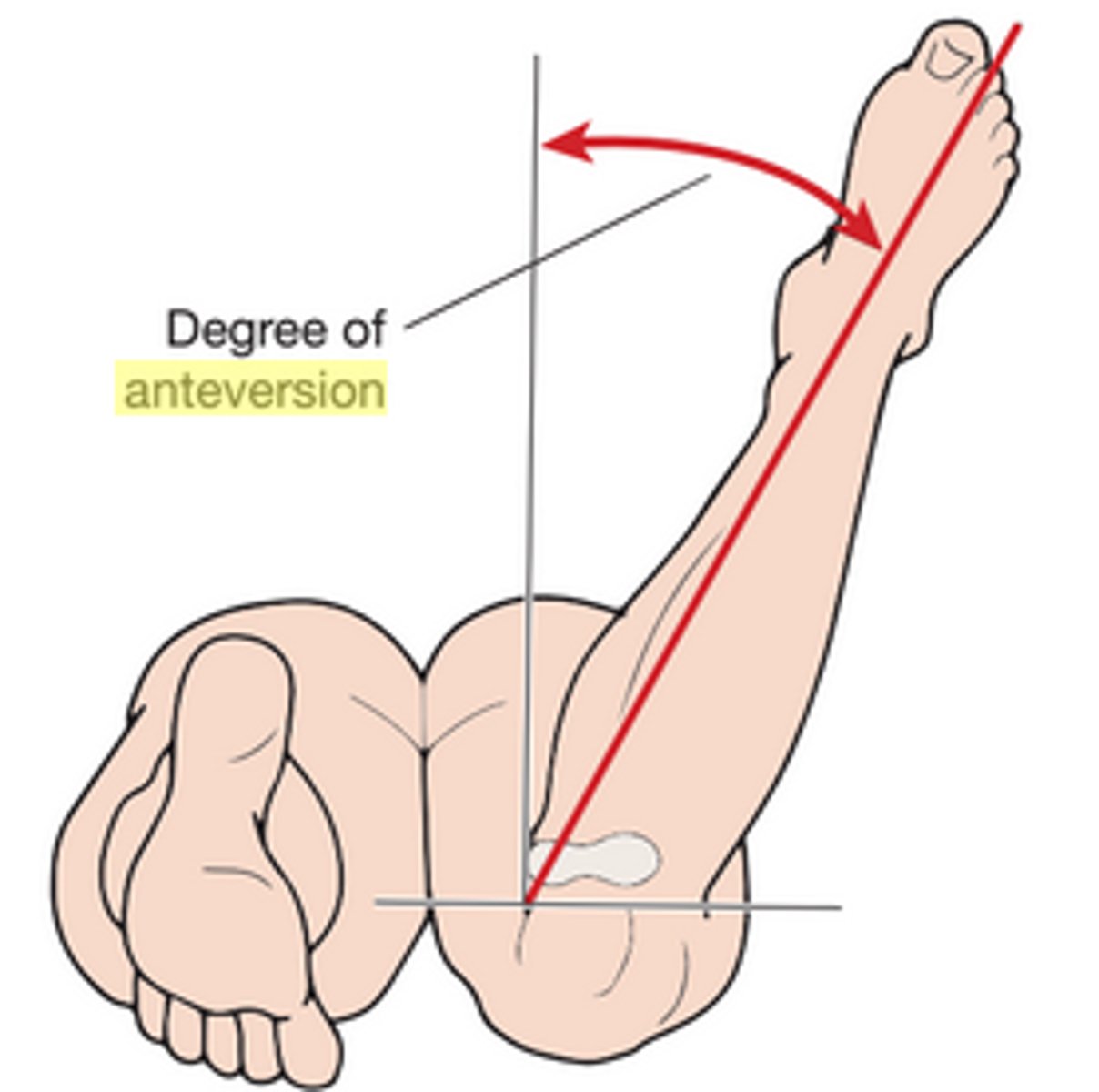
craigs test
for femoral anteversion:
<8 deg is retroversion, >15 degrees is anteversion
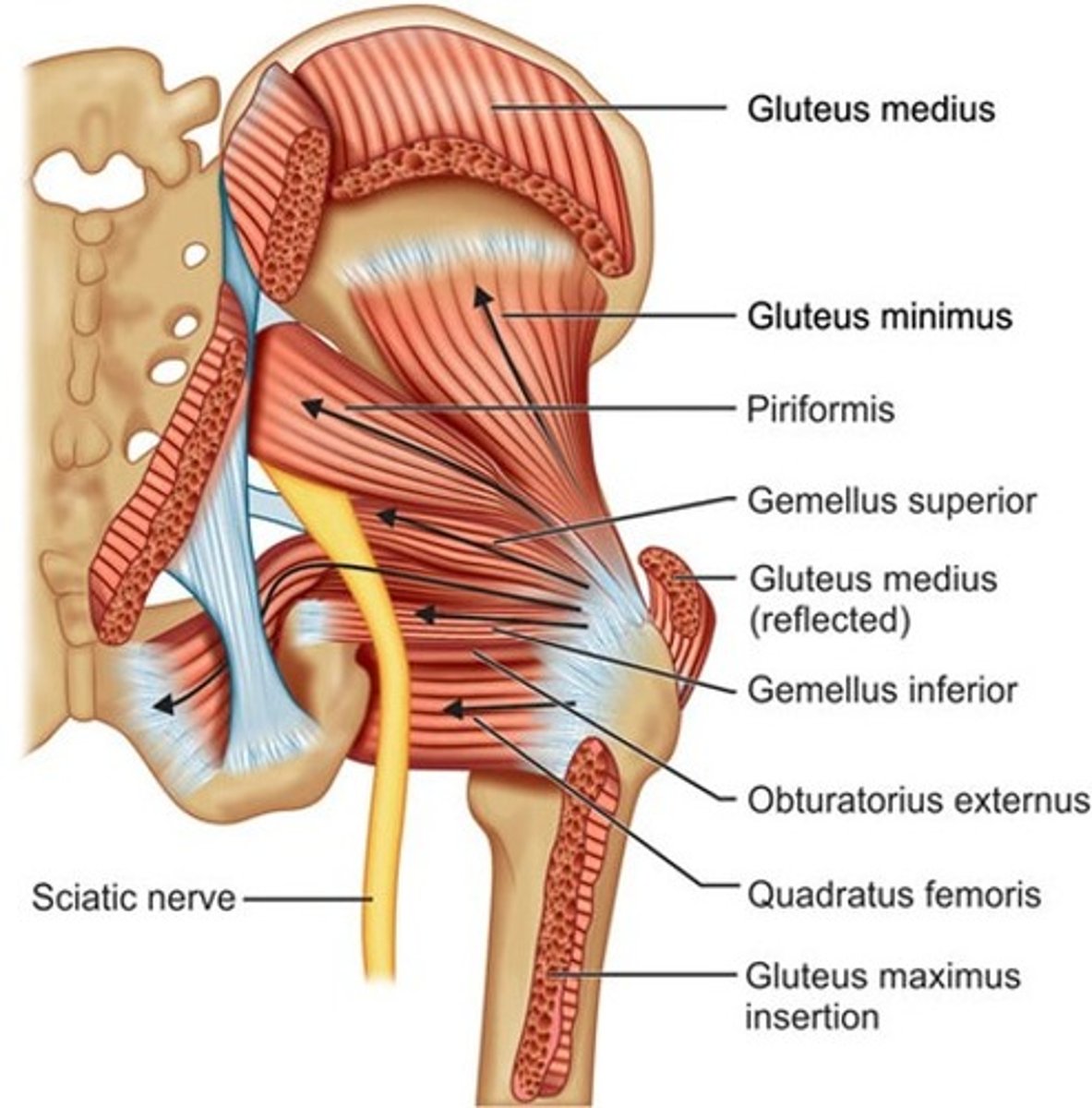
Hip ERs
piriformis, OI, gemellus (inferior and superior), quadratus femoris, obturaror externus, glute max
Hip IRs
glute min and TFL
Hip abductors
TFL and glute med
hip adductors
adductor magnus, longus, brevis, gracilis, pectineus
hip extensors
glute max and hamstrings
hip flexors
pectineus, RF, psoas (major and minor), iliacus
SLR biases:
Sciatic
tibial
sural
common peroneal
nerve root/disc prolapse
sciatic: extension and DF
tibial: extension, DF, eversion
sural: extension, DF, inversion
common peroneal: extension, PF, inversion
nerve root/prolapse: crossed SLR
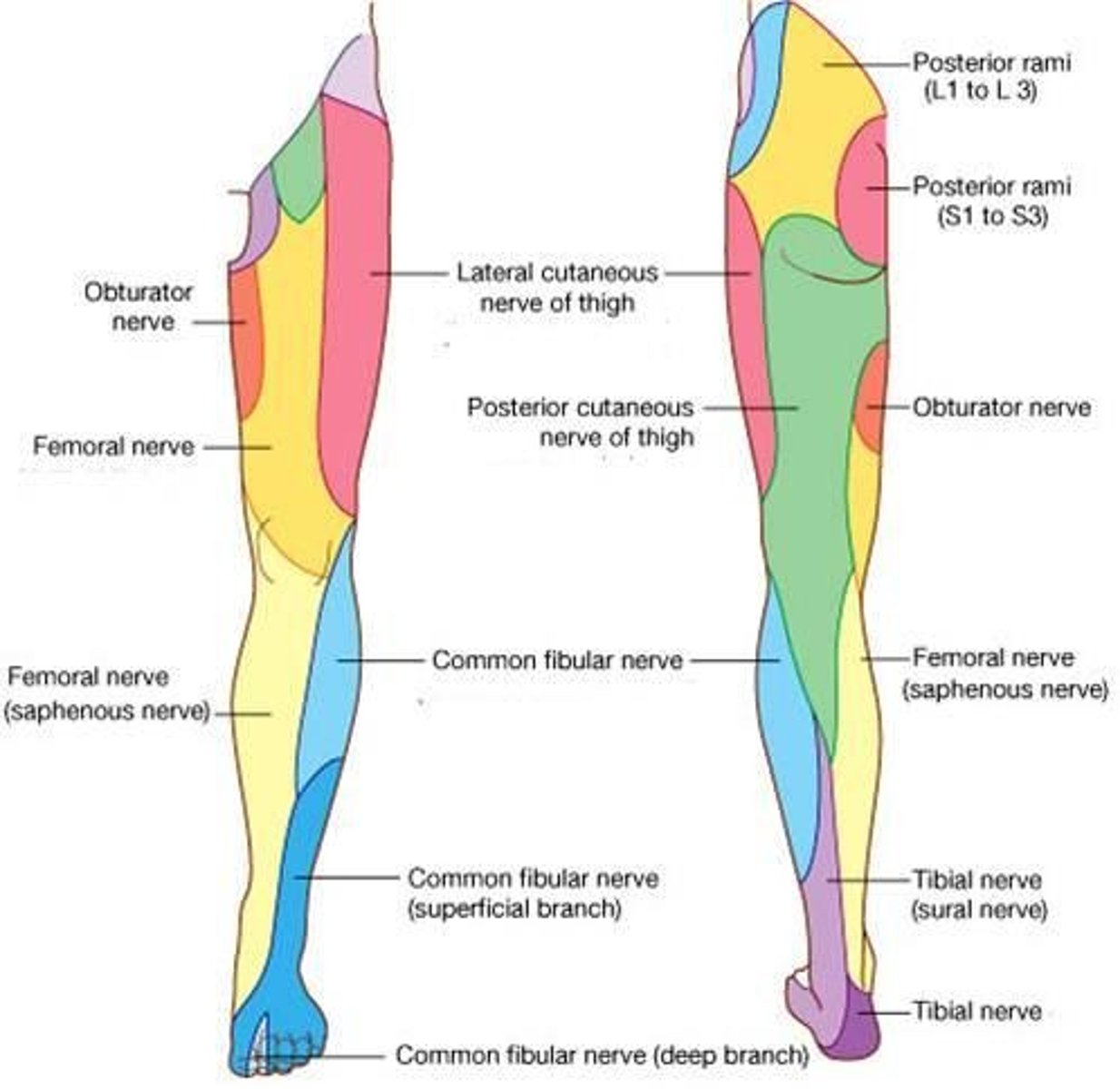
Superior gluteal nerve
glute med, glute min, TFL
inferior gluteal nerve
glute max
piriformis innervation
anterior rami of S1 and S2
obturator nerve (anterior)
adductor longus and brevis, gracilis
obturaror nerve (posterior)
obturator externus, adductor magnus
sciatic nerve innervates
hamstring muscles, adductor magnus, and most muscles in leg and foot
femoral nerve
rect fem, sartorius, iliacus, pectineus, quads
tibial nerve (from sciatic) innervates
gastroc, soleus, plantaris, popliteus, tib post, FHL, FDL
tibial nerve branches
lateral and medial plantar nerves
medial plantar nerve
FHB, lubrical 1, FDB, abductor hallicus
lateral plantar nerve
plantar interossei, dorsal interossei, quadratus plantae, abductor digiti minimi, lubricals 3-4, adductor hallicus
leg and foot sensory
deep peroneal nerve: between 1st and 2nd toes
SF peroneal nerve: dorsum of foot except for between 1st and 2nd toes, AL part of lower leg
tibial nerve: lower posterolateral leg, heel and foot
saphenous nerve: medial leg/foot
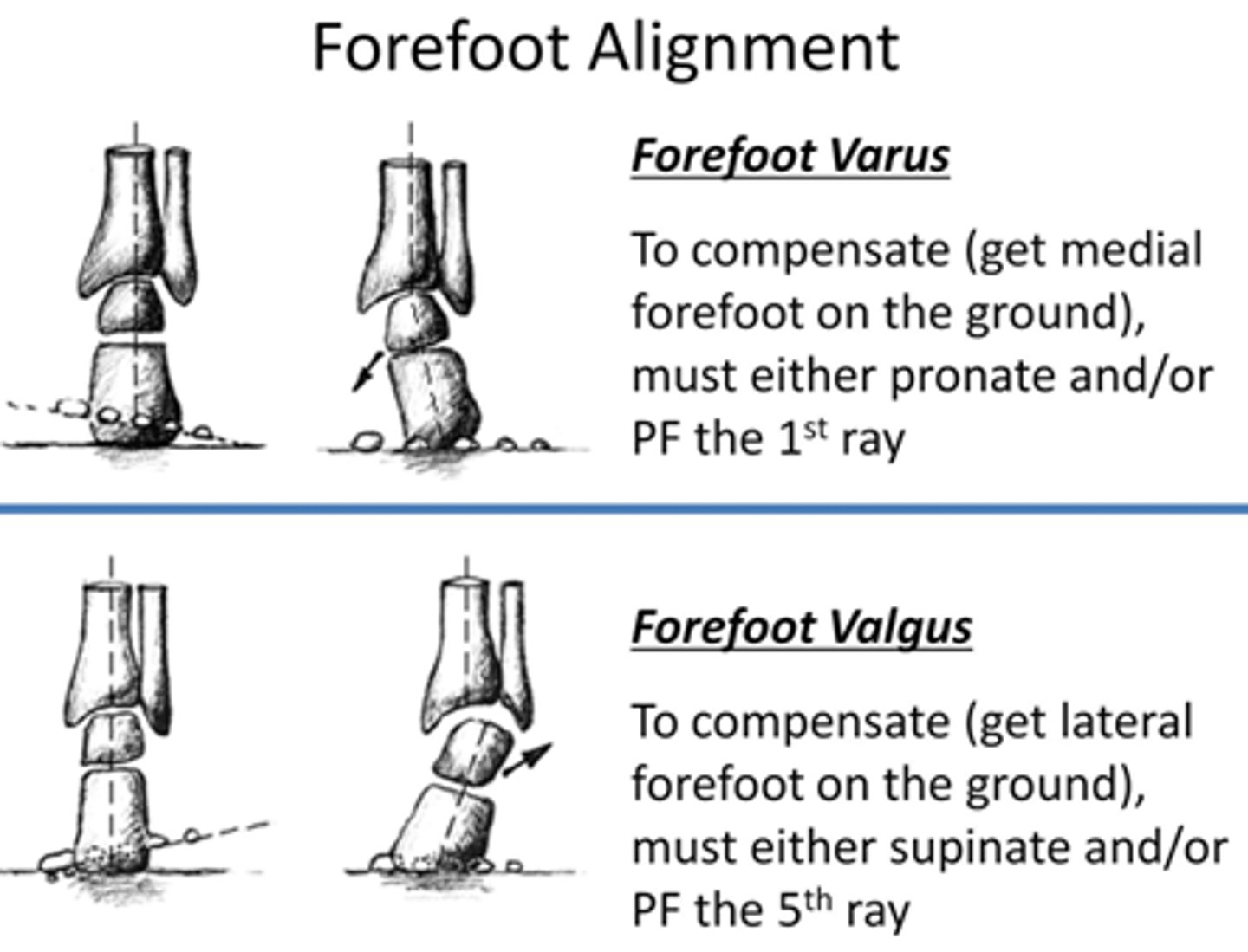
Forefoot varus:
compensation for it?
first MT (medial border) is higher than fifth MT (lateral border) (inversion)
compensation is RF valgus --> low arch
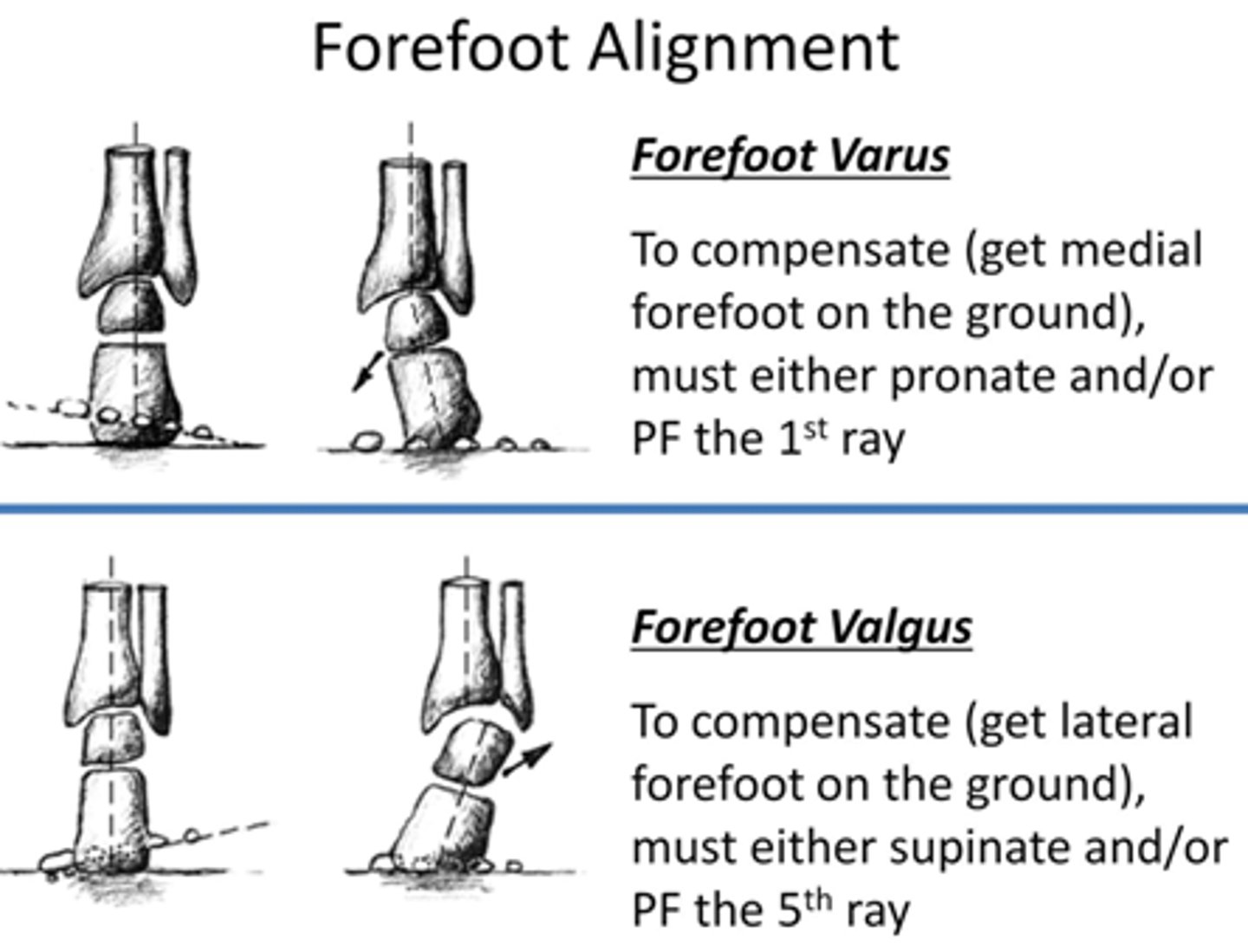
Forefoot valgus
Lateral border is higher than medial border (eversion)
compensation: RF varus (supination/high arch)
HU joint and HR joint kinematics
HU joint: concave ulna moves on convex humerus (open chain), same direction
same with HR joint (concave radius moves on convex humerus in open chain).
thompson test
Achilles tendon rupture--prone, knee extended, squeeze calf looking for PF of ankle
Anterior Drawer Test
hip 45 deg flexion, knee 90 deg flexion for ACL tear
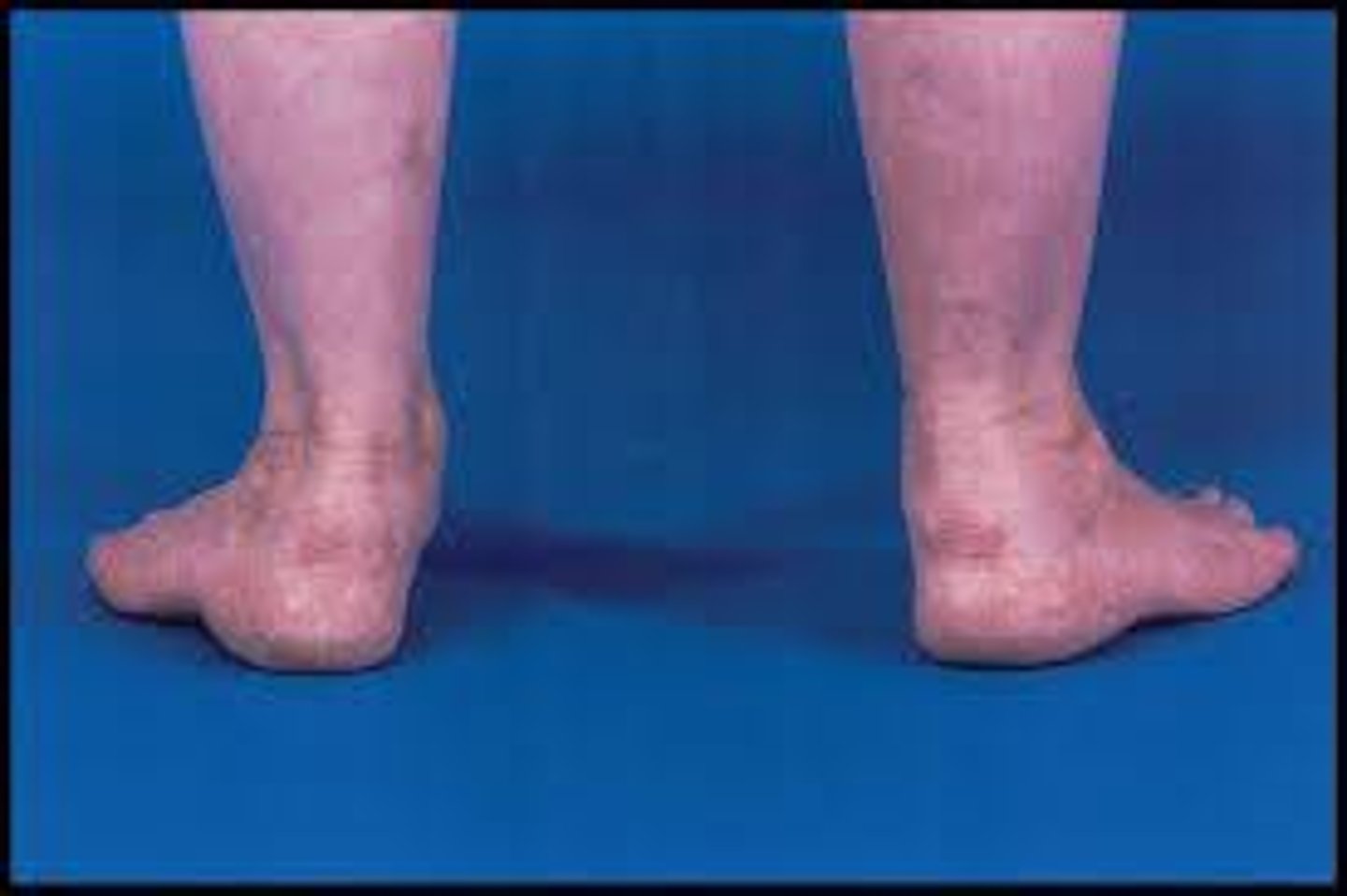
Post tib tendon dysfunction is associated with
Hindfoot valgus and forefoot abduction
loss of strength when grasping a cup, but less difficulty holding onto a pencil. Which nerve is likely affected?
ulnar
ulnar nerve is primarily power grips (spherical/cylindrical), requiring both radial and ulnar sides of hand, thumb.
median nerve controls flexion of radial digits and would be involved in both power and precision (pencil grip, lateral and digital prehension) with thumb to hold smaller objects.
Hand of Benediction
median nerve injury--only digits 4 and 5 flex completely
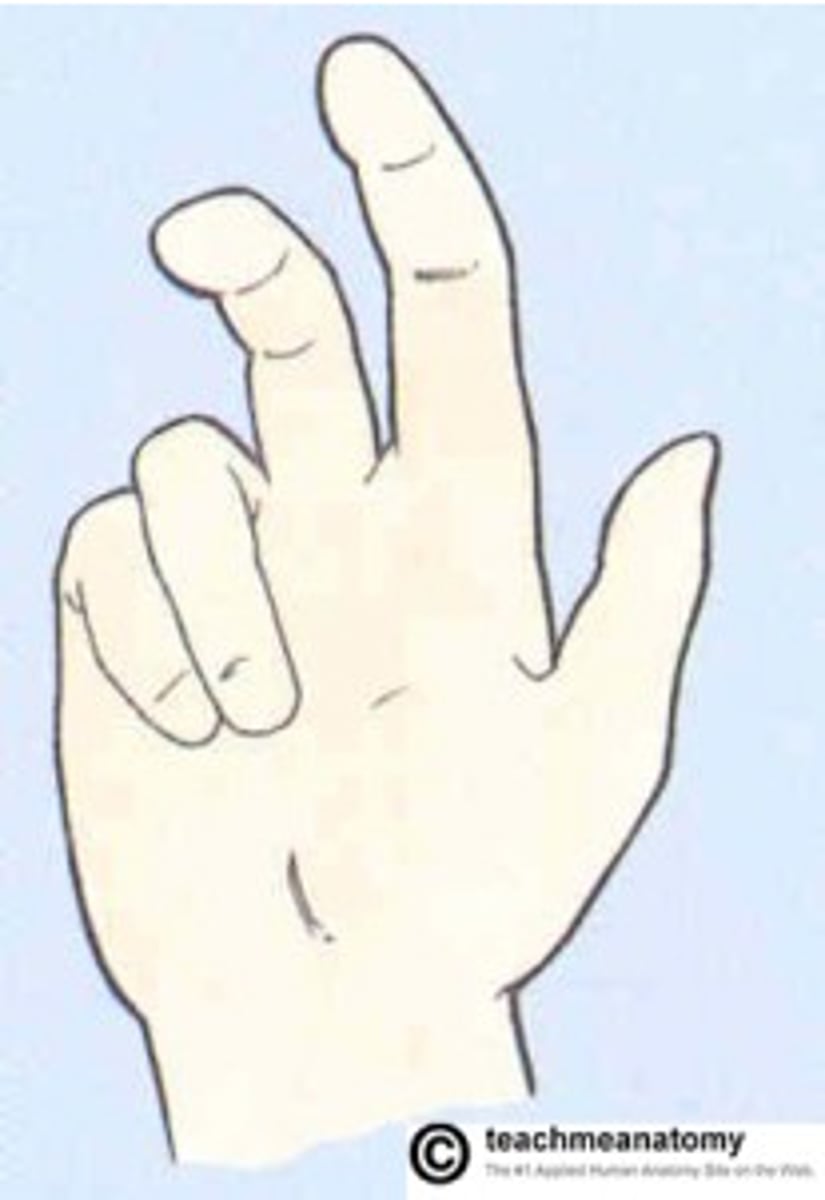
Froments sign
identifies ulnar nerve dysfunction
thumb wants to flex instead of adduct to keep paper