W11 - Urinary System
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
Urinary System Organs
2 Kidneys
2 Ureters
Urinary Bladder
Urethra
Functions of the Kidneys
regulates electrolyte levels in blood, pH of blood, blood volume
regulates BP thru secreting renin
secretes erythropoietin for RBC synthesis
excretion of waste products
activates Vitamin D for Ca2+ homeostasis
Functions of the Ureters, Bladder and Urethra
transportation, storage and excretion of wastes in the urine
Kidneys Location
within retroperitoneal space
located T12-L3
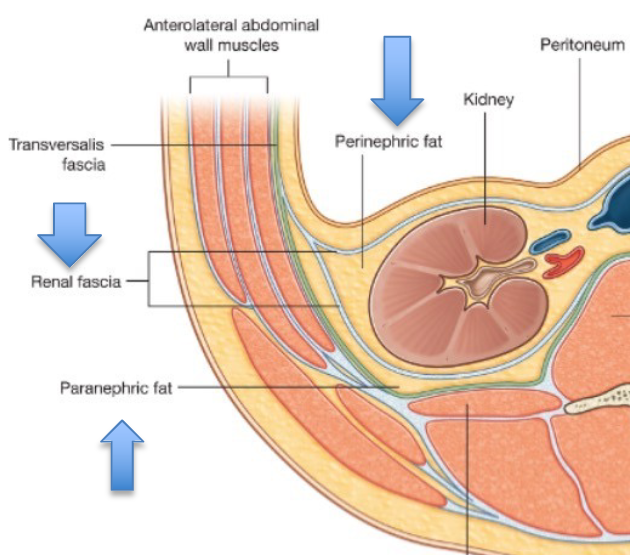
Additional Supporting Connective Tissue for Kidneys
renal fascia = superficial layer that anchors kidneys to ABD wall
adipose capsule = provides protection
renal capsule = covers kidney surface to maintain shape
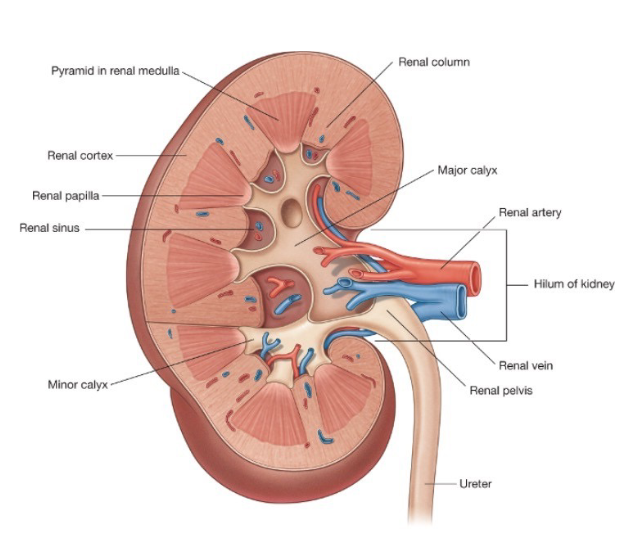
Renal Hilum Composition
renal artery
renal vein
ureter
renal nerves
Kidney Composition
Parenchyma = contains nephrons, which produce urine
Renal Cortex → Renal Medulla/Renal Column → Renal Papilla → Renal Sinus/Minor Calyx → Major Calyx → Renal Pelvis → Renal Hilum
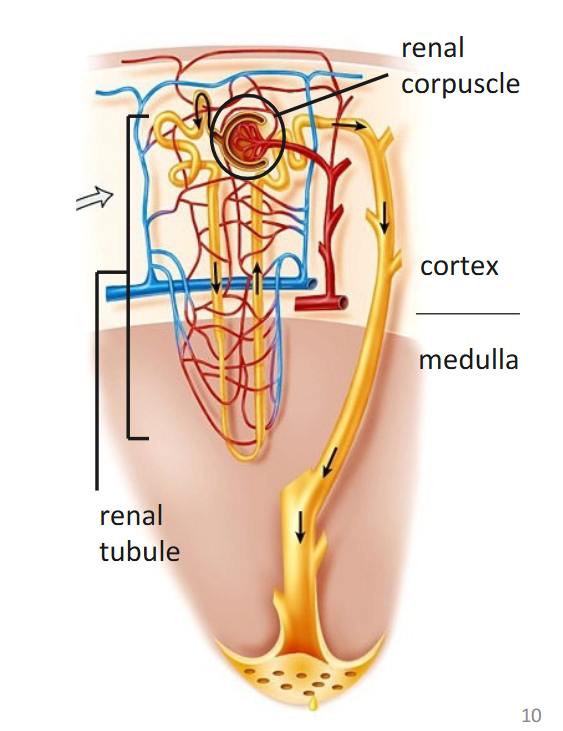
Nephron
basic functional unit of the kidney
comprised of
renal corpuscle = filters blood
renal tubule = transports filtered fluid
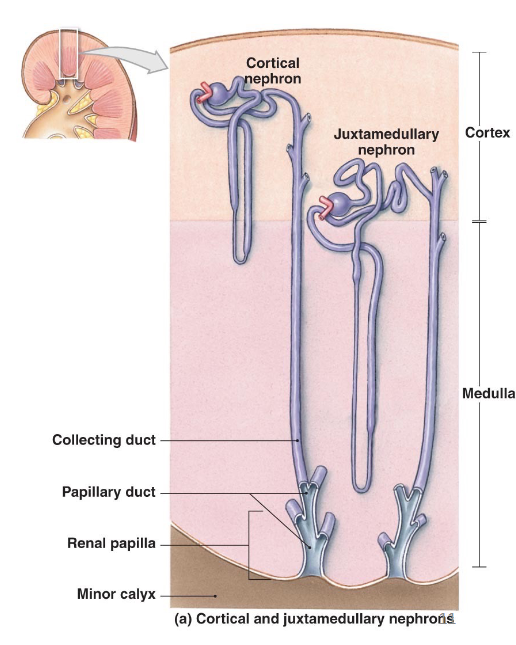
Classification of Nephrons
cortical nephrons 80-85%
renal corpuscle in outer cortex
performs most reabsorption and secretion
no thin ascending limb
juxtamedullary nephrons 15-20%
renal corpuscle in inner cortex
performs urine concentration
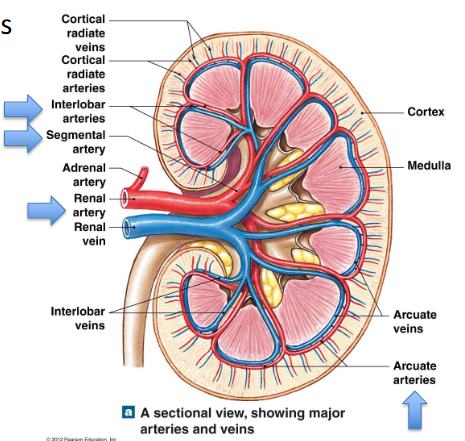
Blood Flow to Nephrons
renal artery → segmental arteries → interlobar arteries → arcuate arteries → cortical radiate (interlobular) arteries → afferent arterioles
→ nephrons → glomerulus (capillary where filtration occurs) → efferent arteriole → peritubular capillaries/ vasa recta (both function to return fluid/solutes reabsorbed back to bloodstream)
→ cortical radiate (interlobular) veins → arcuate veins → interlobar veins → segmental veins → renal vein
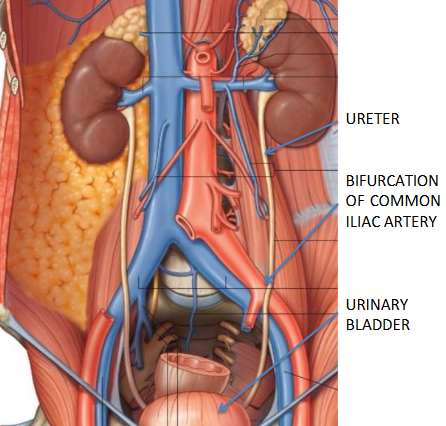
Ureters
transport urine from renal pelvis to bladder via peristalsis, hydrostatic pressure and gravity
descends retroperitoneally, then cross over the bifurcation of the common iliac arteries to enter pelvic cavity → pass thru posterior bladder wall
Histology of Ureters
Adventitia
Smooth Muscle
Lamina Propria, transitional epithelium
Lumen
Urinary Bladder
hollow, distensible muscular organ located in pelvic cavity
Average Bladder Capacity
700-800ml, may be less for female due to uterus
Histology of Bladder
Adventitia: Serosa, Areolar Connective tissue
Muscularis = smooth muscle
Mucosa: transitional epithelium, lamina propria, presence of rugae
Ureter to Urethra
ureters enter bladder posteriorly → bladder → trigone (smooth inner surface comprised of rugae)→ urethra exits bladder inferiorly via internal urethral orifice → external urethral sphincter
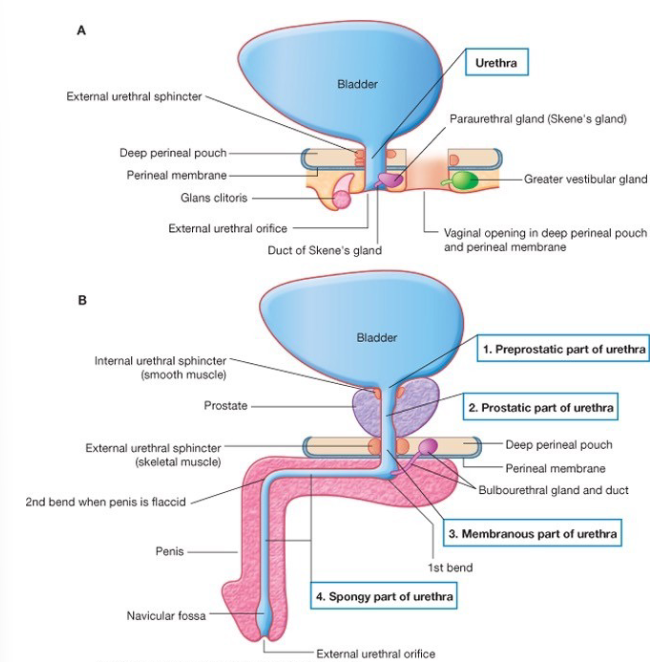
Male vs. Female Urethrae
female: 4cm passageway from internal urethral orifice to exterior of body
male:
PREPROSTATIC
PROSTATIC
MEMBRANOUS
SPONGY
Micturition
= discharge of urine from bladder
occurs through involuntary + voluntary innervation to smooth and skeletal muscle
triggered when urine volume exceeds 200-400ml → stretch receptors send nerve impulses to micturition center (S2-3) → trigger micturition reflex (parasympathetic response, inhibits somatic motor neurons)