Honors Physical Science Final
1/114
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
115 Terms
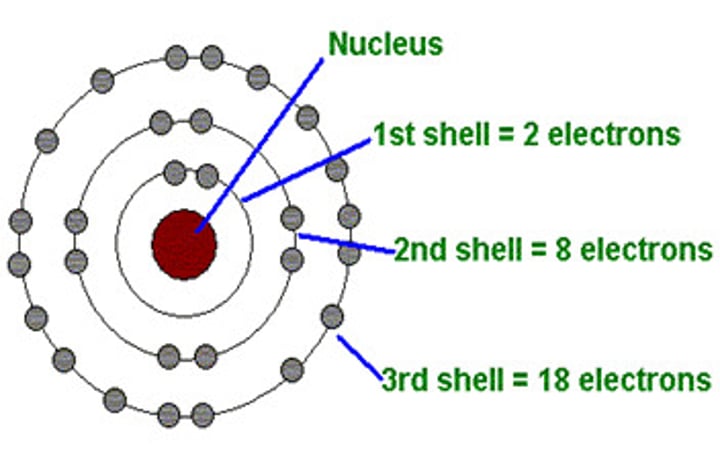
orbital
region in an atom where there is a high probability of finding an electron; path an electron takes
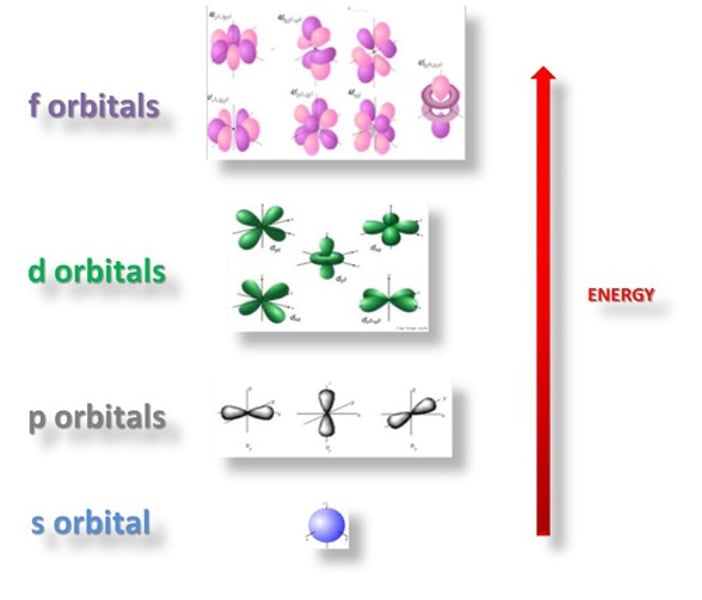
energy level
a region of an atom in which electrons of the same energy are likely to be found which fill up lowest to highest
sublevel
group of orbitals that increase as the energy level increases

ground state
the lowest state of energy of an electron
excited state
when an electron gains or absorbs energy and moves levels
electron configuration
the organization of orbitals and sublevels in the lowest energy level
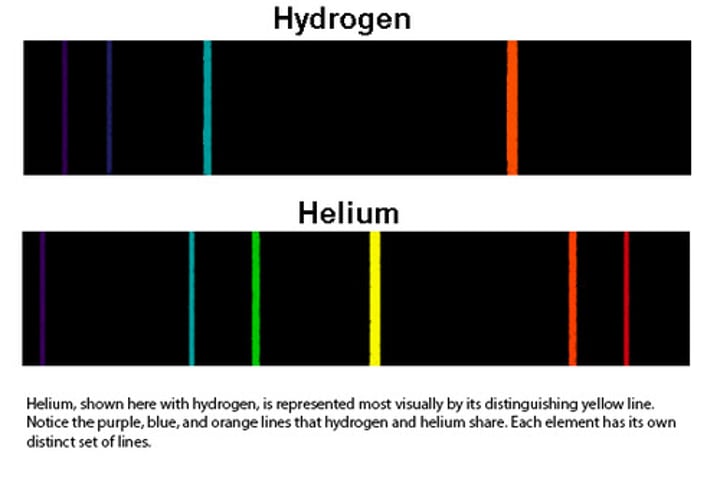
Emission Spectra
atoms absorb and emit light are certain wavelengths that help tell what the element is aka atomic fingerprint
Noble Gas Notation
abbreviated electron configuration only using the Noble Gases
Valence Electrons
outermost electrons
orbital diagram
the use of boxes and arrows to represent the electrons in an atom
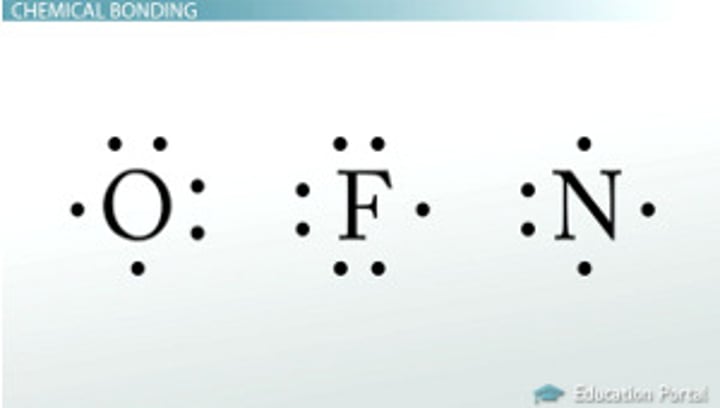
Lewis Dot Diagram
depicts the the amount of valence electrons around the atomic symbol
What is the electron configuration for Chlorine?
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p5
What is the abbreviated electron configuration for Calcium?
[Ar] 4s2
What is the electron configuration for Copper?
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s1 3d10
What element has an electron configuration of: 1s²2s²2p⁶3s²3p⁶4s²?
Calcium
Make an orbital diagram for Zinc
⇵ ⇵ ⇵ ⇵ ⇵ ⇵ ⇵ ⇵ ⇵ ⇵ ⇵ ⇵ ⇵ ⇵ ⇵
What is this electron configuration: ⇵ ⇵ ⇵ ⇵ ⇵ ⇵ ⇵ ⇵ ⇵ ⇵ ⇵ ⇵ ⇵ ⇵ ⇵?
1s²2s²2p⁶3s²3p⁶4s²3d¹⁰
What is this Lewis Dot Diagram: ⇵ ⇵ ⇵ ⇵ ⇵ ⇵ ⇵ ⇵ ⇵ ⇵ ⇵ ⇵ ⇵ ⇵ ⇵?
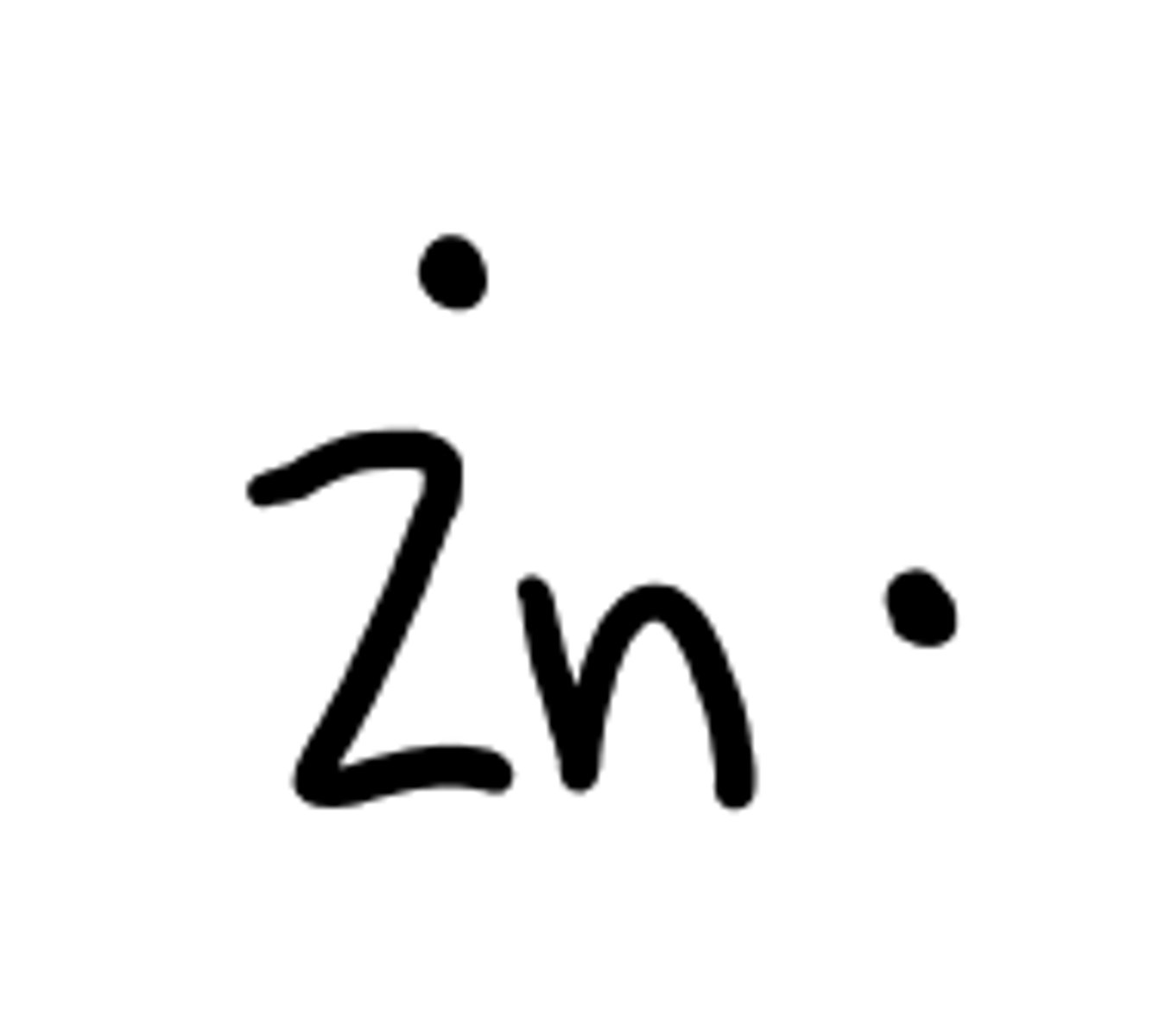
How are elements arranged on the modern periodic table?
increasing atomic number
Why do elements in the same group have similar properties?
they all share the same number of valence electrons
What happens when an atom gains or loses an electron?
Gains: the charge will be come negative due to an additional negative charge and the radius will increase because the repulsion produced caused the atom to expand
Loses: the charge will become positive due to more protons and the radius will decrease because the positive charge will pull the electrons in closer
Why are some elements more likely to become positive?
Some elements are more likely to become positive because they have less shielding. This means the electronegativity is greater than its competitors.
Why are some elements more likely to become negative?
Some are more likely to become negative because they have more shielding, meaning that the electrons are able to be pulled away easier than it is for them to attract.
What are the three main categories for elements?
Metalloids: fall on both sides of the staircase and have characteristics of both metals and nonmetals
Metals: shiny solids that can be stretched and conduct heat and electricity
Nonmetals: can be solids, liquids, or gases and dull and brittle
Describe and give an example for metal
elements that are solids at room temperature and can conduct electricity
Ex. Potassium
Describe and give an example for a nonmetal
brittle, don't conduct electricity, can be solids, liquids, or gases at room temperature
Ex. Chlorine
Describe and give an example for a metalloid
Has some qualities of nonmetals and metals
Ex. Boron
What does each element family have in common?
They have similar characteristics
Example: Noble Gases are always stable
What are some of the families of nonmetals?
halogens and noble gases
What are semiconductors?
elements that have some properties of metals and are able to conduct heat and electricity under some circumstances
Ionic Charge
a positive or negative charge of an atoms
Across: more likely to become negative due to shielding
Down: more likely to become negative due to shielding
Number of Valence Electrons trends
Across: more valence electrons because the more protons being added the more electrons
Down: stays the same
Atomic Number trends
Across: increase
Down: increase
Atomic Radius trends
Across: decreases due to more protons, increasing the Coulombic Attraction
Down: increases due to more energy levels
Ionization Energy trends
Across: increases because the valence electrons are closer to the nucleus, so they are held more tightly
Down: decreases because of shielding
Electronegativity trends
Across: increases because the nucleus has a stronger pull, meaning it can attract more easily
Down: decreases because the nucleus is farther away and has a weaker pull due to shielding
compound
A substance made up of atoms of two or more different elements joined by chemical bonds
bond
the force/forces that hold ions and atoms together in a compound
bond length
the distance between the nuclei of two bonded atoms
bond angle
the angle formed by two bonds on the same atom, tells which way the atoms in a compound/molecule point
structural formula
shows the structure of compounds using chemical models to represent the atoms of certain elements
molecule
-the smallest particle of a substance that has the same chemical properties of that substance and it made up of one or more atoms bonded together
-made of neutral atoms
cation
positively charged ion
anion
negatively charged ion
ionic compound
compounds that are made of one atom that gives it's extra electron to another atom to create a cation and an anion
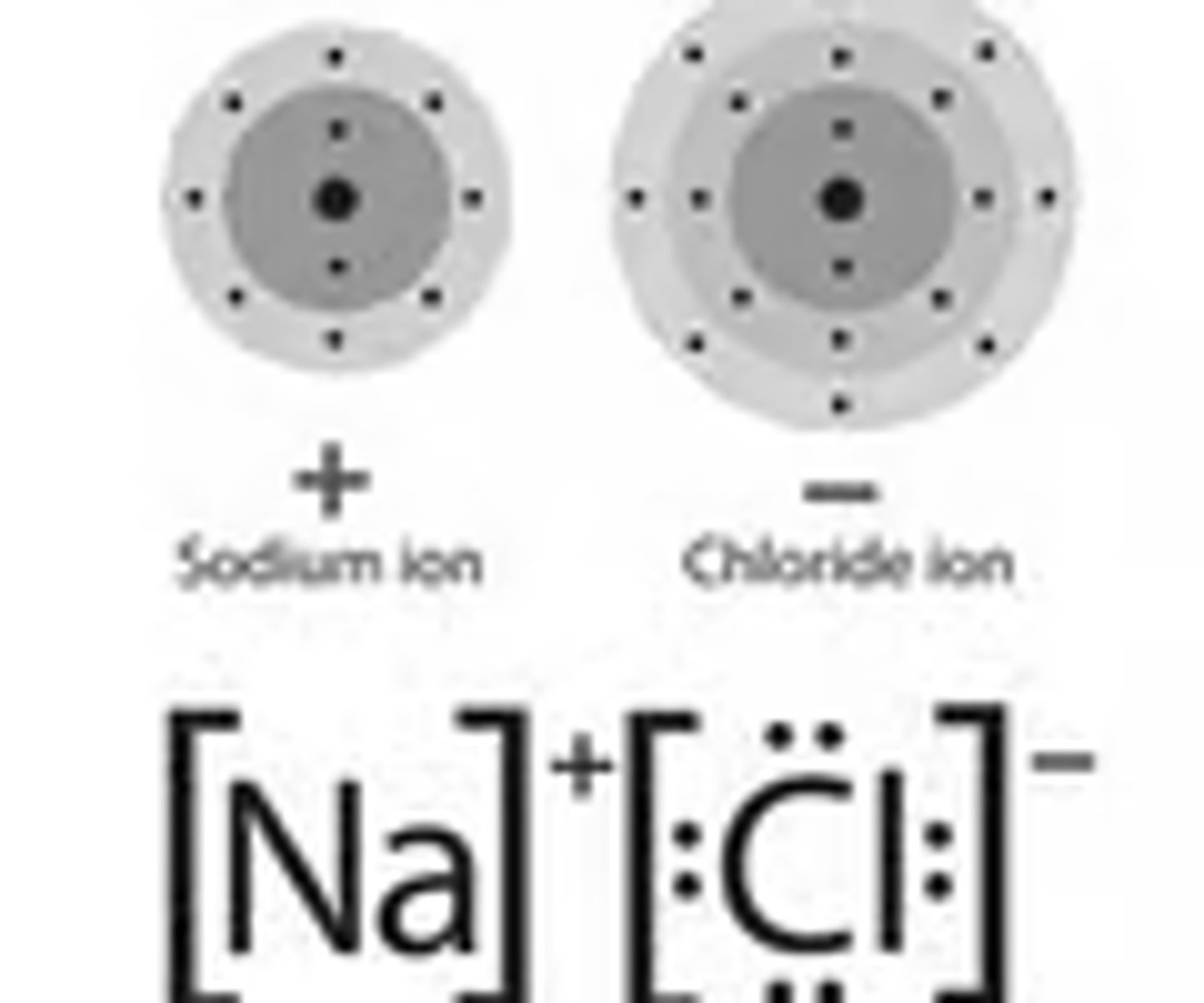
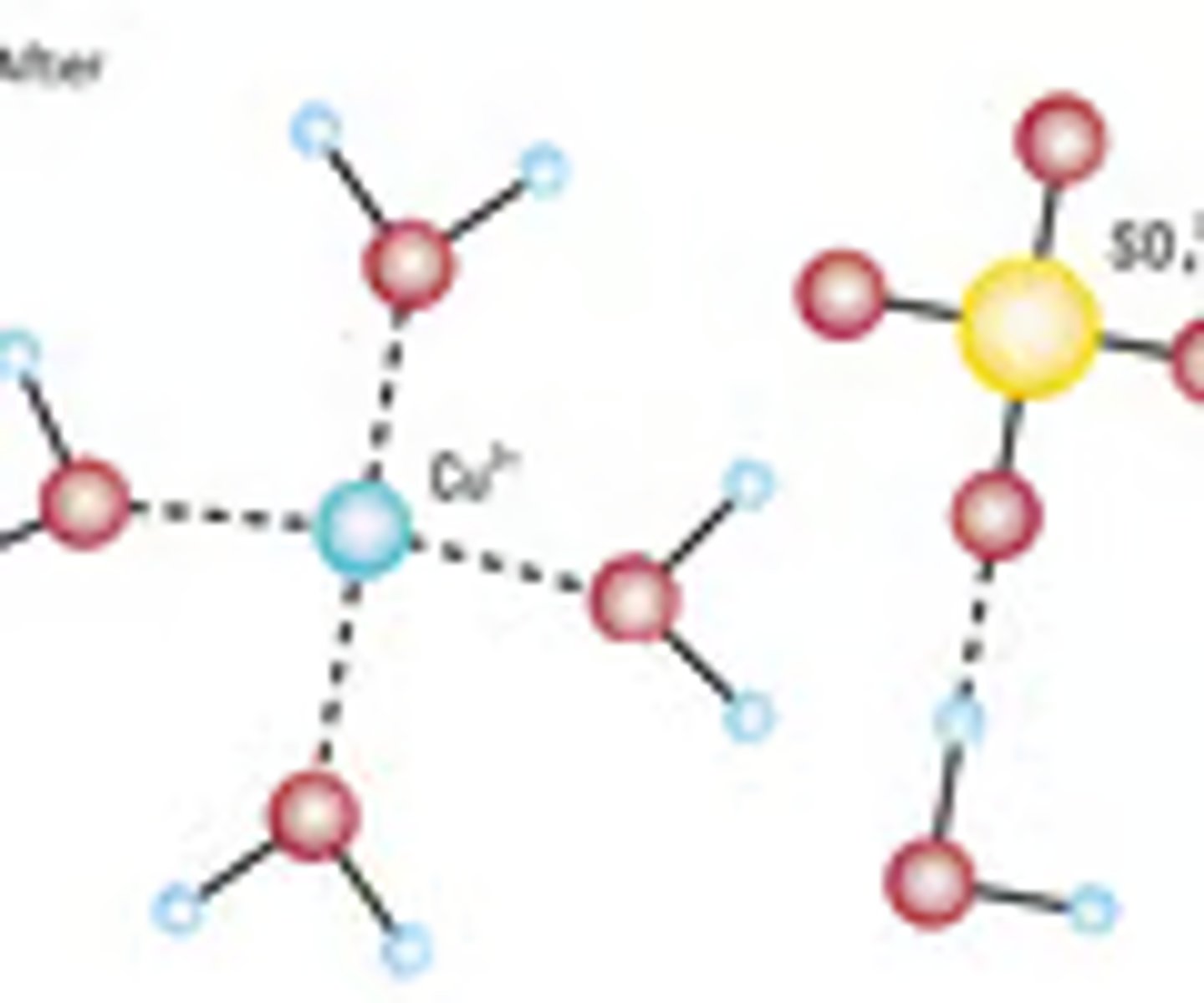
hydrate
ionic compounds that have water molecules attached to each formula unit
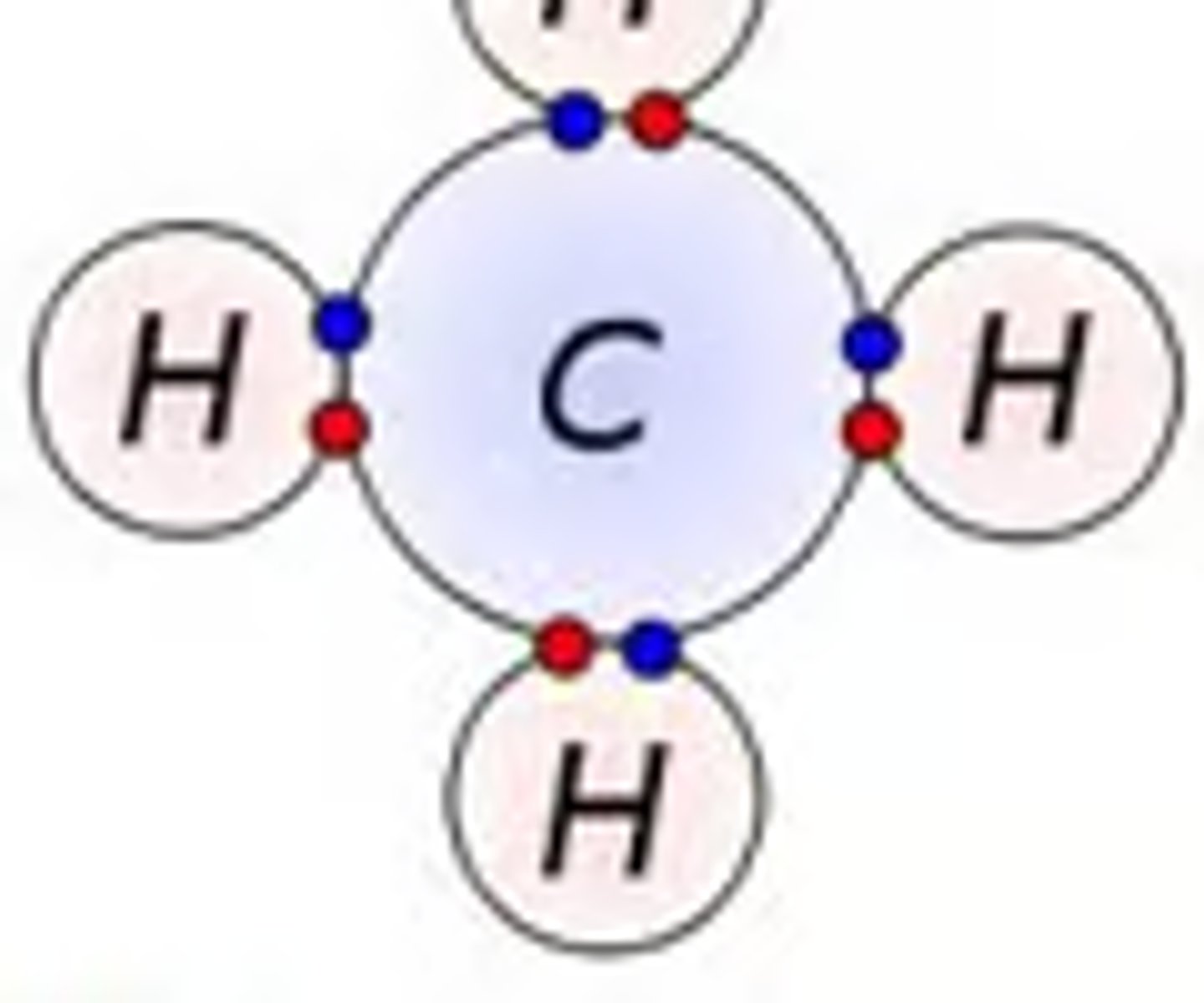
covalent compound
compounds made of two nonmetals that are close by on the periodic table that share an electron to become stable
formula unit
-only for ionic
-the simplest ratio in a compound
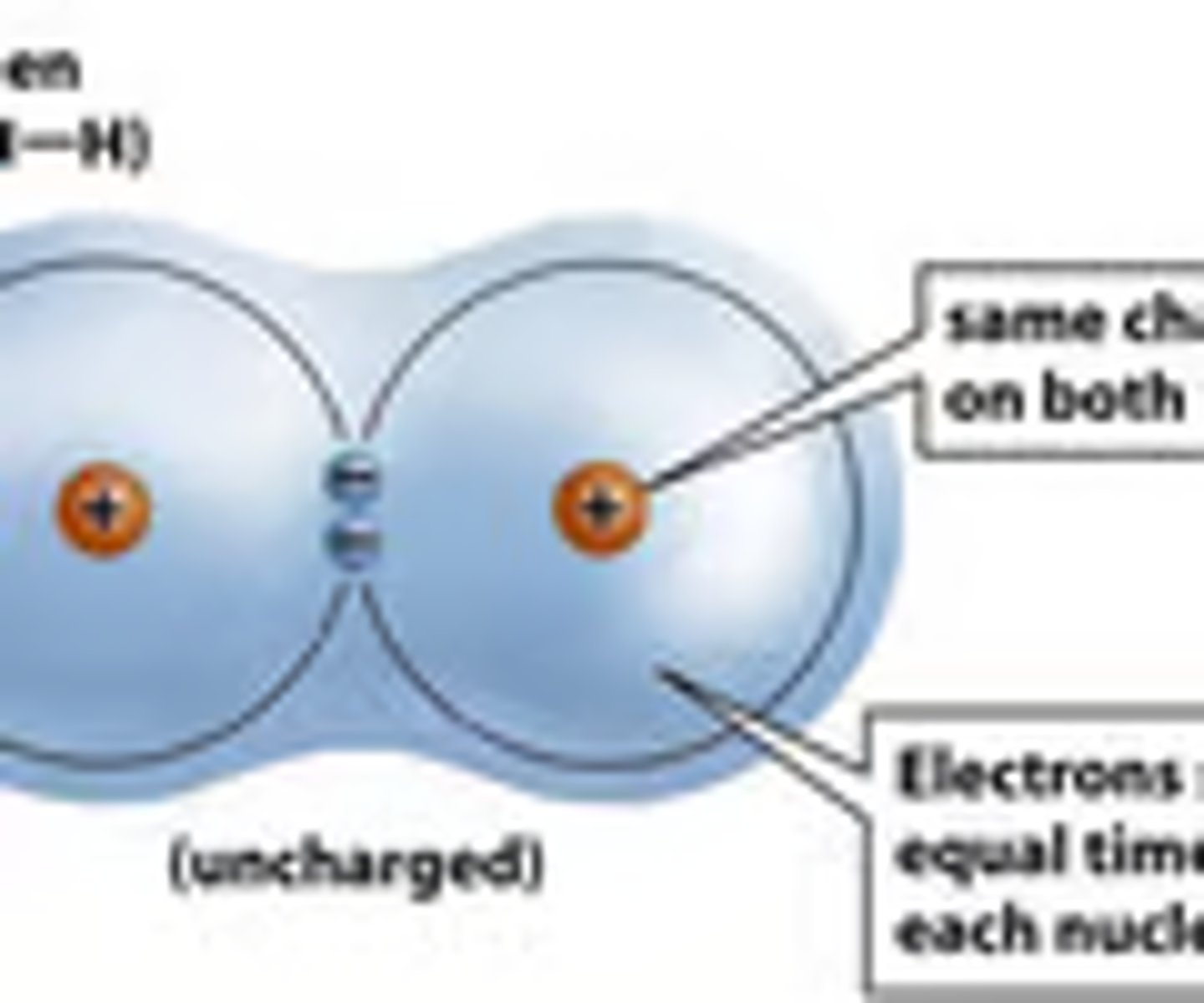
nonpolar covalent bond
when electrons are shared between two atoms equally
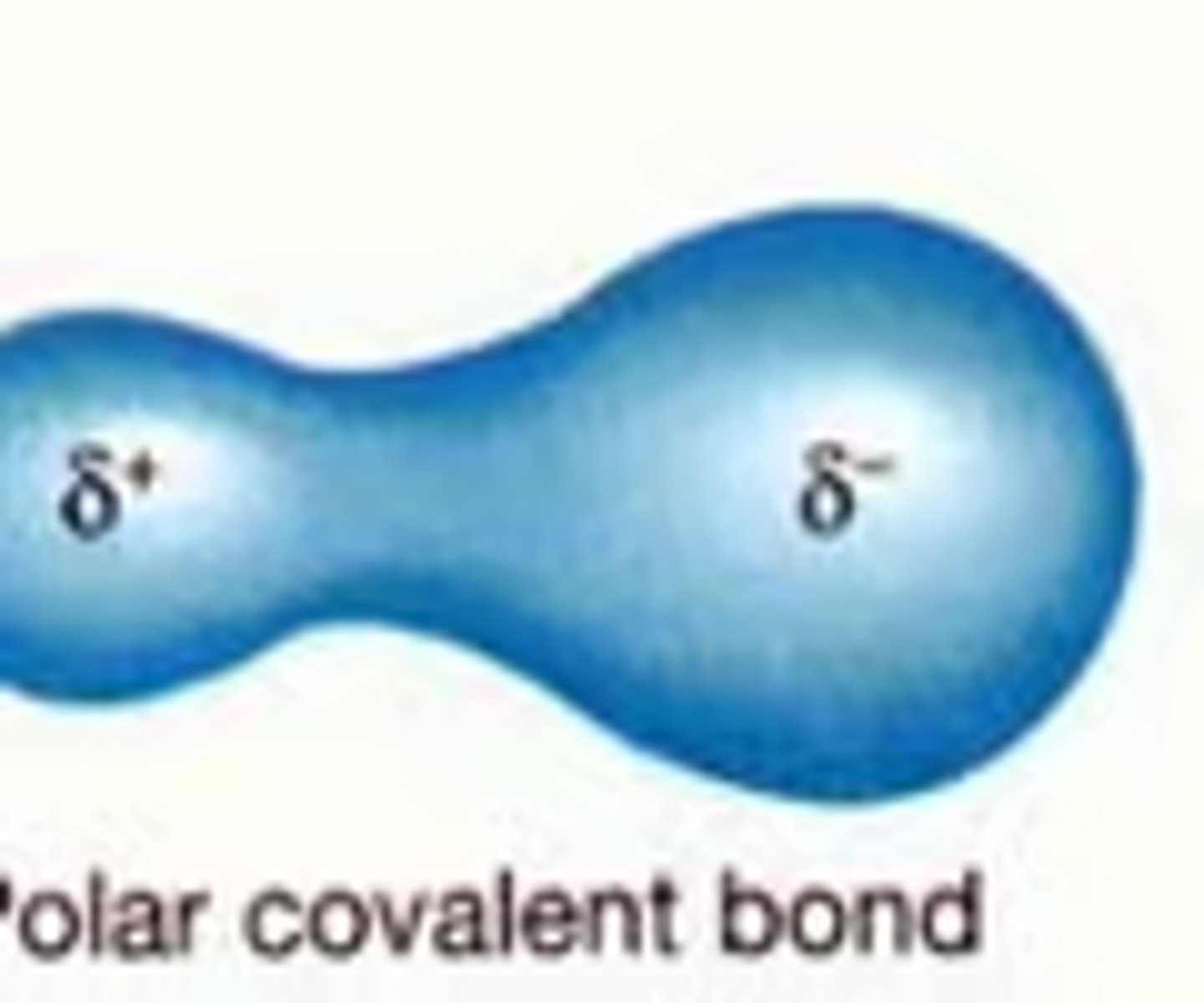
polar covalent compound
when electrons are unequally shared between two atoms represented by a curly s, meaning the one atom is slightly positive and the other slightly negative
Sea of Electrons
metallic bond
binary compound
compound made of two elements but can consist of two or more atoms
polyatomic ion
groups of covalently bonded atoms that have a positive or negative charge as a group
WHat are the properties of a chemical bond?
strength: bonds can stretch, bend, and rotate without breaking
length: the stronger the bond the shorter the bond length is
polarity: the electron is equally shared with two atoms of the same element but when the elements are different the electron will not be equally shared because one is more positive and the other is more negative
How can you distinguish between nonmetal atoms, ions, or molecules?
Ions: unbalanced charge
Molecules: have the same characteristics as the larger substance and groups of nonmetals
Nonmetal atoms: balanced group of one nonmetal atoms
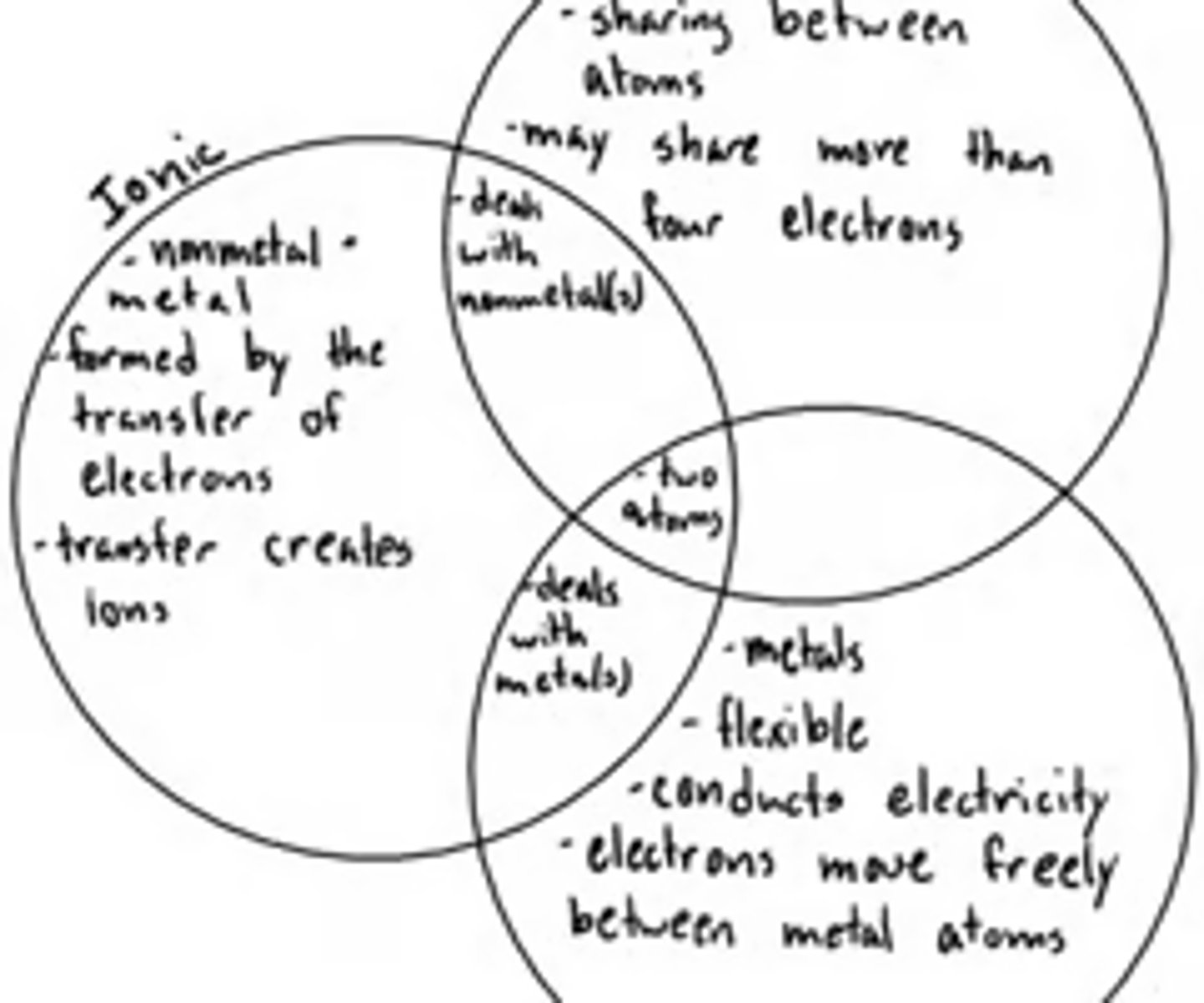
Compare and contrast metal, covalent, and ionic bonds?
How do ionic bonds form?
the form when one element wants to get rid of an electron and another one needs it, so there is a complete transfer of electrons
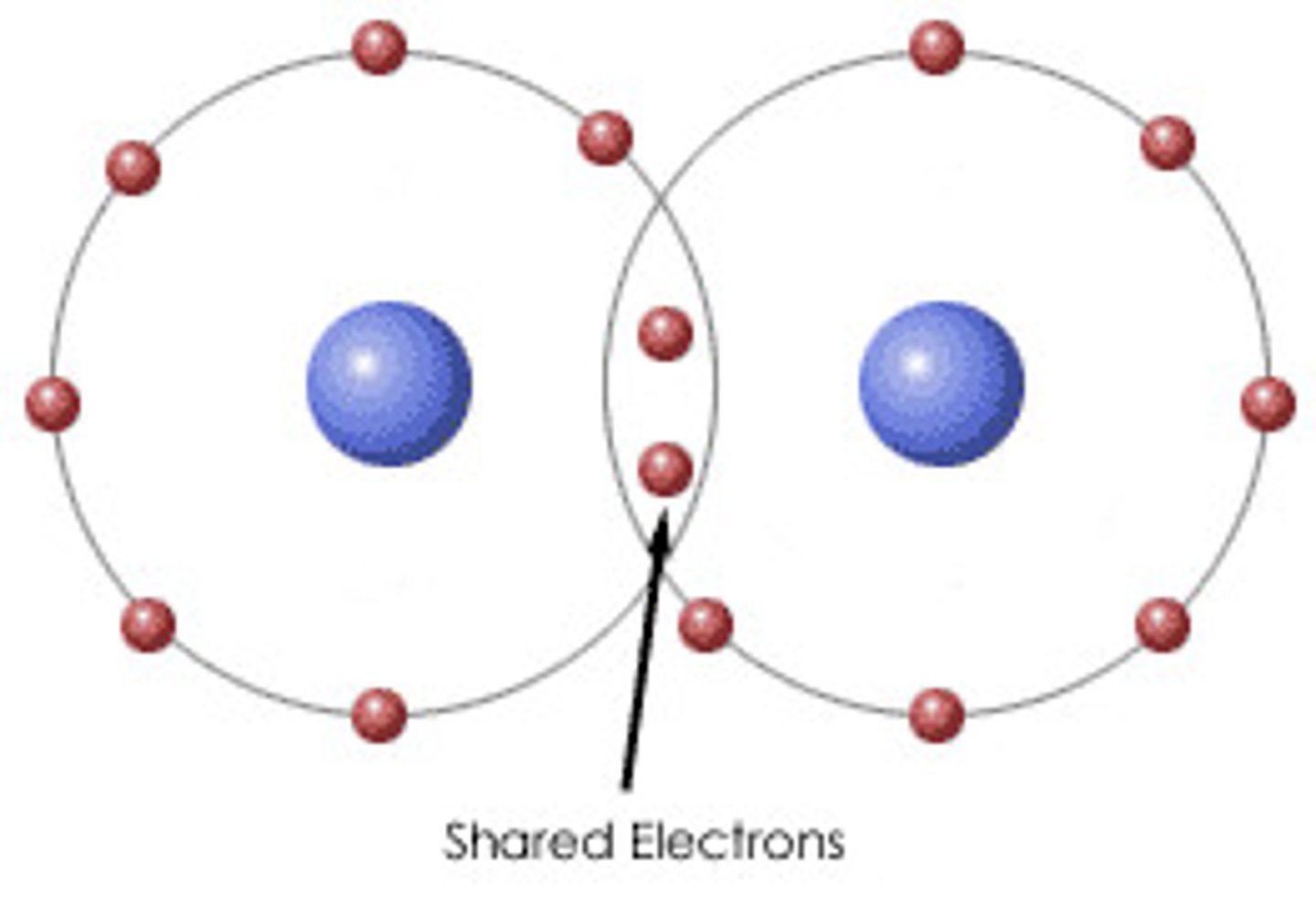
How do covalent bonds form?
two atoms share an electron to become stable
Why are ionic compounds only conductive when dissolved?
The electrons are able to move about freely
Compare and Contrast Polar Covalent and Nonpolar Covalent Bonds
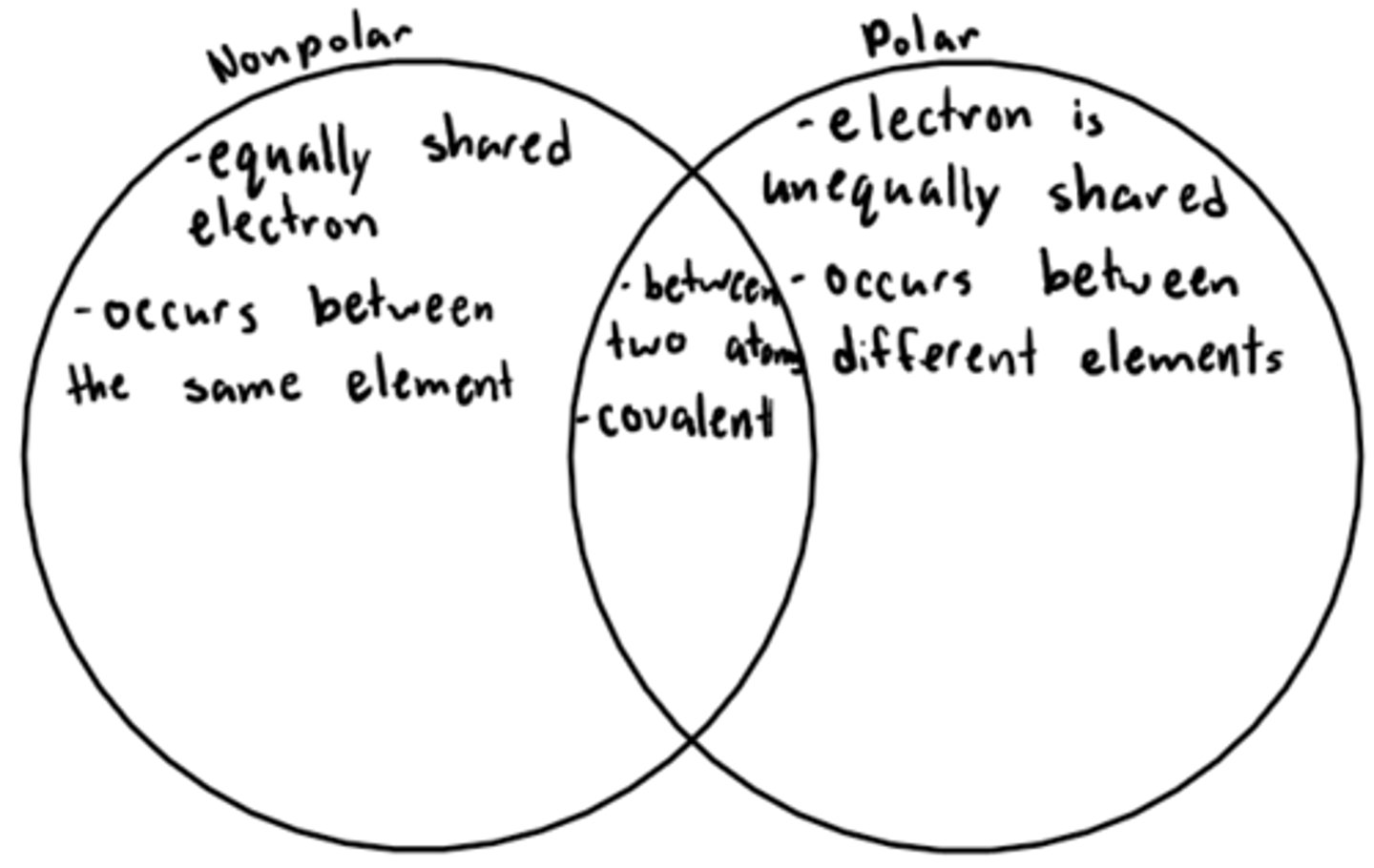
How do you determine the poles of a molecule?
The more electronegative atom will pull the electron closer causing it to have a slight negative charge and the other a slight positive charge
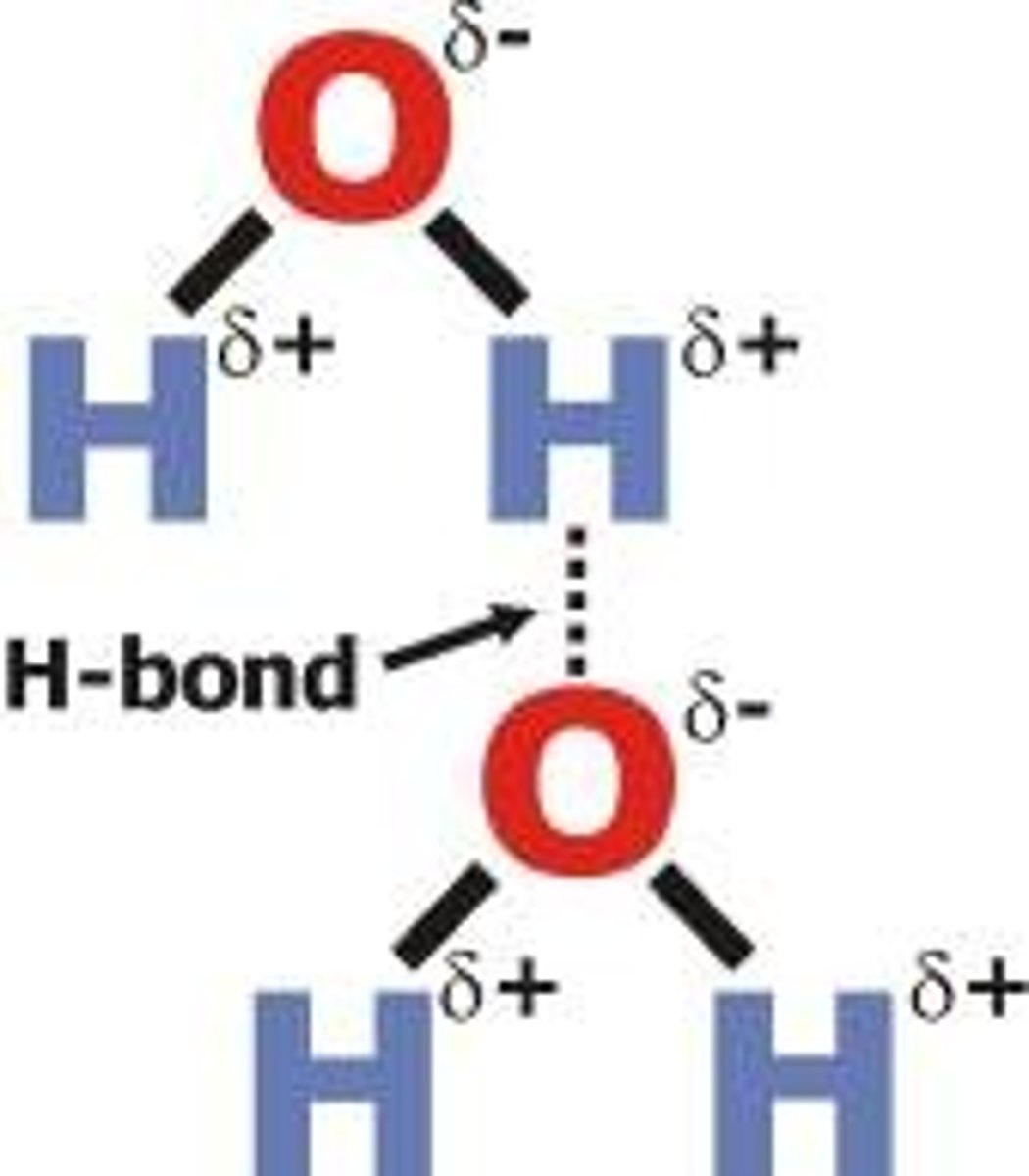
How does the structure of metallic bonds give them their properties?
the electrons are able to move freely in the Sea of Electrons and are able to conduct electricity, thus giving them that property
Name Li₂0
Lithium Oxide
Name PbO₂
Lead (IV) Oxide
Name NBr₃
Nitrogen tribromide
Name CuCl₂ ∙ 5H₂O
Copper (II) chloride pentahydrate
Formula for Carbon monoxide
CO
Formula for Carbon tetrachloride
CCl4
Formula for Sodium acetate trihydrate
NaC₂H₃O₂ ∙ 3H₂O
What are the differences between ionic, hydrate, and covalent compounds?
Ionic: compound that is made to completely transfer one electron to a different atom to create a cation and an anion
Covalent: compound that is made from two nonmetals that share the electron to become stable
Hydrate: ionic compound that has a water molecule attached to the formula unit
chemical reaction
the process by which one or more substances change to produce one or more different substances by rearranging atoms
reactant
a substance the participates in a chemical reaction
product
a substance produced in a chemical reaction
Law of Conservation
matter cannot be created or destroyed
exothermic
reactions that release heat
endothermic
reactions that absorb heat
coefficient
the number in front of a chemical equation
mole ratio
tells relative amounts of products and reactants
synthesis
chemical reaction that combines two or more substances into one
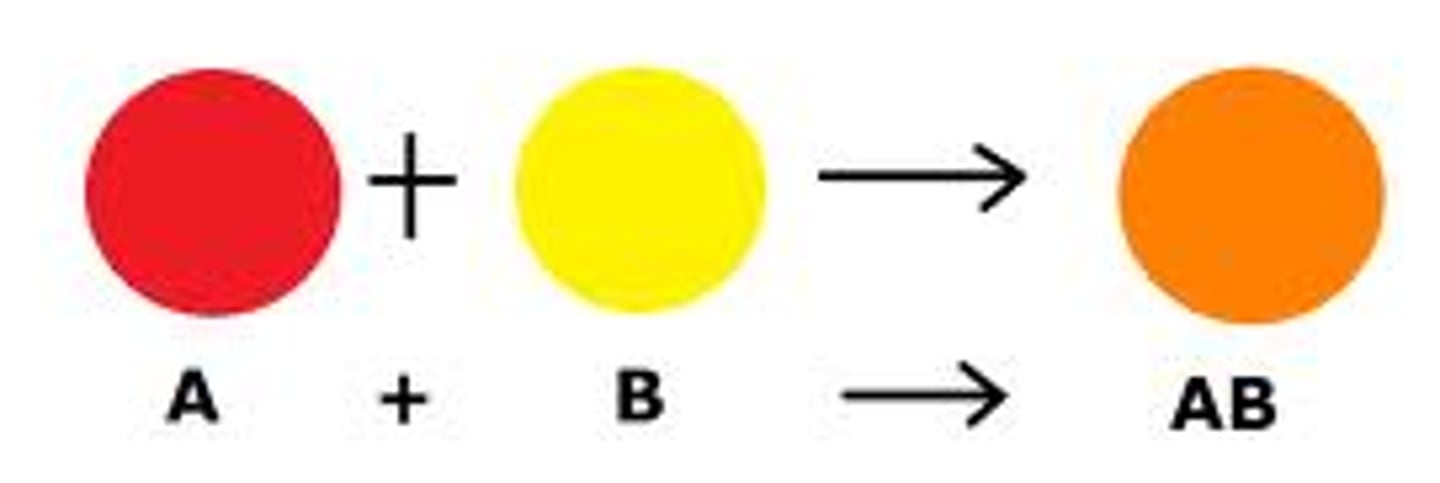
decomposition
a compound breaks down to produce smaller atoms
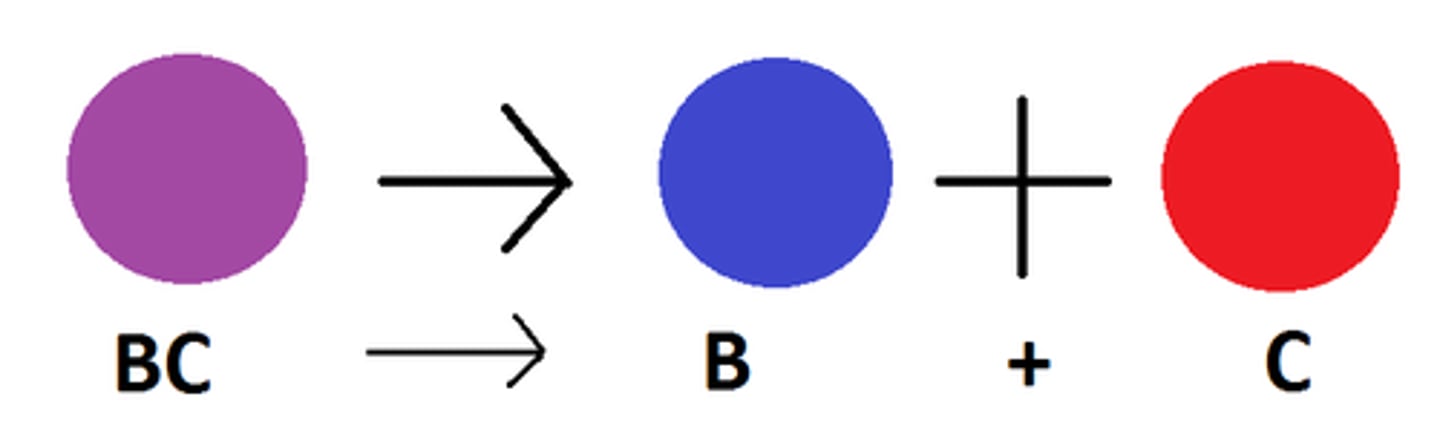
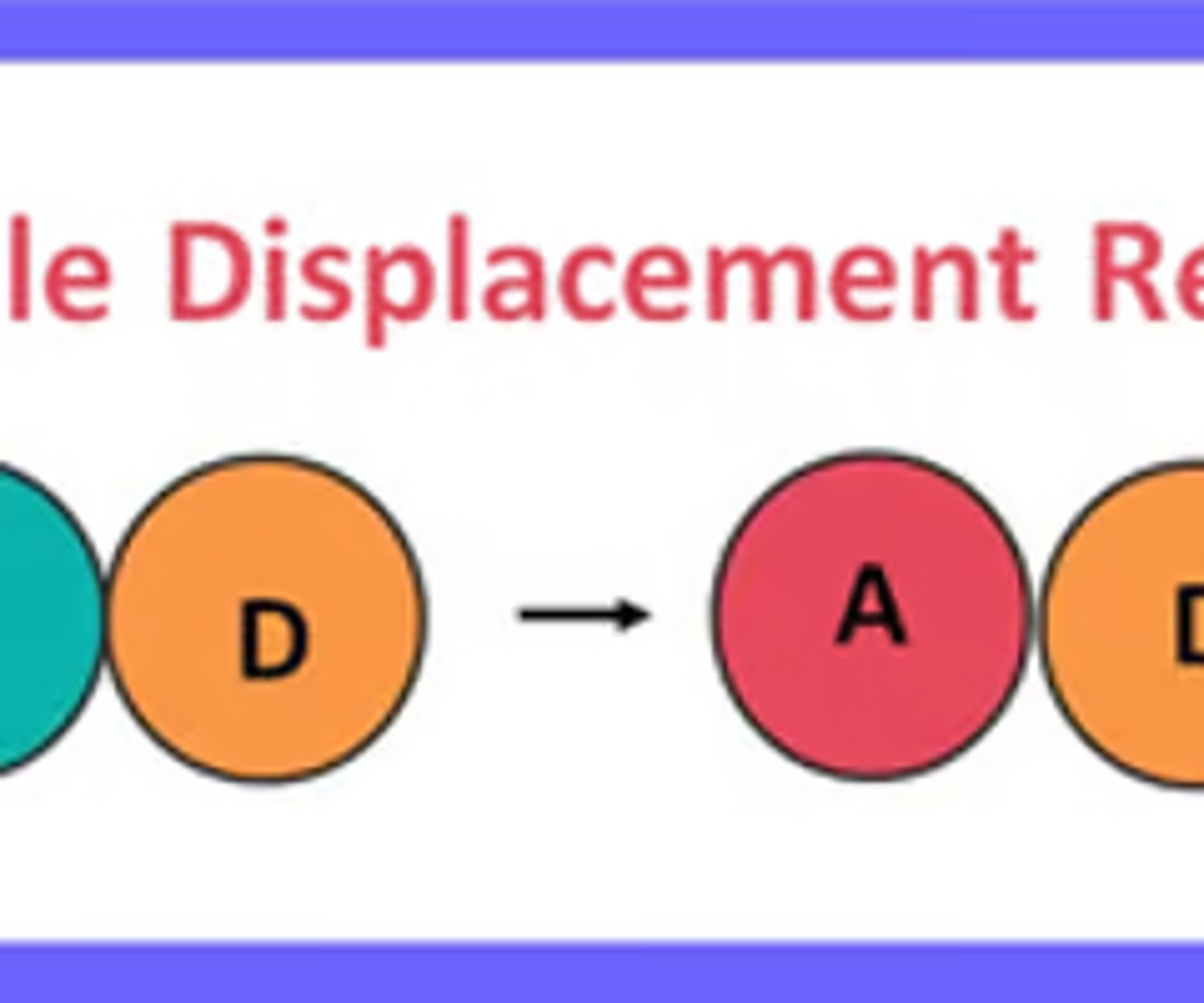
single displacement
a single element trades places with the one most like it in a compound
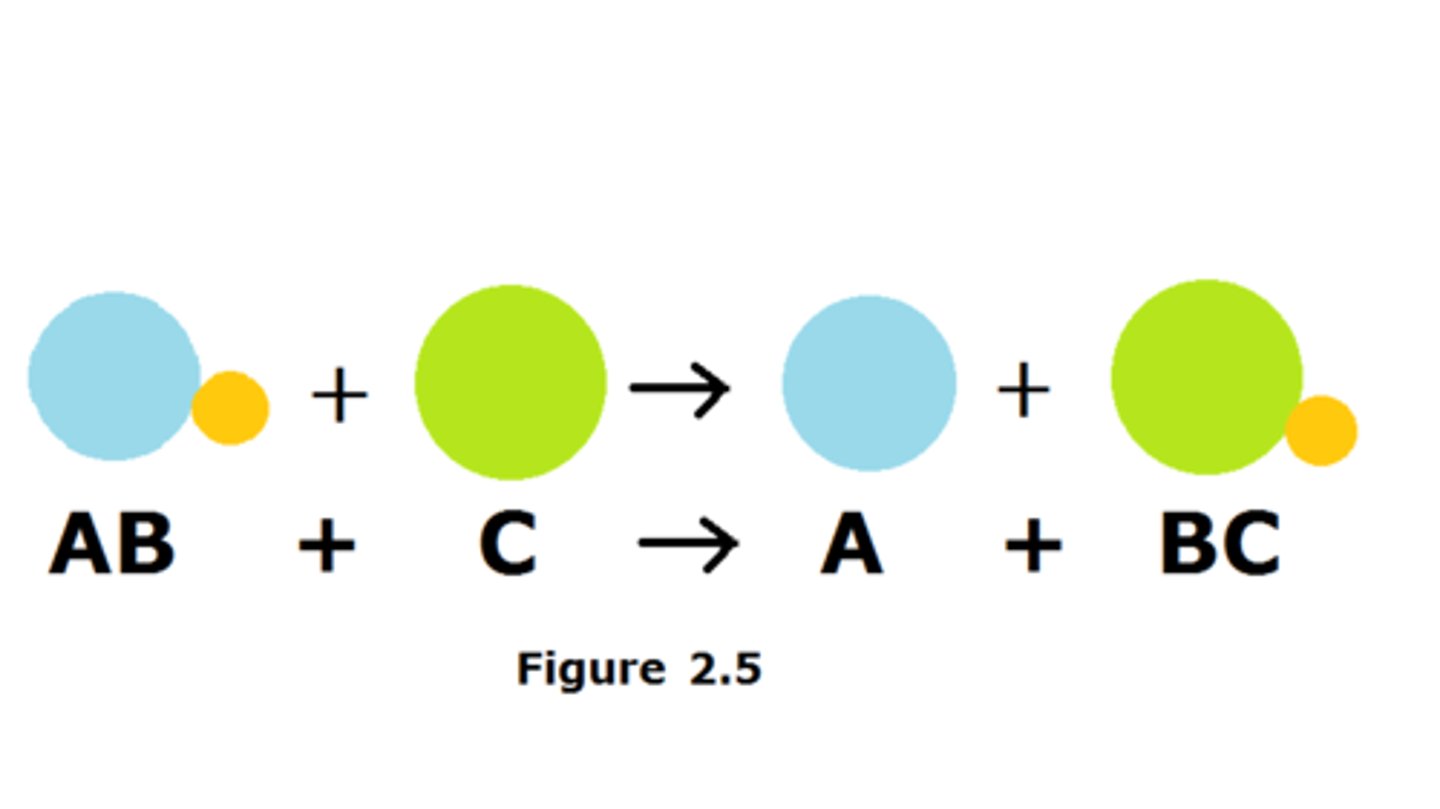
double displacement
two elements from different compounds trade places with like elements
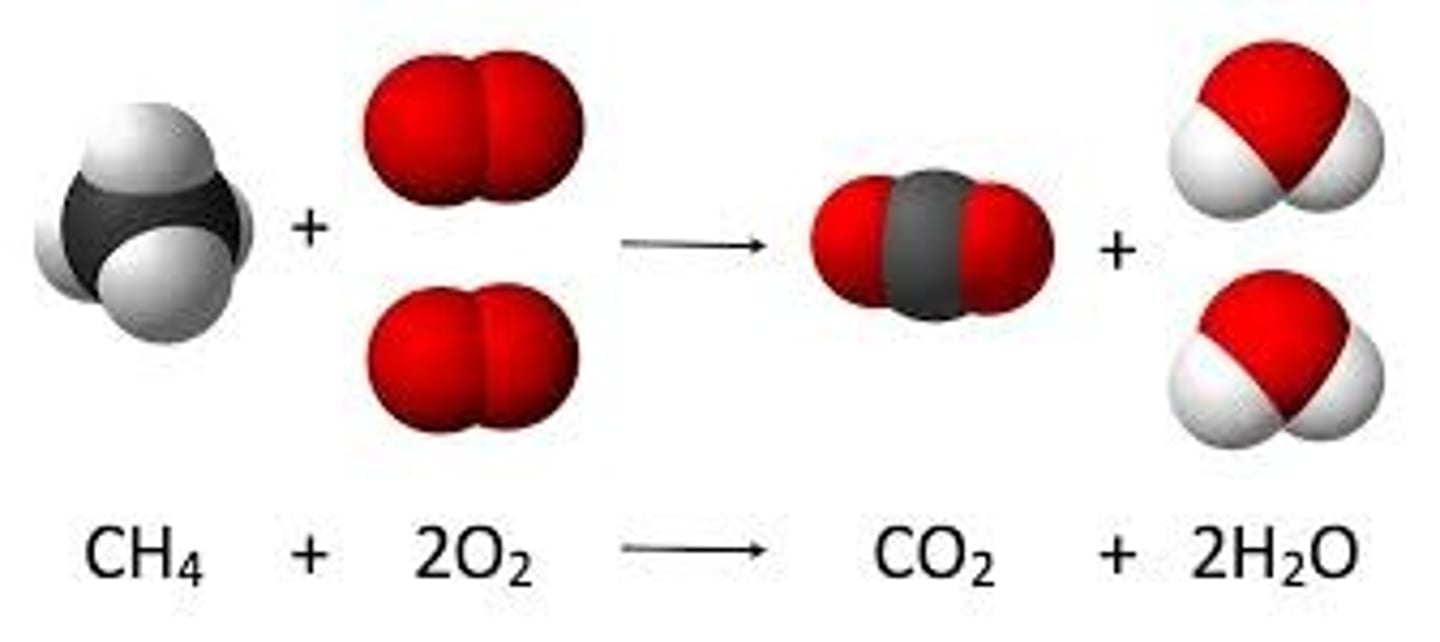
combustion
hydrocarbon compound and oxygen gas with heat combine to make water amd a carbon oxygen compound
surface area
increasing the surface area speeds up the reaction time due to the reactant being more exposed
catalyst
something that speeds up or slows down a reaction
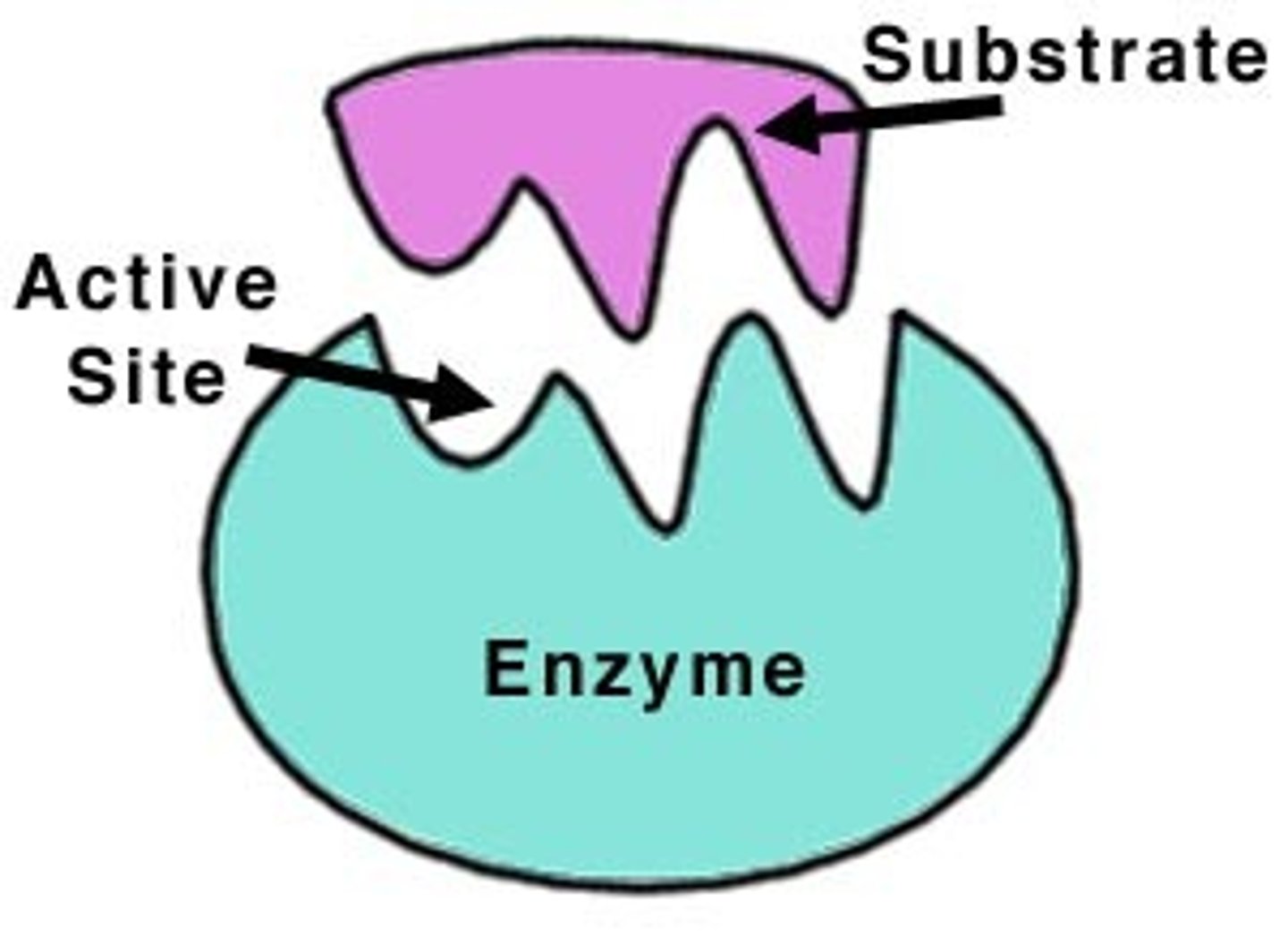
enzyme
a substance that speeds up a reaction
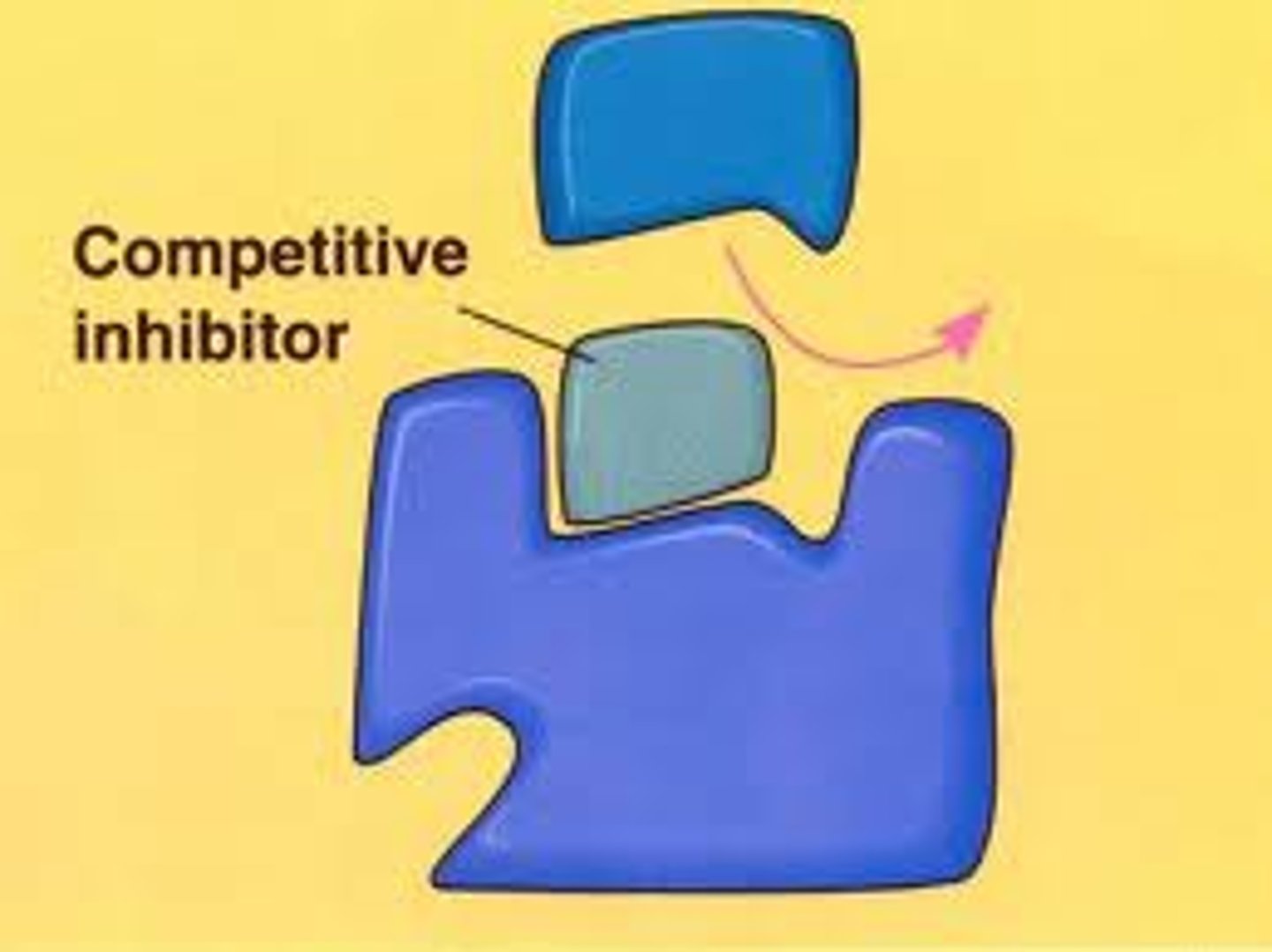
inhibitor
a substance that slows down a reaction

What type of chemical reactions occur everyday?
grow, ripen, digest, decay, and breathe
What observation would you see if a chemical reaction occurs?
formation of a solid, gas (bubbling or fizzing), or odor and energy in the form of light or heat
How is energy related to breaking and forming bonds?
forming bonds releases energy and breaking bond absorbs energy
Understand this graph
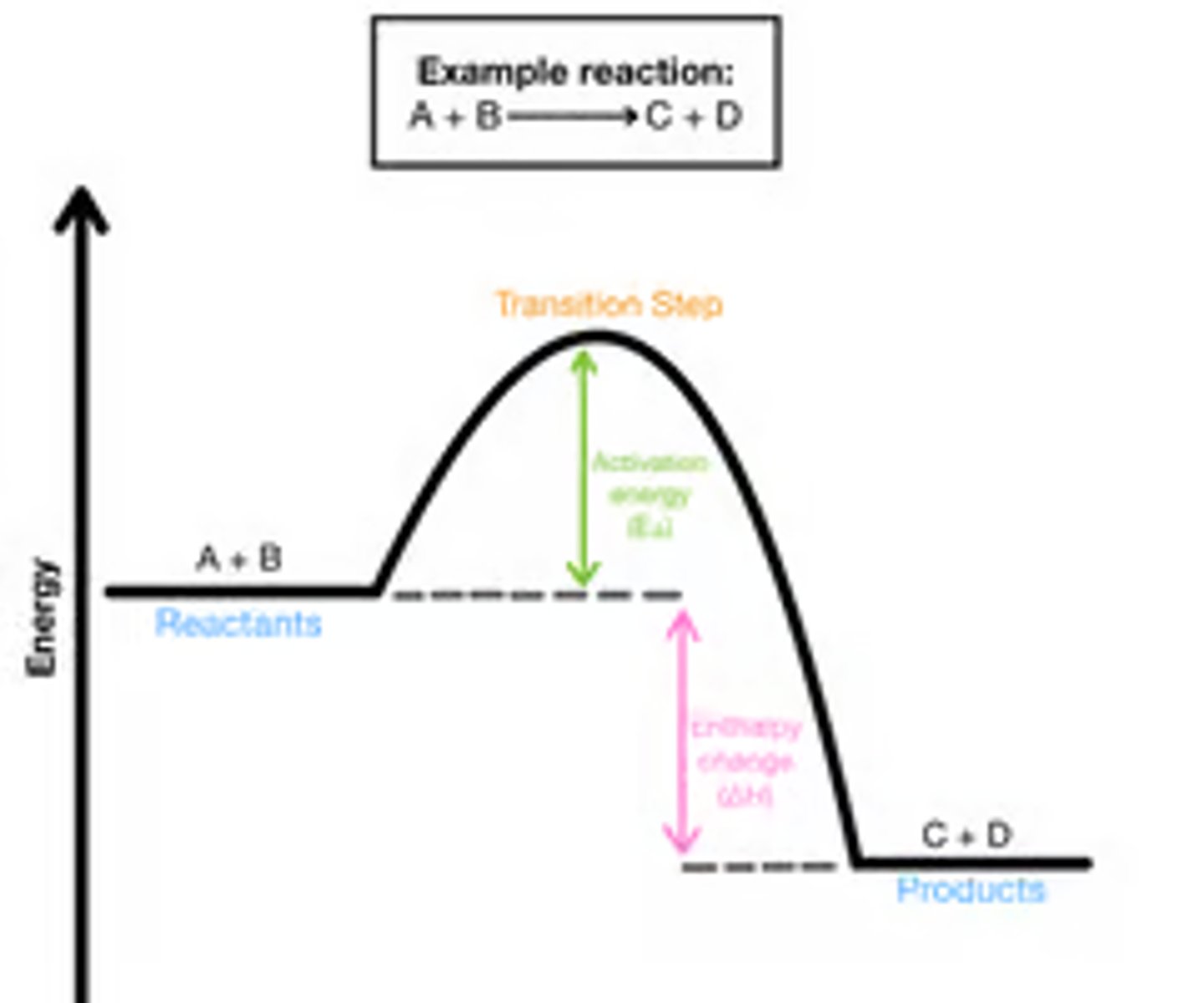
Understand this graph
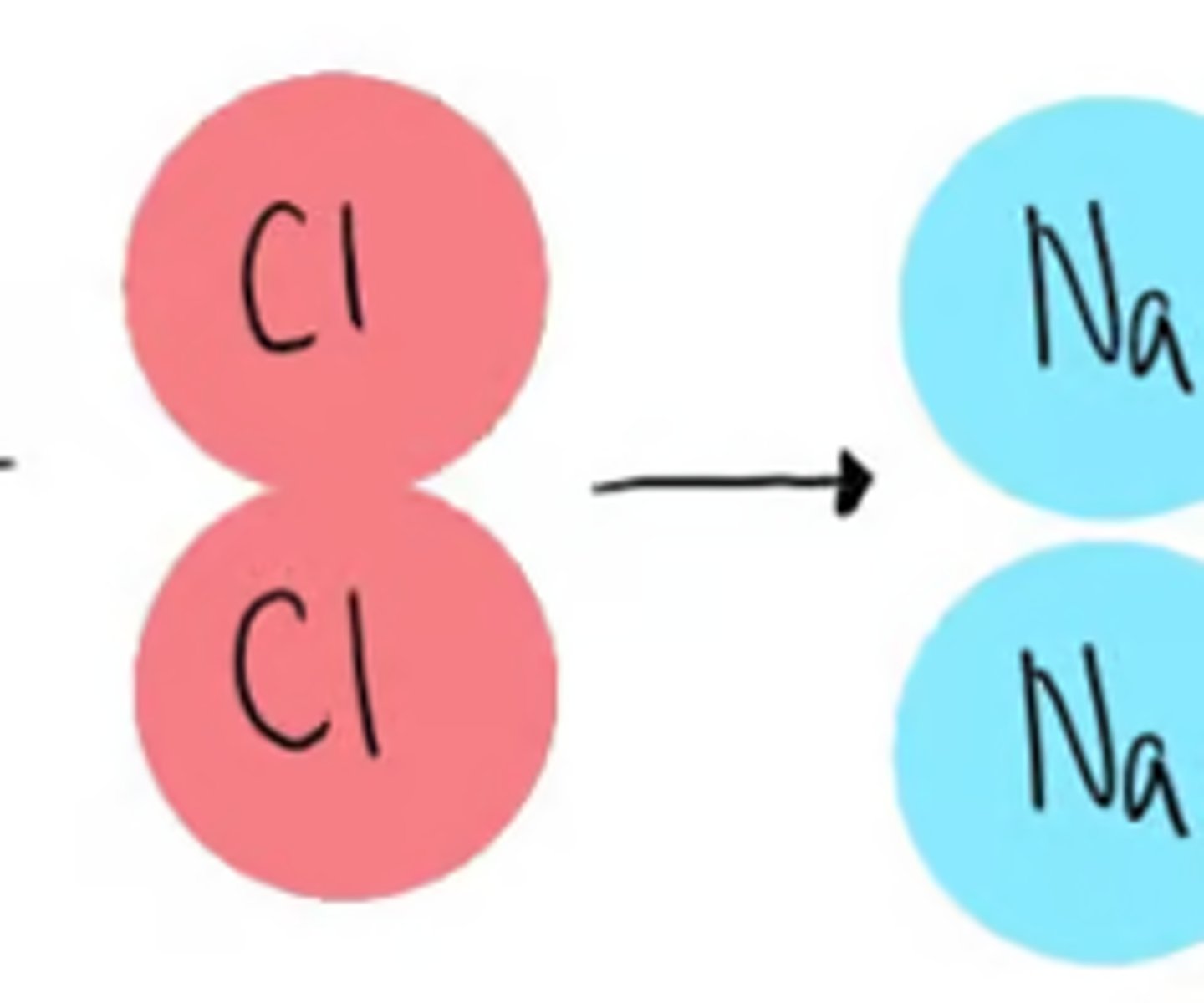
Three ways a chemical reaction can be described
Words-Sodium and Chlorine yield Sodium Chloride
Formulas-2Na + Cl₂ → 2NaCl
Models-
How is Law of Conservation related to balancing chemical equations?
to have a balanced equation everything must be even on both sides, meaning nothing is created or destroyed
Balance ZnS + O₂ → ZnO + SO₂
Z2nS + 3O₂ → 2ZnO + 2SO₂
How is chemical reactions like a recipe?
everything must be to the correct ratio to turn out okay
How do we determine the mole ratio of a chemical reaction?
you take the coefficients and list them left to right to tell the relative amounts of reactant and products
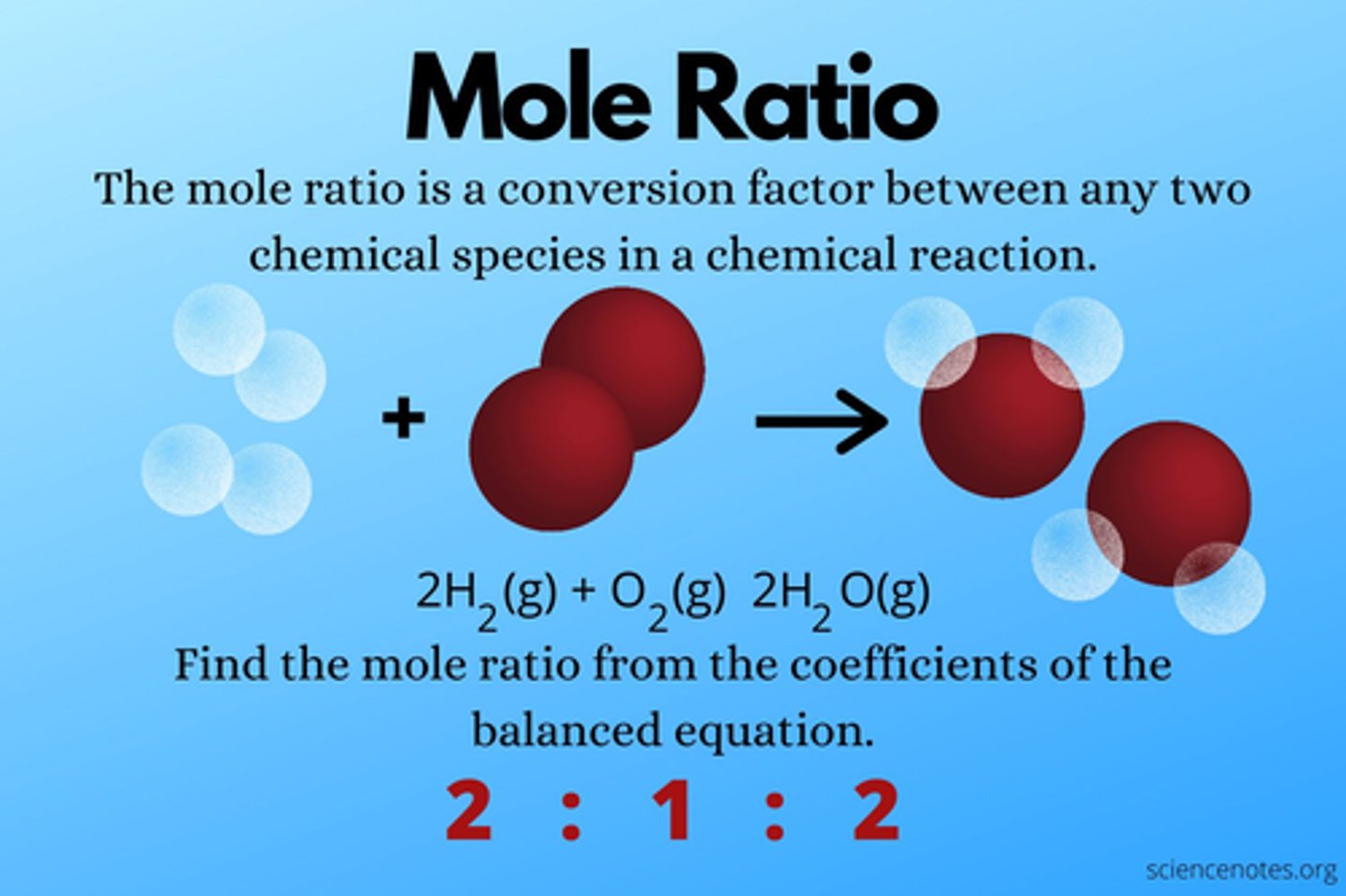
KNOW THE CHART

Compare and Contrast complete and incomplete combustion
Complete combustion produces H₂0 and CO₂ and incomplete produces H₂0 and CO
Speed
distance an object travels per unit of time