exam 3 review motor skills
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
germinal period
first prenatal period; lasts approximately two weeks

embryonic period
Organogenesis and myogenic movements occur during this period; lasts approximately six weeks
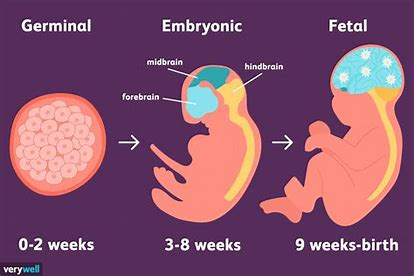
fetal period
• Rapid growth and neurogenic movements occur during this period; lasts from end
of embryonic period until birth
reflexive movements
sterotypical responses, elicited by external
stimuli, stimulus consistenly produces the reflex.
primitive reflexes
protection ; example sucking reflex and palmar grasp reflex
postural reflexes
maintain posture ; example neck righting reflex and parachute reflex
locomotor reflexes
practice ; example stepping reflex and swimming reflex
reaching and grasping
Attainment of sitting allows the infant to reach,
grasp, and manipulate objects
power grip
occurs during the 20 weeks; grabs with the whole hand
precision grip
occurs 52 weeks; holds the object with 2 fingers
stability skills
fundamental movement skill: balancing the body in stillness and in motion (example: landing and balancing)
locomotor skills
fundamental movement skill: transporting the body in any direction from one point to another (example: walking, running, hopping)
manipulative skill
fundamental movement skill: control of objects using various body parts (example: catching, throwing, kicking)
failure and obstacles with the proficiency barrier
There is significant research that suggests being motorically
unskilled (and, thus, being unable to cross the proficiency
barrier) is increasing at an alarming rate
• It makes intuitive sense that decrements in skill would be
magnified by such factors as socioeconomic status, access to
education, and geography
nature versus nurture
nature = genes
nurture = environment
genotypes
twins: identical genotypes is monozygotic
different genotype is dizygotic
what type of constraints are impacted by physical growth?
Changes over the life span in skeletal, muscular, and
nervous systems will affect motor performance and
learning
what are the key developmental changesin the systems?
Physical growth in first year after birth—50 percent gain in
height (length) and 200 percent gain in weight—is
remarkable; this high rate of change occurs only during the
first year
peak height velocity of women vs men
boys have a height velocity of 7.9 cm/year
girls have a height velocity of 7.25 cm/year.
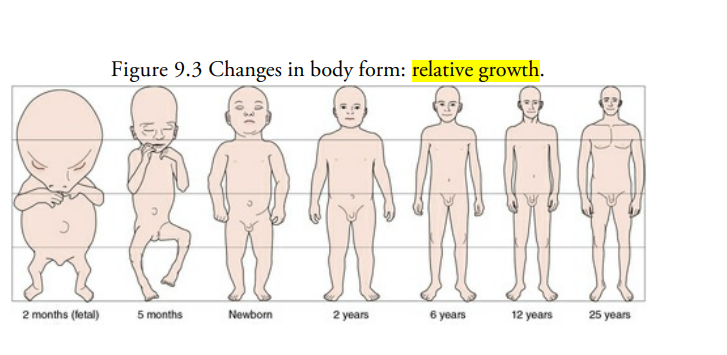
relative growth
different rates of growth of different
body parts; the head grows quicker than the legs during
prenatal months but slower than the legs after birth
why do women tend to be better at balance activities ?
females are more flexible than males due to
body size and composition, hormone levels, and physical
activities
when does rate of decline increases?
for most systems, it increases around the age of 75
adults can slow decline down of the rate of decline ?
Healthy, physically active adults experience
average rates of decline after age 75 but are
starting at higher levels, thus enabling them to
maintain their physical function much longer than
their sedentary peers
declarative knowledge
type of knowledge: factual and conceptual information (ex: Knowing the difference between a softball and a Nerf
ball or between an underhand throw and an overhead
throw)
procedural knowledge
type of knowledge: knowing how to do something (ex: Knowing how to execute an overhand throw or where to throw the ball, based on the game situation)
metacognitive knowledge
type of knowledge: higher level of declarative knowledge (Ex: Knowing one’s own strengths and weaknesses)
strategies used in memory for movement?
Meaningfulness: whether new movements are similar
to previous movements
• Visual imagery: for example, picking an apple from a
tree
• Verbal labels: move arm to 2 o’clock
• Rehearsal strategies: keep the head between the arms
when diving
• Explicit intent to remember: we will use this movement
tomorrow
• Subjective organization: these four dance steps can be
viewed as one
intrinsically motivation
provides pleasure and satisfaction from participating, in the absence of material towards rewards or constraints (Ex:long-distance runner who enjoys the peace and tranquility of the outdoors )
extrinsically motivation
provide a means to an end and are not engaged in for their own sake (ex: completing additional fitness workouts to make a team)
amotivation
present when people do not see any relationship between outcomes and actions (ex: people feel that whatever they do)
self regulatory skills
involves the ability to resist an impulse. It requires executive functions, setting goals, controlling impulses, socializing and motivating oneself, managing emotions, and using mental processes and tracking progress
spontaneous movements
(rhythmical stereotypies) when a baby does something out of impulse that is involuntary
ex: infant kick his legs rhythmically, thrust his arms into the air, or extend his fingers,
motor milestones
controlled movements that follow a fairly predictable sequence, although people may vary widely in terms of when a given skill will appear. (the sequence that a baby goes through in learning things)
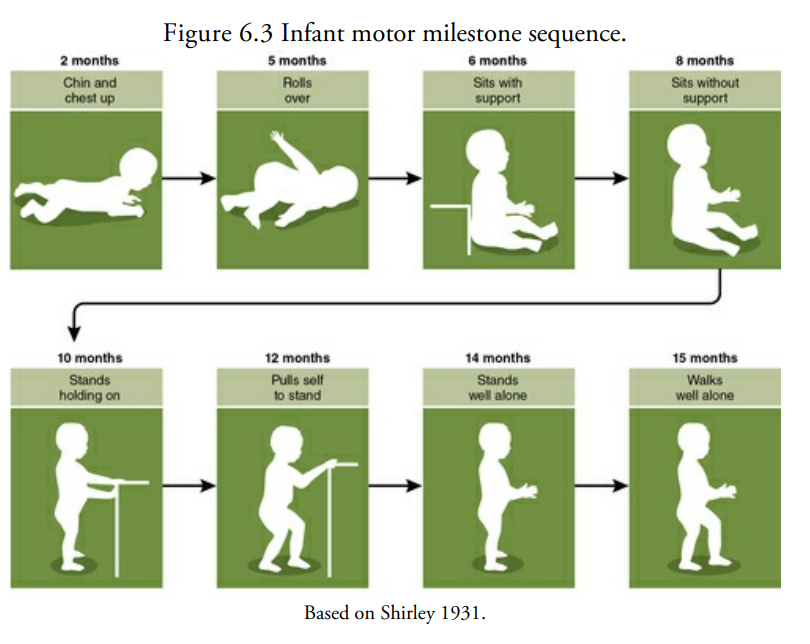
basic order of motor milestones
2 months : chin and chest up
5 months : rolls over
6 months: sits with support
8 months: sits without support
10 months: stands holding on
12 months: pulls self to stand
14 months: stands well alone
15 months: walks well alone
sensory development
particular importance to motor development and motor learning, because it has many implications for skillful performance in infants