T3 - IE1 - Cardiology - Kaur - Hypertension Medicinal Chemistry
1/93
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
94 Terms
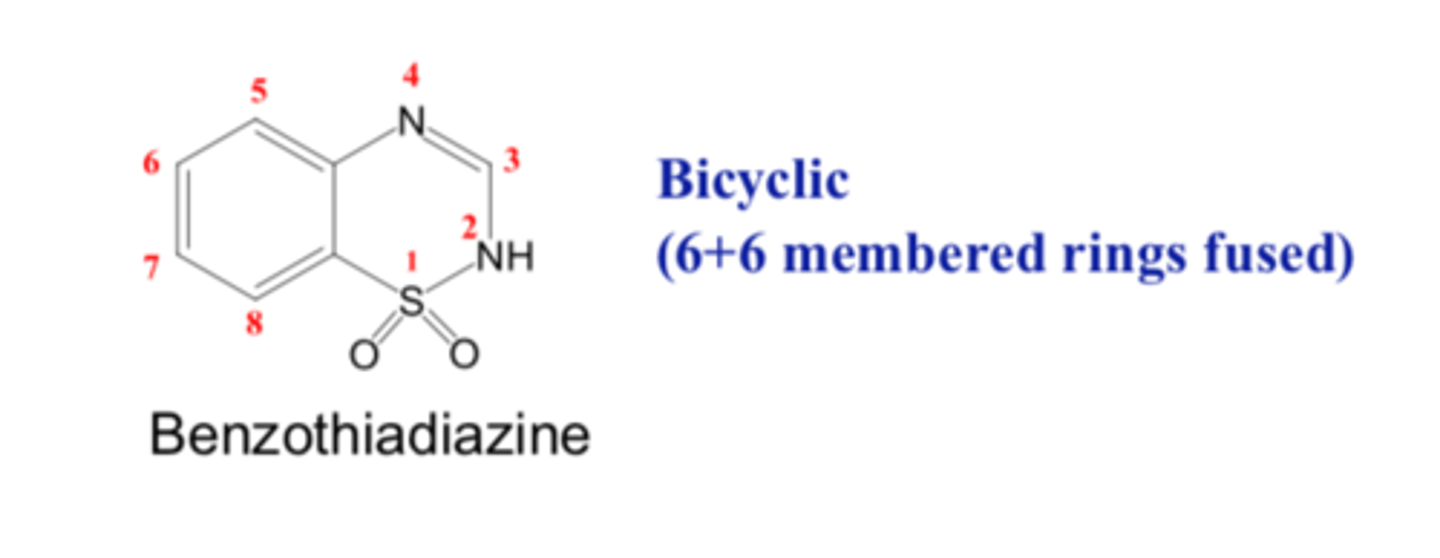
Thiazide
Benzothiadiazine
Benzo refers to the benzene ring.
"Thia" refers to the sulfur
Diazine refers to the two nitrogen.
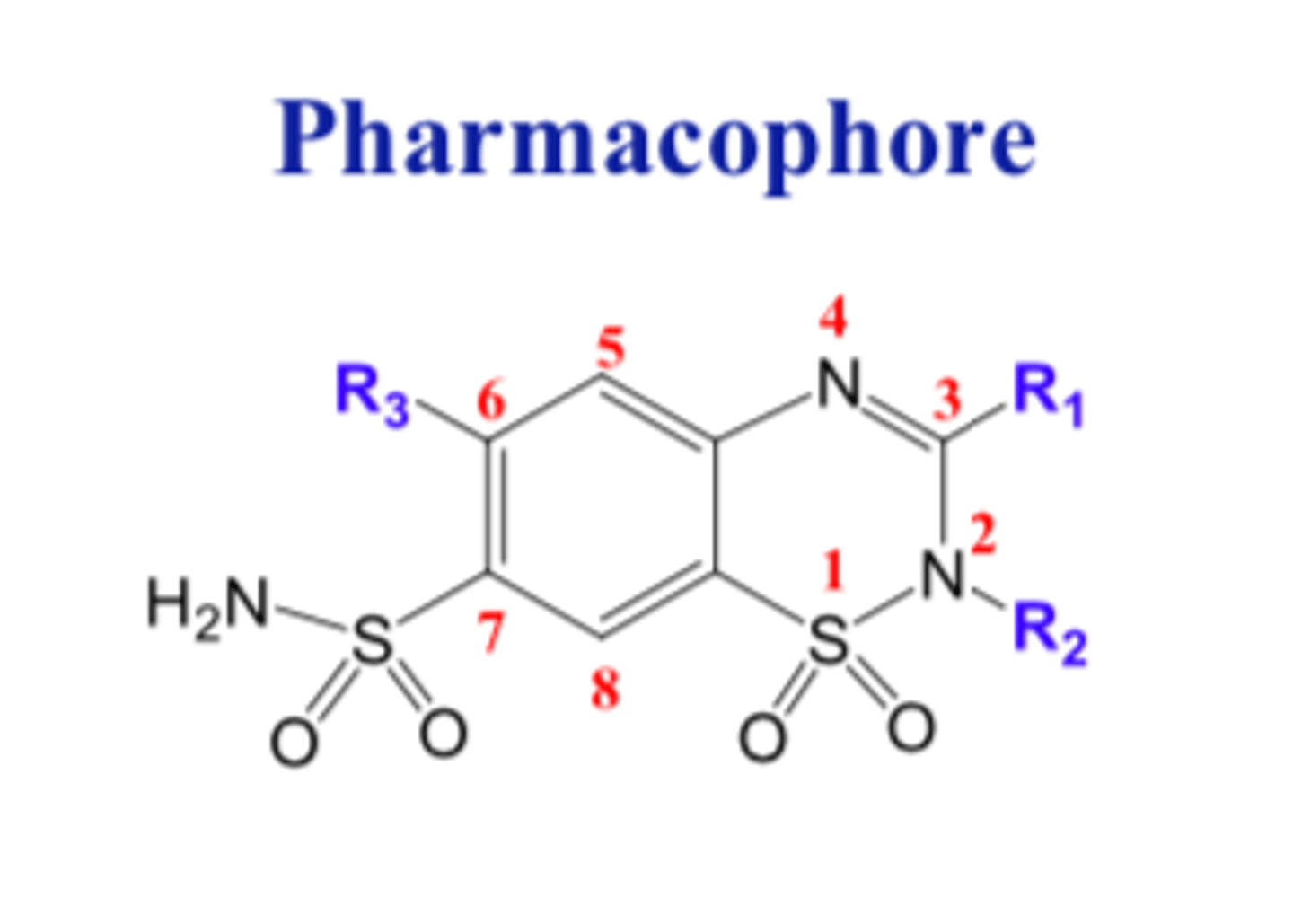
Benzothiadiazine (Thiazide) has a _________ structure
- bicyclic
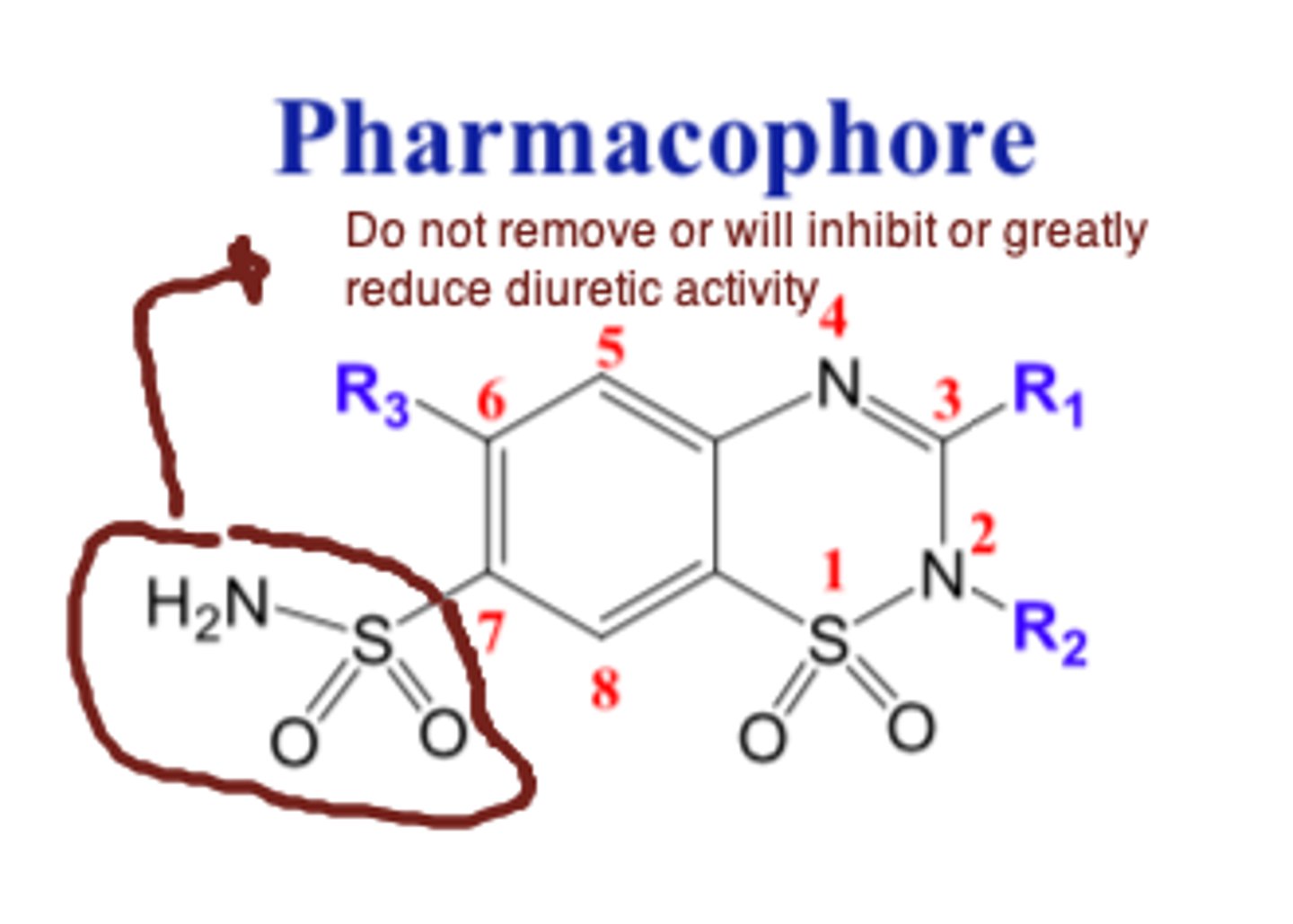
For thiazide diuretics, replacement or removal of the sulfonamide group at position 7 yields compounds with...
little or no diuretic activity
For thiazide diuretics, replacement or removal of the _____________ group at position 7 yields compounds with little or no diuretic activity
- sulfonamide
For thiazide diuretics, replacement or removal of the sulfonamide group at _____________ __ yields compounds with little or no diuretic activity
- position 7
For thiazide diuretics, __________-__________ group is necessary at position 6 for diuretic activity
- electron-withdrawing
For thiazide diuretics, electron-withdrawing group is necessary at _________ ___ for diuretic activity
- position 6
Little diuretic activity is seen with a hydrogen atom at position 6, whereas compounds with a chloro or trifluoromethyl substitution are highly active. The trifluoromethyl-substituted diuretics are more lipid-soluble and have a longer duration of action than their chloro-substituted analogs.
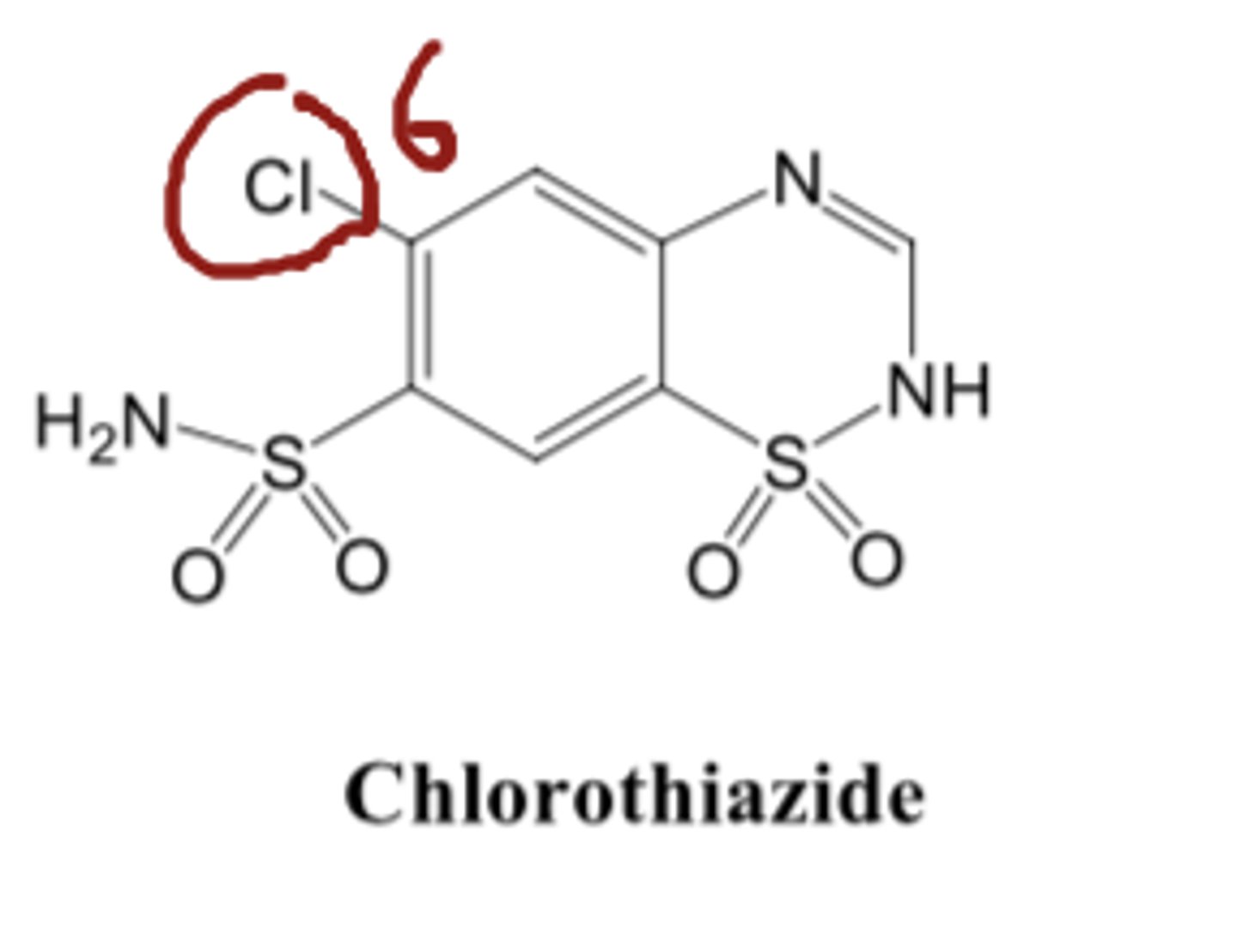
For thiazide diuretics, little diuretic activity is seen with a hydrogen atom at position 6, whereas compounds with a ______ or _____________ substitution are highly active.
- chloro
- trifluoromethyl
The trifluoromethyl-substituted diuretics are more lipid-soluble and have a longer duration of action than their chloro-substituted analogs.
Bioisosteres
"compounds" that fit the broadest definition for isosteres and have similar biological activity
For thiazide diuretics, ________ of the double bond to give a 3,4-dihydro derivative produces a diuretic that is ___-_____ more active than the unsaturated derivative.
- saturation
- 10-fold
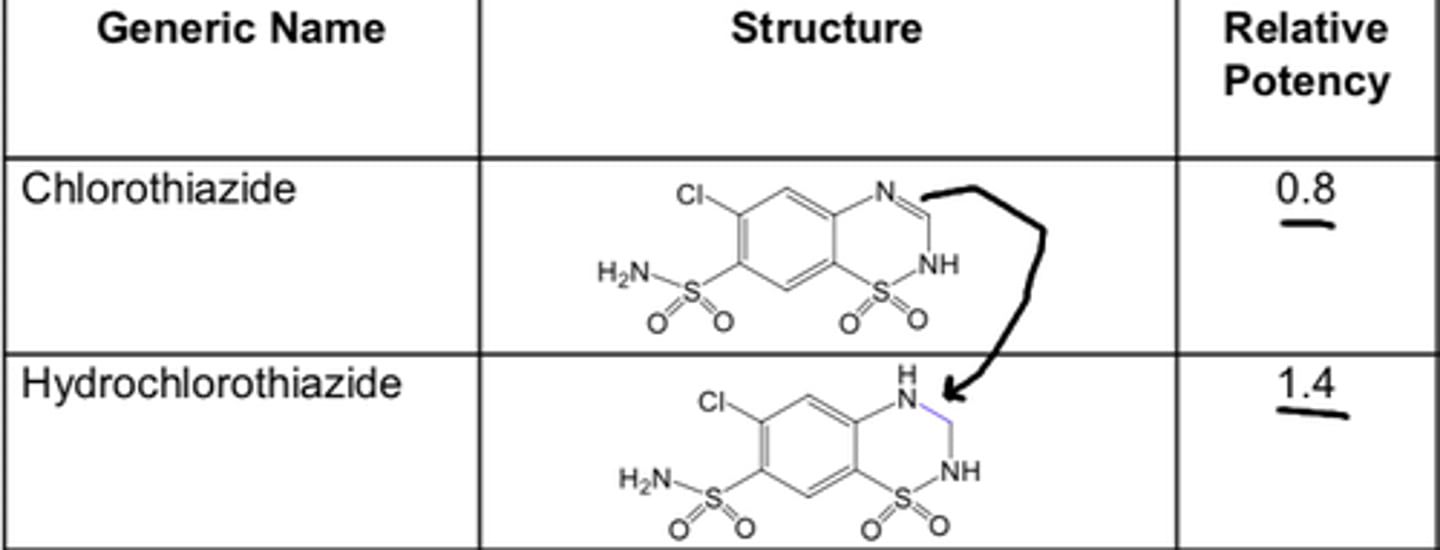
For thiazide diuretics, substitution with a lipophilic group at ________ __ gives a marked increase in the diuretic potency.
- position 3
Haloalkyl, aralkyl, or thioether substitution increases the lipid solubility of the molecule and yields compounds with a longer duration of action
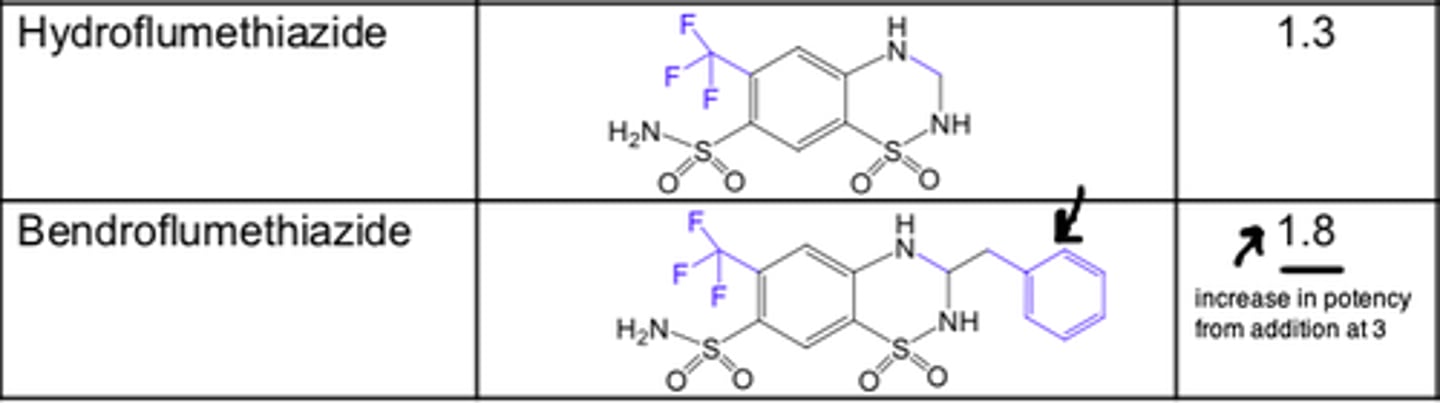
For thiazide diuretics, ______ substitution on the 2-N position also decreases the polarity and increases the duration of diuretic action
- alkyl
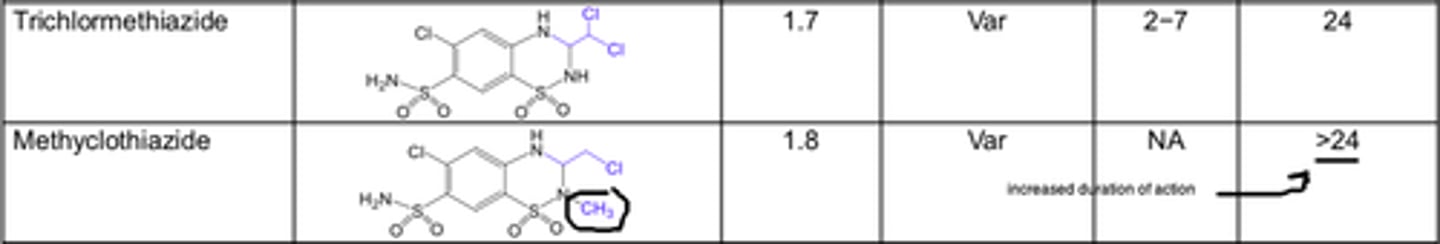
For furosemide, The_______ and ___________ substitutions are features also seen in other diuretics.
Because the molecule possesses a free _________ group, furosemide is a stronger acid than the thiazide diuretics (pKa = 3.9).
- chlorine
- sulfonamide
- carboxyl
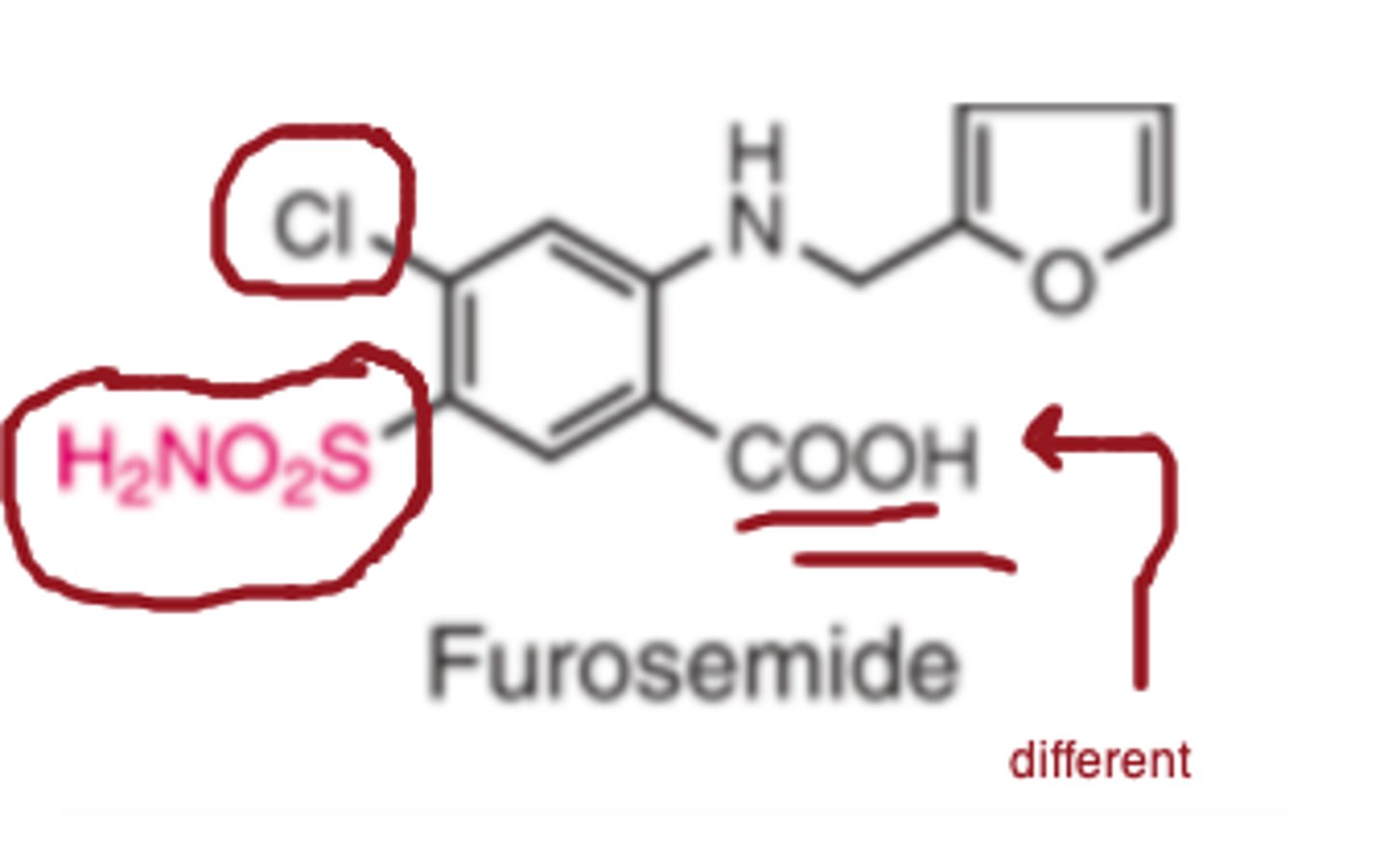
Furosemide pKa
3.9
Furosemide is excreted primarily ___________
- unchanged
A small amount of metabolism can take place on the furan ring
Furosemide has a ________ duration of action
- short (~6 to 8 hours)
In bumetanide, A _______ group has replaced the customary chloro or trifluoromethyl substitutions seen in other diuretics
- phenoxy (electron-withdrawing group)

In bumetanide, the amine group customarily seen at position 6 has been moved to...
position 5

In bumetanide, the amine group customarily seen at position in other diuretics ___ has been moved to position 5
- 6
These minor variations including the phenoxy substitution instead of the chlorine / trifluoromethyl substitutions have lead to marked increase in potency (~50x more potent)
Bumetanide Duration of Action
~ 4 hours
Triamterene is a ______ derivative
- pteridine
70% absorbed on oral administration
Potassium-sparing diuretics are ______ _________ ______
- weak organic bases
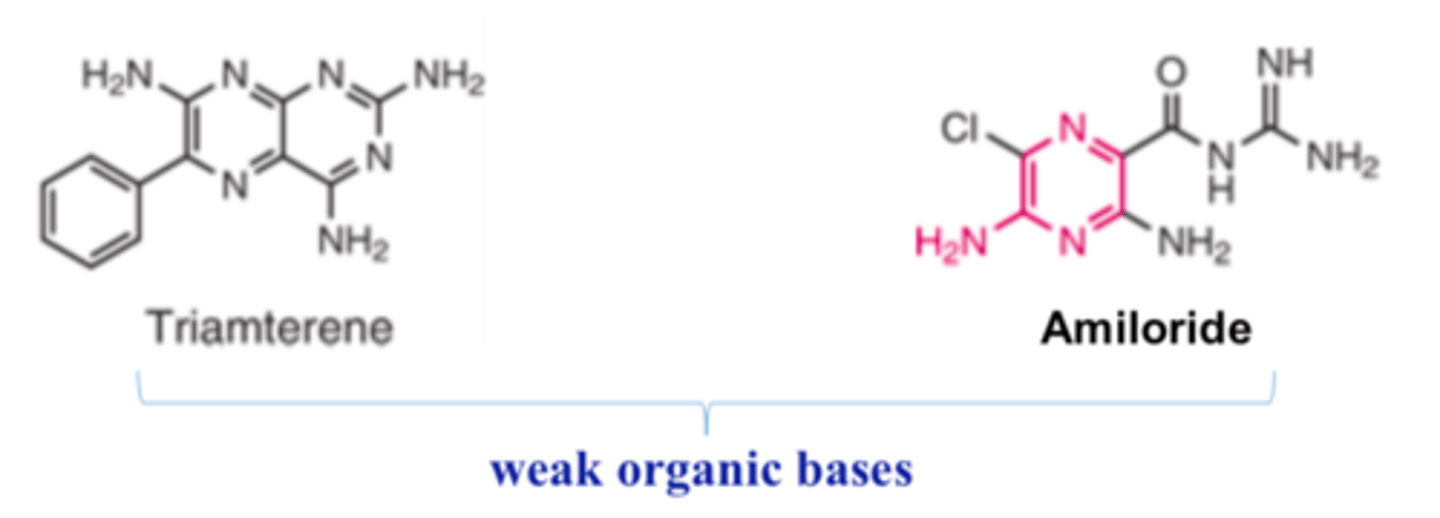
Amiloride is an ________________ structurally related to triamtere as an open-chain analog
- aminopyrazine
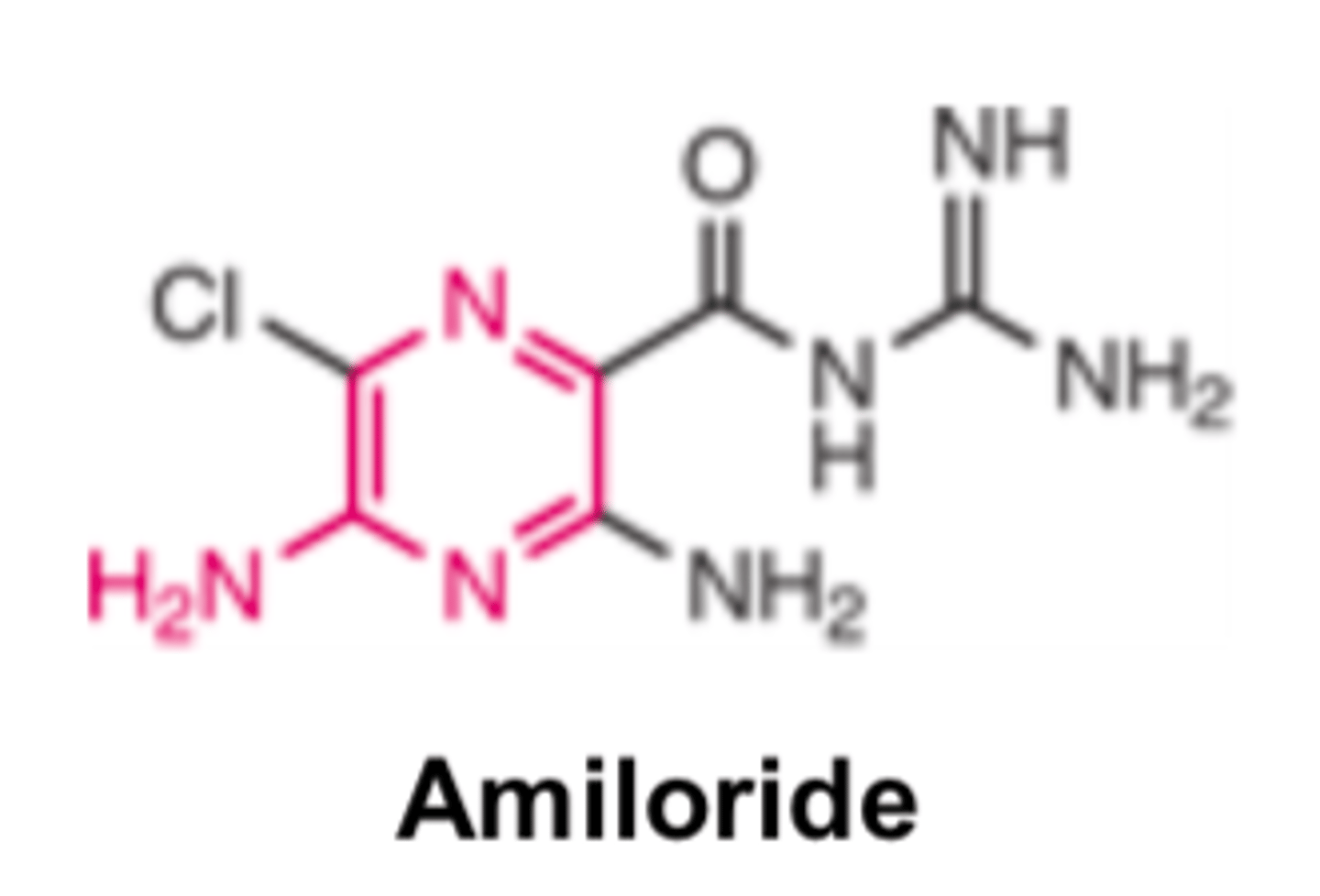
Amiloride is ______ more potent than triamterene
- 10x
50% absorbed on oral administration
Glucocorticoid Example
Cortisol (hydrocortisone; drug name)
Mineralocorticoid Example
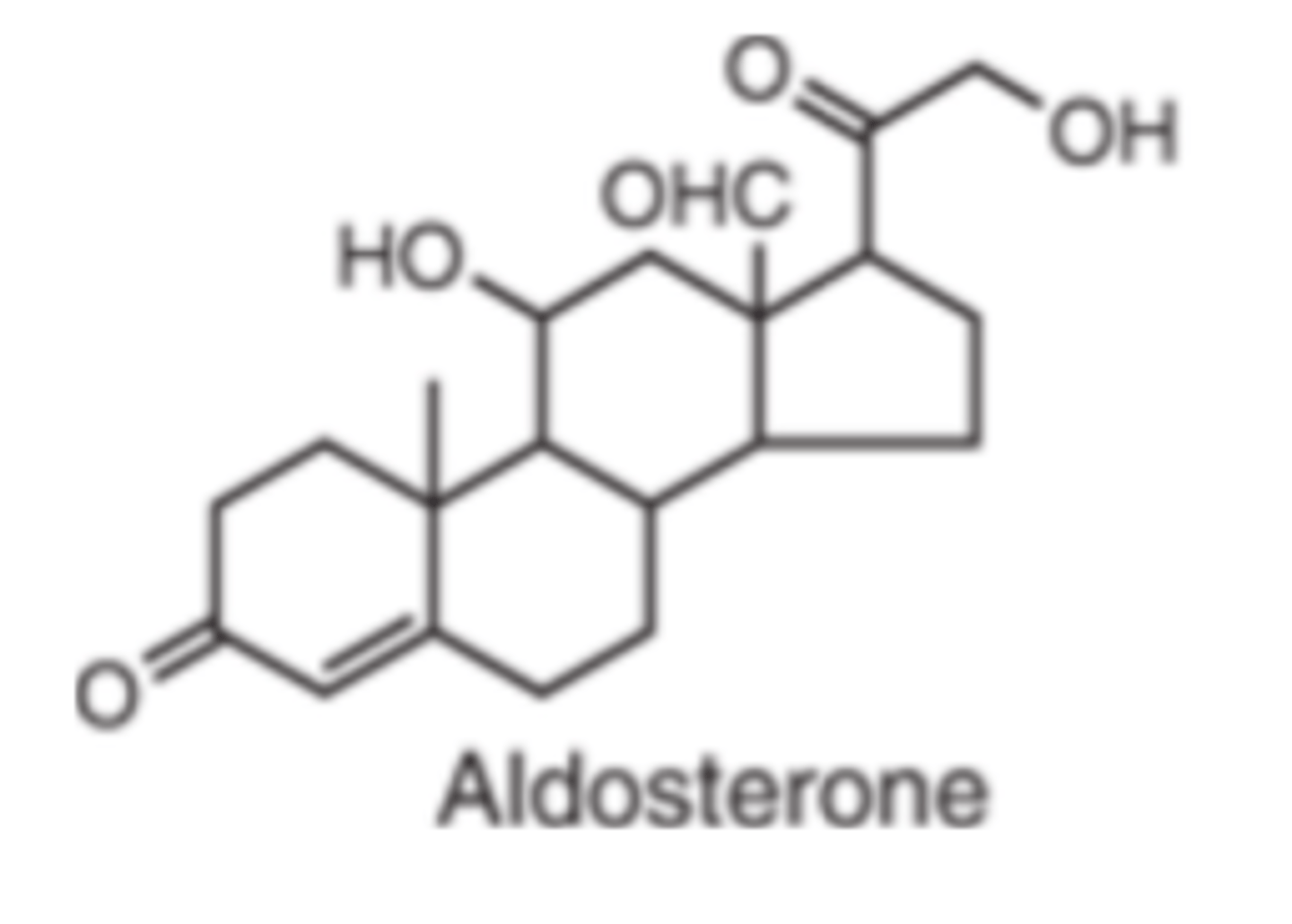
Aldosterone
Glucocorticoids function
carbohydrate, lipid, and protein metabolism
Mineralocorticoids function
promote salt and water retention
promote potassium and hydrogen ion excretion
A substance that antagonizes/blcoks the effects of aldosterone could conceivably be a good diuretic drug
Spironolactone ___________ ________ aldosterone binding to the mineralocorticoid receptor
- competitively inhibits
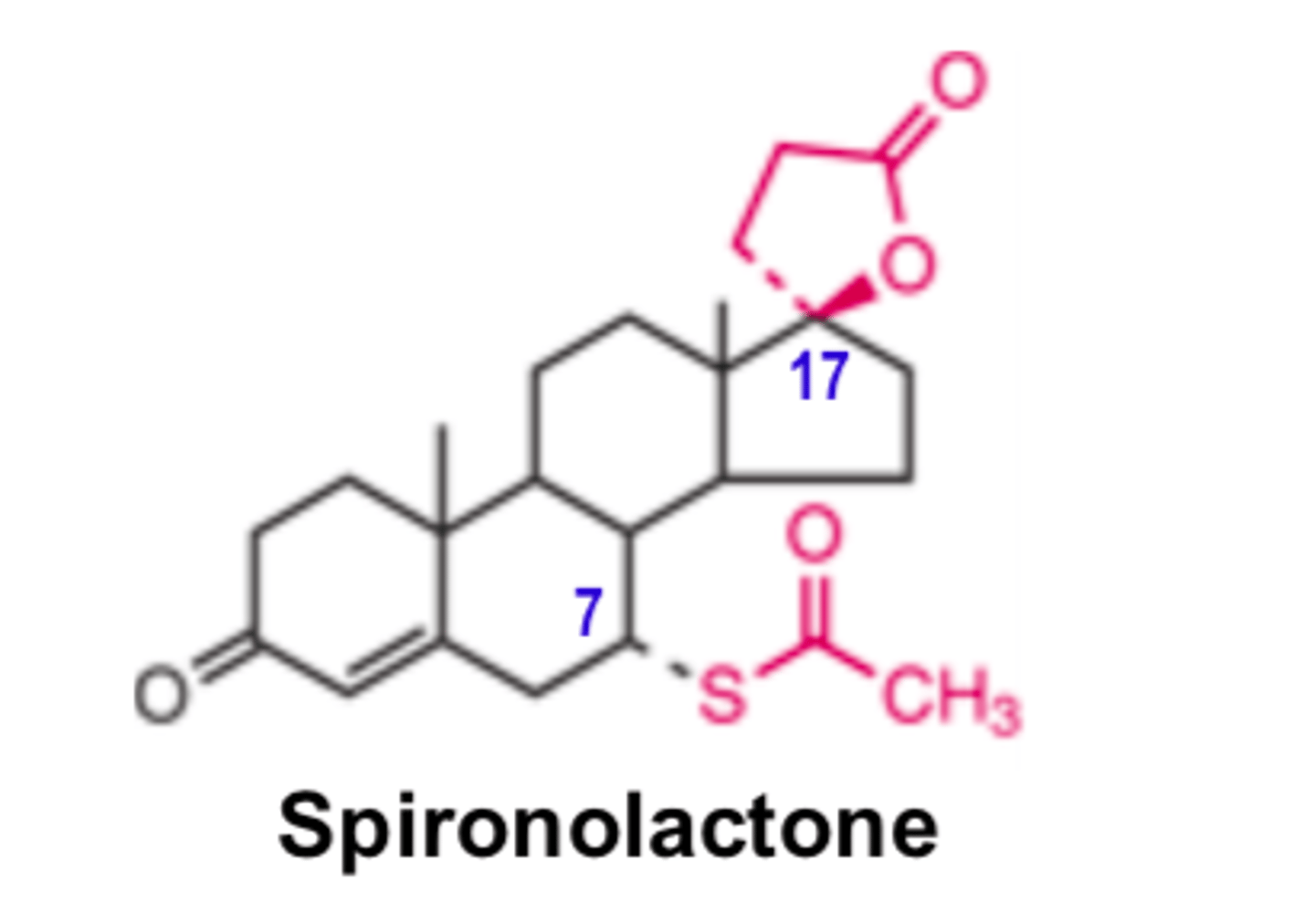
Spironolactone competitively inhibits ________ bindings the mineralocorticoid receptor
- aldosterone
Eplerenone is a newer drug. Because of the _____ _________ it has lower affinity for the mineralocorticoid receptor than Spironolactone. However, in contrast to Spironolactone, Eplerenone is MORE _____________ aldosterone antagonist with limited or no inhibitory effects on GR and PR (progesterone). So it has fewer sexual side effects.
- epoxy group
- selective
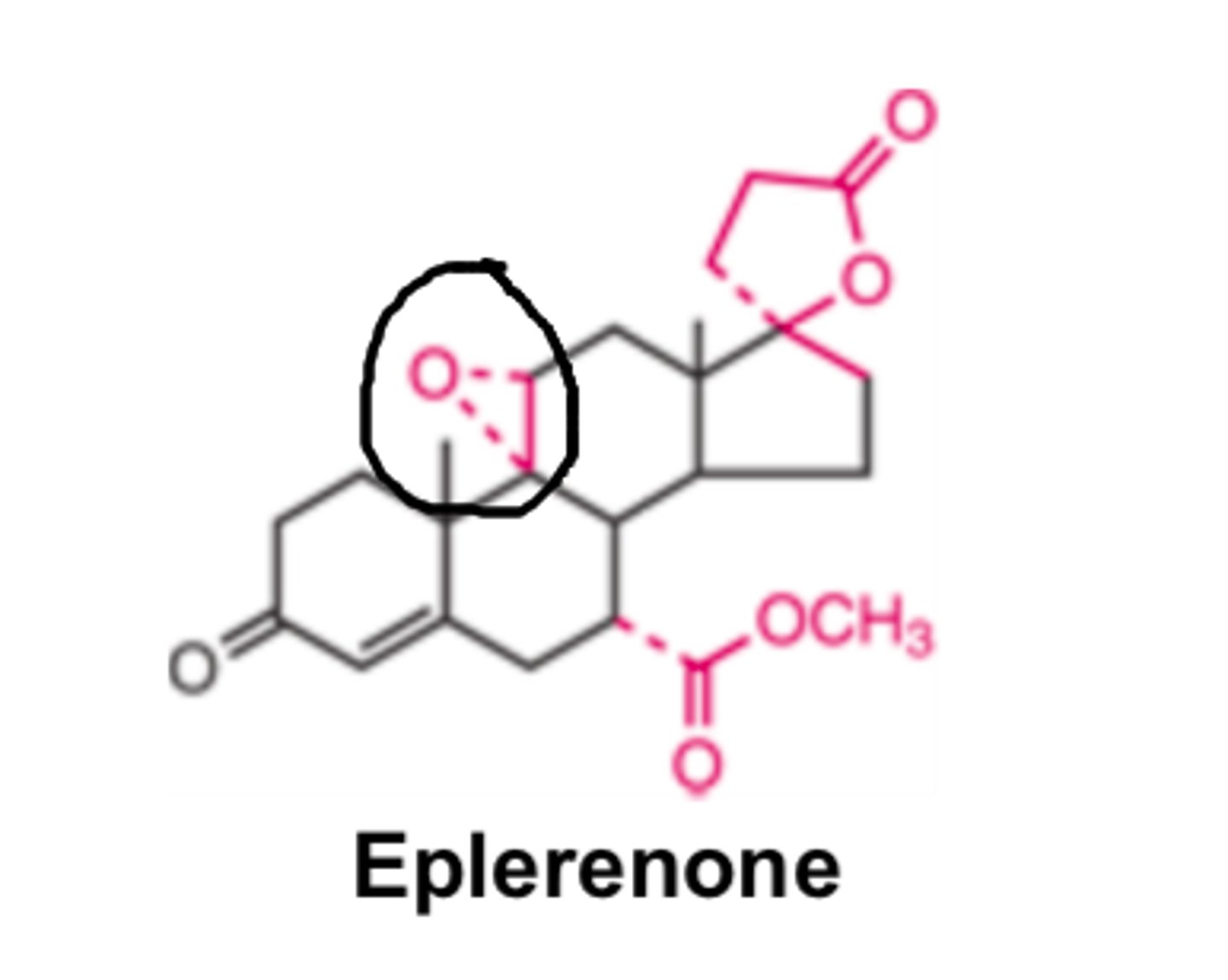
Due to eplerenone's epoxy group it has _______ affinity for the mineralocorticoid receptor. However unlike spironolactone, eplerenone is a more ________ _______________ _________ with limited or no inhibitor effects on GR and PR (progesterone) so it has fewer sexual side effects
- lower
- selective aldosterone antagonist
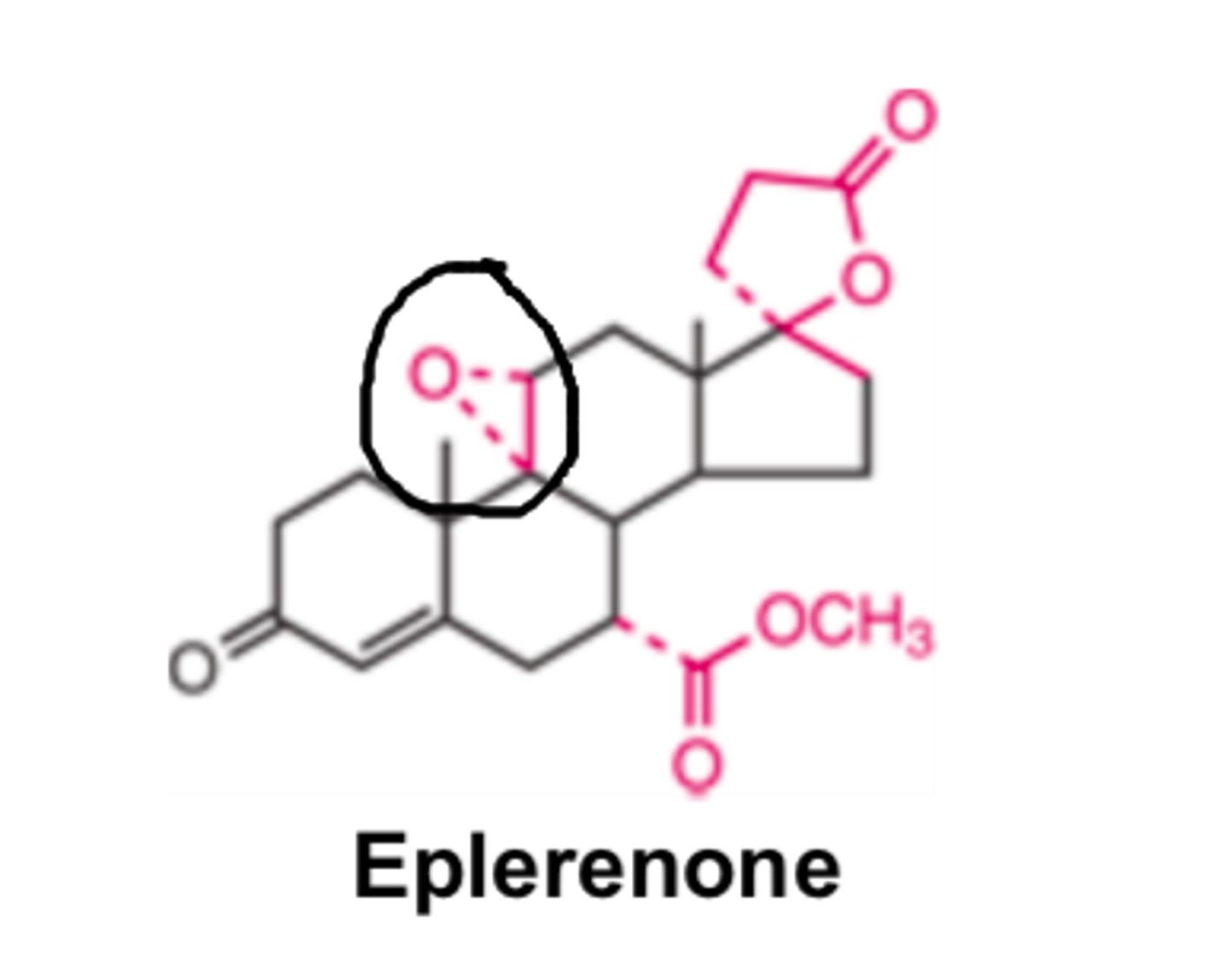
Eplerenone has _______ sexual side effects than spironolactone
- fewer
Due to limited / no effects on GR and PR
β-Adrenergic Antagonists (Sympatholytics) are all...
aryloxypropanolamines
Propanolol is __________ lipophilic
- HIGHLY
Enters CNS far better than less lipophilic agents like nadolol
Propanolol is ______________ β antagonist
- non-selective (β1 and β2)
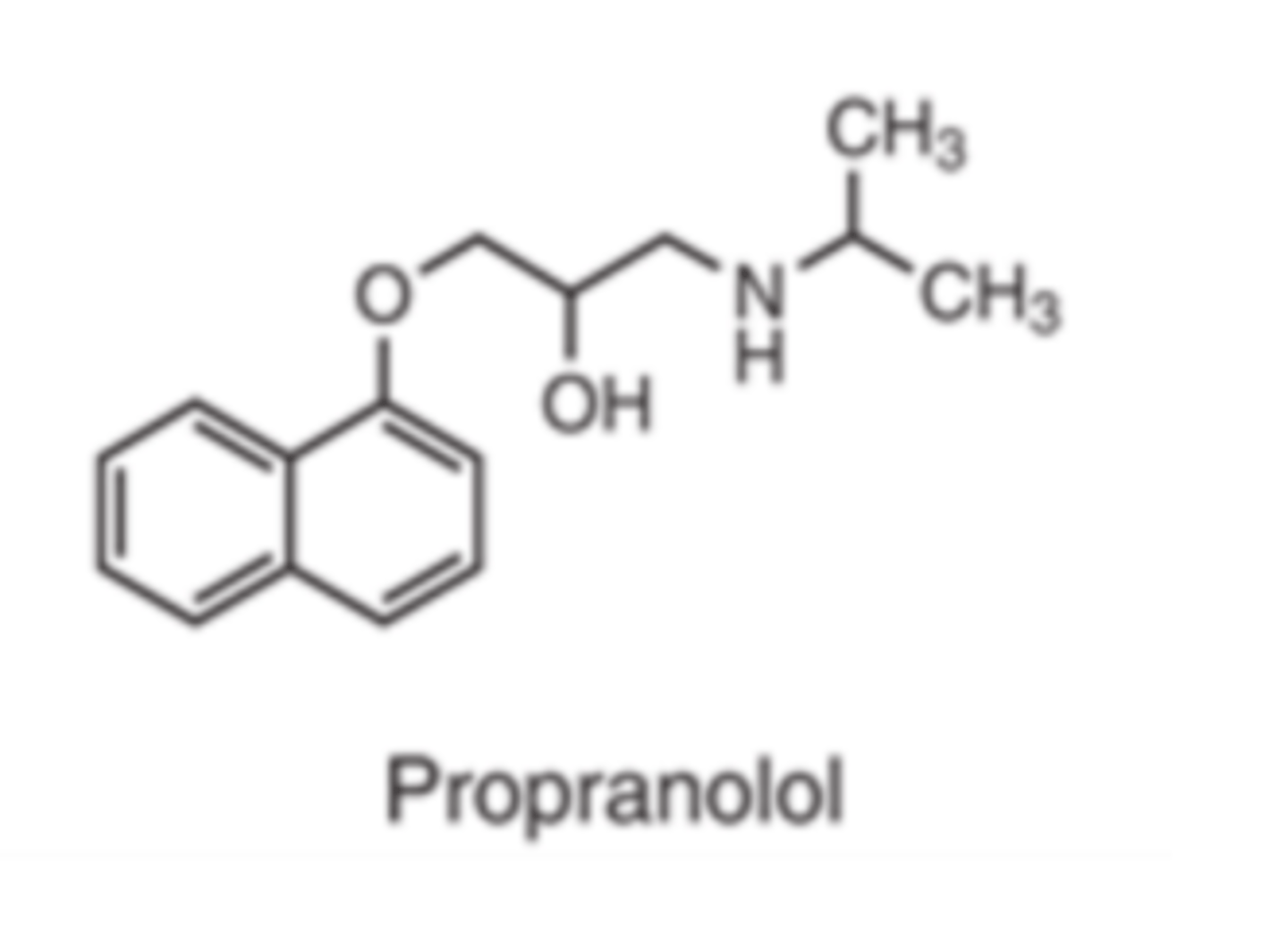
Esmolol is a __________ β antagonist
- selective (β1)
4-substituted aryloxypropanolamine
Esmolol has a ___-_______ _____________ structure
- 4-substituted aryloxypropanolamine
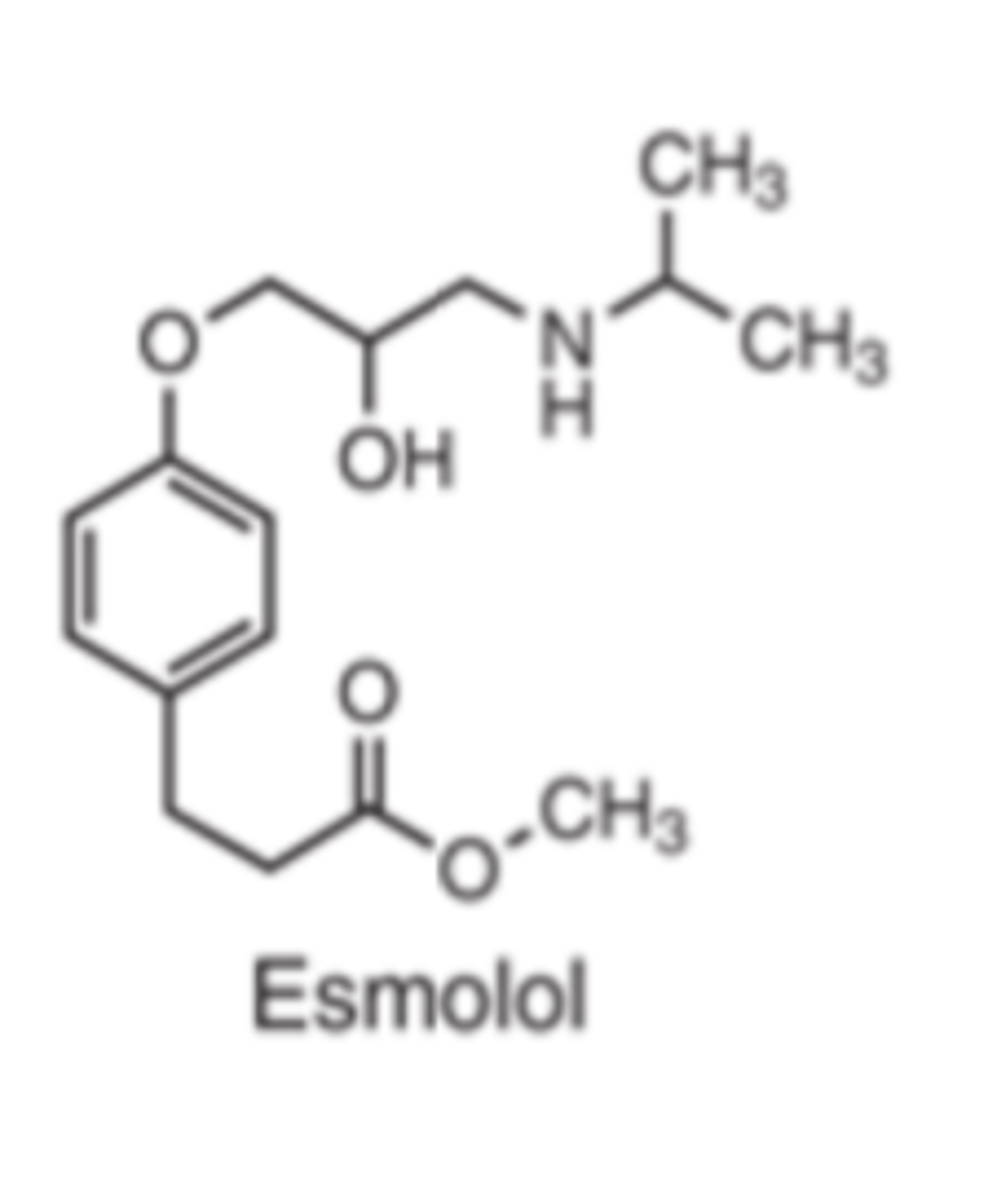
The 4-substitution of esmolol is a _________ _______ of a carboxylic acid
- methyl ester
Makes it susceptible to hydrolysis by serum esterase's.
The acid metabolite generated is essentially inactive thus, esmolol has a half-life of 8 minutes
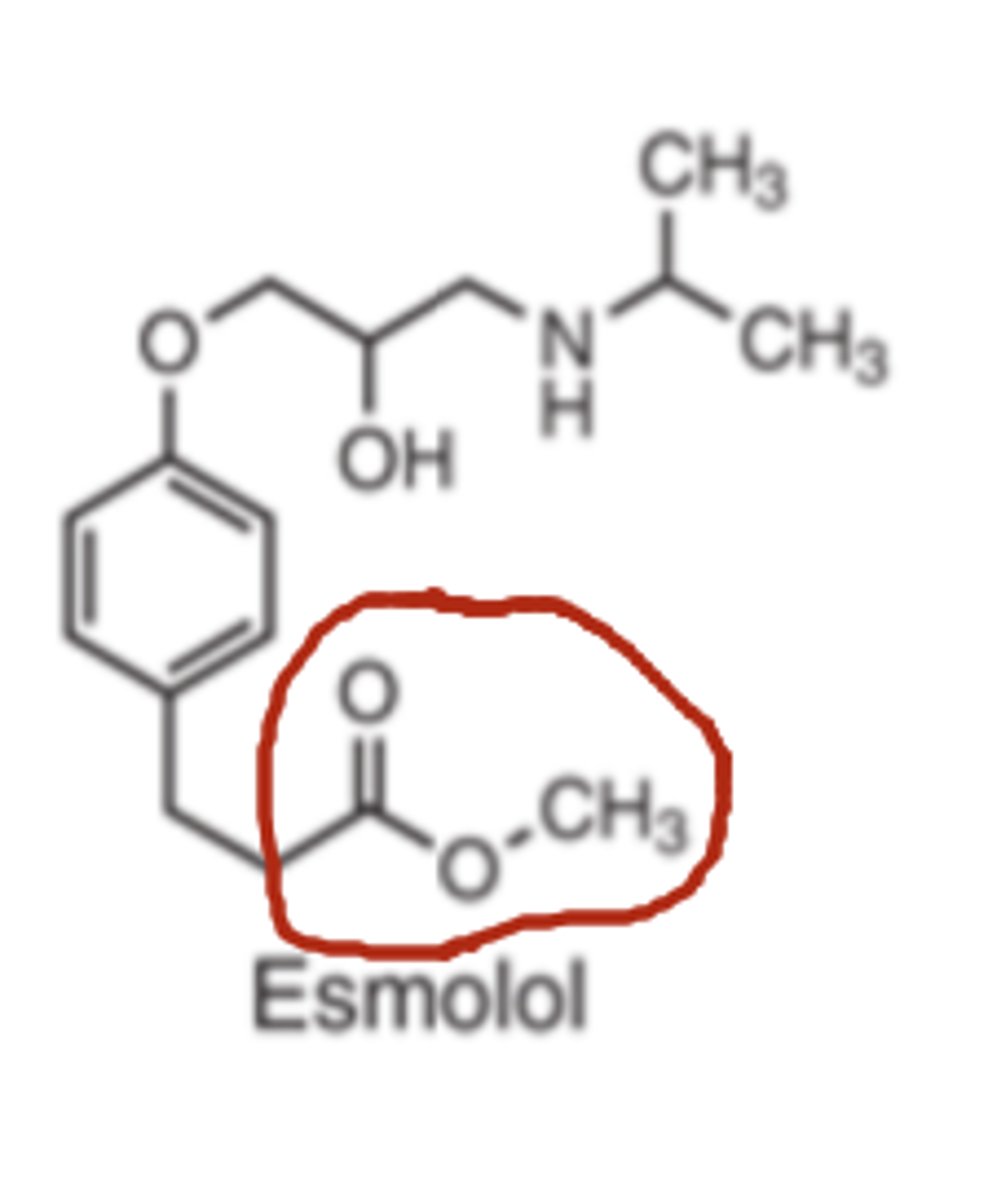
Esmolol half life
8 minutes
Used to control supra ventricular tachycardia during surgery (versus e.g., atenolol 6-9 hrs)
Selective α1-adrenergic antagonists are all...
4-amino-6,7-dimethoxyquinazoline
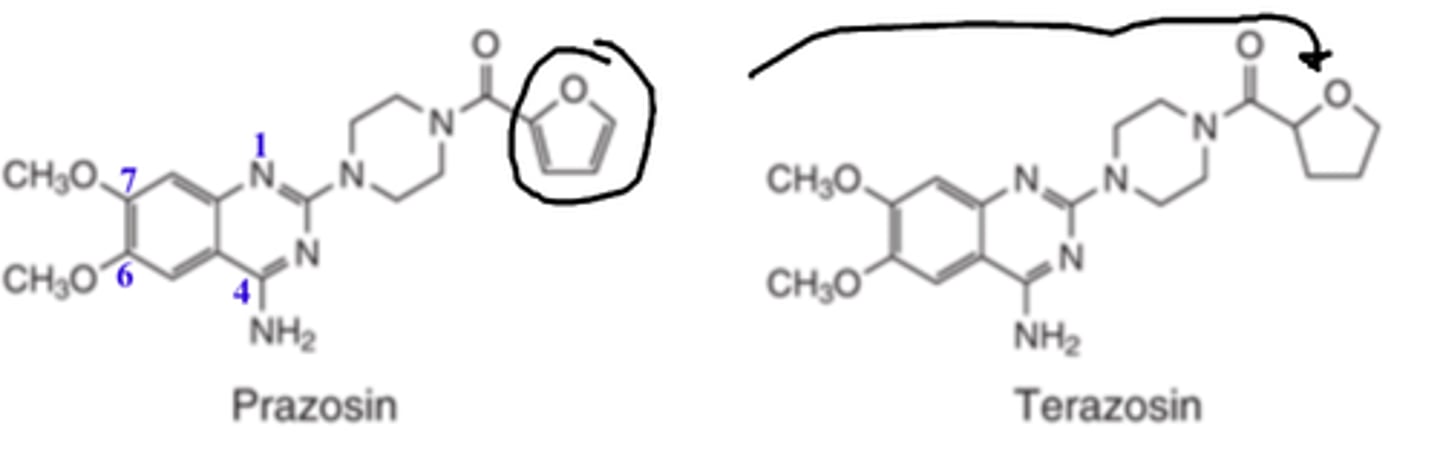
In α1-adrenergic antagonists such as prazosin, __________ of the __________ _____ to the tetrahydrofuran ring of terazosin _____________ its duration of action by altering its rate of metabolism
- reduction
- furan ring
- INCREASES
Long-half lives and durations of actions for terazosin, doxazosin, tamsulosin, and silodosin permit once-a-day dosing and lead to increased patient compliance
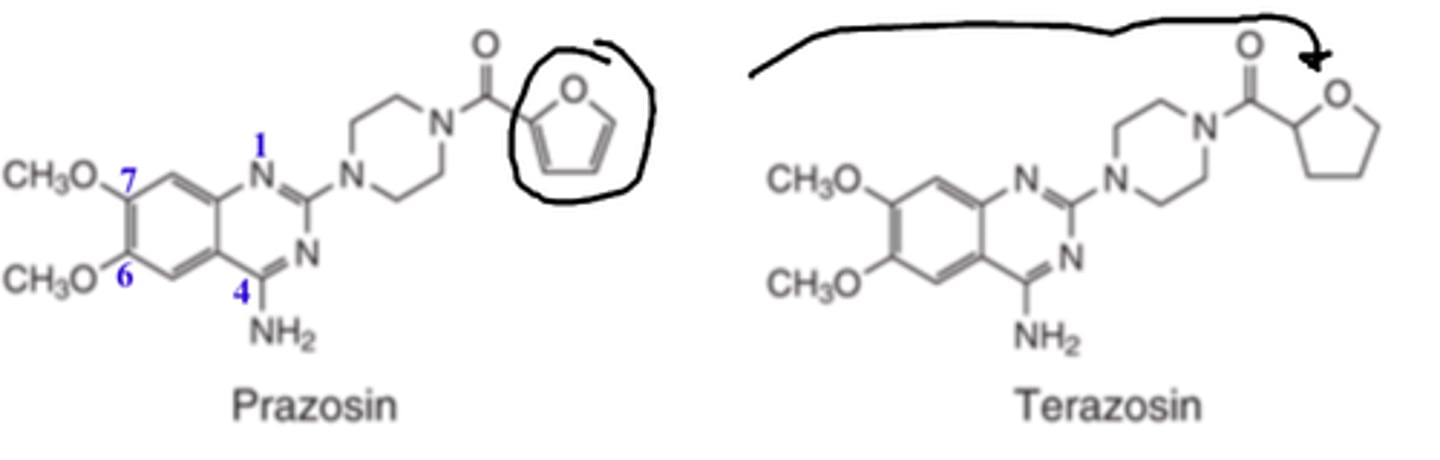
In α1-adrenergic antagonists such as prazosin, reduction of the furan ring to the ________ __________ of terazosin _____________ its duration of action by altering its rate of metabolism
- tetrahydrofuran ring
- increases
_________ is an equimolar mixture of 4 stereoisomers
- Labetalol

Labetalol is an equimolar mixture of...
4 stereoisomers (two active and two inactive isomers)
The β blocking activity of labetalol is approximately ___ that of its α1-blocking activity
- 4-5x
Carvedilol and labetalol are both...
combined α/β adrenergic antagonists

Carvedilol has an estimated β-blocking activity ____ to _____ fold its α1-blocking activity
- 10
- 100
Nifedipine is an example of a _________, calcium channel blocker
- dihydropyridine
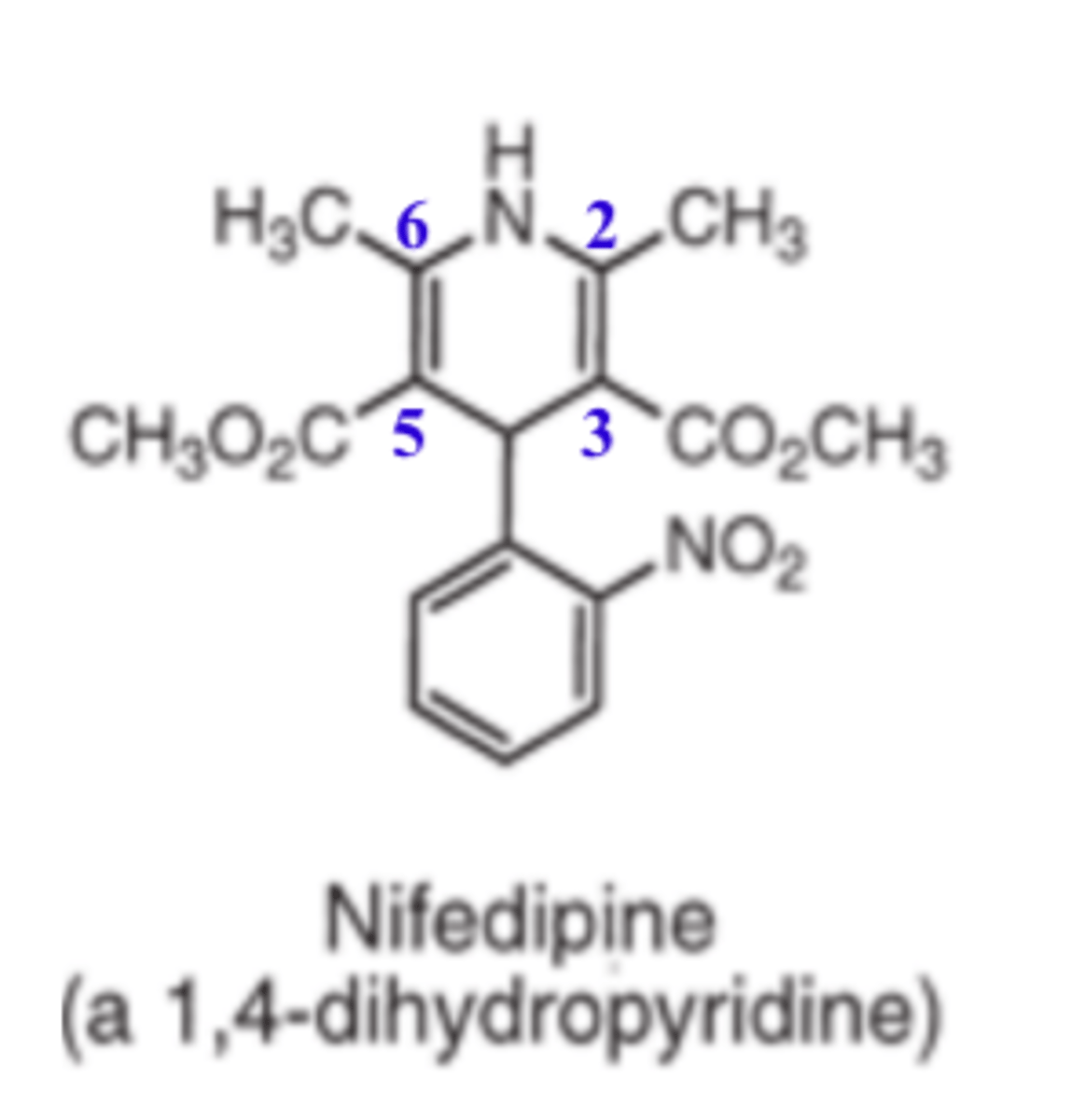
Verapamil is an example of a __________, calcium channel blocker
- phenylalkylamine
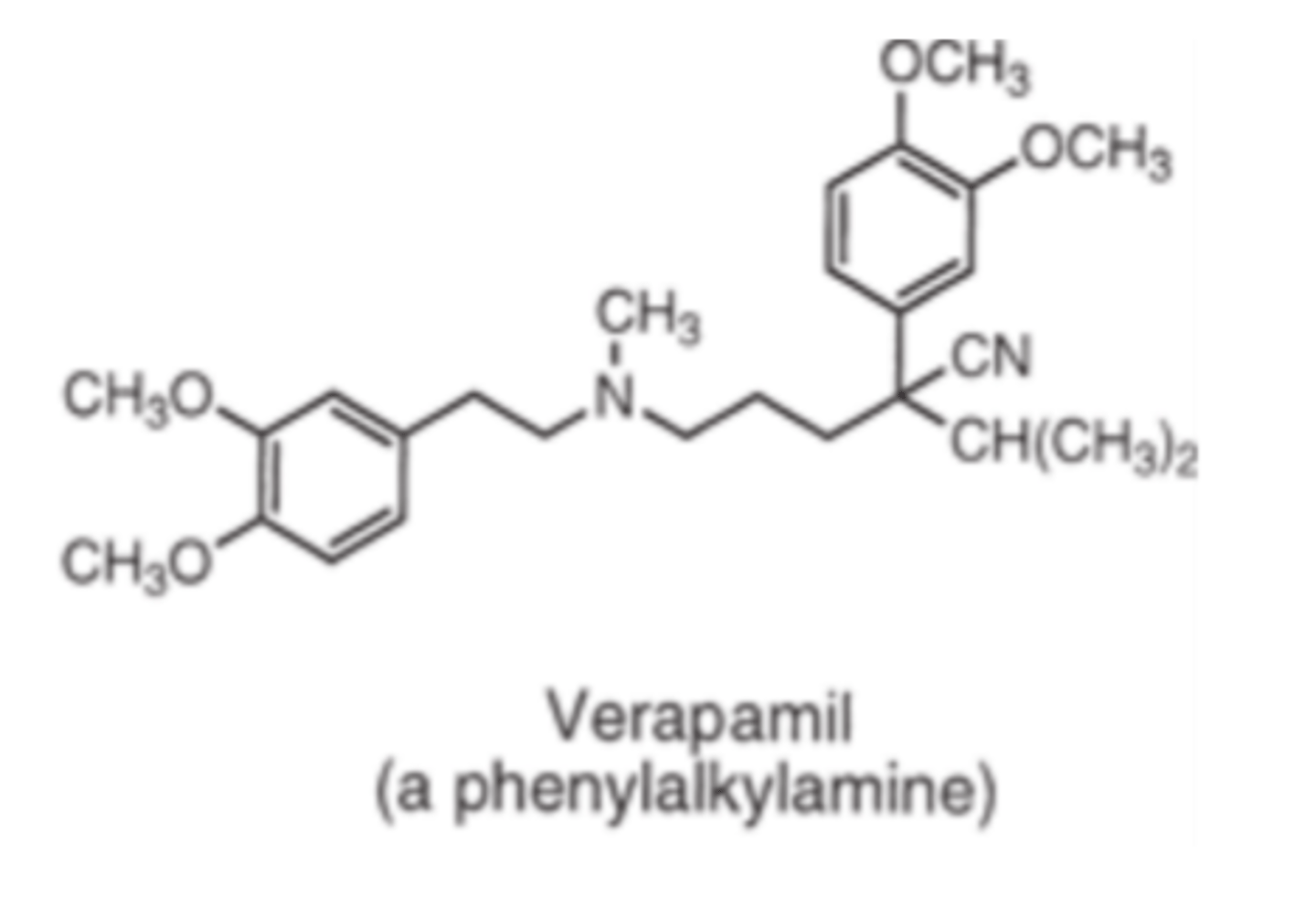
Diltiazem is an example of a _________, calcium channel blocker
- benzothiazepine
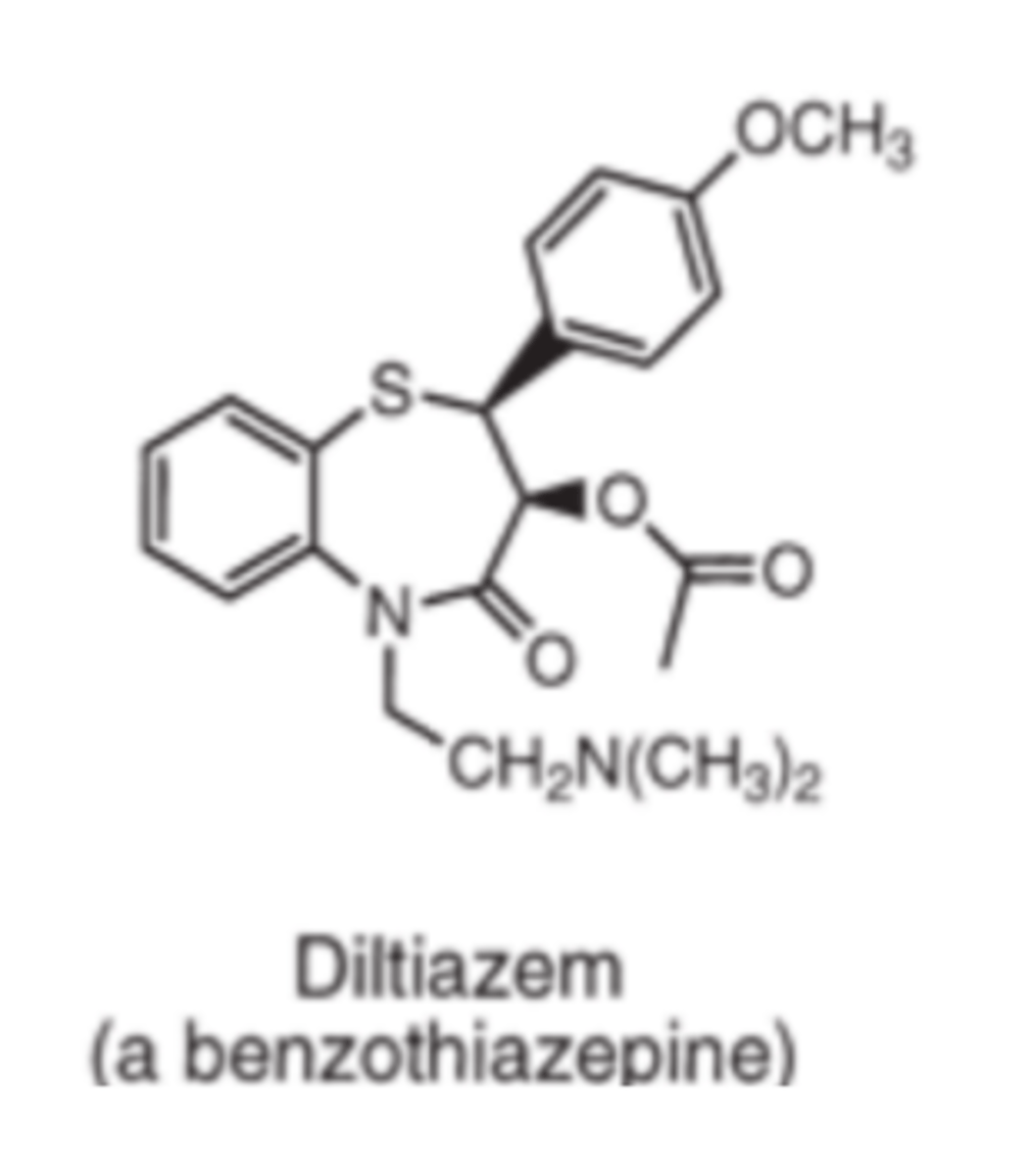
Verapamil and diltiazem both contain _________ _______ with pKa values of 8.9 and 7.7 respectively
- tertiary amines
In contrast the nitrogen of the 1,4-DHPs (dihydropyridines) is much less basic
At physiologic pH, verapamil and diltiazem are primarily ionized, whereas 1,4-DHPs are primarily un-ionized
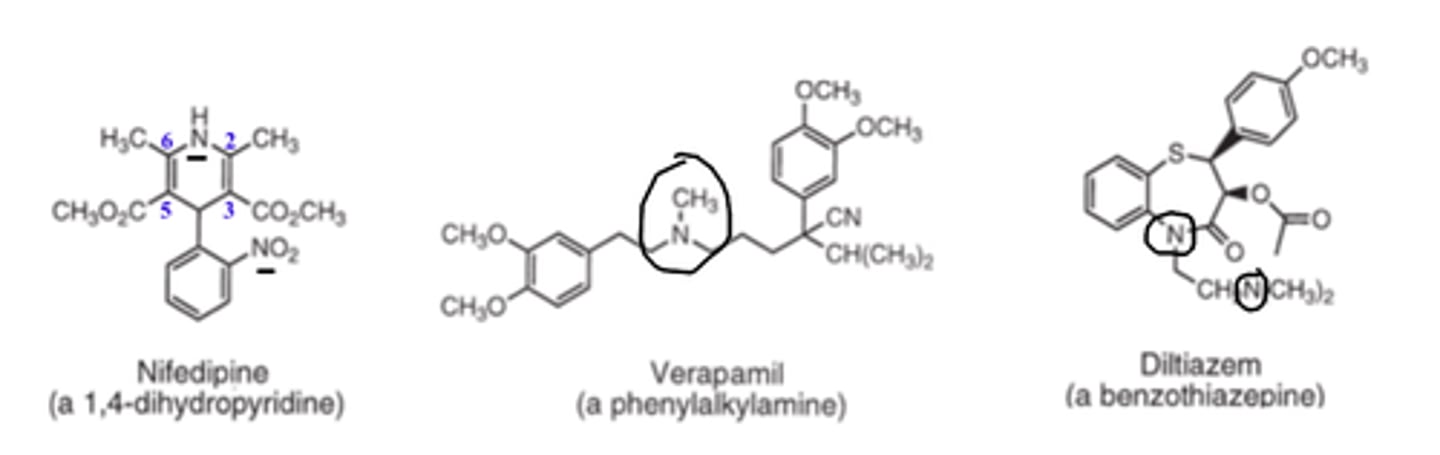
At physiologic pH, verapamil (Class II CCB) and diltiazem (Class III CCB) are primarily _________, whereas 1,4-DHPs (Class I CCB) are primarily ___-________
- ionized
- un-ionized
Because 1,4-DHPs' nitrogens are less basic (due to resonance delocalization)
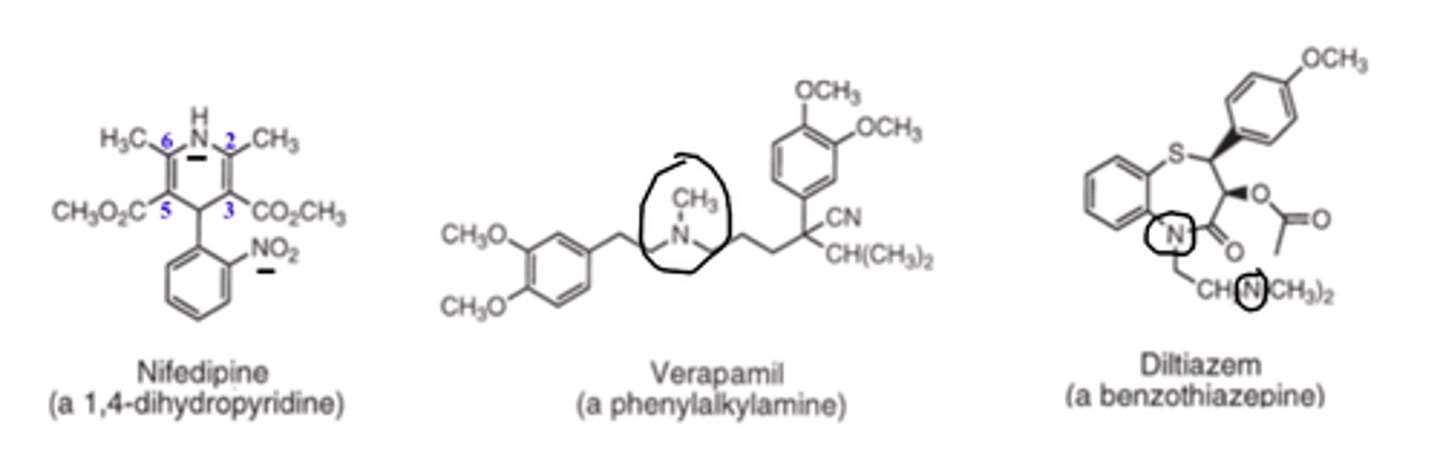
All CCBs possess good _____ ___________ and, hence excellent oral absorption
- lipid solubility
All CCBs possess good lipid solubility and hence...
excellent oral absorption
All CCBs, with the exception of ________ contain at least one chiral center; however, they are all marketed as ______ ________. Some enantiomers are more _____ than others
- nifedipine
- racemic mixtures
- potent
For 1,4-DHP, substitution at the N1 position or the use of ________ or _______ ring systems greatly decreases or abolishes activity
- oxidized (pyridine)
- reduced (piperidine)
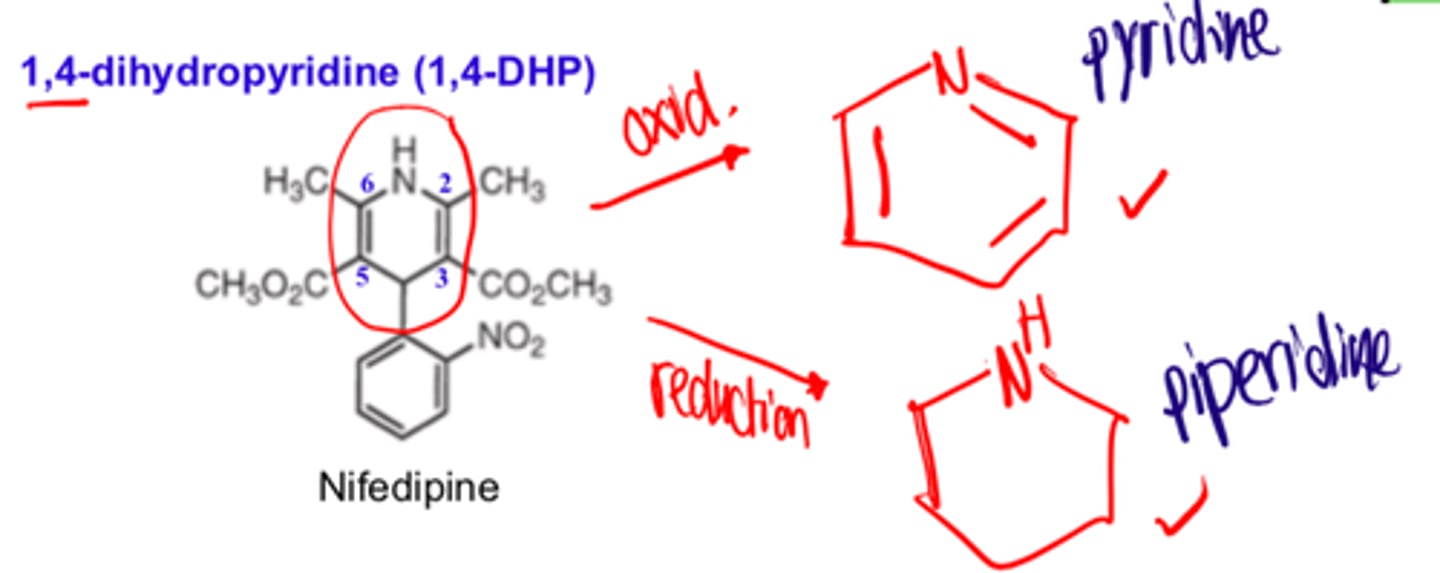
For 1,4-DHP, with the exception of ___________, all 1,4-DHP have C2 and C6 methyl groups
- amlodipine
For 1,4-DHP, with the exception of amlodipine, all 1,4-DHP have ___ and ___ methyl groups
- C2
- C6
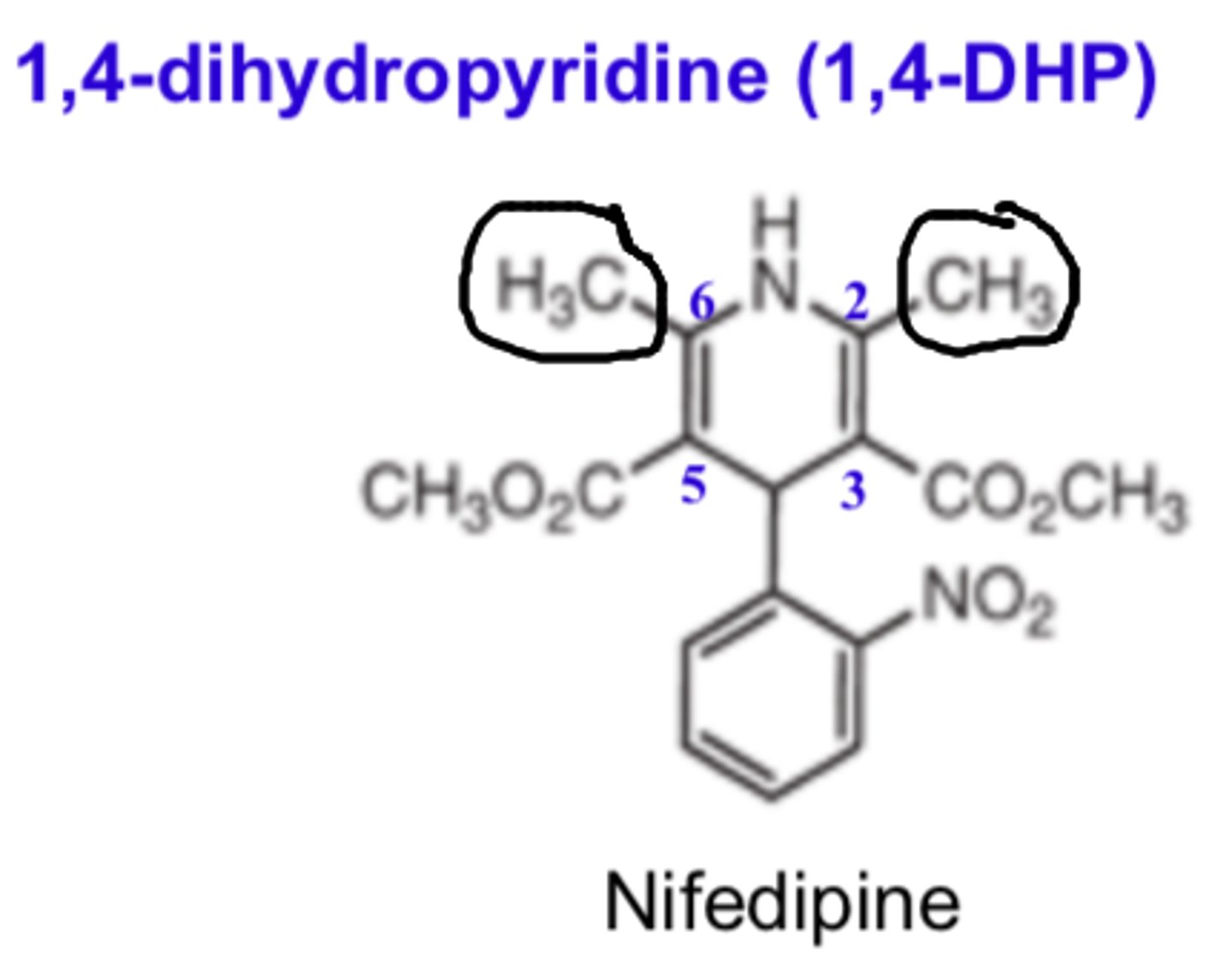
In 1,4-DHP, ______ groups at the C3 and C5 positions optimize activity
- ester
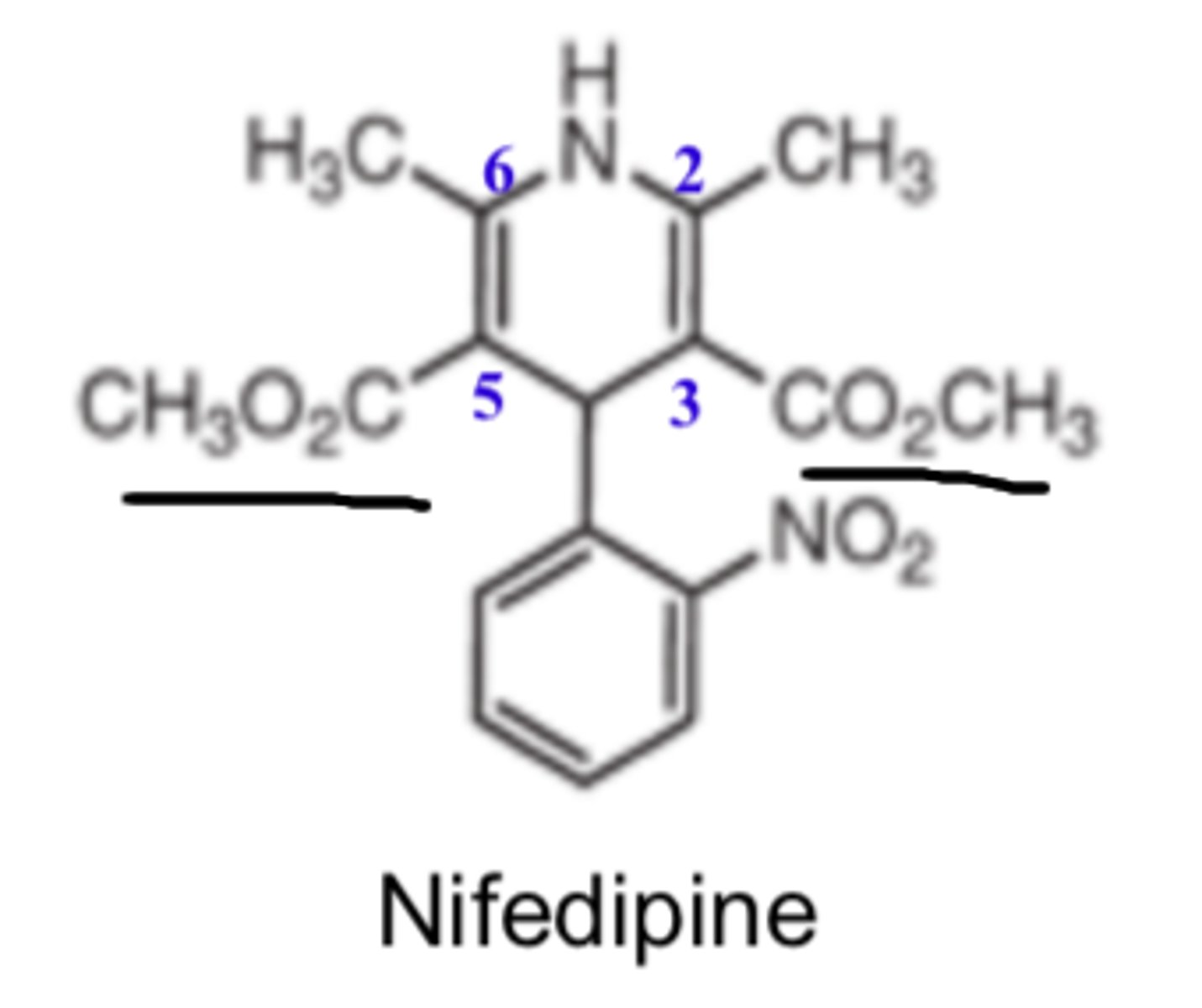
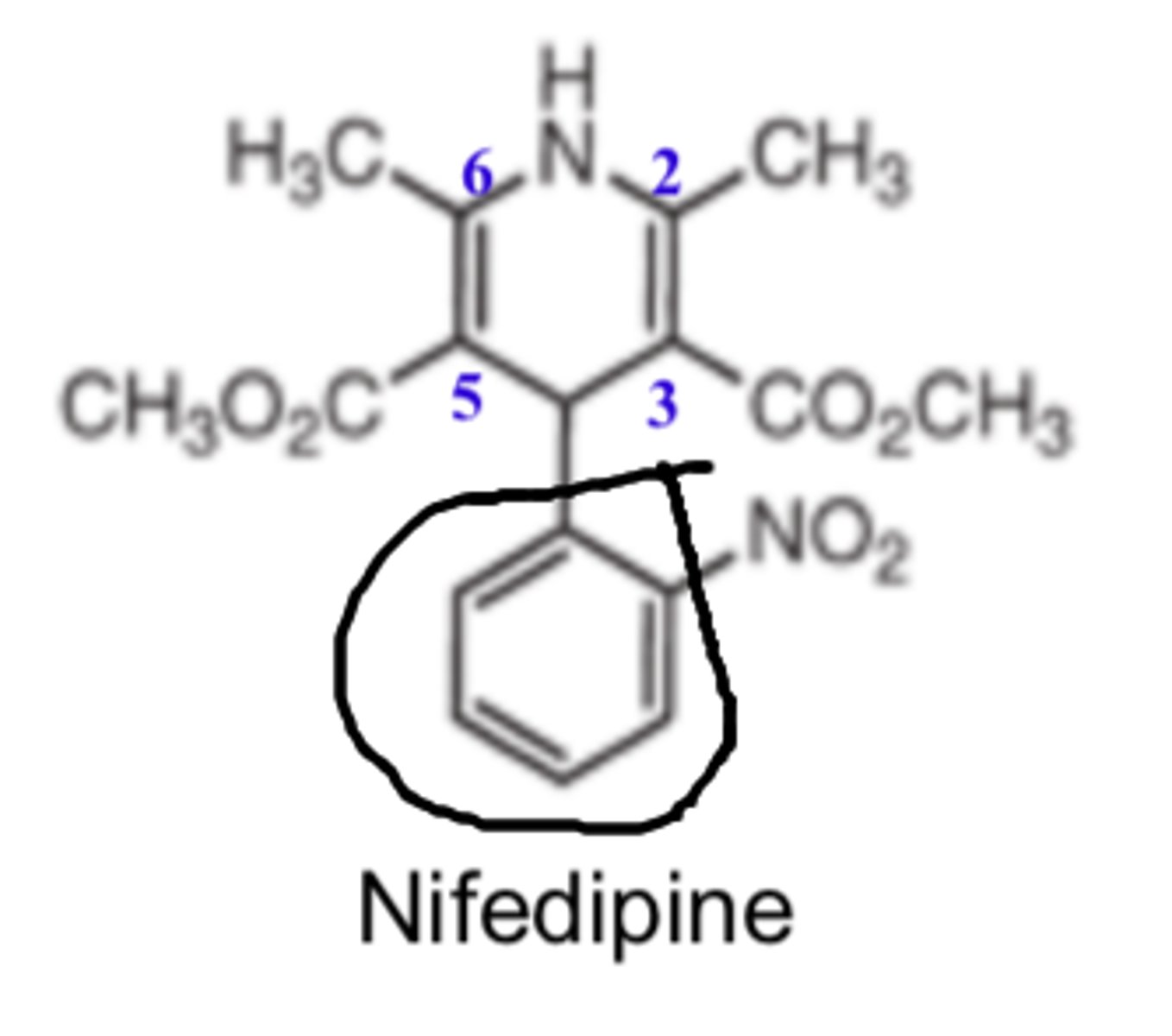
In 1,4-DHP, a substituted phenyl at the ____ position optimizes activity
- C4
Whereas, C4 substation with a nonplanar alkyl or cycloalkyl decreases activity
Ortho or meta substitution of phenyl rings give optimal activity
All CCBs undergo extensive...
first-pass metabolism in the liver (except clevidipine)
All CCBs are substrates for ____________
- CYP3A4
Several CCBs can inhibit CYP3A4
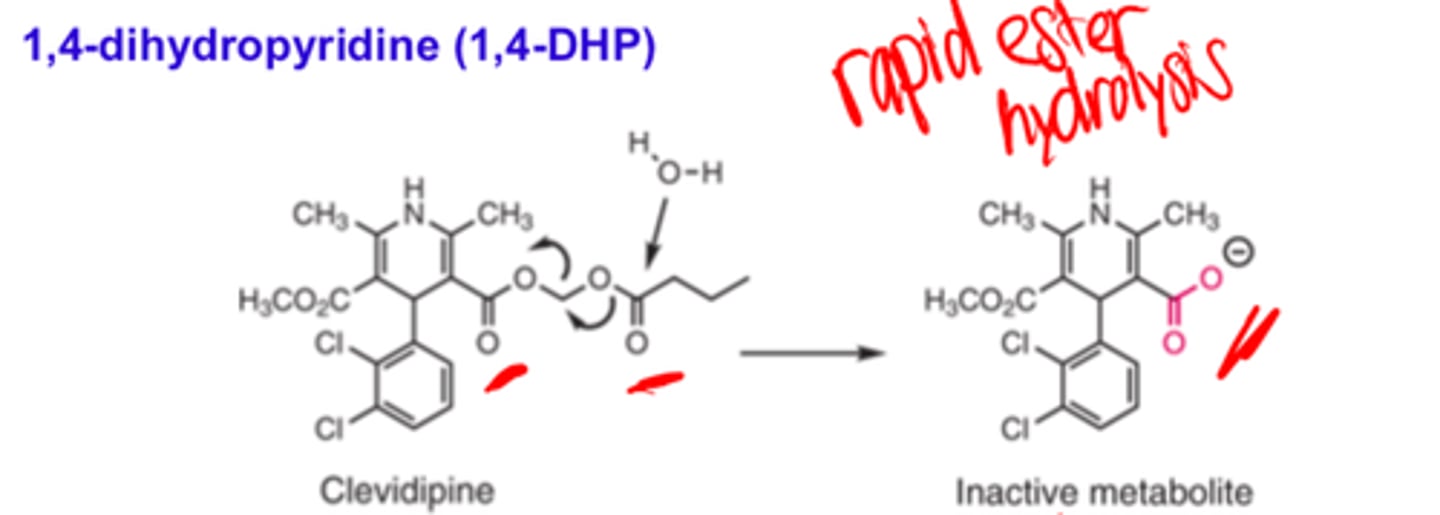
Clevidipine was designed to have an ________ _____ duration of action
- ultra short
Upon IV infusion, clevidipine enters its antihypertensive actions within 2 to 4 minutes. Rapid ester hydrolysis (two esters) inactivates the compound and allows it to be used in patients with either renal or hepatic dysfunction without any dose adjustments.
Upon IV infusion, clevidipine enters its antihypertensive actions within 2 to 4 minutes. ______ ________ __________ inactivates the compound and allows it to be used in patients with either renal or hepatic dysfunction without any dose adjustments.
- rapid ester hydrolysis (of two esters)
All other 1,4-DHPs with the exception of clevidipine are _________ metabolized to a variety of inactive compounds
- oxidatively
In many cases, the dihydropyridine ring is initially oxidized to an inactive pyridine analog.
In may cases of 1,4-DHPs (exception of clevidipine), the dihydropyridine ring is initially oxidized to an...
inactive pyridine analog
In addition the DDI, an interesting drug-food interaction occurs with 1,4-DHPs. Co-administration of 1,4-DHPs with ________ _________ produces an increase systemic concentration of the 1,4-DHPs
- grapefruit juice
Grapefruit juice is an inhibitor of CYP3A4 and thus CCBs like 1,4-DHPs will have increased levels
Verapamil is metabolized by ___________ N-demethylation to its principal metabolite _______________
- CYP3A4
- norverapamil (20% of activity of verapamil)
Thus, increasing its duration of action.
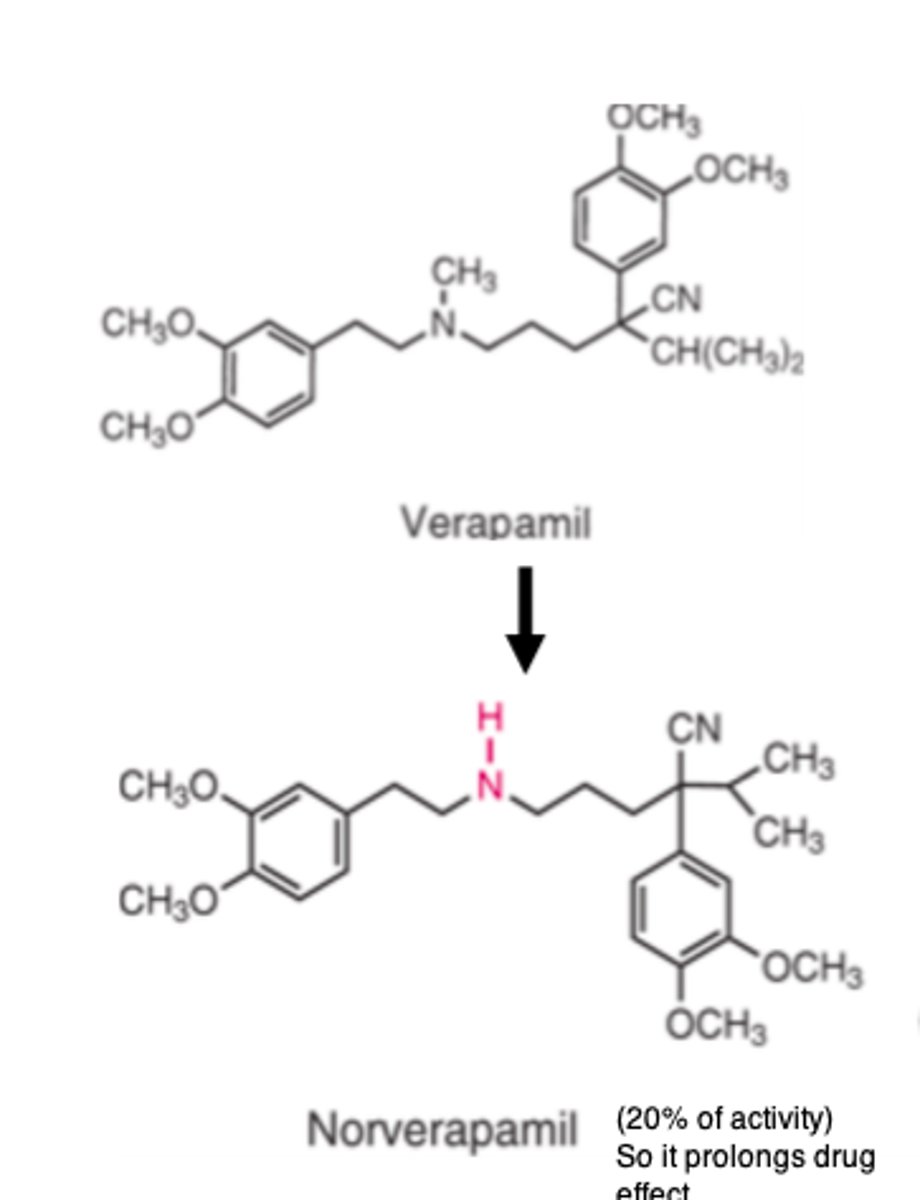
Verapamil also has inactive metabolites that are metabolized by...
O-demethylation (CYP2D6)
Verapamil also has _________ metabolites that are metabolized by O-demethylation (CYP2D6)
- inactive
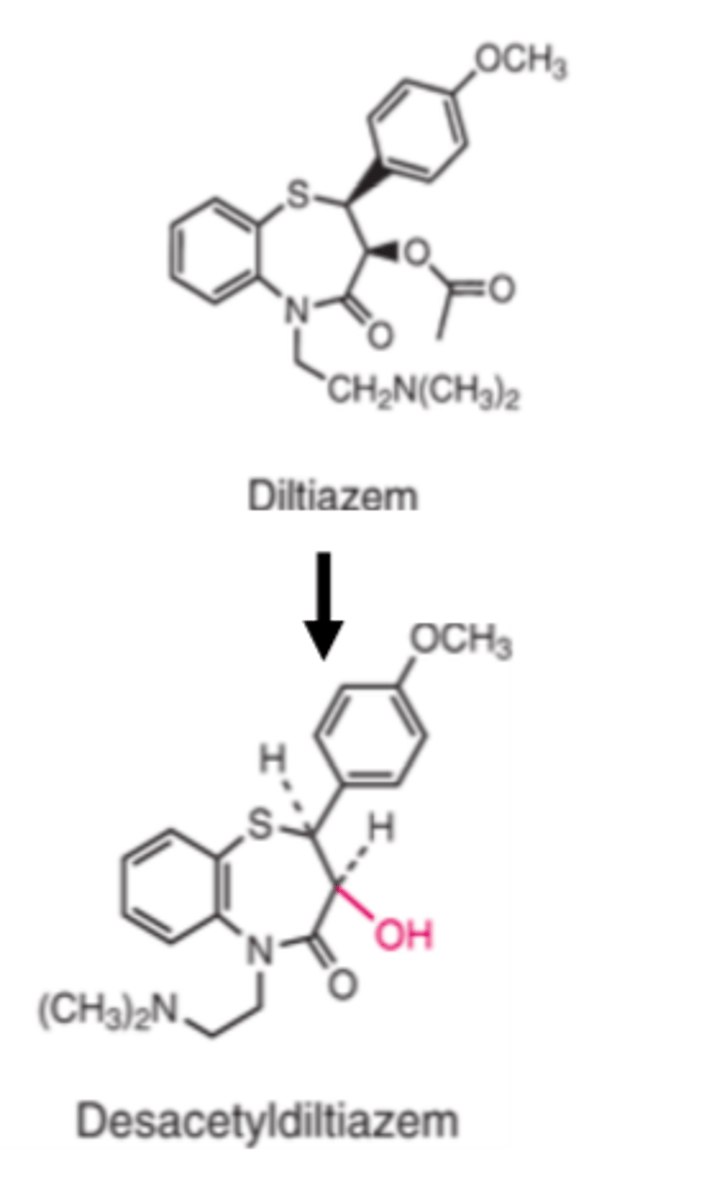
Diltiazem is metabolized by enzyme hydrolysis to its primary metabolite, desacetyl derivative, which retains approximately _____ to _____ of the activity of diltiazem
- 25%
- 50%
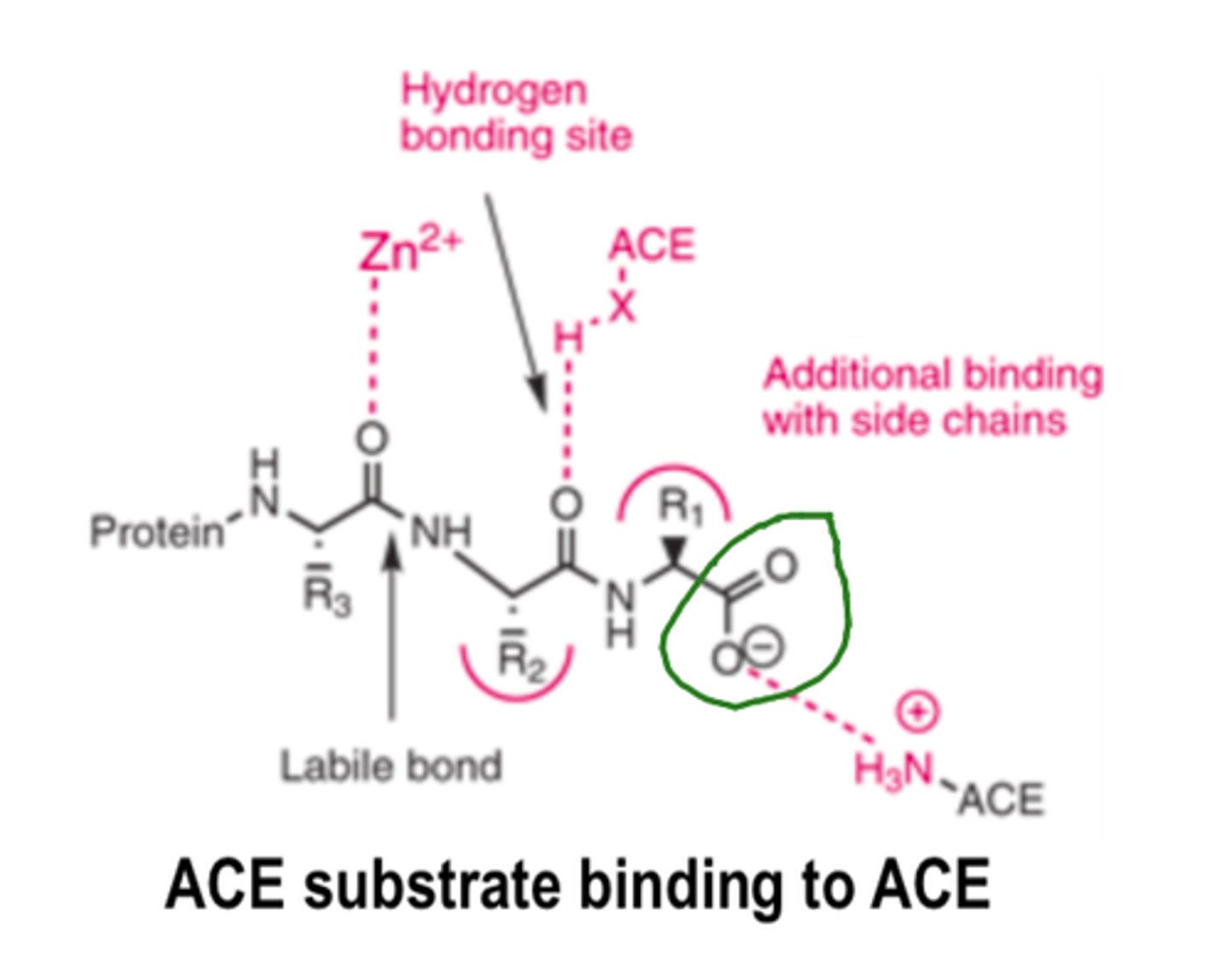
ACE is a ____________ drug target
- stereoselective
ACE needs L-stereochemistry
ACE needs __-_________
- L-stereochemistry
Currently ACE inhibitors act as either di- or tripeptide substrate analogs, they must contain a stereochemistry that is constant with the L-amino acids present in the natural substrates
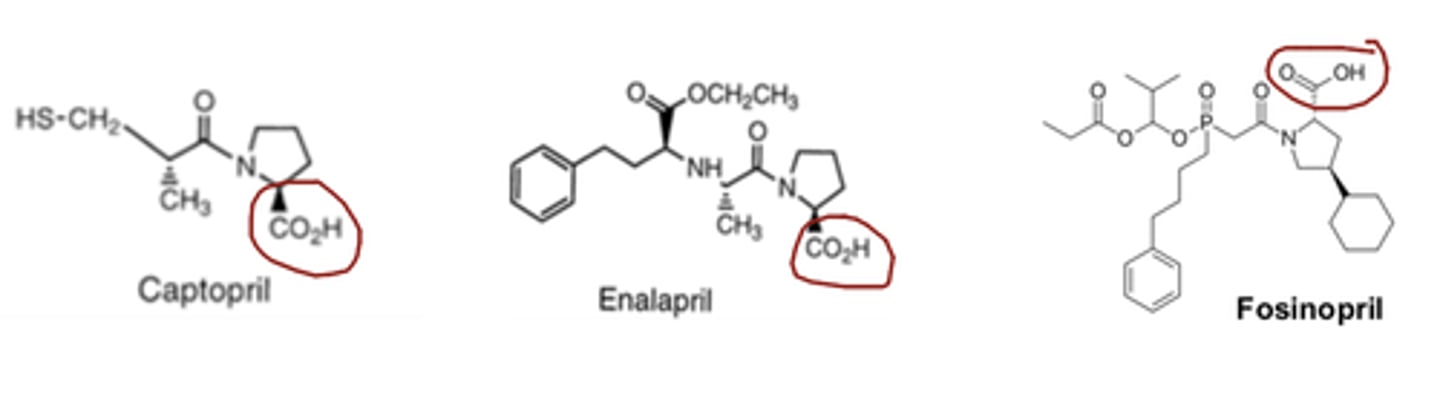
________ and ______ of the ACE inhibitors are acidic drugs but all other ACE inhibitors are ____________
- captopril
- fosinopril
- amphoteric
For ACE inhibitors, several ______ ________ have been approved
- dicarboxylate inhibitors
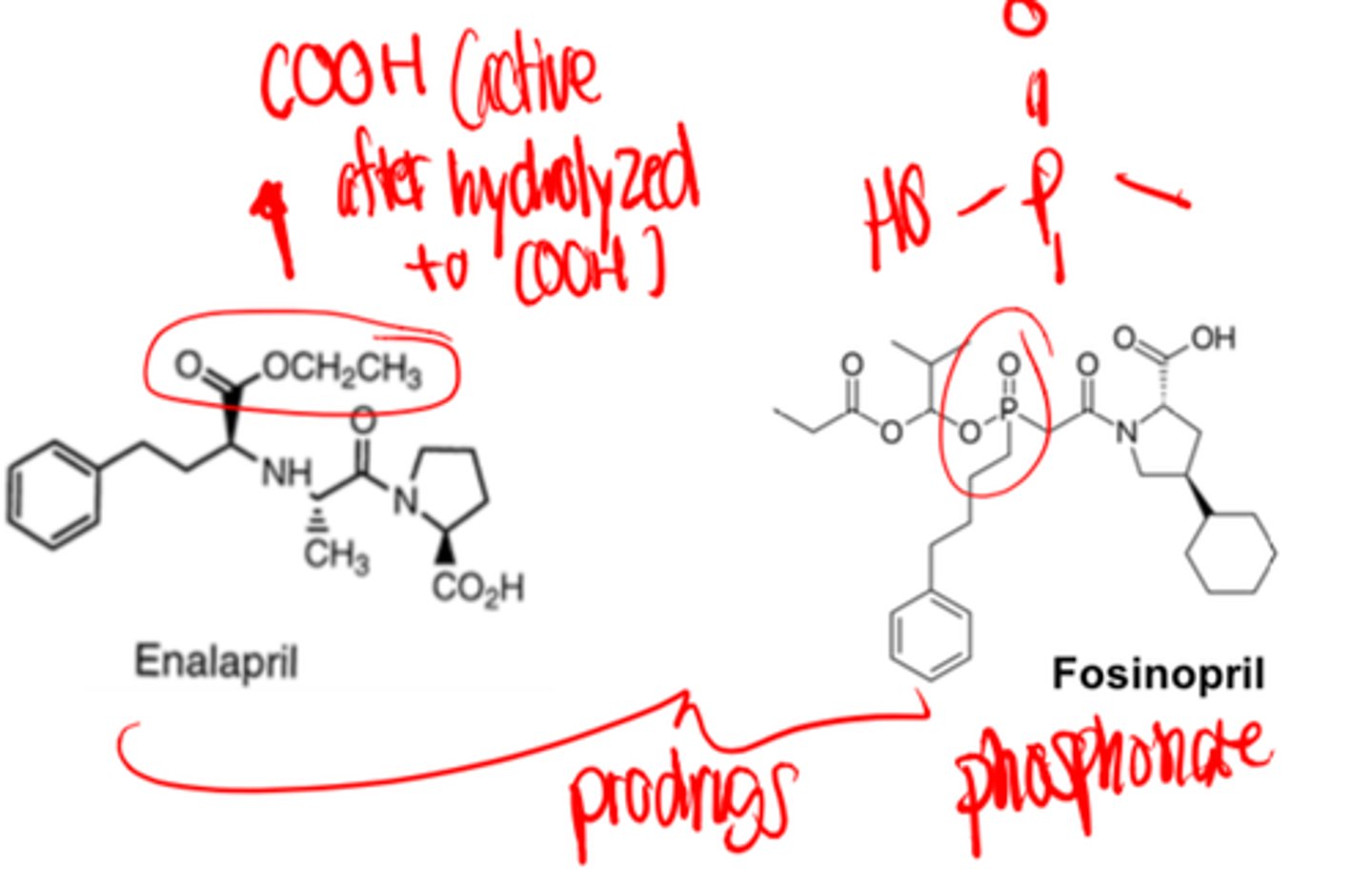
_______ and ______ are the only two ACE inhibitors that are NOT prodrugs
- lisinopril
- captopril
Lisinopril and captopril are the only two ACE inhibitors that are...
NOT prodrugs
All ACE inhibitors have a similar onset of action, duration of action, and dosing interval with the exception of...
Captopril.
Captopril has more rapid onset of action, however it has shorter duration and requires more frequent dosing. Captopril (along with lisinopril) is also NOT a prodrug.
For ACE inhibitors, the N-ring must contain a _________ ______ to mimic the C-terminal carboxylate of ACE substrates
- carboxylic acid
For ACE inhibitors, the N-ring must contain a carboxylic acid to mimic the...
C-terminal carboxylate of ACE substrates
For ACE inhibitors, large hydrophobic ___________ rings increase potency and alter pharmacokinetic parameters
- heterocyclic (i.e., the N-ring)
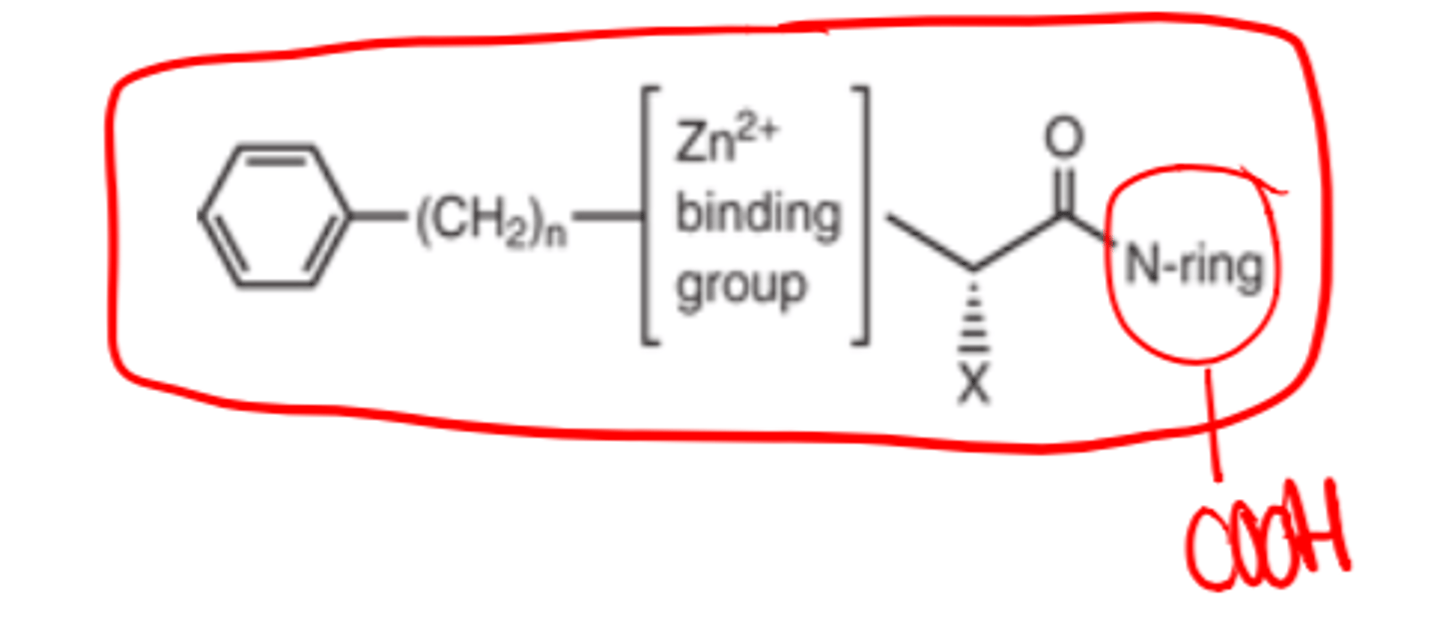
The Zinc Binding Groups for ACE inhibitors can be either...
1) sulfhydryl
2) carboxylic acid
3) phosphinic acid (phosphonate)
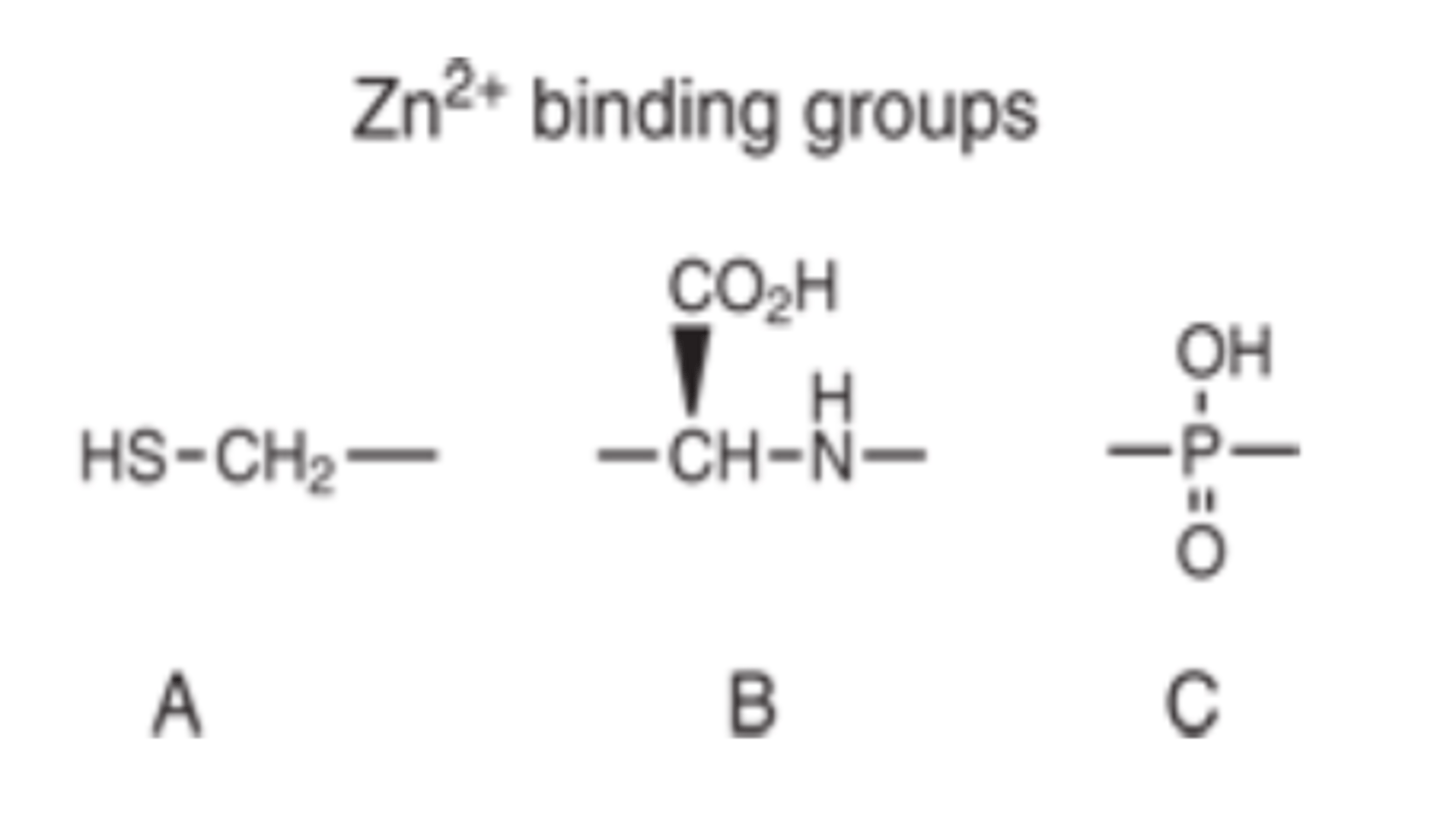
In ACE inhibitors, the ________ of the carboxylate or phosphinate produces an orally bioavailable prodrug
- esterifiation
Optimum activity for ACE inhibitors when stereochemistry of inhibitor is consistent with ___-______ ____ __________ present in normal substraces
- L-amino acid stereochemistry
All ARBs have similar...
onsets, are highly protein bound and have elimination half-lives that allow once a day or twice-daily dosing
With the exception of irbesartan, telmisartan all of the ARBs have ____, but _________ oral bioavailability
- low (15% to 33%)
- adequate
Irbesartan (60% to 80%)
Telmisartan (42% to 58%)
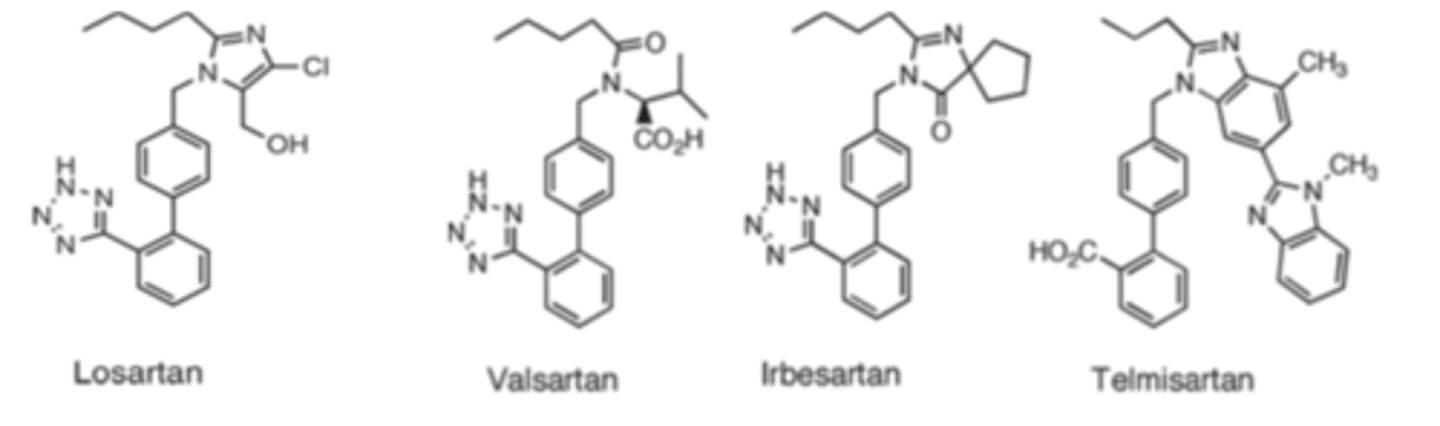
Most probable reason for low bioavailability for ARBs are...
poor lipid solubility and incomplete absorption
Most of these compounds are excreted unchanged
For ARBs, the "acidic" group is thought to mimic either the...
Tyr4 phenol or Asp1 carboxylate of Angiotensin II
Groups capable are carboxylic acid, phenyl tetrazole or isostere or a phenyl carboxylate
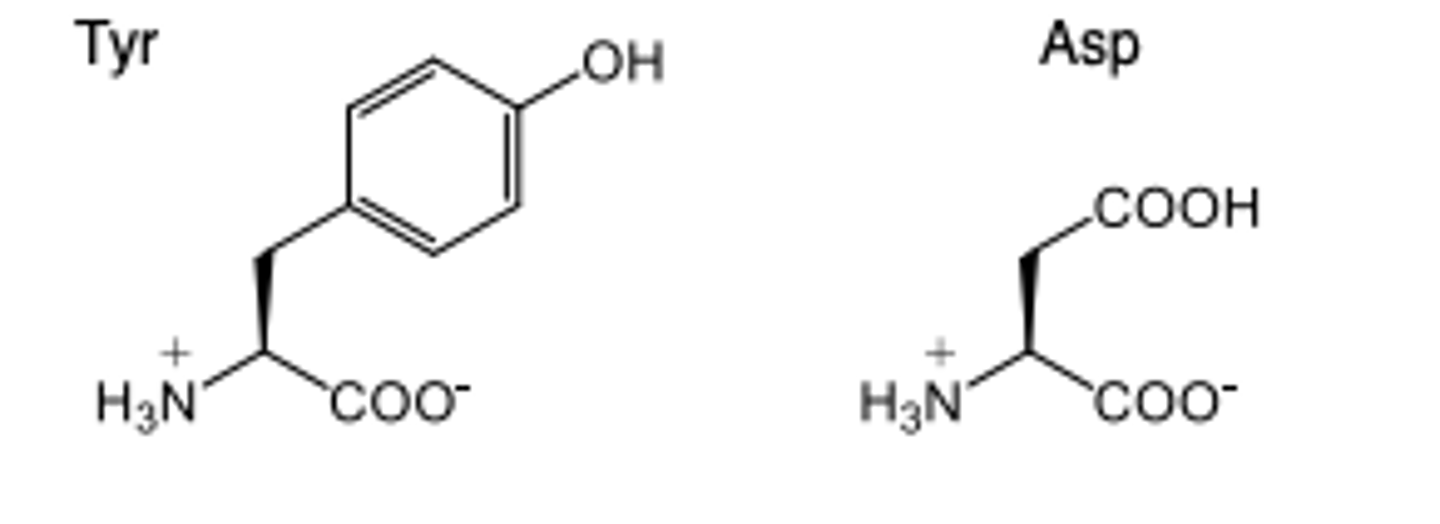
Groups that can mimic the acidic group of angiotensin II
- carboxylic acids
- phenyl tetrazole or isostere
- phenyl carboxylate
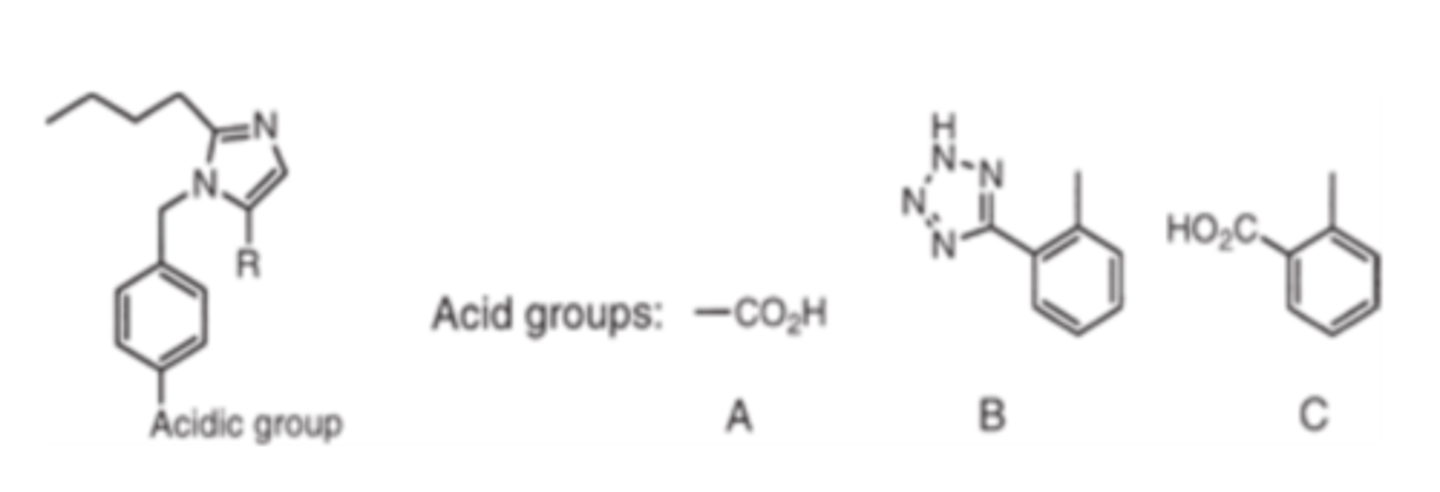
In the biphenyl series of ARBs, the tetrazole and carboxylate groups must be in the _______ position for optimal activity
- ortho
(Tetrazole is superior in terms of metabolic stability, lipophilicity and oral bioavailability)
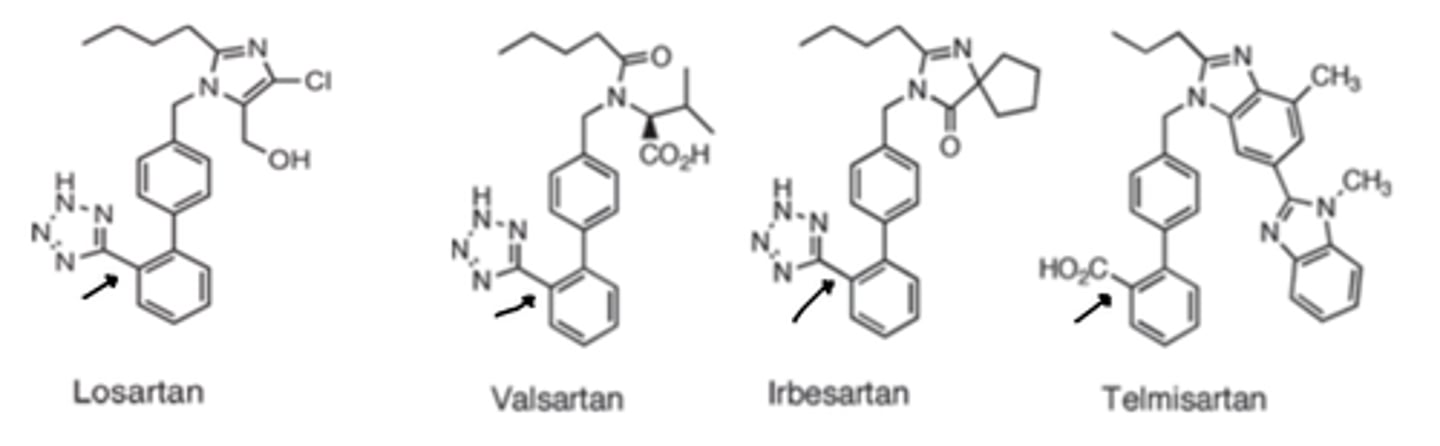
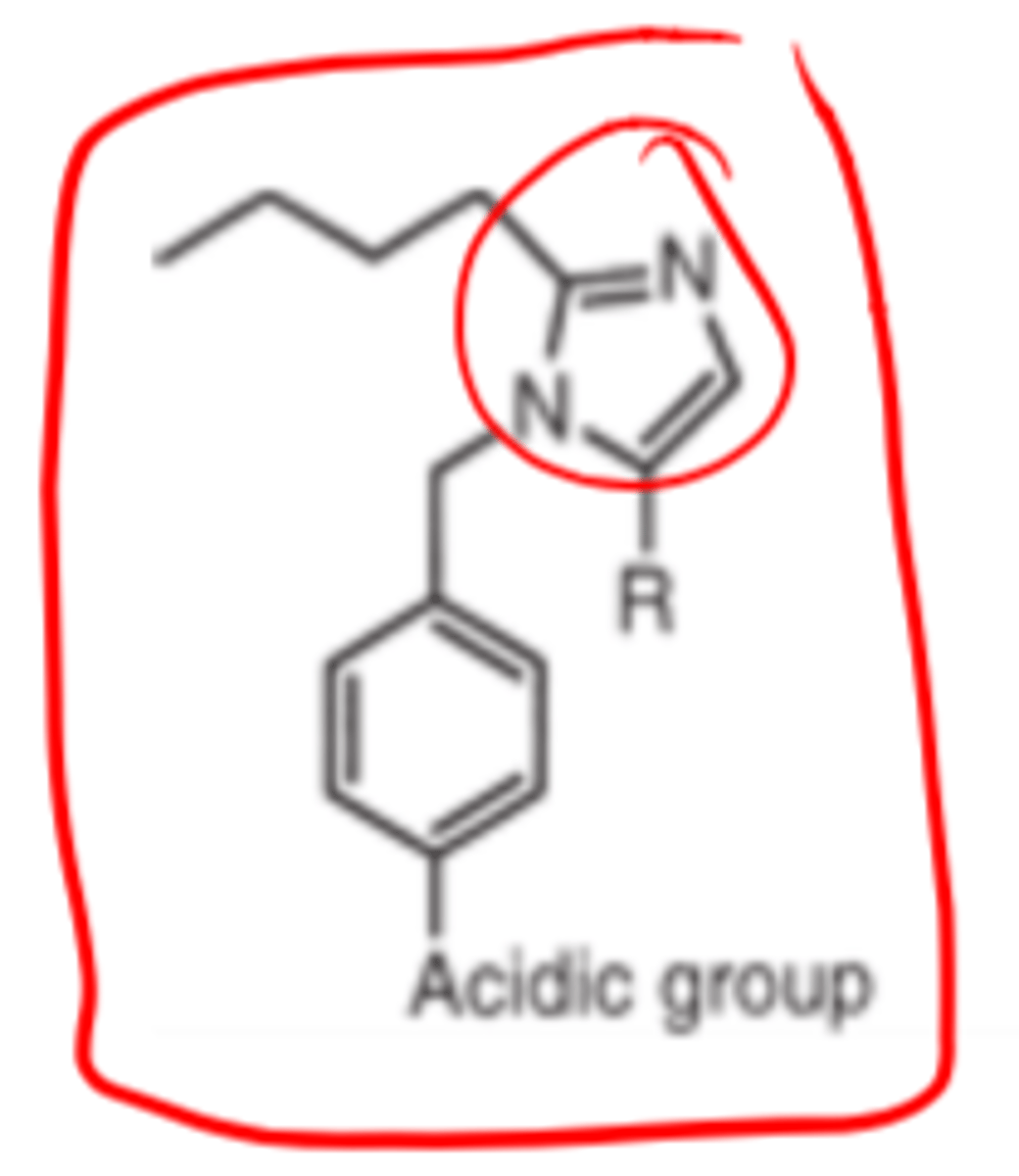
In ARBs, the __________ group provides hydrophobic binding and most likely mimics the side chain of Ile5 of angiotensin II
- n-butyl (or an ethyl ester or an n-propyl group)
The _________ ring or an ______ equivalent is required to mimic the His6 side chain of angiotensin II
- imidazole
- isometric
Most of the ACE inhibitors are _______
- prodrugs
Only exceptions are captopril and lisinopril