L11 Ylides and anions in selective C=C bond forming reactions
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
Second row elements that can stabilise a carboanion to a similar degree as a ketone.
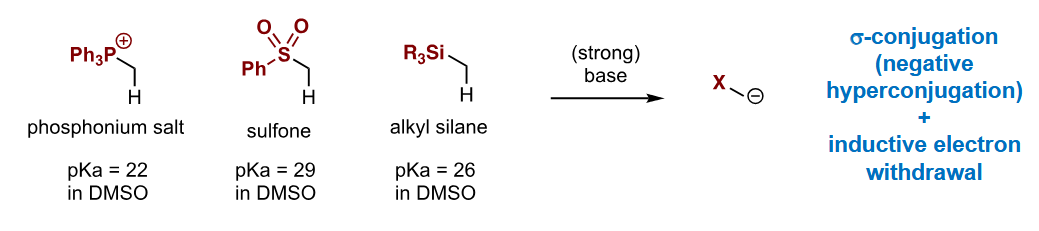
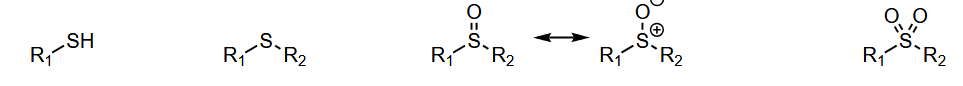
Name of these sulfur groups
How much does each of them affect the pKa
Oxidation can be done using mCPBA
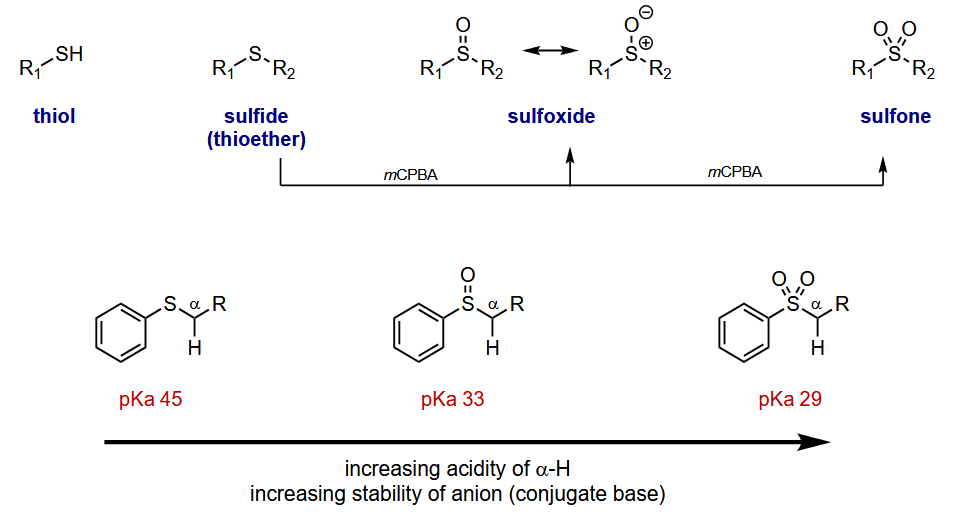
How does sulfur stabilise the anion
Sigma conjugation - not a resonance stabilisation like ketones an pi bonds are not involved

Using sulfones as anion nucleophiles
Deprotonation with BuLi or LDA gives a carbon nucleophile.
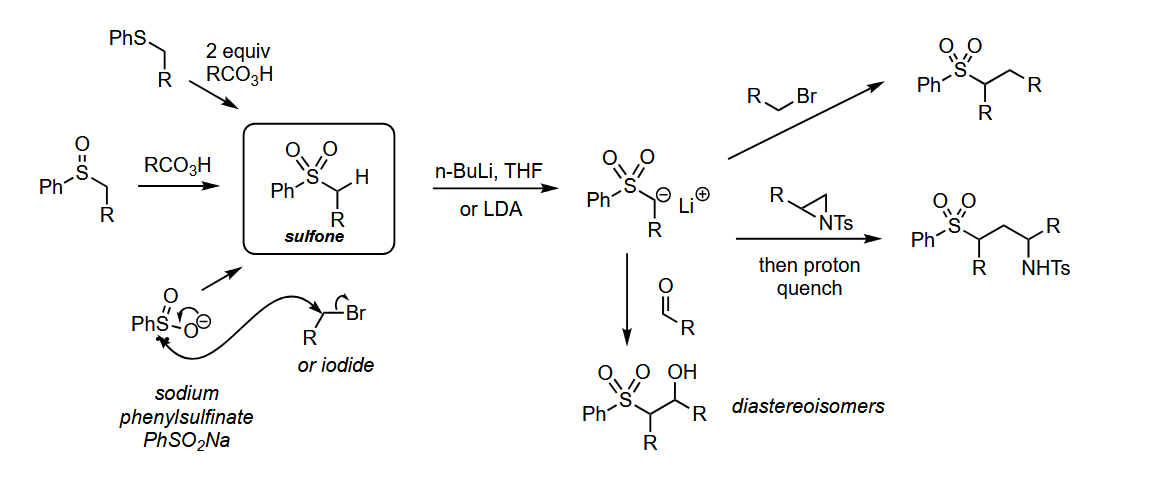
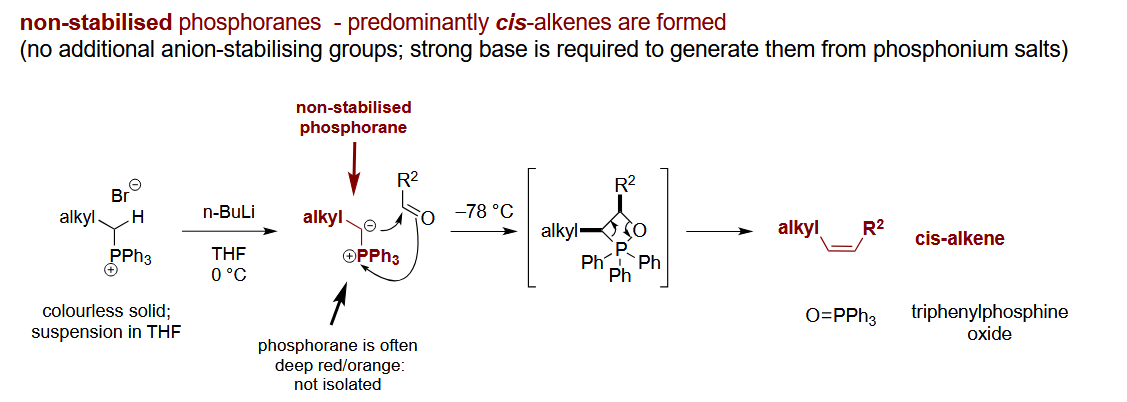
Which alkene geometry do unstabilised phosphonium ylides form
Z-alkene
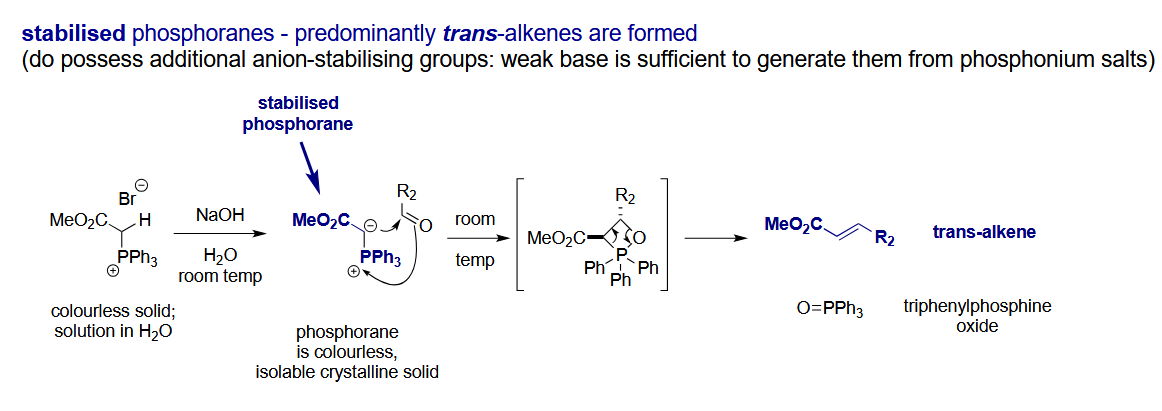
What about stabilised ylides
E-alkene - note how the geometry is determined by the transition state in which the R2 attaches on the opposite face in this case and the same face with an unstabilised ylide.
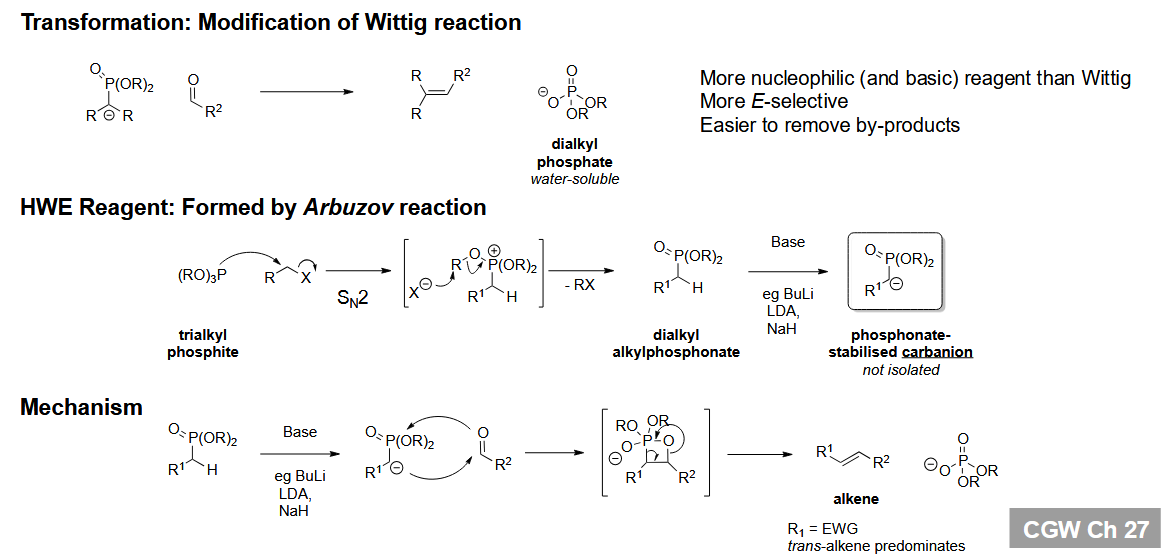
Horner-Wadsworth-Emmons reaction - an alternative to the Wittig reaction
This reaction is more E-selective with stabilised anions.
Julia Olefination
Forms a trans alkene regardless of stabilisation and diastereomer formed
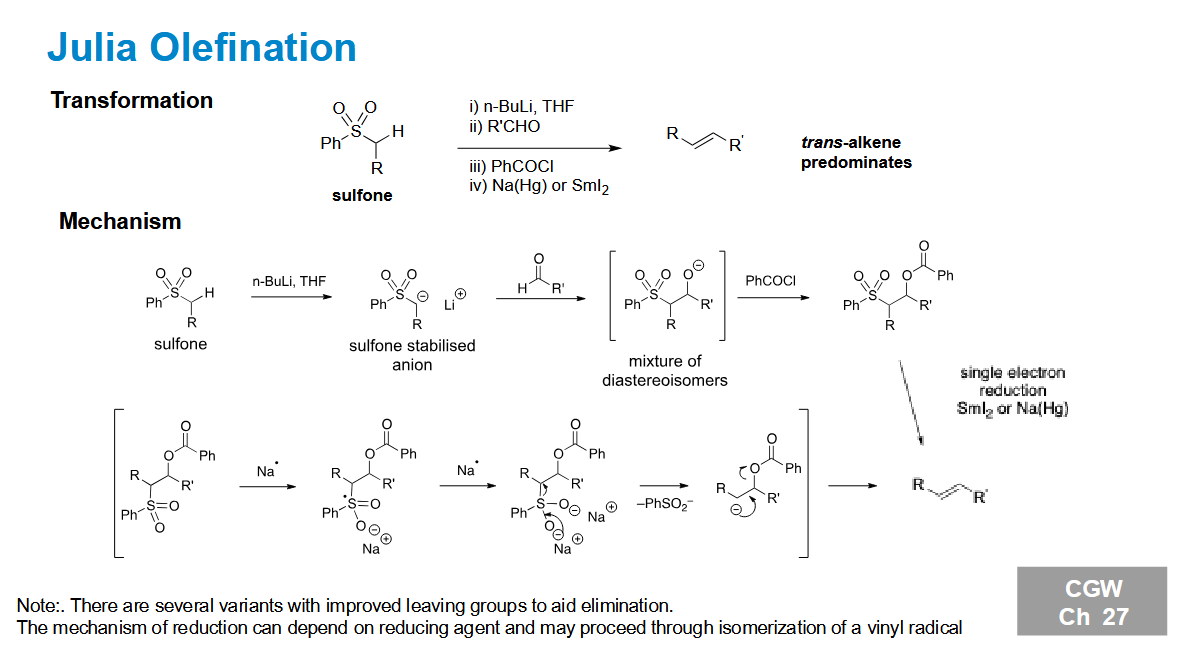
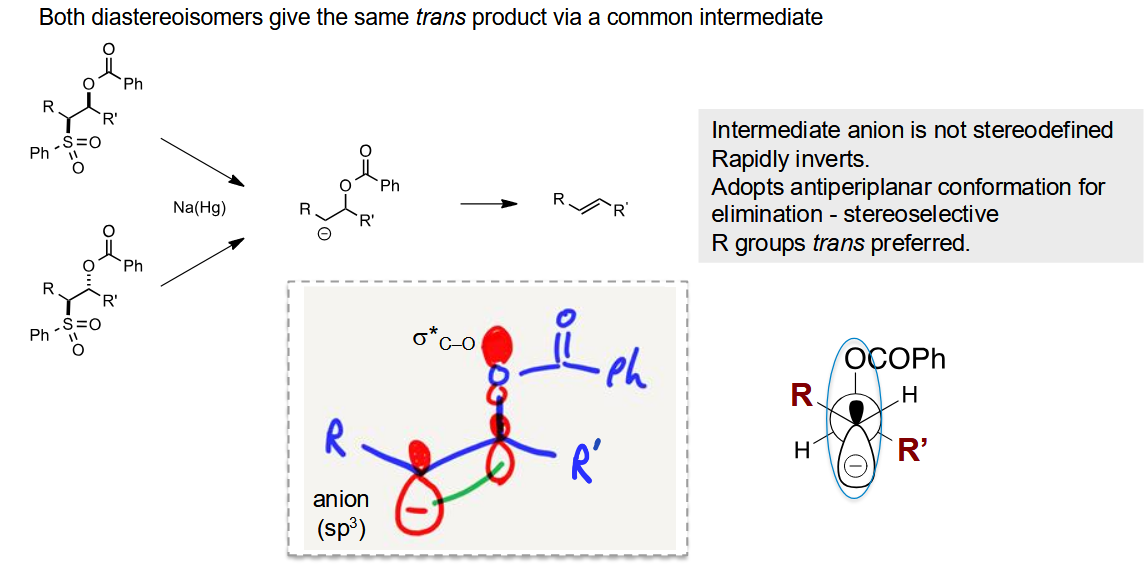
Why is the trans product favoured
The elimination needs an antiperiplanar position. With this conformation, the R groups rotate to be opposite to each other to minimise steric clash
Peterson Olefination - addition stage
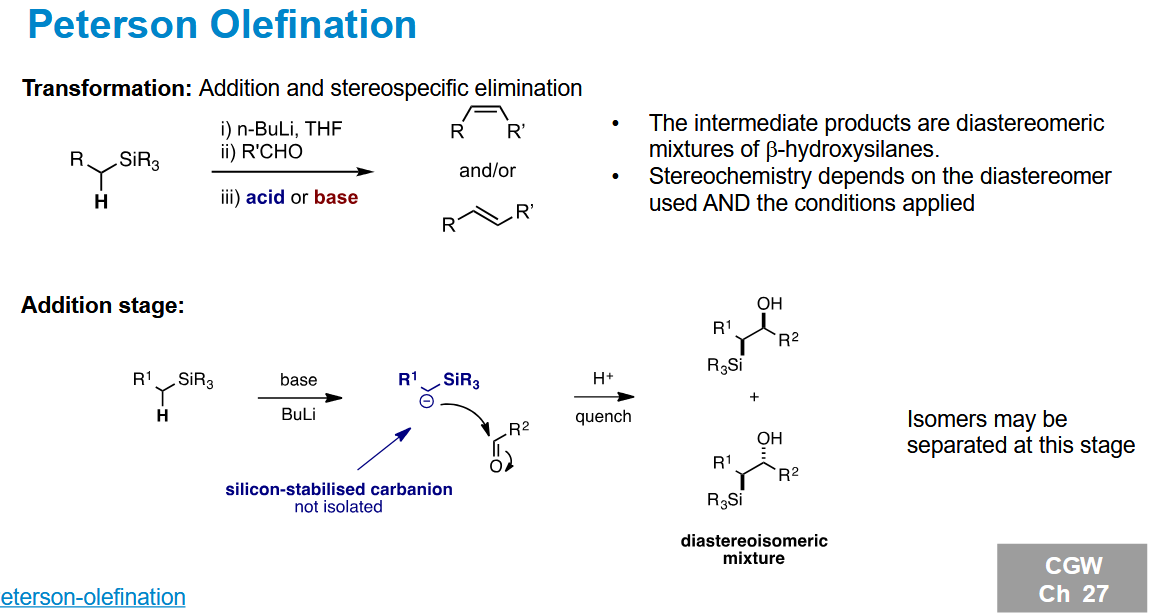
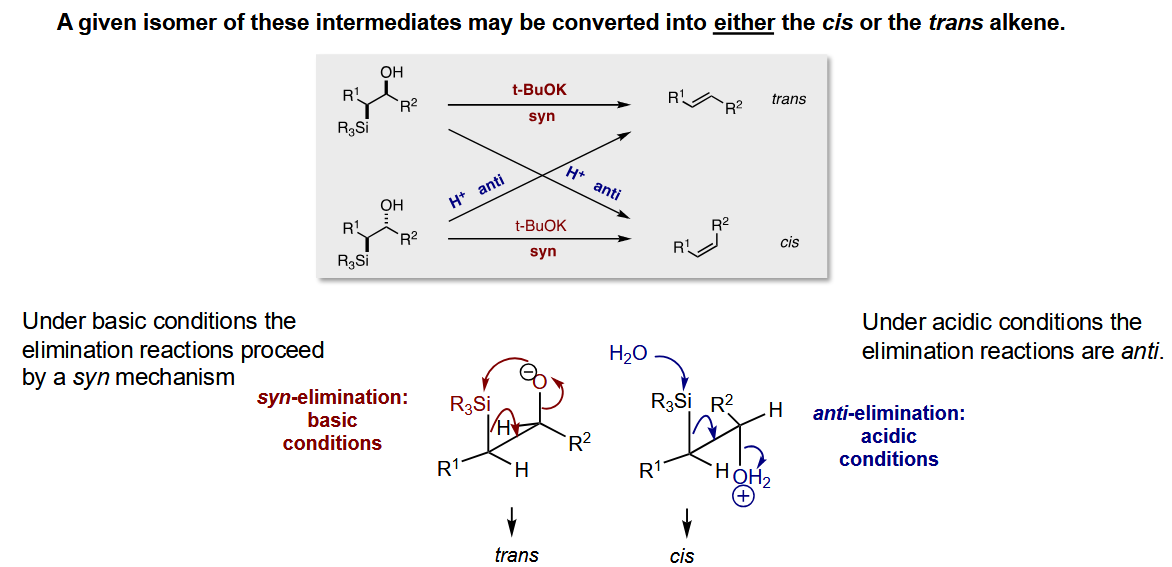
What can you do with the isolated diastereomers
Use either of them to form cis or trans alkenes.
Depending on whether you use acid or base, the mechanism changes which geometry of alkene forms. Flipping one of the stereocentres means the geoemtry formed by acid/base swaps.