30 MCQs
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Acute lymphoblastic leukaemia (ALL) typically arises from which stage of lymphocyte development?
A. Mature B cells or T cells
B. Hematopoietic stem cells
C. Early B-cell or T-cell progenitors in the bone marrow
D. Granulocyte-monocyte progenitors
Early B-cell or T-cell progenitors in the bone marrow
During the induction phase of chemotherapy for acute lymphoblastic leukaemia (ALL), which of the following is the primary goal?
A. To maintain long-term remission by reducing leukemic cells to undetectable levels
B. To eradicate leukemic blasts in the bone marrow and achieve complete remission
C. To reduce the risk of CNS involvement by administering intrathecal chemotherapy
D. To prepare the patient for hematopoietic stem cell transplantation
To eradicate leukemic blasts in the bone marrow and achieve complete remission
A patient's laboratory results show a normal prothrombin time (PT), normal activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT), and a significantly elevated Thrombin Time (TT). Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation (DIC)
B. Fibrinogen deficiency
C. Haemophilia A
D. von Willebrand disease
Fibrinogen deficiency
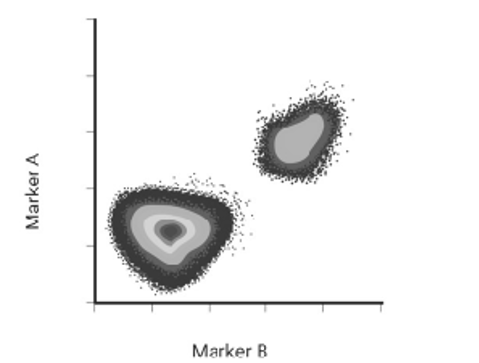
In the flow cytometry dot plot below, there are two distinct clusters of dots in a quadrant plot of fluorescence marker A versus fluorescence marker B. What do they suggest?
A. Two distinct cell populations with different fluorescence characteristics
B. Variability in cell size
C. Differences in cell granularity
D. Experimental error or instrument malfunction
Two distinct cell populations with different fluorescence characteristics
Which hormonal imbalance best explains glucose homeostasis imbalance in type 2 diabetes?
A. Elevated glucagon and inadequate insulin
B. Increased insulin causing hypoglycaemia
C. Low cortisol causing hypoglycaemia
D. High IGF-1 stimulating glucose production
Elevated glucagon and inadequate insulin
Which method is most effective for diagnosing pancreatic beta cell death?
A. Fasting blood glucose
B. Liver function test
C. Complete metabolic panel
D. C-peptide levels
C-peptide levels
Why is the oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) considered the gold standard for diagnosing Type 2 diabetes?
A. Measures glucose after fasting with quick results
B. Assesses glucose metabolism and insulin sensitivity
C. Less invasive, with a single blood sample
D. Evaluates long-term glycaemic control
Assesses glucose metabolism and insulin sensitivity
How does weight loss improve diabetes management?
A. Reduces insulin production
B. Increases appetite, improving food intake control
C. Decreases glucagon, preventing glucose release
D. Enhances insulin sensitivity and reduces inflammation
Enhances insulin sensitivity and reduces inflammation
Which staining technique is most commonly used to highlight the cellular features in the histological examination of uveal melanoma?
A. Gram stain
B. Periodic Acid-Schiff (PAS) stain
C. Haematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) stain
D. Giemsa stain
Haematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) stain
What is a key histological feature of uveal melanoma?
A. Presence of multinucleated giant cells
B. High density of small, round blue cells
C. Spindle-shaped melanoma cells with prominent nucleoli
D. Extensive fibrous stroma with no melanoma cells
Spindle-shaped melanoma cells with prominent nucleoli
In uveal melanoma, what histological feature is associated with a higher risk of metastasis?
A) presence of necrosis
B) well-defined tumour margins
C) low Mitotic spindle cell morphology
D) Predominantly spindle cell morphology
presence of necrosis
What is a significant limitation of CT imaging in the early diagnosis of ischemic stroke compared to MRI?
A. Lower radiation exposure
B. Lower cost
C. Delayed identification of early ischemic changes
D. Inability to visualize haemorrhagic stroke
Delayed identification of early ischemic changes
Which of the following best describes the process of drug absorption in pharmacokinetics?
A. The conversion of a drug into its active or inactive metabolites.
B. The distribution of a drug throughout the body's tissues and fluids.
C. The elimination of a drug from the body, primarily through the liver and kidneys.
D. The process by which a drug enters the bloodstream from the site of administration
The process by which a drug enters the bloodstream from the site of administration
Which of the following best describes an agonist?
A. A molecule that binds to a receptor but does not produce any effect.
B. A molecule that binds to a receptor and prevents other substances from binding.
C. A molecule that binds to a receptor and activates it, producing a physiological response.
D. A molecule that permanently blocks a receptor site.
A molecule that binds to a receptor and activates it, producing a physiological response
The 'lock and key' model is used to describe which aspect of pharmacodynamics?
A. Drug distribution and metabolism
B. The binding of drugs to specific receptors
C. The interaction between drugs and plasma proteins
D. The elimination of drugs through the kidneys
The binding of drugs to specific receptors
What advantage does tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS) offer in toxicology studies?
A. Faster sample preparation
B. Lower cost per analysis
C. Improved selectivity and reduced interference from matrix components
D. Ability to analyse larger molecules
Improved selectivity and reduced interference from matrix components
Which of the following describes the typical process for extracting and identifying ketamine in a toxicology sample?
A. Acid-base extraction followed by HPLC-UV analysis
B. Solid-phase extraction followed by GC-MS analysis
C. Protein precipitation followed by immunoassay screening
D. Liquid-liquid extraction followed by LC-MS/MS analysis
Solid-phase extraction followed by GC-MS analysis
Which of the following is a tumour suppressor gene?
A. Ras
B. P53
C. Cyclin D
D. E2F
P53
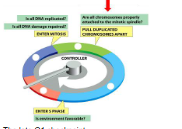
From the associated cell cycle diagram, which of the following cell checkpoints is indicated by the red arrow?
A. The late G1 checkpoint
B. G2/M checkpoint
C. Metaphase to anaphase transition checkpoint
D. Mid S phase checkpoint
The late G1 checkpoint
Which of the following factors is associated with a better prognosis in uveal melanoma?
A. Epithelioid cell type
B. Extra-scleral extension
C. Chromosome 6p gain
D. High mitotic rate
Chromosome 6p gain
What is the role of glutamate in the pathogenesis of ischaemic stroke?
A. It reduces neuronal excitability and protects brain cells
B. It acts as an anti-inflammatory agent in the brain
C. It promotes neurogenesis and repair of damaged neurons
D. It causes excitotoxicity leading to neuronal damage and death
It causes excitotoxicity leading to neuronal damage and death
Which of the following is true? A monoclonal antibody:
A. Recognises one epitope on an immunogen
B. Recognises several epitopes on one immunogen
C. Contains large amounts of non-specific antibodies
D. Can only be produced in rabbits
Recognises one epitope on an immunogen
What is an epitope?
A. The region of an antibody that recognises an antigen
B. Part of a molecule that is recognised by an antibody
C. The isotype-determining region of an antibody heavy chain
D. The constant region of an antibody
Part of a molecule that is recognised by an antibody
What is the primary purpose of using beta-blockers in the treatment of myocardial infarction?
A. Increase myocardial contractility
B. Reduce myocardial oxygen demand
C. Dilate coronary arteries
D. Prevent blood clot formation
Reduce myocardial oxygen demand
What is the main therapeutic target of ACE inhibitors in hypertension management?
A. Decreasing LDL cholesterol synthesis
B. Increasing sodium absorption in the kidneys
C. Blocking calcium channels in the myocardium
D. Reducing the activity of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system
Reducing the activity of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system
An inborn error of metabolism is commonly caused by:
A. Mutation(s) which result in a gain of function of a metabolic enzyme
B. Mutation(s) which result in a loss of function of a metabolic enzyme
C. An increase in expression of a metabolic enzyme caused by a chromosomal duplication
D. An increase in expression of a cofactor required for the activity of a metabolic enzyme
Mutation(s) which result in a loss of function of a metabolic enzyme
A child has been diagnosed with a genetic disease that has an X-linked recessive inheritance pattern. The child’s mother is already 10 weeks pregnant. What is the most effective and safest way of determining the risk to the unborn baby of this genetic disease?
A. Determine the biological sex of the foetus without offering any other genetic testing
B. Test the foetus's father for the mutation seen in the proband followed by further genetic testing if required
C. Test the foetus's mother for the mutation seen in the proband followed by further genetic testing if required
D. Take a chorionic villus sample or carry out an amniocentesis and test this sample for the mutation seen in the proband
Test the foetus's mother for the mutation seen in the proband followed by further genetic testing if required
Phenylketonuria is caused by a genetic mutation in the enzyme which breaks down phenylalanine. Which of these approaches would not be an effective approach for treating this disease?
A. Increase the amount of glucose in the patient's diet
B. Reduce the amount of the phenylalanine in the patient's diet
C. Treat the patient with an alternative enzyme to break down phenylalanine
D. Treat the patient with a vitamin cofactor to try to increase the activity of the mutated enzyme
Increase the amount of glucose in the patient's diet
Which of the following best describes the primary goal of personalised medicine?
A. Developing a universal drug that works for all patients
B. Tailoring medical treatment to an individual's genetic profile
C. Reducing the cost of healthcare for insurance companies
D. Eliminating the need for clinical trials in drug development
Tailoring medical treatment to an individual's genetic profile
Which of the following is an approach which is being used to improve the clinical outcome of gene therapy trials?
A. Isolating stem cells from a patient, carrying out experiments ex vivo to introduce genetic changes into the cells and infusing the patient with the genetically altered cells
B. Injecting the patient with high amounts of the correct gene sequence packaged in a viral vector such as AAV
C. Correcting the DNA sequence of human embryos using CRISPR-Cas
D. Using a vaccine to immunise the patient against the genetic mutation within their genome
Injecting the patient with high amounts of the correct gene sequence packaged in a viral vector such as AAV