Cellular Respiration
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
What is cellular respiration?
Combination of aerobic and anaerobic catabolic pathways that cells use to completely break down organic compounds (e.g. glucose) into ATP.
What are the three steps of aerobic cellular respiration of glucose?
1. Glycolysis (in cytosol).
2. Citric acid/krebs/tricarboxylic acid cycle (in mitochondrial matrix).
3. Oxidative phosphorylation/electron transport chain (across inner mitochondrial membrane).
What is the site of aerobic cellular respiration in eukaryotic cells called?
Mitochondria
What is the reaction of cellular respiration?
C6H12O6 (glucose) + 6O2 ➞ 6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy
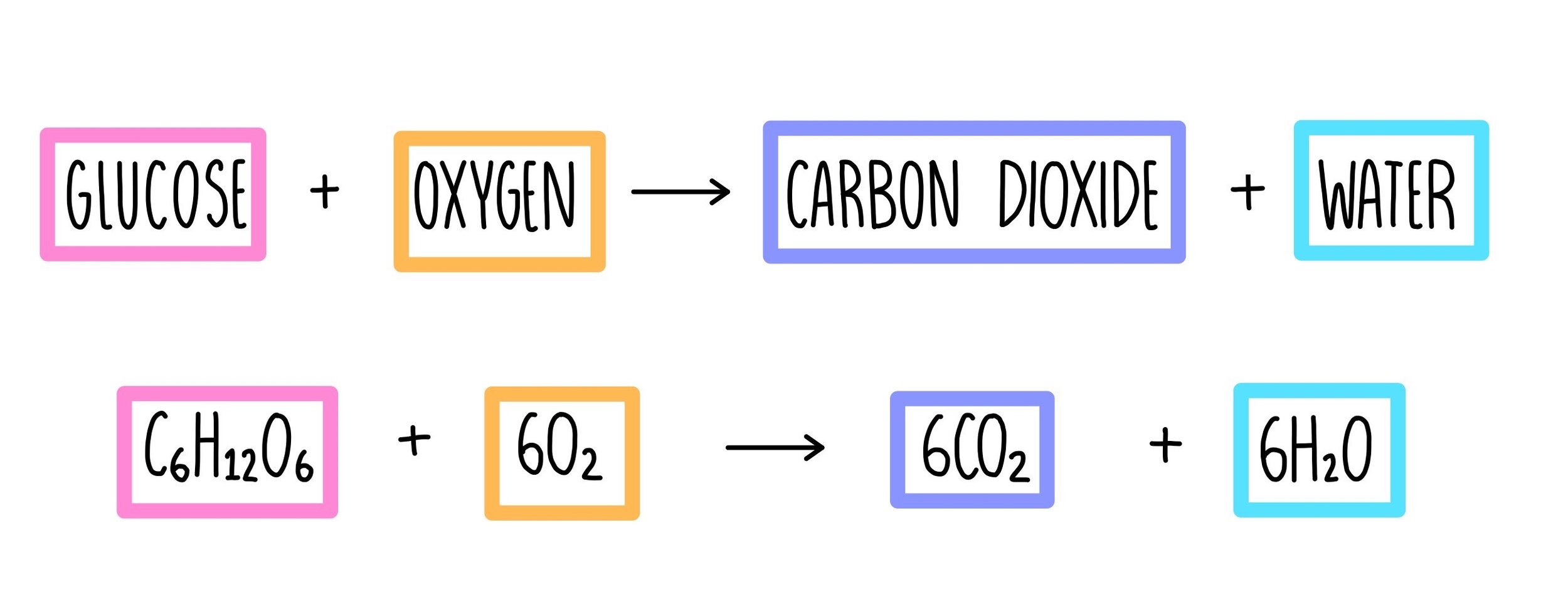
Cellular respiration is _____and _____
Oxidative (glucose loses electrons) and exergonic (spontaneous, energy released).
What are the two ways to produce ATP?
Substrate-level Phosphorylation: an enzyme directly transfers phosphate onto ADP to form ATP.
Oxidative Phosphorylation: ATP is produced using energy from electron flow through the electron transport chain.
Does glycolysis require O2?
No, its anaerobic
What is glycolysis?
The breakdown of glucose into two pyruvate molecules which occurs in the cytosol of all living cells. It produces ATP via substrate-level phosphorylation
Why is hexokinase important?
It uses 1 ATP to convert glucose ➞ glucose 6-phosphate, making glucose negatively charged and preventing its diffusion out of the cell.
Why is phosphofructokinase important?
Uses 1 ATP to convert fructose 6-phosphate ➞ fructose 1,6- bisphosphate, committing the molecule to glycolysis (irreversible, key regulatory step).
High ATP inhibits PFK=
prevents glycolysis
Low ATP disinhibits PFK=
Promotes glycolysis
Glycolysis has two distinct phases, creating a net production of _ATP, _pyruvate, _ NADH: how many?
2,2,2
Energy investment phase #ATP?
2
Energy payoff phase #ATP and # NADH
4 and 2
What is NADH?
electron carrier that transports high energy electrons to the electron transport chain (ETC)
Why must NAD+ be available?
For glycolysis to occur and create NADH.
Following glycolysis, pyruvate has two possible paths, What are they?
1. Respiratory path: oxygen is present (the Krebs cycle and ETC are active).
2. Non-respiratory path: oxygen is absent (fermentation).
Citric Acid Cycle (CAC) produces ATP via ____ and occurs in the mitochondrial matrix
substrate level phosphorylation
Acetyl CoA from pyruvate decarboxylation merges with ___to form ____
oxaloacetate
citrate
One glucose molecule yields _NADH, _FADH2, __ATP, and _CO2, from the CAC.
6,2,2,4
What two molecules function as high energy electron carriers?
NADH & FADH2
During glycolysis and CAC, glucose is stripped of high energy electrons and these carriers are ___as they gain the electrons
Reduced
NAD+ ➞ NADH
FAD ➞ FADH2
NADH and FADH2 are __as they pass their high energy electrons to the proteins in the ETC.
Oxidized
• NADH ➞ NAD+
• FADH2 ➞ FAD
H+ accumulates in intermembrane space, establishing an ___ (a difference in concentration and charge) across the membrane.
Electrochemical gradient
__ transfer of electrons through the ETC is coupled to __ pumping of protons against their concentration gradient.
Exergonic
Endergonic
What is the final step of the Electron Transport chain?
Electrons are transferred to O2. The O2, protons, and electrons combine to form water (H2O).
What is the final electron acceptor?
Oxygen
What is ATP Synthase?
makes ATP from ADP via oxidative phosphorylation, powered by the proton-motive force. Embedded in inner mitochondrial membrane.
What is proton motive force?
energy produced by the movement of protons down an electrochemical gradient (high [H+] in intermembrane space, low [H+] in mitochondrial matrix).
What is chemiosmosis?
Movement of ions down a concentration gradient across a semipermeable membrane
In prokaryotes, the ETC is embedded in the?
Cellular membrane
The ETC yields a total of approximately _ATP.
34
What is the function of fermentation?
Anaerobic recycling of NADH into NAD+ from pyruvate. Occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell and does not generate any ATP (only regenerates NAD+).
What are the two types of fermentation?
Alcohol fermentation: occurs in yeast and some bacteria.
Lactic acid fermentation: takes place in human muscle cells, fungi and bacteria
What are the two steps of alcohol fermentation? What is the final electron acceptor?
1. Pyruvate ➞ Acetaldehyde + CO2
2. Acetaldehyde + NADH ➞ Ethanol + NAD+
- Acetaldehyde acts as the final electron acceptor.
What is the one step of lactic acid? Occurs during ?
Pyruvate + NADH ➞ Lactate + NAD
In animals, lactate is transported from muscles to the liver and transformed back into glucose Cori Cycle.
Occurs during intense physical exercise (when O2 availability is too low for aerobic respiration).
If glucose is absent what other energy sources can be used?
carbohydrates, lipids, or proteins
What is glycogenesis?
The body stores extra glucose as glycogen by linking glucose molecules together.
Glycogen is mostly stored in liver and skeletal muscles
Energy cost: ATP is used to turn glucose into glucose-6-phosphate (G6P).
What is Glycogenolysis?
The breakdown of stored glycogen into glucose for energy. Occurs when glucose levels are low.
What is gluconeogenesis?
Synthesis of glucose from noncarbohydrate molecules (proteins and lipids). Occurs in the liver and the kidney when glucose and glycogen levels are low.
Carbohydrate metabolism is regulated by two pancreatic endocrine hormones, What are they? + their effeccts
Insulin: released when blood glucose is high.
Effects of Insulin: a. Stimulates cells to uptake glucose
Promotes glycogenesis and glycolysis
Glucagon: released when blood glucose is low.
Effects of Glucagon: a. Triggers glycogenolysis
Inhibits glycogenesis and glycolysis (preserves glucose for brain function)
In _, carbons are cut away from the fatty acid chain to produce acetyl CoA, NADH, and FADH2
Beta oxidation
What produces more ATP ,but what energy source is preferred?
Fats but carbohydrates are the preferred cellular energy source since they can be catabolized quicker
Beta oxidation occurs in ?
mitochondrial matrix
The brain prefers to use for energy but when glucose is low, the brain uses _(produced from fatty acids).
glucose
ketones
What is oxidative deamination?
The removal of amino group from amino acids in order to make other metabolic intermediates. Mostly occurs in the liver.
• Remaining ammonia molecule is toxic so the body converts it to urea for excretion.
Is oxygen the final electron acceptor in anaerobic respiration?
no! It's SO4-2, NO3-, S etc.
Oxidative phosphorylation consist of what two parts?
electron transport chain and chemiosmosis
prokaryotic respiration yields how many atp molecules?
38
The purpose of pyruvate decarboxylation?
syn. of acetyl-CoA
What are the products of beta-oxidation?
acetyl-CoA, NADH, & FADH2
What is the common intermediate shared between glycogenesis, glycogenolysis, and gluconeogenesis
glucose 6-phosphate
What is the function of the cori cycle?
convert lactate back into glucose