Unit 1: Biological Bases of Behavior (1A,1B,2)
1/110
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
111 Terms
Behavior approach
an approach to psychology emphasizing that human behavior is determined mainly by what a person has learned, especially from rewards and punishments
Scientist: Watson
Biological approach
an approach to psychology focusing on the body, especially the brain and nervous system
Cognitive approach
an approach to psychology emphasizing the mental processes involved in knowing: how we direct our attention, perceive, remember, think, and solve problems
Dualism
the presumption that mind and body are two distinct entities that interact
Eclectic approach
an approach to psychotherapy that uses techniques from various forms of therapy
Empiricism
the belief that accurate knowledge can be acquired through observation
Evolutionary approach
an approach to psychology centered on evolutionary ideas such as adaptation, reproduction, and natural selection as the basis for explaining specific human behaviors
Scientist: David Buss
Functionalism
A school of psychology that focused on how our mental and behavioral processes function - how they enable us to adapt, survive, and flourish.
Humanistic approach
an approach to psychology emphasizing a person's positive qualities, the capacity for positive growth, and the freedom to choose any destiny
Scientist: Abraham Maslow and Carl Rogers
Multicultural approach/sociocultural approach
therapy that relies on awareness, knowledge, and skills of the client's sociocultural context
Psychodynamic approach
an approach to psychology emphasizing unconscious thought, the conflict between biological drives (such as the drive for sex) and society's demands, and early childhood family experiences
Scientist: Sigmund Freud
Structuralism
an early school of psychology that used introspection to explore the elemental structure of the human mind
Operational definition
a statement of the procedures used to define research variables
Experiment
a research method in which an investigator manipulates one or more factors to observe the effect on some behavior or mental process
Correlational study
a research project designed to discover the degree to which two variables are related to each other
Survey
the collection of data by having people answer a series of questions
Interview
A face-to-face or telephone questioning of a respondent to obtain desired information.
Naturalistic observation
observing and recording behavior in naturally occurring situations without trying to manipulate and control the situation
Participant observation
a research method in which investigators systematically observe people while joining them in their routine activities
Structured observation
a method that involves presenting an identical situation to each child and recording the child's behavior
Case study
an observation technique in which one person is studied in depth in the hope of revealing universal principles
Longitudinal study
research in which the same people are restudied and retested over a long period
Cross-sectional study
research that compares people of different ages at the same point in time
Single subject design (aka independent subject)
a research design that requires only one or a few subjects in order to conduct an entire experiment
Mean, median, mode, range
mean: average
median: middle number (ordered)
mode: most common
range: biggest - smallest
Positive correlation
A correlation where as one variable increases, the other also increases, or as one decreases so does the other. Both variables move in the same direction.
Negative correlation
as one variable increases, the other decreases
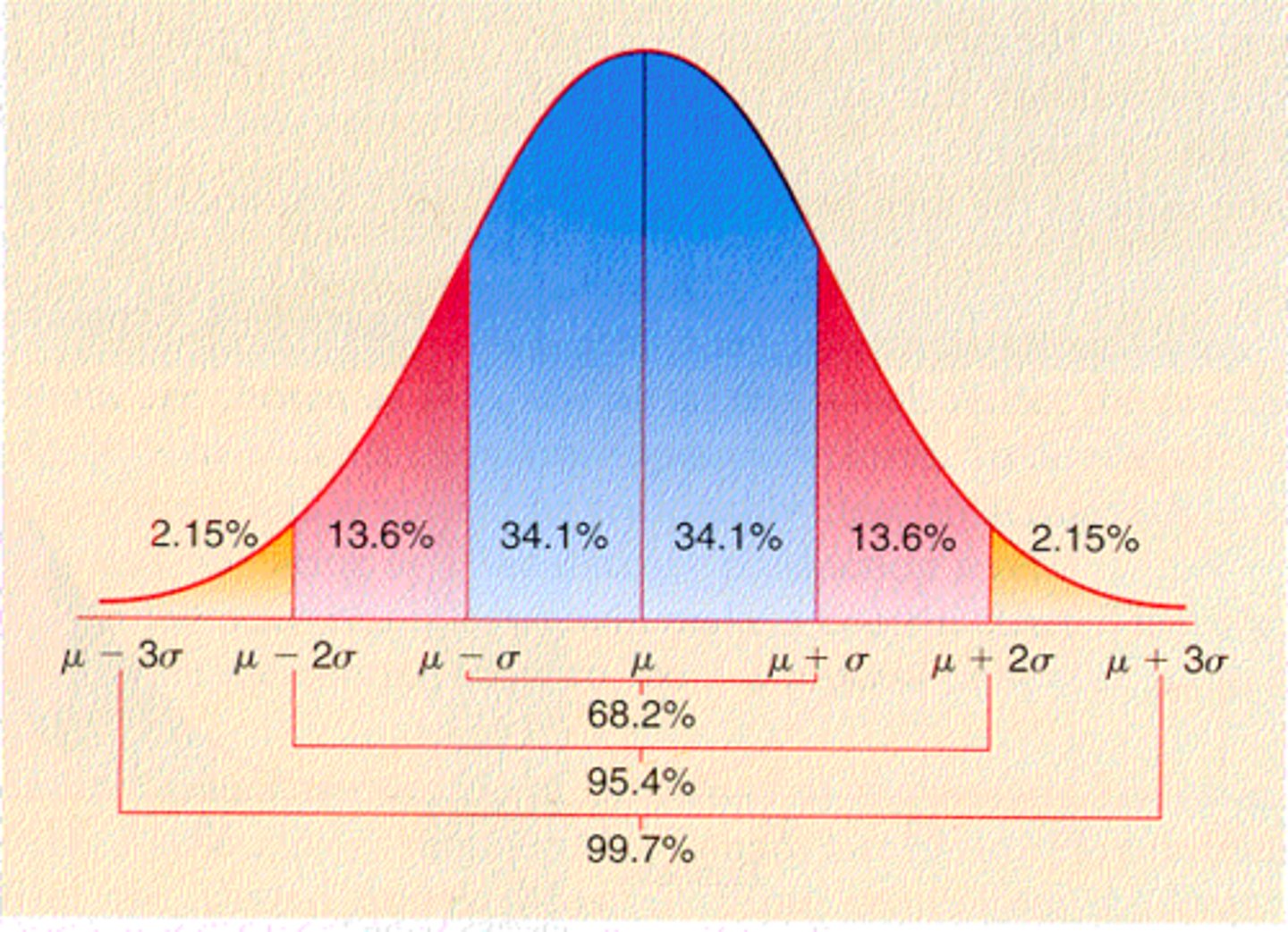
Normal distribution
A function that represents the distribution of variables as a symmetrical bell-shaped graph.
Skewed distribution
a representation of scores that lack symmetry around their average value
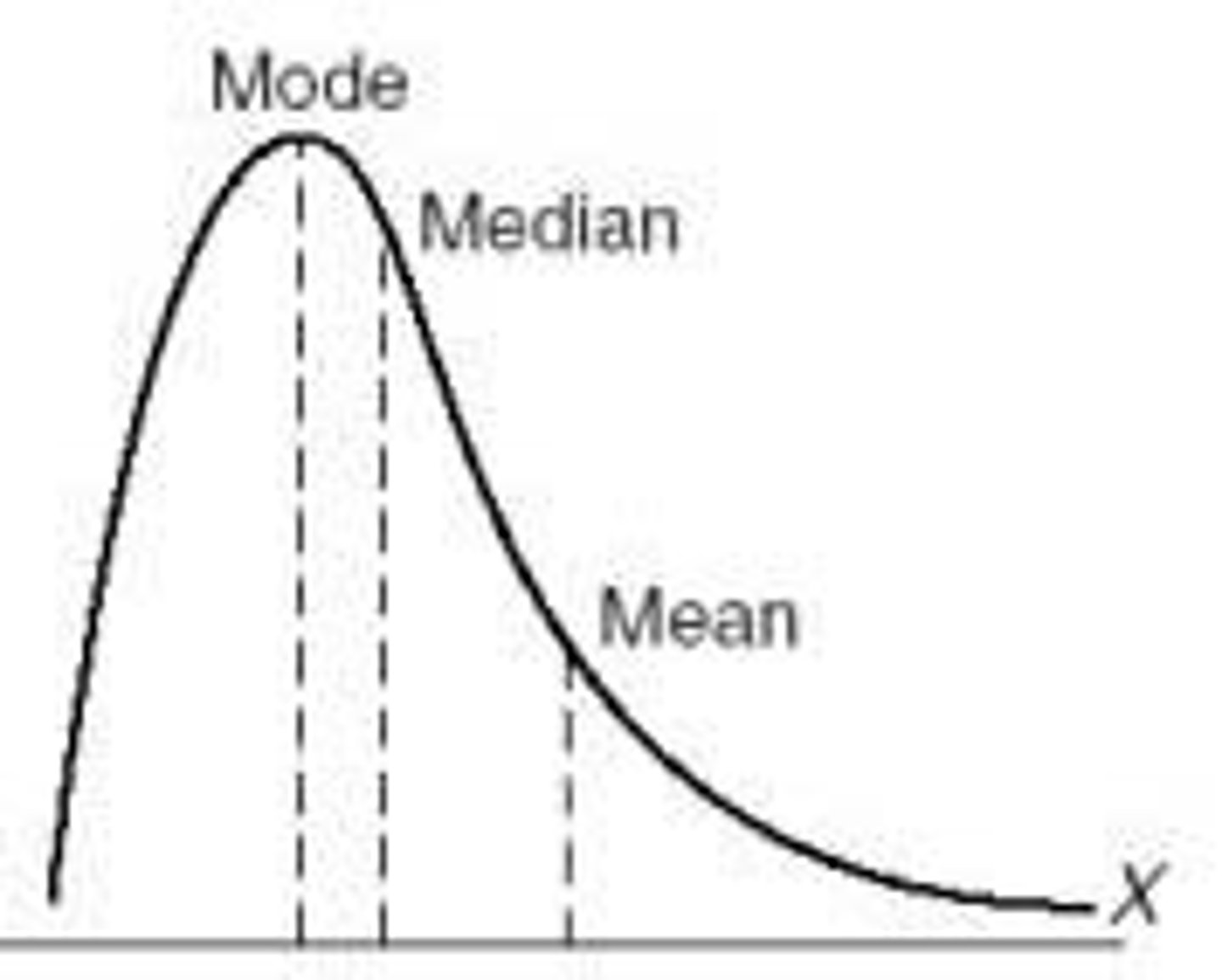
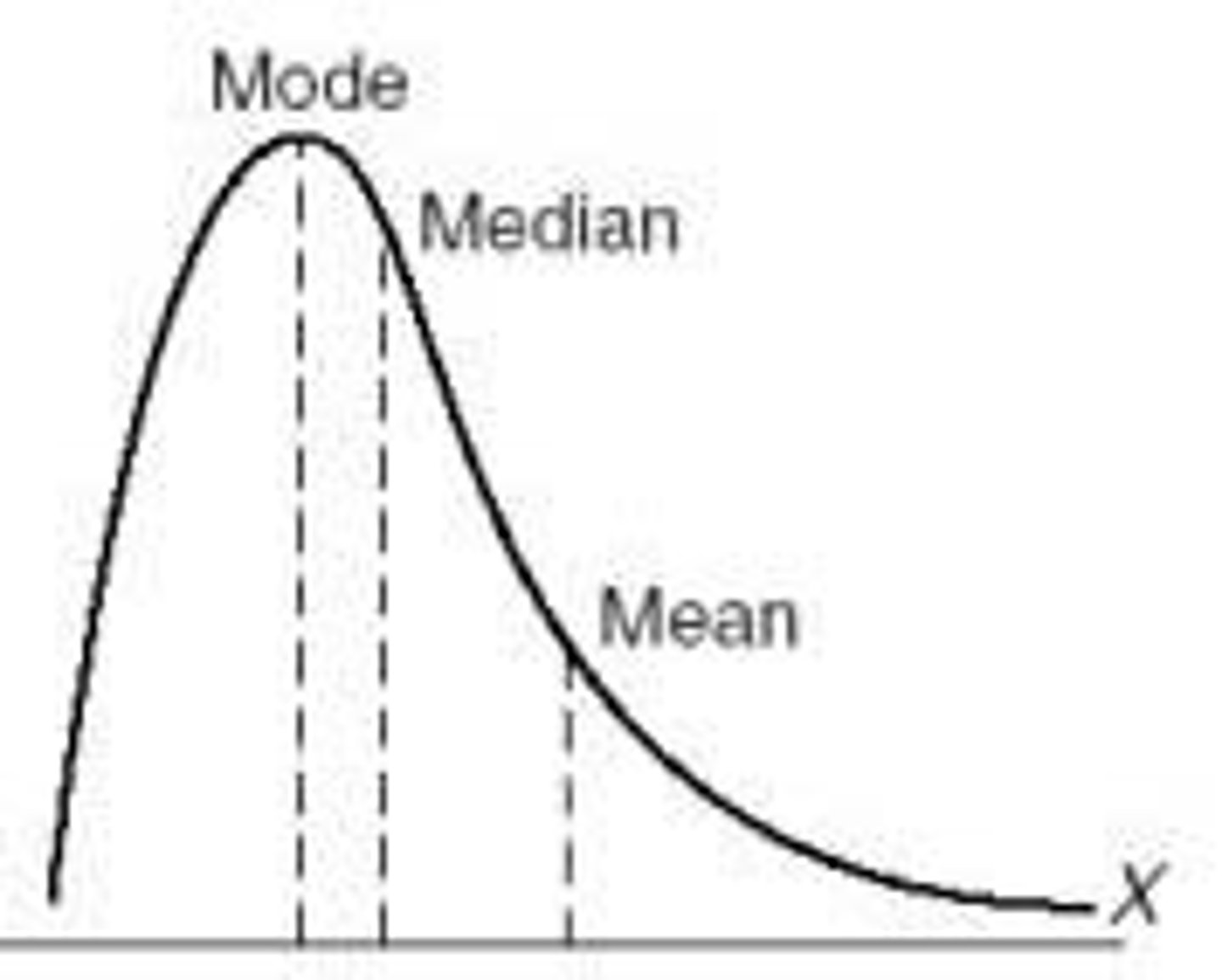
Positively skewed distribution
A distribution where the scores pile up on the left side and taper off to the right.
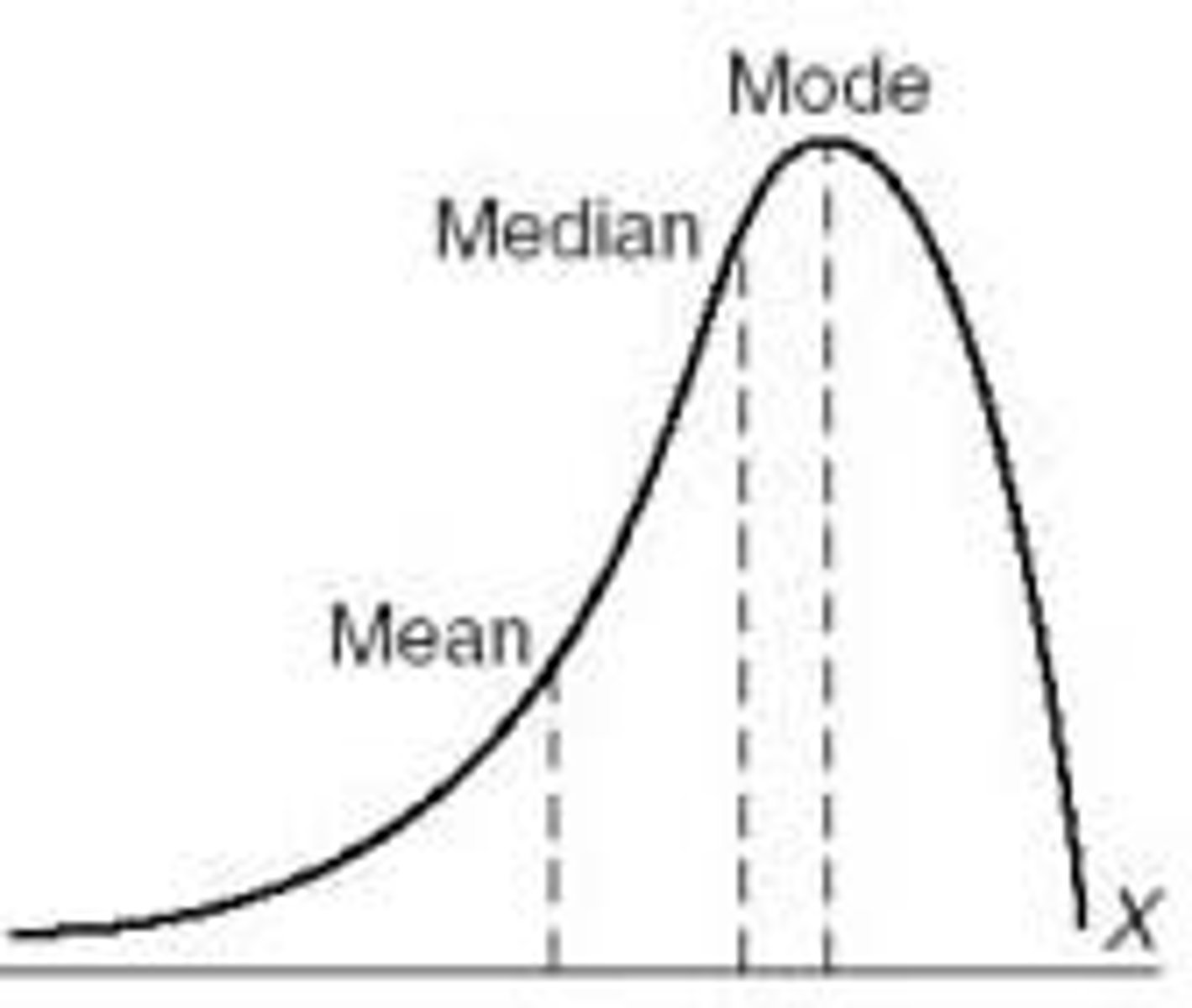
Negatively skewed distribution
A distribution in which most scores pile up at the high end of the scale.
Statistical significance
a statistical statement of how likely it is that an obtained result occurred by chance
smaller p value = statistical significance
Standard deviation
a computed measure of how much scores vary around the mean score
Matched pairs design
A method of assigning subjects to groups in which pairs of subjects are first matched on some characteristic and then individually assigned randomly to groups.
Repeated measures (within-subjects design)
the same individuals will participate in all conditions
Independent variable
The experimental factor that is manipulated; the variable whose effect is being studied.
Dependent variable
The outcome factor; the variable that may change in response to manipulations of the independent variable.
Random sampling
a sample that fairly represents a population because each member has an equal chance of inclusion
Convenience sampling
choosing individuals who are easiest to reach
Representative sample
randomly selected sample of subjects from a larger population of subjects
Experimental group
In an experiment, the group that is exposed to the treatment, that is, to one version of the independent variable.
Control group
In an experiment, the group that is not exposed to the treatment; contrasts with the experimental group and serves as a comparison for evaluating the effect of the treatment.
Random assignment
assigning participants to experimental and control conditions by chance, thus minimizing preexisting differences between those assigned to the different groups
Single-blind technique
When information about the study is withheld from the participants
Double-blind technique
An experimental control in which neither the participants nor the researchers interacting with the participants are aware of the group or condition to which the participants have been assigned.
Reliability
consistency of measurement
Validity
the extent to which a test measures or predicts what it is supposed to
Confounding variables
factors that cause differences between the experimental group and the control group other than the independent variable
Inferential statistics
numerical data that allow one to generalize- to infer from sample data the probability of something being true of a population
Frequency distribution
an arrangement of data that indicates how often a particular score or observation occurs
Ethical guidelines
- informed consent
- participant's right to withdraw
- justification for the use of deception
- confidentiality of findings
- debriefing procedure
Falsifiability
Can the claim be disproved?
Extraneous variables
any variables other than the independent variable that seem likely to influence the dependent variable in a specific study
Neuron
a nerve cell; the basic building block of the nervous system
Afferent neuron
Neuron that conducts impulses toward the CNS from the body periphery.
Efferent neuron
Neuron that conducts impulses away from the CNS to muscles and glands.
Dendrites
Branchlike parts of a neuron that are specialized to receive information.
Axon
the extension of a neuron, ending in branching terminal fibers, through which messages pass to other neurons or to muscles or glands
Soma
cell body
Myelin sheath
A layer of fatty tissue segmentally encasing the fibers of many neurons; enables vastly greater transmission speed of neural impulses as the impulse hops from one node to the next.
Nodes of Ranvier
gaps in the myelin sheath
Synapse
the junction between the axon tip of the sending neuron and the dendrite or cell body of the receiving neuron
Synaptic cleft
The narrow gap that separates the presynaptic neuron from the postsynaptic cell.
Resting potential
The difference in electric charge between the inside and outside of a neuron's cell membrane
Depolarization
The process during the action potential when sodium is rushing into the cell causing the interior to become more positive.
Action potential
a neural impulse; a brief electrical charge that travels down an axon
Absolute refractory period
The minimum length of time after an action potential during which another action potential cannot begin.
Post synaptic potential
a voltage change at a receptor site on a postsynaptic cell membrane
Neurotransmitters
chemical messengers that cross the synaptic gaps between neurons
Dopamine
influences movement, learning, attention, and emotion
Serotonin
Affects mood, hunger, sleep, and arousal
Endorphin
chemical in the brain that plays a specialized role in pain reduction
GABA
a major inhibitory neurotransmitter; reduces anxiety
Acetylcholine
A neurotransmitter that enables learning and memory and also triggers muscle contraction
Norepinephrine
helps control alertness and arousal
Neuromodulators
chemicals released in the nervous system that influence the sensitivity of the receiving neuron to neurotransmitters
Substance P
A neurotransmitter that is involved in the transmission of pain messages to the brain.
Agonist
a molecule that, by binding to a receptor site, stimulates a response
Antagonist
a chemical or drug that binds to receptors in the brain and prevents an agonist from having a reaction
Electroencephalograph (EEG)
a device that monitors the electrical activity of the brain over time by means of recording electrodes attached to the surface of the scalp
Lesioning
destroying a piece of the brain
Electrical Stimulation of the Brain (ESB)
sending a weak electric current into a brain structure to stimulate it
Computerized Tomography (CT)
the use of a device that employs a computer to analyze data obtained by a scanning beam of X-rays to produce a two-dimensional picture of a "slice" through the body
Positron Emissions Tomography (PET)
a visual display of brain activity that detects where a radioactive form of glucose goes while the brain performs a given task
magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
brain-imaging method using radio waves and magnetic fields of the body to produce detailed images of the brain
Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI)
an imaging technique used to examine changes in the activity of the working human brain by measuring changes in the blood's oxygen levels
Central nervous system
brain and spinal cord
Peripheral nervous system
the sensory and motor neurons that connect the central nervous system to the rest of the body
Autonomic nervous system
the part of the peripheral nervous system that controls the glands and the muscles of the internal organs (such as the heart). Its sympathetic division arouses; its parasympathetic division calms.
Somatic nervous system
the division of the peripheral nervous system that controls the body's skeletal muscles
Sympathetic nervous system
the division of the peripheral nervous system that controls the body's skeletal muscles
Parasympathetic nervous system
the division of the autonomic nervous system that calms the body, conserving its energy
Cerebrum
Area of the brain responsible for all voluntary activities of the body
Cerebellum
A large structure of the hindbrain that controls fine motor skills.
Thalamus
the brain's sensory switchboard, located on top of the brainstem; it directs messages to the sensory receiving areas in the cortex and transmits replies to the cerebellum and medulla
Hypothalamus
A neural structure lying below the thalamus; it directs several maintenance activities (eating, drinking, body temperature), helps govern the endocrine system via the pituitary gland, and is linked to emotion and reward.
Reticular formation
a nerve network in the brainstem that plays an important role in controlling arousal
Medulla
the base of the brainstem; controls heartbeat and breathing
Substantia Nigra
An area of the midbrain that is involved in motor control and contains a large concentration of dopamine-producing neurons
Amygdala
two lima bean-sized neural clusters in the limbic system; linked to emotion.