Developmental Psychology PSYC1030
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
At what age - smile in response to social cues
3 months
AWA - tuned into more familiar people
6 months
AWA - contagious crying
6 months
AWA - joint attention (trying to look at the same thing as another person to get their attention)
6 to 18 months
AWA - Sense of self and desires
18 months
AWA - talk about thoughts and beliefs
30 months
AWA - acquire other people’s thoughts, desires and beliefs
3+ years
AWA - share when only prompted to
18 months
AWA - spontaneously share without being prompted
3.5 to 4 years
AWA - development of theory of mind
4 years old
Mental states
Desire
Thoughts
Beliefs
Knowledge
AWA - start to engage in prosocial behaviour
6 to 18 months
AWA - recognise themselves in photos
2 years old
AWA - recognise themselves in videos
3 years old
AWA - start helping (first prosocial behaviour)
14 months
Length of infant increases by
50% by end of infancy
Infant’s brain volume grows to ___ by end of infancy
80 percent
Newborn acuity
20/500
Fixed focal distance
20cm
Cochlea matures by
24 gestational week
Cutaneous receptors along lips at
7 to 8 gestational week
When does head control occur
Head control at 6 wks, full antigravity by 3 months
AWA - integrate touch with vision and proprioception (knowing where own body is)
9 months
AWA - distinguish mother’s smell from stranger’s
1 month old
AWA - hearing fully mature
6 months
AWA - Goal-directed reach
3 to 4 months
Thomas and Chess axes
Biological regularity
Does it eat/sleep regularly
Hedonic tone
Are babies generally happy or distressed
Approach/withdrawal to novelty
Do they go towards something new or withdraw
Thomas and Chess - classes of babies and percentage in each
Easy = 40 percent
Regular, positive, approach
Difficult = 10%
Irregular, negative, withdrawal
Slow to warm = 15%
Low activity, mild negativity, gradual approach
Rest were a mix
AWA - attachment first emerges
6 to 9 months
Ainsworth - 3 types of attachment
Percentage of each
Type of caregiver
What they did in experiment
Secure (B)
60 percent
Calmed down quickly after mother returned
Caregiver is sensitive, responsive and consistent
Anxious-avoidant (A)
20%
Explores freely, little concern for caregiver
Caregiver dislikes closeness
Anxious-ambivalent (C)
20%
Very clingy, when parent returns wants contact but resists it
Caregiver is inconsistent
Piaget 4 stages of how children develop knowledge
Sensorimotor
0 - 2 years old
Explore through senses
Object permanence, mental representation of the world
Preoperational
2 -7 years old
Develop ability to engage in symbolic activity (language, pretend play)
Centration (number of coins)
Egocentric
Concrete operational
7 - 11 years old
Develop logical thinking for concrete things
Formal operational
11 years onwards
More abstract logic
Scientific thinking
AWA - develop concept of an object
8 - 12 month
What is object permanence and AWA does it develop
Objects exist even if they aren’t visible
Fully develops age
Disequilibrium
When schema conflicts with real world
3 theories of moral development
social learning - what do children copy
cognitive development - how do children think of the rules
parenting style
Social learning - 4 steps
Attention - notice behaviour
Retention - encode and store behaviour
Motor reproduction - translate stored code into action
Motivation - reason to perform behaviour
2 stages of cognitive development - when
Heteronomous
Age 4 to 8
Rule and consequence focused
Autonomous
Age 8 onwards
Fairness, morals
Kohlberg’s 6 stages
Preconventional (childhood)
Obedience - morality externally controlled
Exchange - self-interest with fairness
Conventional
Approval - social roles and expectations
Law and order - broader society
Postconventional
Social contract - fundamental rights
Universal principles - it’s the right thing to do
Baumrind’s two axes and 4 parenting styles
Responsiveness and demandingness
Authoritative, authoritarian, indulgent, neglectful
Types of errors at one-word stage
Overextension
Underextension
When is the one-word stage
1 to 1.5 year
Old age
65+
How to calculate speed of ageing
How long it takes for proportion of people 65+ to double
7 percent to 14 percent
Ageing categories
Young-old
65 to 74
Old-old
75 to 84
Oldest-old
85+
Centenarians
100+
Super-centenarians
110+
Gene Cohen’s stages of development
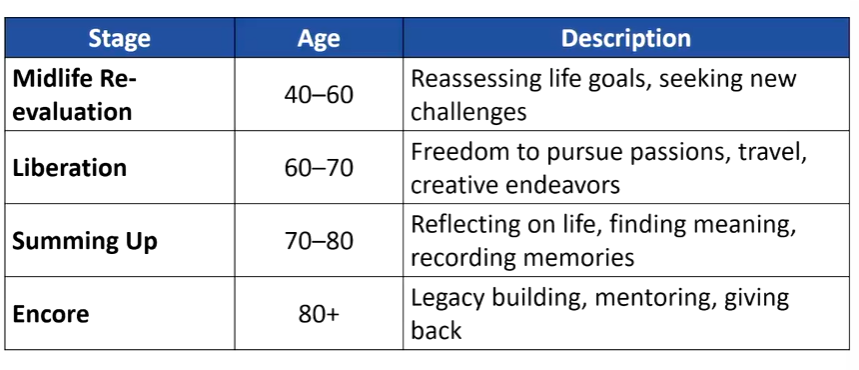
Rowe and Kahn successful ageing
Minimise disease and disability
Maintain high physical and cognitive function
Actie engagement with life
Baltes SOC model
Selection
Optimisation
Compensation
What adolescents have to come to terms with
Physical change
Adult identity
Survive
When do growth spurts occur
Girls - 11
Boys - 13 to 14
When asking people what they want to change about themselves
Boys
Scholastic ability - 47%
Personality - 23%
Physical appearance - 14%
Girls
Personality - 39%
Scholastic ability - 27%
Physical appearance - 24%
4 identity statuses
Foreclosure
Commitment without crisis
Identity diffusion
No crisis and no commitment
Moratorium
Crisis but no commitment
Identity achievement
Crisis and commitment
Parts of brain involved in risk-taking behaviour
Nucleus accumbens
Motivates us to get things that are desirable
Prefrontal cortex
Long-term planning
Logic
Reasoning
Nucleus accumbens develops before prefrontal cortex
Mary ainsworth - attachment
2 motivations that children balance
Security - staying close to caregiver
Exploration - learning about environment
Adult attachment styles
Secure
Comfortable with intimacy and independence
Supportive, balanced, resilient relationships
Avoidant
Distant, difficulty trusting others
Uncomfortable with closeness
Withdraw under stress
Anxious/ambivalent
Clingy, fear of abandonment
Crave closeness
Fear rejection
High emotional intensity
Assimilate vs accommodate infant schemas
assimilate - include new info in existing schema
accommodate - create new schema to include new info
Experiencing a crisis process
Something bad happens
Think about issues
Evaluate patterns from childhood
Decide whether or not you want to continue those patterns
trends for identity statuses
Younger adolescents
More identity diffusion and foreclosure
Not thinking through crises
16 to 18 yo
Starting to think through issues carefully and just starting to commit to changes
Slow increase in identity achievement