the mind's machine ch. 6
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/33
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
1
New cards
auditory world
all around us, increases in density the closer it gets to us
2
New cards
sound waves
perterbations in atmosphere (made of gas, smoke, wator vapor, under pressure) that create pressure waves
3
New cards
wave length/ frequency
measured in Hertz (Hz) and describes pitch
4
New cards
amplitude
measured in decibels (db) and describes loudness
5
New cards
we experience sin waves in multitudes
6
New cards
outer ear
pinna and ear canal. everyone is a little bit different. pinna gathers sound waves and canal funnels them
7
New cards
middle ear
ear drum (tympanic membrane) and ossicles. tympanic membrane gets pushed by air wave, then pushes the ossicles to move. ossicles then hit inner ear (oval window)
8
New cards
inner ear
cochlea (oval window, vestibular and tympanic canal, organ of corti (in medial canal)) and vestibulocochlear nerve. cochlea is filled with water and the oval window is a flexible membrane that when hit moves this water. the circular membrane on other end allows for water to move.
9
New cards
vestibular canal and tympanic canal
have water
10
New cards
middle canal /organ of corti
in between the vestibular and tympanic canal. contains the basilar membrane, tectoral membrane, and the sensory hair cells. basilar membrane is flexible tectoral membrane is rigid
cell’s bases are in basilar membrane and the inner hair cells are not embedded in the tympanic canal and outer hair cells are.
patter of pressure from waves travels in cochlea and reduced space by applying pressure and bends the hair
cell’s bases are in basilar membrane and the inner hair cells are not embedded in the tympanic canal and outer hair cells are.
patter of pressure from waves travels in cochlea and reduced space by applying pressure and bends the hair
11
New cards
inner hair cells
one row not embedded, don’t bend just stretch or compress, give us sense of hearing. three rows of hair on each cell, linked via tip links that look like springs so that when one bends they all do. based on which row bends tells nervous system about force and frequency of wave. tip links like a hatch opening, open ion channel allows influx of ions, AP, sent to vetibulocochlear nerve
glutamate and ACh released
glutamate and ACh released
12
New cards
outer hair cell
three rows, embedded in tectoral membrane, are bent or pulled with pressure waves, tells us timing of vibration and amplitude of force.
GABA and ACh released
GABA and ACh released
13
New cards
tonotopic organization
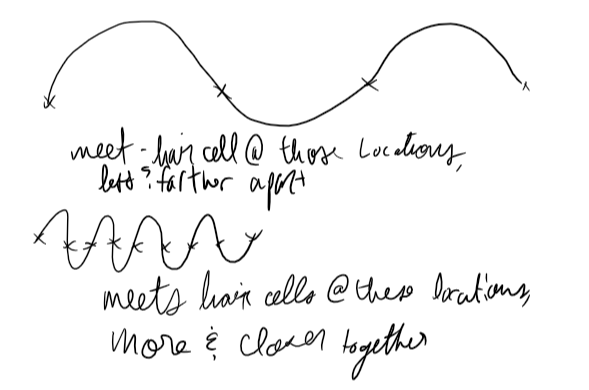
the base of the cochlea (where coil starts) hears higher frequency sounds and the apex (center) hears lower frequency. there is an overrepresentation of biologically relevant vibration ranges (the range where the voice falls)
we can hear 20,000hz (20000 oscillations in a second) but we can’t fire 20000 AP in a second
Volley theory: when we get AP that are seperated temporally (wave have to travel down cochlea) we can get info that tells us about perceived pitch
we can hear 20,000hz (20000 oscillations in a second) but we can’t fire 20000 AP in a second
Volley theory: when we get AP that are seperated temporally (wave have to travel down cochlea) we can get info that tells us about perceived pitch
14
New cards
organization of hearing
in brainstem synapses at **cochlear nucleus** and crosses over at the **superior olivary nucleaus.** most info crosses but some stays. then goes up into the **inferior colliculus** in top half of midbrain (toast shaped thing) then up into the **medial geniculate nucleus,** in the thalamus, then sent out into the **auditory cortex,** where sound reaches conscious awareness
15
New cards
place coding
pitch is determined by location of activated hair cells
16
New cards
temporal coding
encodes frequency of auditory stimuli in the firing rate of auditory neurons
17
New cards
biaural cues locate sound source. 2 kinds of cues: intensity difference and latency difference
\
18
New cards
intensity difference
difference of loundness. created when ears point different direction and/or if head casts a sound shadow
19
New cards
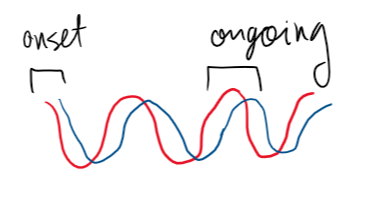
latency differences
difference of arrival. onset disparity is the disparity b/w when the sound initially reaches ears. ongoing phase disparity is the continued difference in the wave from the onset disparity
20
New cards
spectral filtering
physical structure of ear reinforces some frequencies and diminishes other
21
New cards
latency differences
encoded with interneurons and when the interneurons are activated together
22
New cards
auditory cortex
\-specialized for detecting biologically relevant sound. sensitivity is fine tuned by expeirence during development
\-we have specialization for arbitrary (computer warning, *whoosh* of main, speech) and non-arbitrary (clap, thunder, growl of tiger) sounds
\-we are specialised to hearing our name
\-we have specialization for arbitrary (computer warning, *whoosh* of main, speech) and non-arbitrary (clap, thunder, growl of tiger) sounds
\-we are specialised to hearing our name
23
New cards
herschels gyrus (temporal transverse gyrus)
bigger in musciciens than normal people
24
New cards
amusia
the inability to discern tunes or sing, associated with subtle abnormal function in right frontal lobe and poor connections between frontal and temporal cortex.
for most people it’s really dimusia-tone deafness
for most people it’s really dimusia-tone deafness
25
New cards
outer ear deafness
conduction deafness.
disorders of the outter ear prevent sounds from reaching cochlea. can occur from experience (boxing) or just not having a funnel shape
disorders of the outter ear prevent sounds from reaching cochlea. can occur from experience (boxing) or just not having a funnel shape
26
New cards
middle ear deafness
can be from the fusing of the three bones, can’t move anymore
\
\
27
New cards
inner ear deafness
sensorineural deafness- hair cells fail to respond to movement of the basilar membrane, no AP fired
caused by genetic mutation, infections, loud sounds, ototoxic effects of drugs
damage to hair cells can result in tinnitus
caused by genetic mutation, infections, loud sounds, ototoxic effects of drugs
damage to hair cells can result in tinnitus
28
New cards
deafness in brain
central deafness- damage to auditory brain areas from stroke, tumors, or traumatic brain injury. typically talking about people who are born with normal brain circuitry but something goes awry during life. still receive info just can’t process
word deafness= selective difficulty recognizing normal speech sounds, normal speech and hearing of nonverbal sounds. problems with arbitrary sounds, can hear but can’t recognize meanings
cortical deafness= difficulty recognizing all complex sounds, verbal or nonverbal, rare. wipes out arbitrary and non arbitrary sounds
word deafness= selective difficulty recognizing normal speech sounds, normal speech and hearing of nonverbal sounds. problems with arbitrary sounds, can hear but can’t recognize meanings
cortical deafness= difficulty recognizing all complex sounds, verbal or nonverbal, rare. wipes out arbitrary and non arbitrary sounds
29
New cards
balance and the vestibular system gen notes
\-set of semicircular canals (the boney labryinth)
\-three fluid filled tubes, each one connects to a utricle and saccule
\-oriented in three planes of head movement
\-head movement initiates flow of fluid in canals, deflects stereocilia in the ampullas, signalling movement in the brain
\-many vetibulocochlear nerve fibers terminate in the vestibular nuclei in brainstem; some project directly to cerebellum
\-three fluid filled tubes, each one connects to a utricle and saccule
\-oriented in three planes of head movement
\-head movement initiates flow of fluid in canals, deflects stereocilia in the ampullas, signalling movement in the brain
\-many vetibulocochlear nerve fibers terminate in the vestibular nuclei in brainstem; some project directly to cerebellum
30
New cards
three planes of head movement
nodding (pitch, y-axis)
shaking (yaw, z-axis)
tilting (roll, x-axis)
shaking (yaw, z-axis)
tilting (roll, x-axis)
31
New cards
ampulla
enlarged changer at the base of the canals; contains hair cells embedded in gelatinous flipper that gets pushed either direction based on which way it got pushed. Hair cells report what direction and force it got pushed
kinesthetic sense
kinesthetic sense
32
New cards
utricle and saccule
have specialized receptors that provide acceleration and deceleration signals
33
New cards
otoliths (little rocks)
a gelatinous plate with hair cells and otoliths. As you move through day, different pressure Is exerted on the otoliths that tell you where you are in relation to ground
34
New cards
motion sickness
results from too much vestibular excitation
sensory conflict theory: we see one thing but feel another and contradictory info it too much
some ppl. thing we evolved naseus to rid the body of ingested toxins that triggered dizziness. the naseua area is geographically very close to where vestibular nerve enter, they might cross talk
sensory conflict theory: we see one thing but feel another and contradictory info it too much
some ppl. thing we evolved naseus to rid the body of ingested toxins that triggered dizziness. the naseua area is geographically very close to where vestibular nerve enter, they might cross talk